SS201 - West Point - ECON
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Equilibrium
Agents simultaneously optimizing--nobody wants to change what they are doing
Optimization
Economics agents choosing the best feasible option given the available information
Optimization in Levels
Calculating TOTAL net benefit of different alternatives then selecting the best one.
e.g. There are two bags of candy. You look at which bag would bring the most enjoyment and you pick that one.
Optimization in Differences
Calculates the CHANGE in net benefits when a person switches from one thing to another then uses marginal comparison to choose the best alternative.
e.g. using "marginal analysis" to determine which option is best-- two bags of candy exactly the same; however, one has a crying baby inside and one does not. The one without will bring the most enjoyment so you pick that one.
Correlation
Relationship between two variables (not necessarily causation)
Opportunity cost
value of the best available alternative (units could be in goods or dollars)
Feasible options
Available & Affordable
Empiricism
Testing ideas using data
Scientific Method
Develops models of the world and test those ideas with data
Variable
Factor that is likely to change or vary
Consumer surplus
Difference between willingness to pay (demand curve) and the price. Area below the demand curve and above the price
Producer Surplus
Difference between willingness to accept (supply curve) and price. Area above the supply curve and below the price.
Price elasticiy of demand
(%Δ Quantity demanded)/(%ΔPrice). We make this positive for convenience, because law of demand says the relationship between demand and supply is always negative.
Income elasticity of demand
(%Δ Quantity demanded)/(%Δ Income)
Price elasticity of Supply
(%Δ Quantity supplied )/(%Δ Price)
Net Exports =
Exports - imports
Protectionism
Reducing competitive forces faced by domestic firm
Negative Externality
Costs of economic transactions that do not directly impact seller or buyer e.g. Air pollution
Positive externality
Benefits of economic transactions that do not directly impact seller or buyer e.g. Education
Public Good
Non-excludable, Non-rival good (e.g. protection from the military)
Common pool resource
: Non-excludable, Rival good (e.g. international fishing waters)
Governement Paternalism
Policies to encourage citizens to do what the govt think is in the citizens best interest.
Human Capital
Individuals stock of skills
Monopoly
Market with one seller and high barriers to entry. long-run positive economic profits possible.
Oligopoly
Market with few sellers and high barriers to entry. Optimal actions depend on actions of other oligopolistic firms.
Monopolistic competition
Market with many sellers, differentiated goods, and no barriers to entry.
Macro econ
Study of econ as a whole
GDP Deflator
100x (nominal gdp/real gdp)
Nominal GDP
Value of goods at a given year
Real GDP
Value of goods in a year in base year prices
Q_i×P_b=(Nominal GDP)/(GDP Deflator)
CPI
100*cost of basket goods in a year of interst/cost of basket goods in a base year
Solow growth steady state
I=d*x
Catch up growth
Countries try to take advantage of existing technology to grow
Fundamental causes of prosperity
Geography, Culture, Institutions (institutions most important)
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment caused by frictions in the labor marker e.g. job search, hiring procedures, budgets. These workers eventually get jobs, but will be unemployed during the search.
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment as a result of persistant gap between labor supplied and labor demanded. can be due to downward wage rigidity, minimum wages, presence of unions, or efficiency wages.
Defined benefit plan
Receiving a promised payout for retirement. Not typically provided anymore, and not transferable between jobs.
Factors influencing consumption decision
Budget restraints
prices
tastes
preferences
Factors that shift demand
Change in prices
population
income
expectations of the future
Impact of a price cieling
demand exceeds supply, there is a shortage of supply
Impact of price floor
There is an excess of supply
Types of Barriers to entry
Legal barriers
Economies of scale
Nash equilibrium
No player can be made better off by changing his or her actions given what others are doing
Things not counted in GDP
Home Production
Underground economy
leisure time
Unemployment rate =
natural rate of unemployment + cyclical unemployment
US Central Bank ...
Influences money supply, sets federal fund rate, monitors financial institutions
Price Elasticity of demand
Elastic > 1 ... Unit Elastic = 1 ... Inelastic < 1
If inflation is unexpectedly low, who would benefit?
A bank that purchased bonds
&
Banks that made home loans
Marginal Benefit
The amount you benefit from having one more quantity of something.
