Introduction to Ecology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is ecology?
The study of interactions between organisms and their environment
Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919);
1869: «economy of nature»

Eugene P. Odum (1913–2002)
1959: «scientific study of the interrelationships between organisms and their environment »
Charles J. Krebs (*1936)
1972: the scientific study of the interactions that affect the abundance and distribution of organisms
Michael E. Begon (*1951)
1990: understanding structures and processes in nature
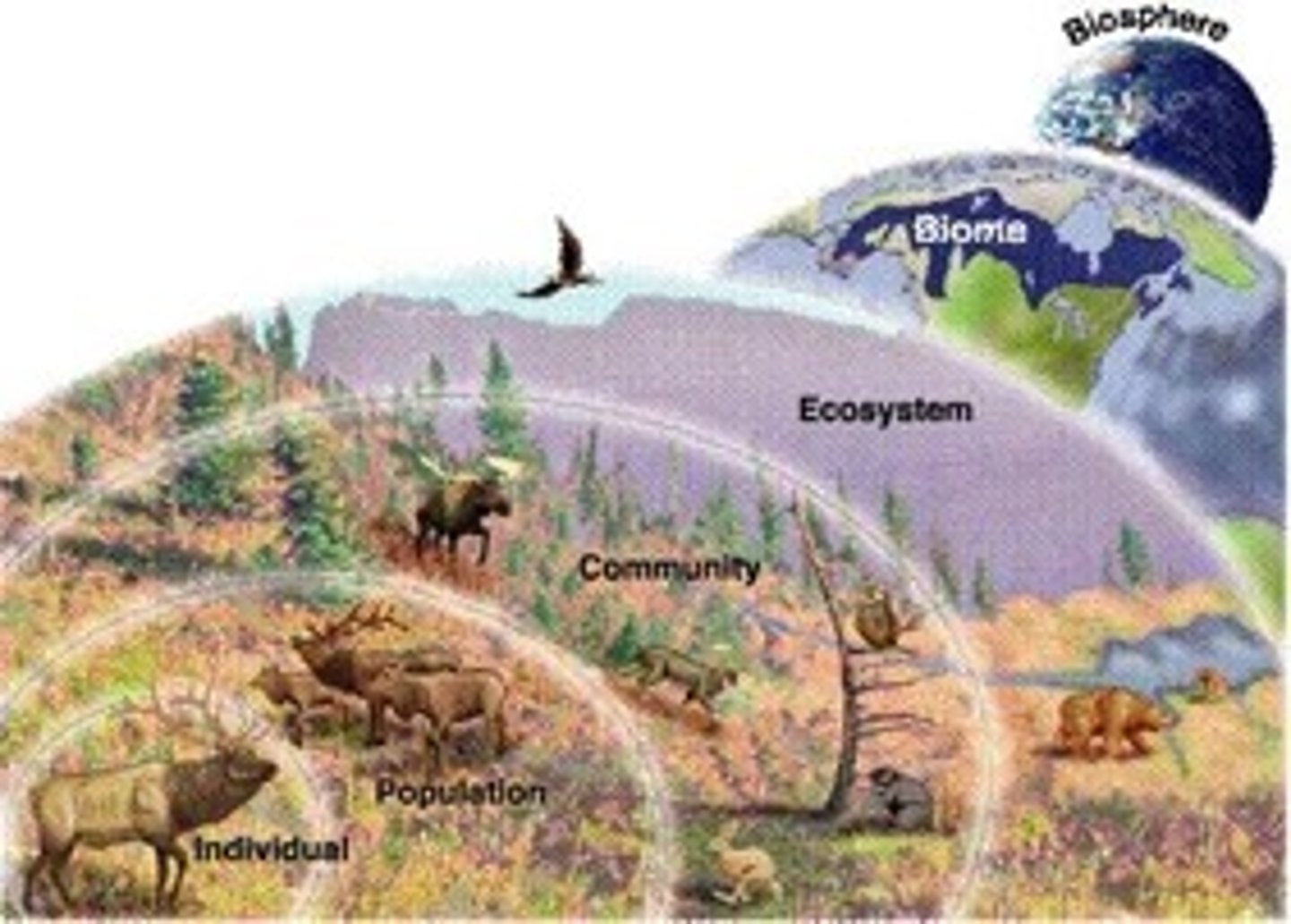
The main study units of ecology
• individuals (of a given species)
• populations (organisms of the same species, occupying a given territory)
• community (structured sets of populations)
• ecosystems (ecological communities related to the physical-chemical environment that hosts them)
• bioms (the most extensive ecosystems on earth, classified according to the dominant vegetation and characterized by the adaptation of organisms to specific environmental conditions)
• biosphere (set of all earth's ecosystems)
What is a population?
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time

What is a community?
All the different populations that live together in an area

Biomes
a broad, regional type of ecosystem characterized by distinctive climate and soil conditions and a distinctive kind of biological community adapted to those conditions.
Biocenosis (community)
A group of populations living together in a specific region, in an abiotic environment (biotope). Biotic components of the community include: producers, consumers and decomposers forming food chains.
Species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile (= interfecond) offspring.
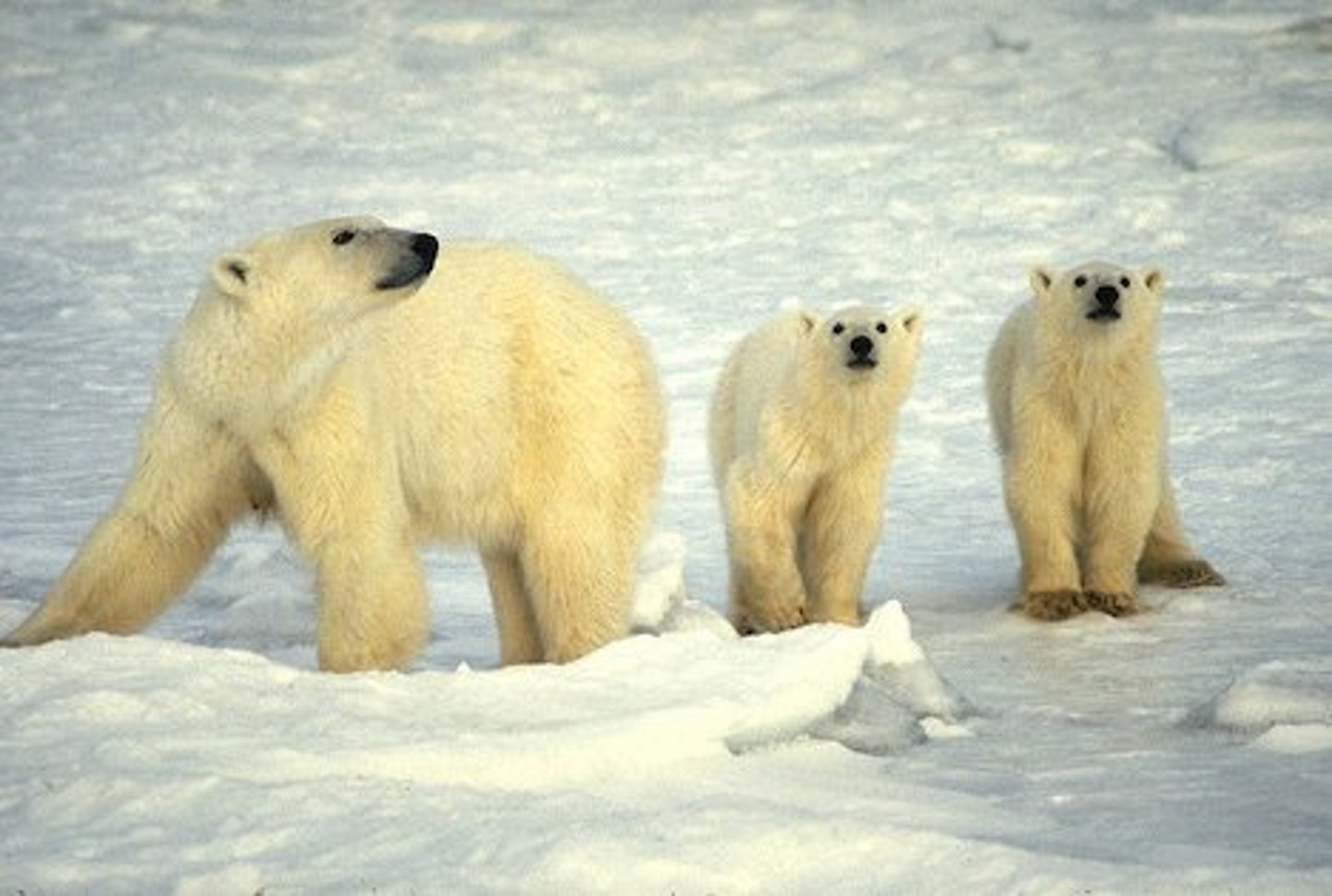

Biotope
Fundamental unit of the environment topographically identifiable and characterized by the biocoenosis that populates it; Abiotic component
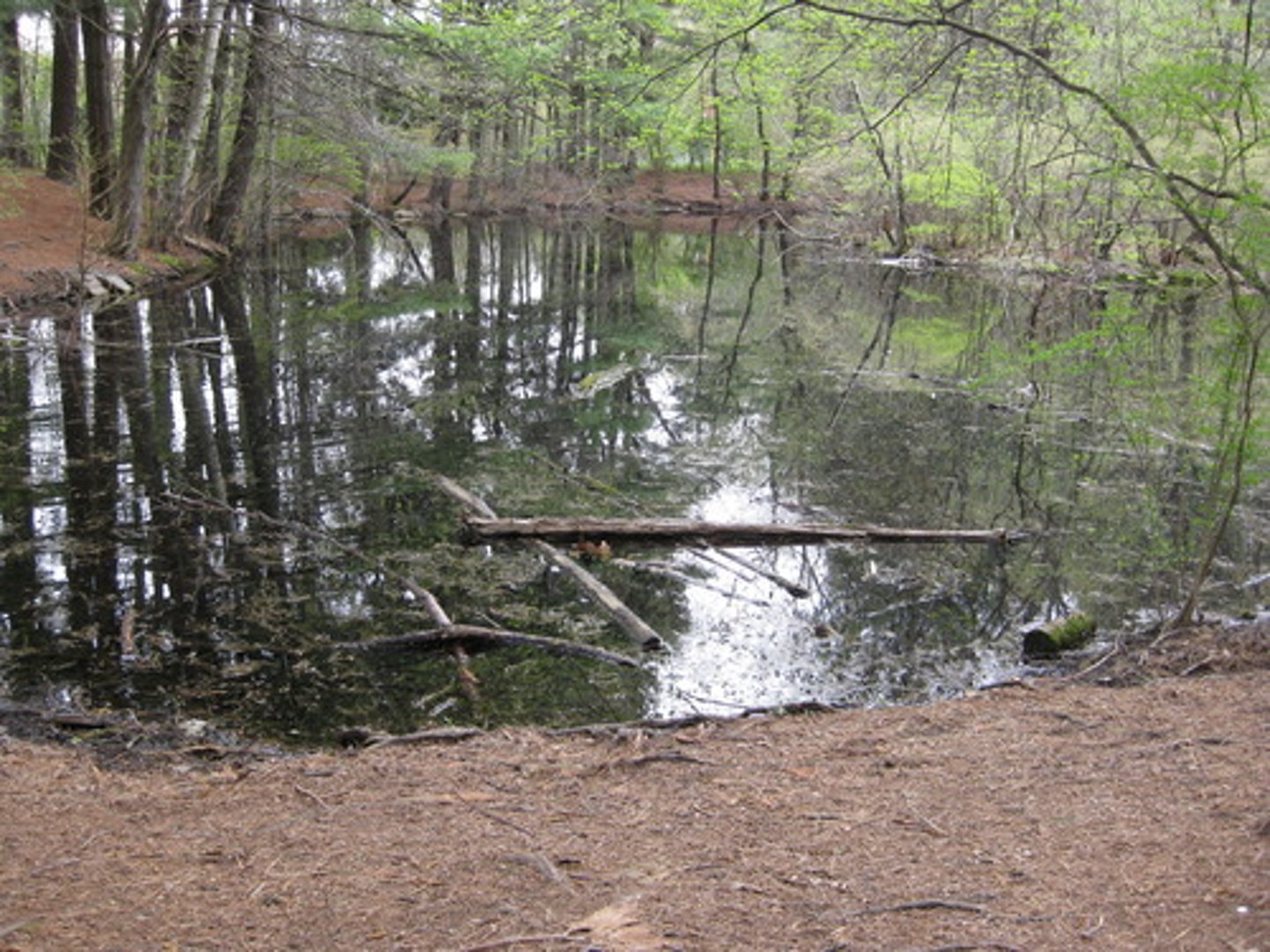

Ecosystem
A community of organisms and their abiotic environment
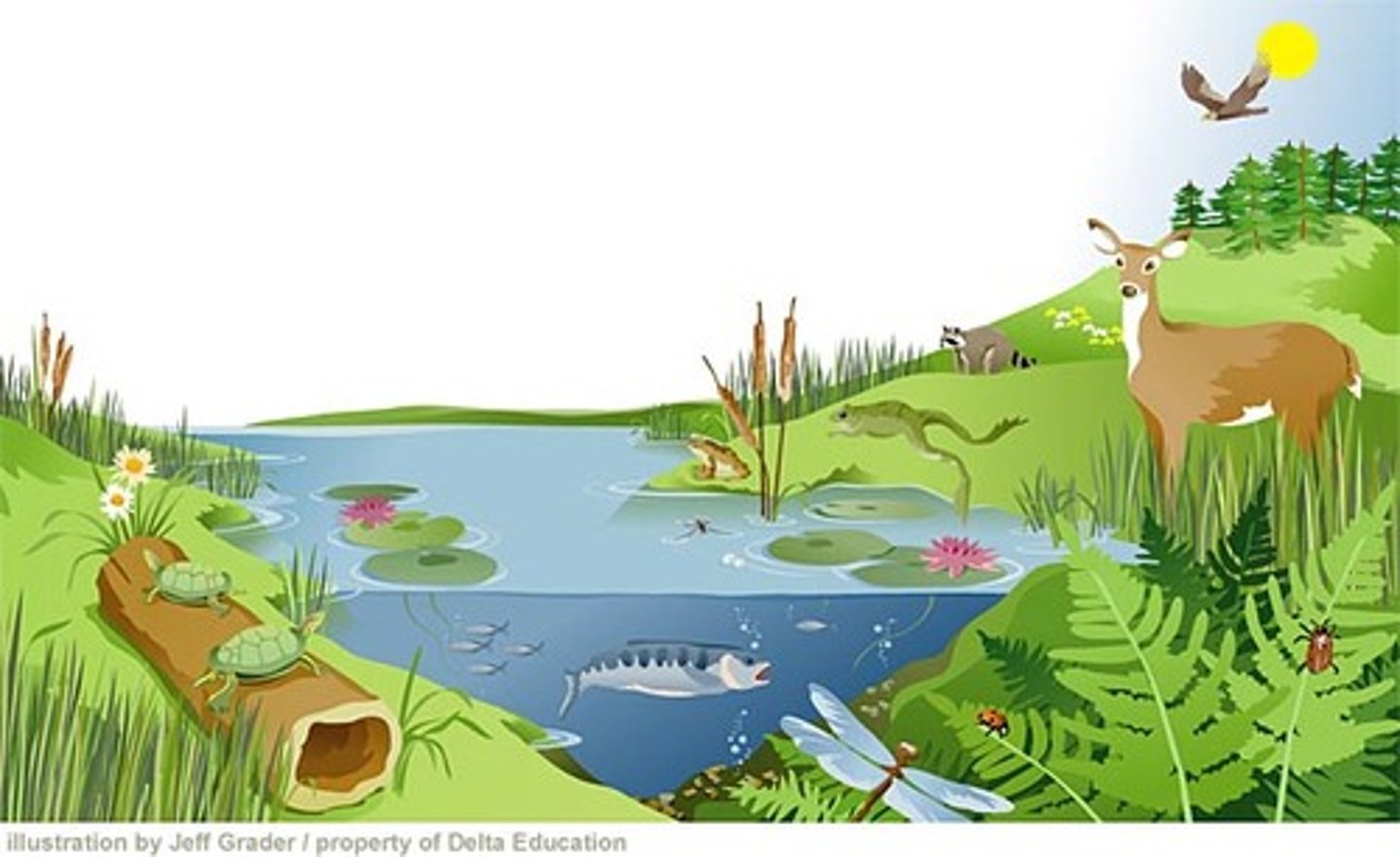

Habitat
Type of environment (physical and biological) in which an organism lives
Ecological niche
A specific role of a species within an ecosystem, including its use of resources, and relationships with other species.
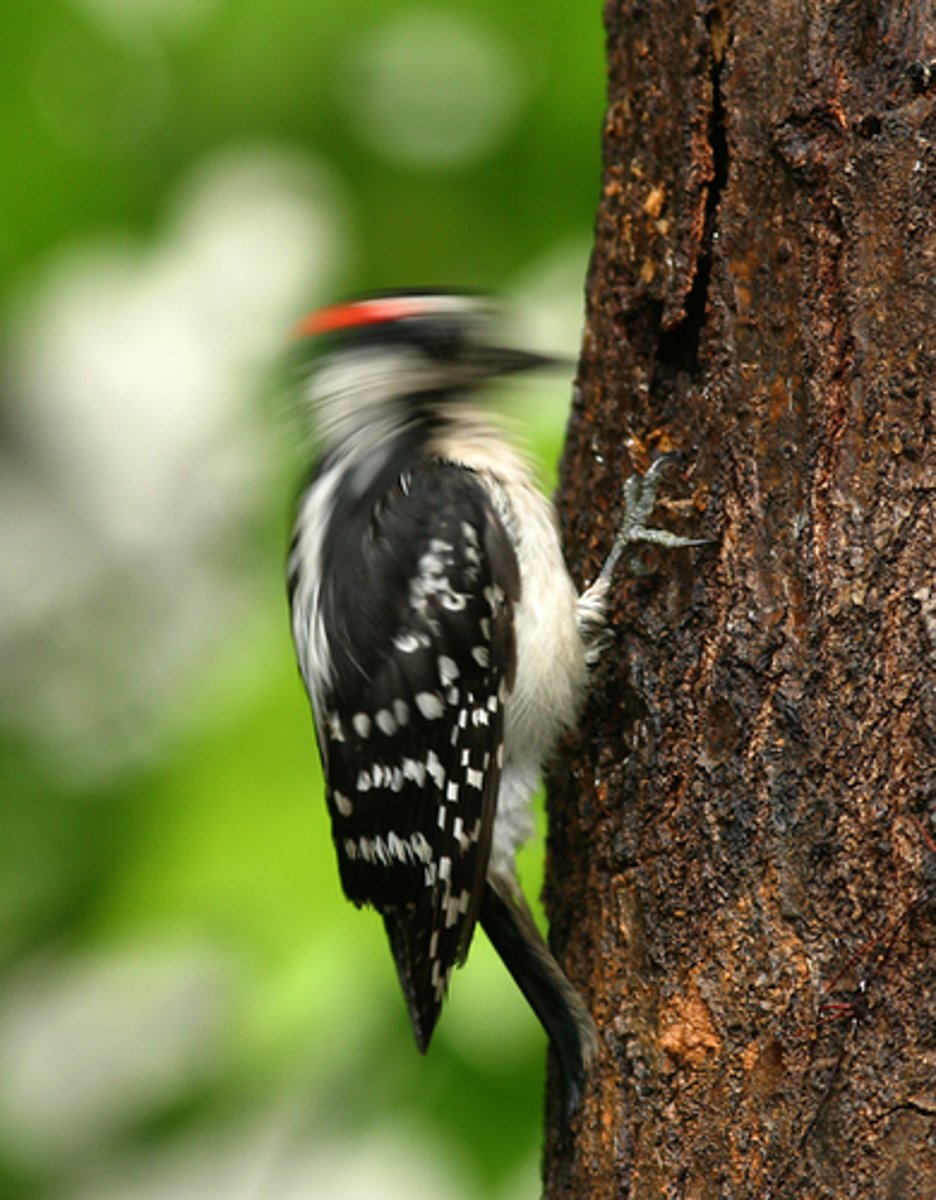

trophic chain
Species organized into chains that eat each other sequentially. Longest chains probably exist in the Oceans.
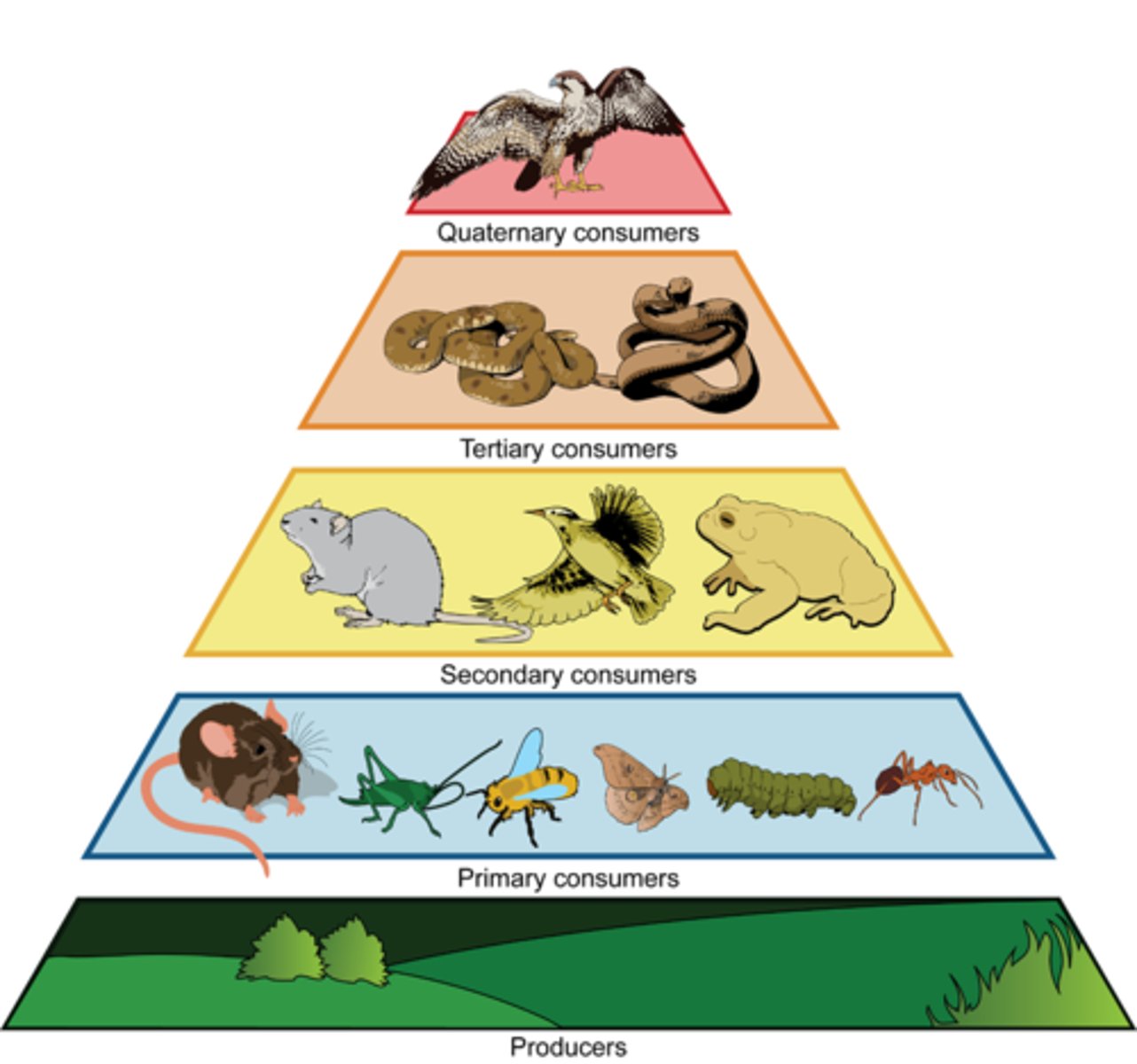
Producers
They are plants, autotrophic organisms (able to synthesize organic matter starting from inorganic material)
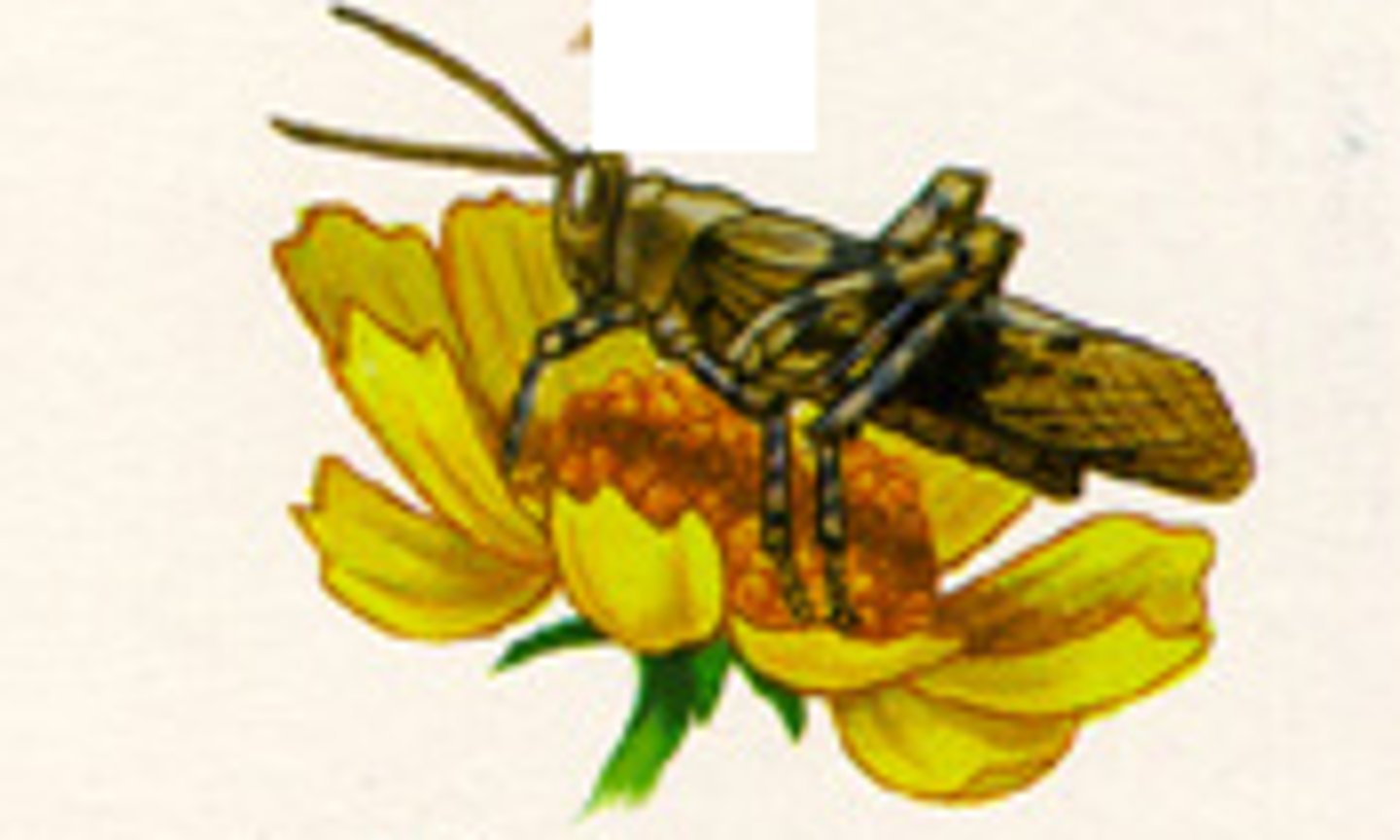
primary consumers (herbivores)
They are herbivores, which feed at the expense of organic matter synthesized by plants

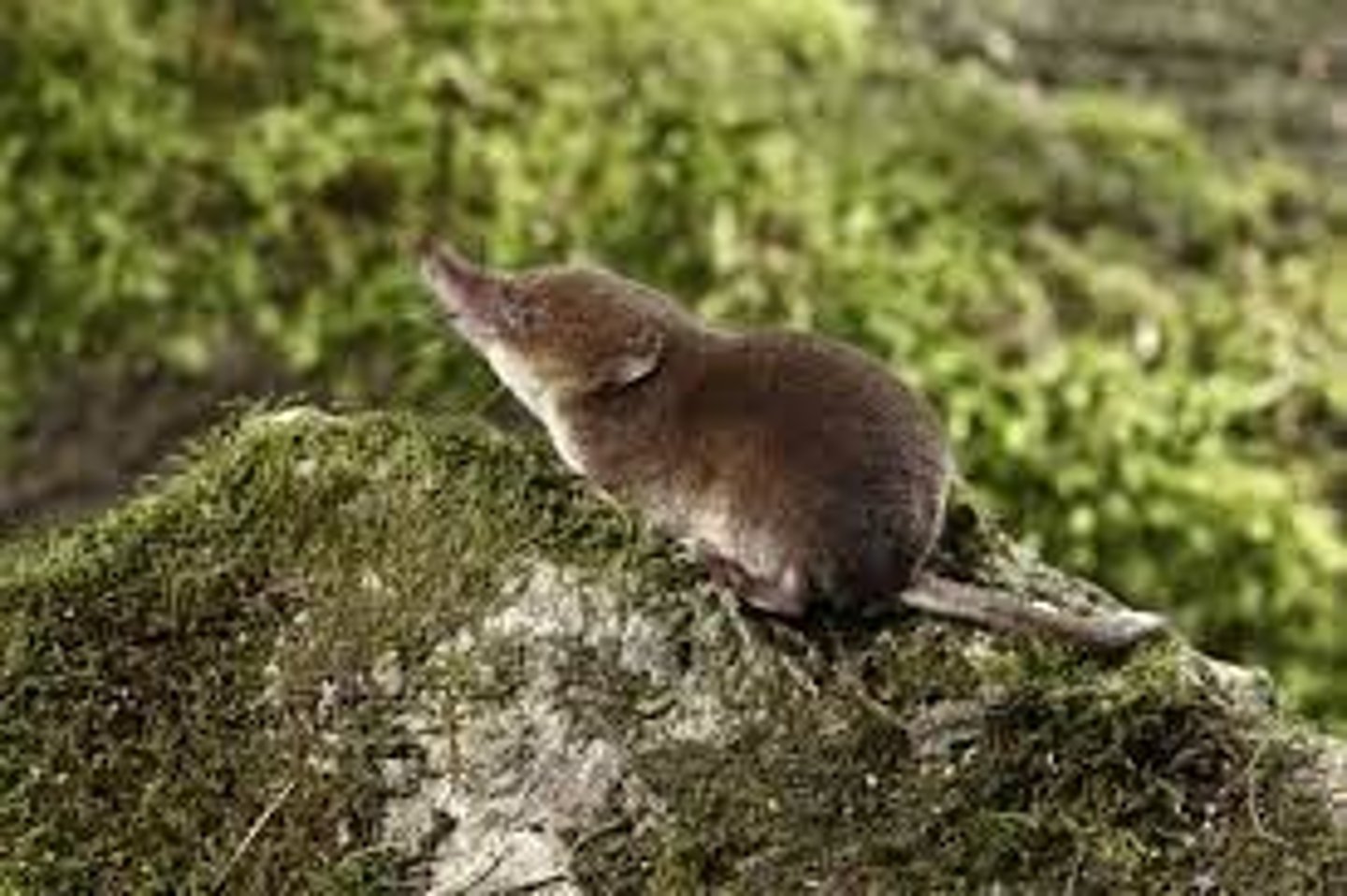
secondary consumers (carnivores)
They are carnivorous predators of herbivores

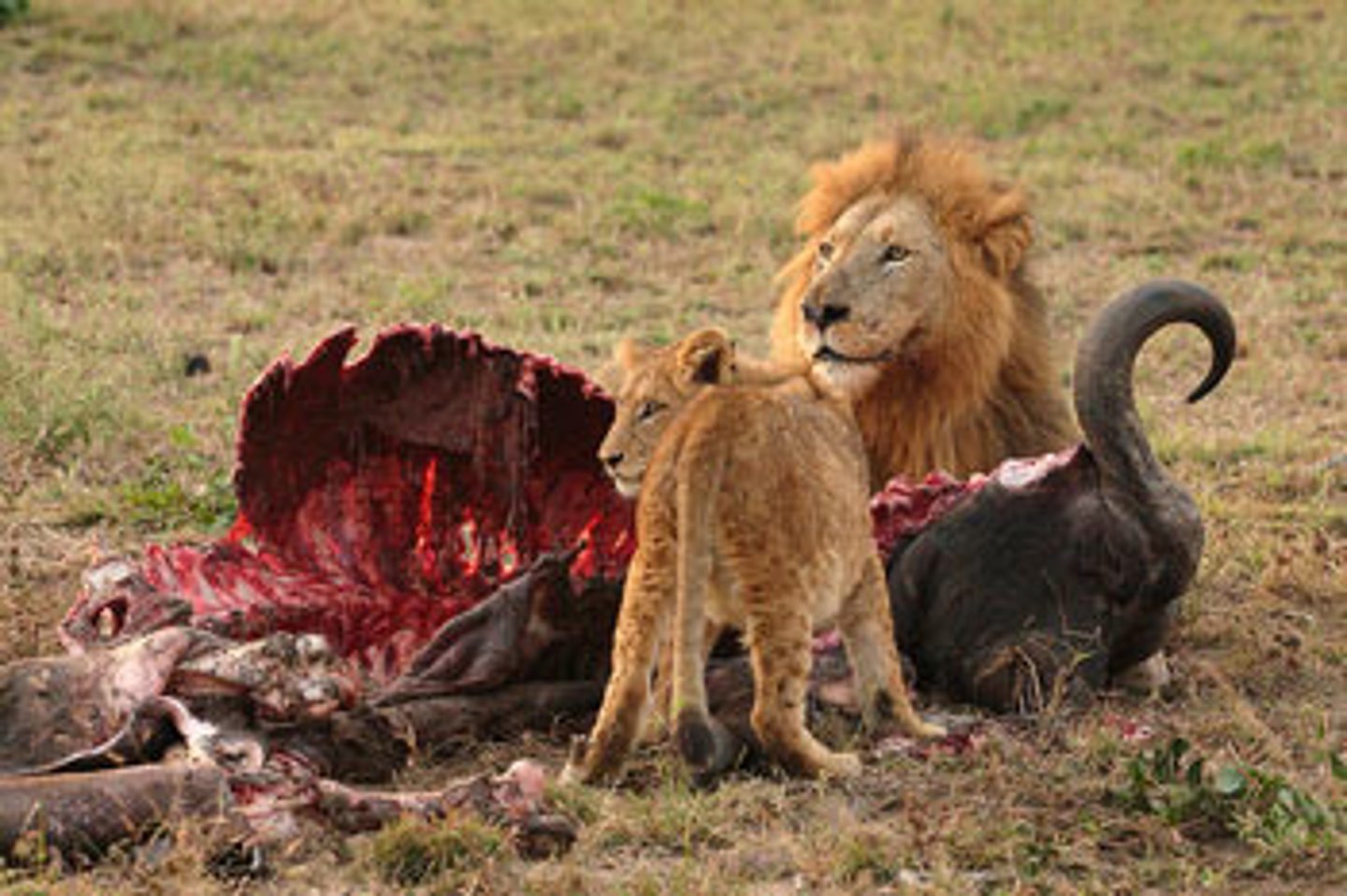
tertiary consumers (carnivores)
They are predatory carnivores of both herbivores and other

Quarternary consumers
Typically eat tertiary consumers, eat tertiary consumers (ex. hawks/killer whales)
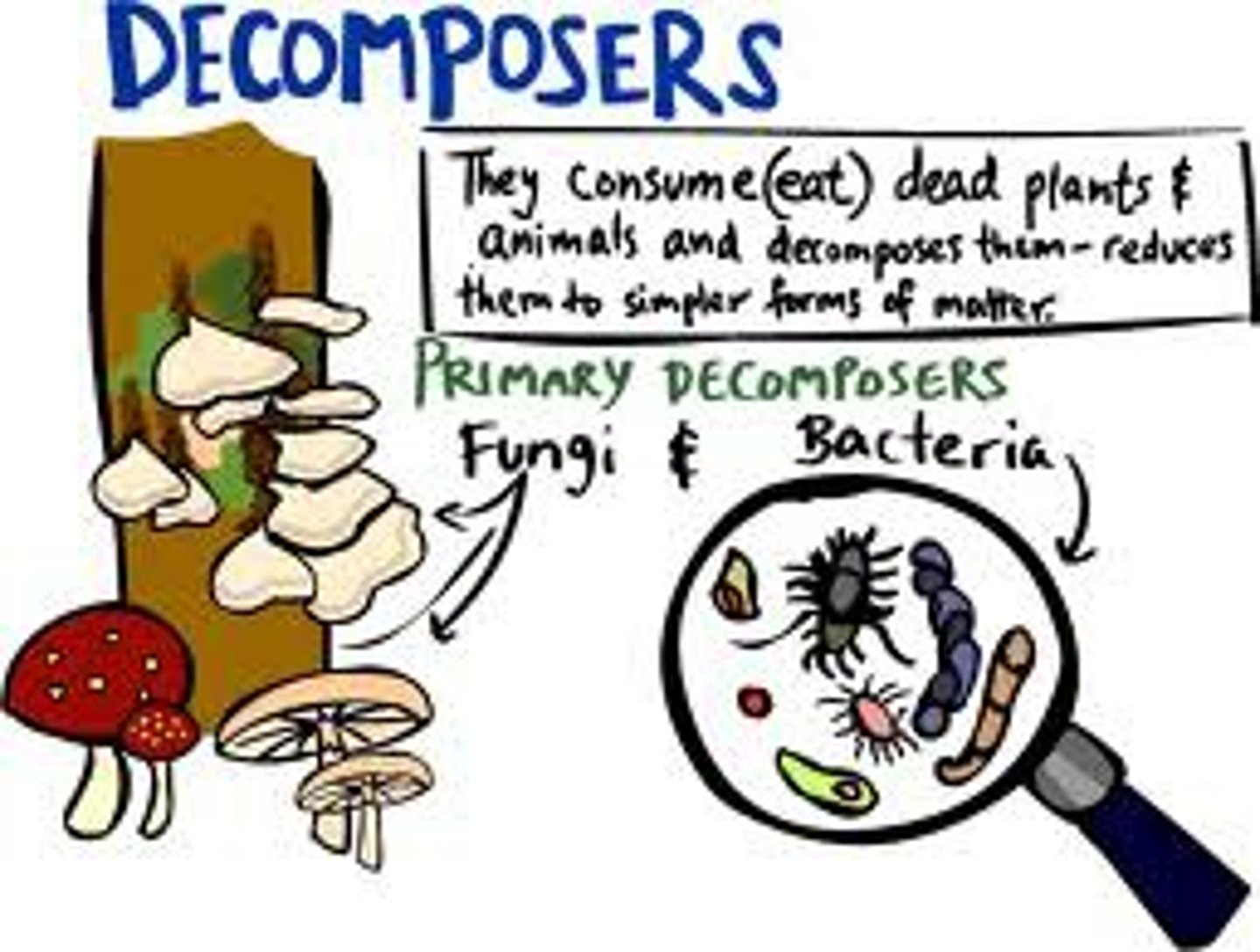
decomposers/detritivores
obtain energy by feeding on the remains of other organisms or waste products
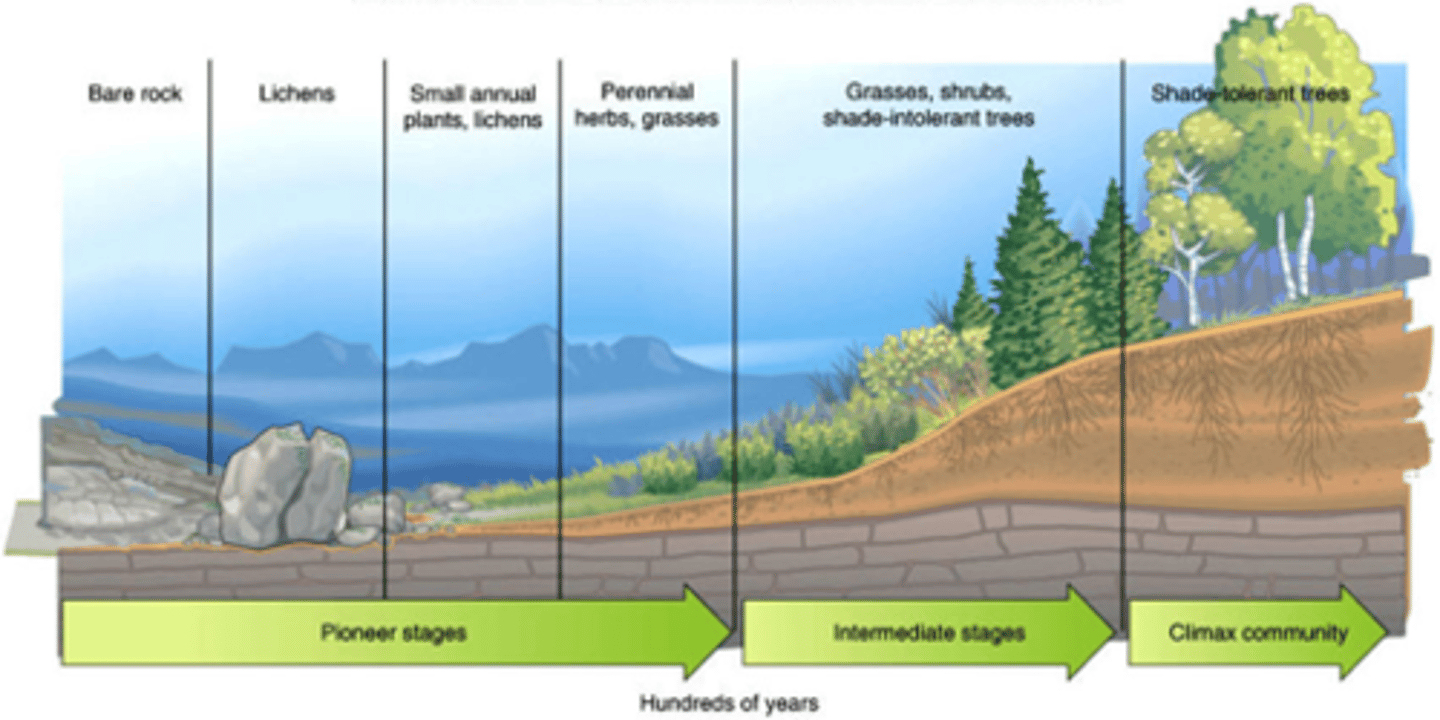
ecological succession
series of gradual changes that occur in a community following a disturbance
Synecology
Study of groups of organisms in relation to their environment, community ecology.
Demecology
Ecology of the population - demography, evolutionary ecology, prediction of persistence of rare species
Autoecology
the branch of ecology that concerns itself with the individual organism or the individual species (its life history, behavior, ecological requirements, etc)

Morphology
study of form
Physiology
The study of body function
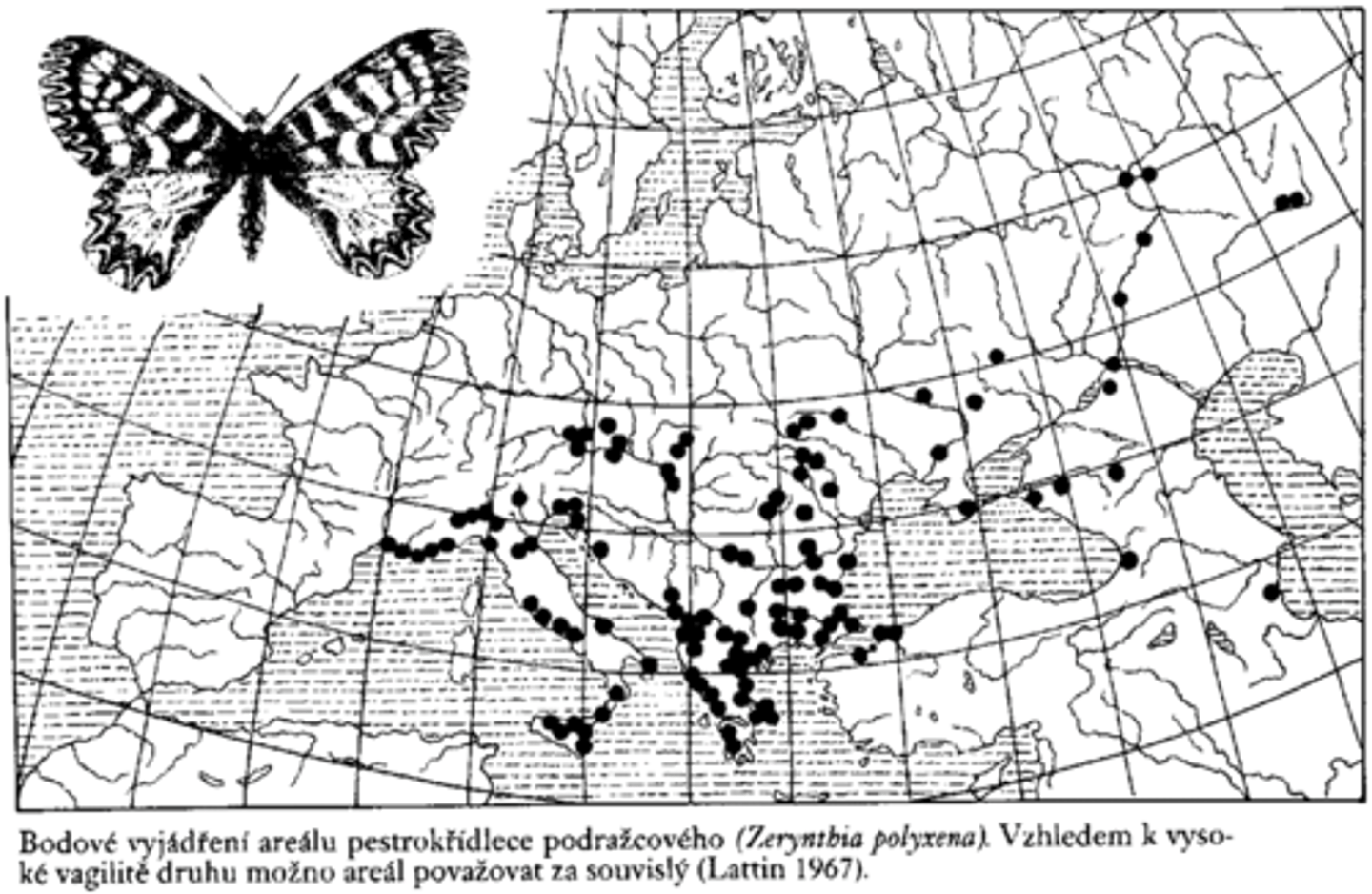
Biogeography
Study of past and present distribution of organisms
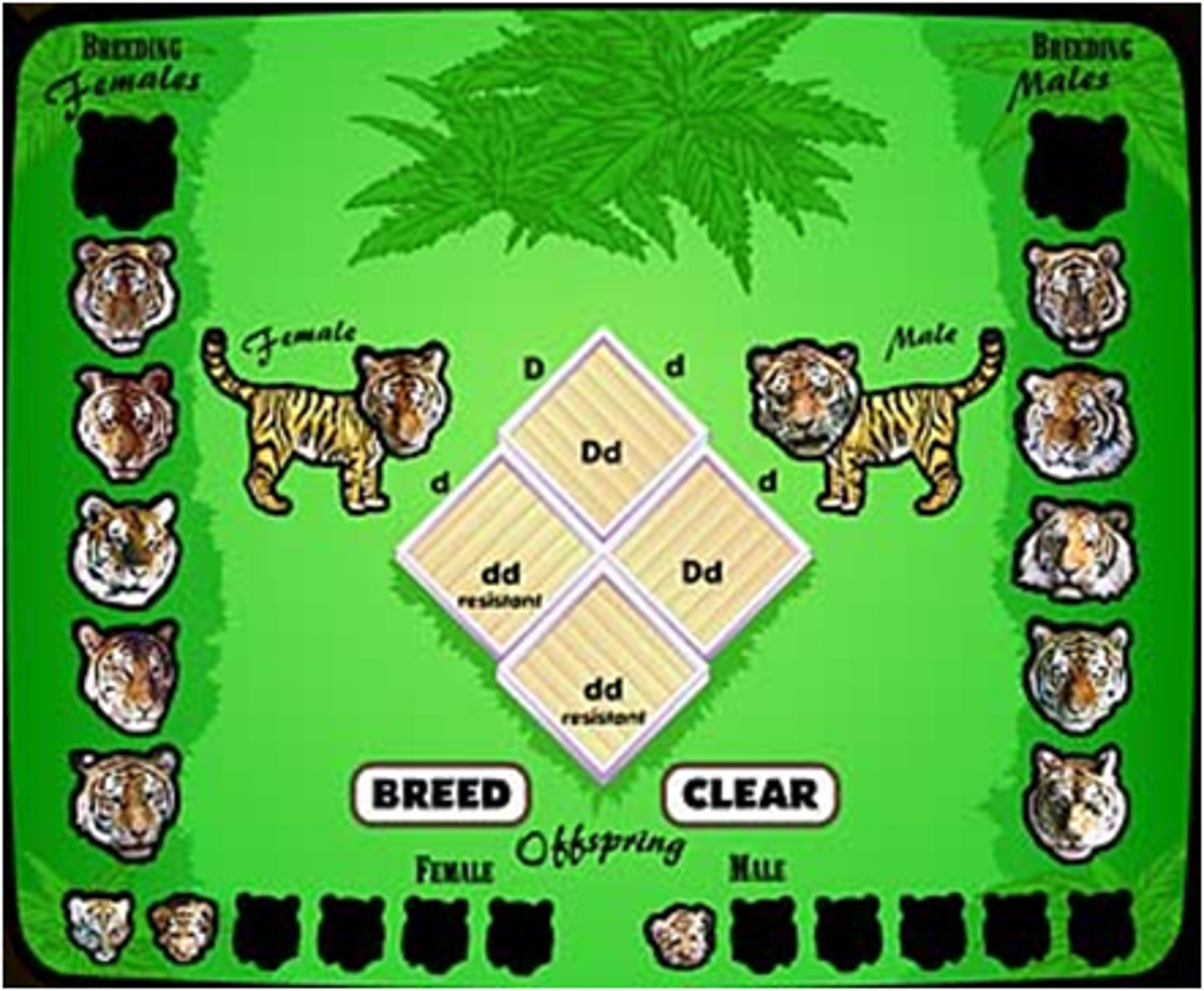
Genetics
Genetic structur of populations
intra- and interspecific differences
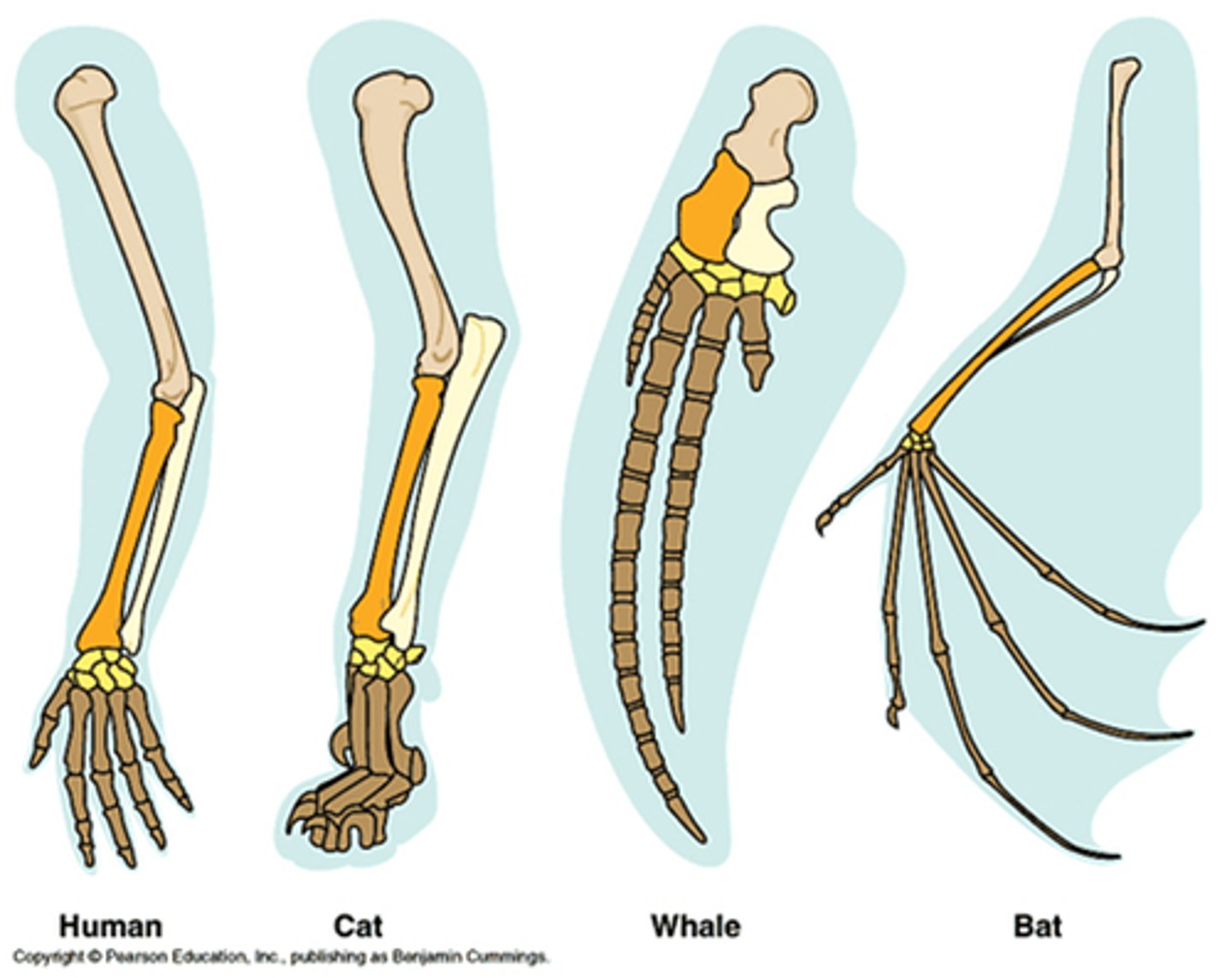
systematic biology
the study of evolutionary history of biodiversity
-infer the evolutionary relationships of organisms and organize biodiversity based on these relationships
evolutionary biology
the study of organisms and their changes
landscape ecology
Multifunctional perspective on landscapes
Human resource
Wildlife habitat and niches
Connectivity tissue and ecological networks

Conservation biology
•Preservation of biodiversity
•Different nature conservation approaches: from protected areas strategy to involving citizen science.
•The concept of dominant-, flag-, umbrella-, keystone- species
•Bioindicators as a cost-effective tool to monitoring and survey the status of environments and species
•Top predators and conservation

Biodiversity
Diversity of populations, species, environment, depending on the scale…

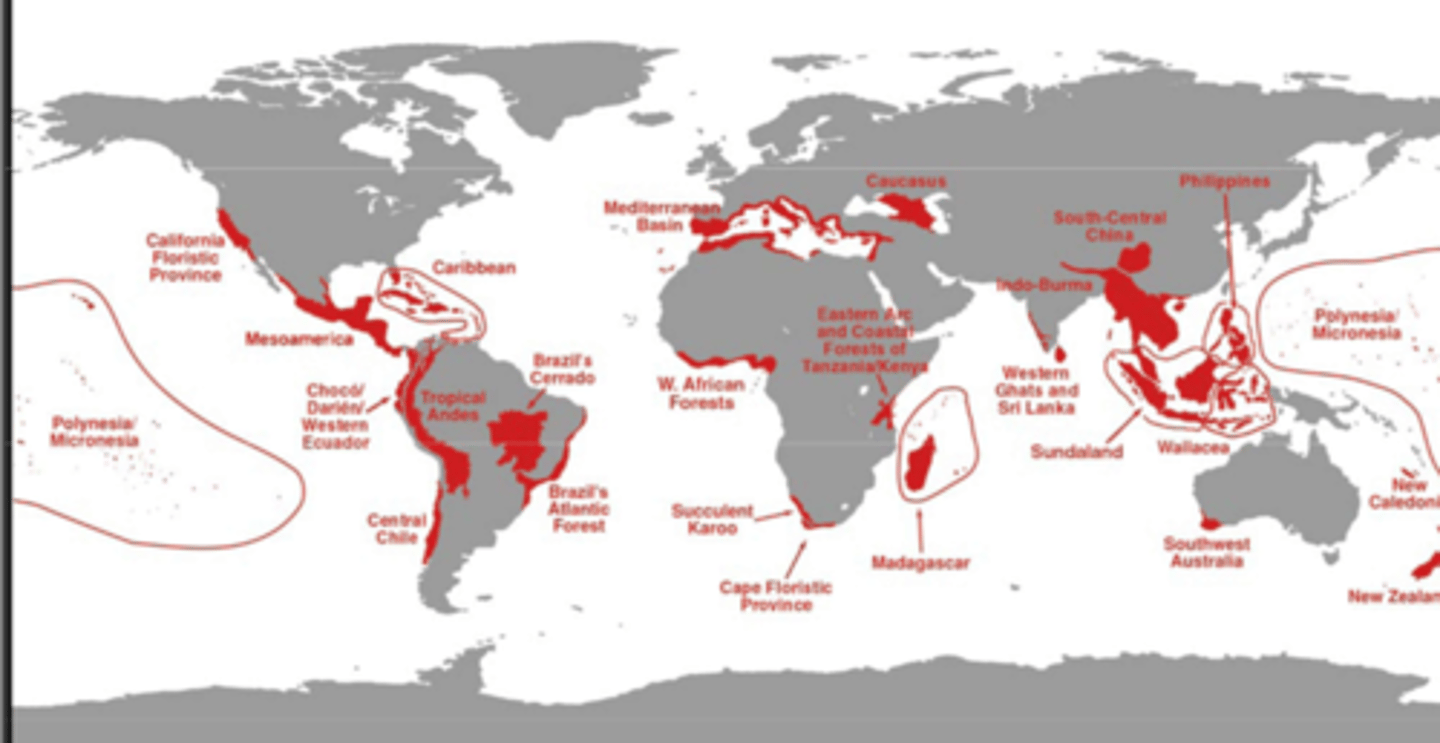
Biodiversity hotspots of the World
regions "where exceptional concentrations of endemic species are undergoing an exceptional loss of habitat"
Global diversity
What fosil deposits teach us about biodiversity, in the timeline:
There was a growth of (bio)diversity in different geological eras, but also repeated mass extinctions
Regional diversity
The scale of larger geographic areas, comparable to the size of species distribution range.
Influence of macroclimate
Local diversity
•Diversity of specific communities
•Number of species and their proportional representation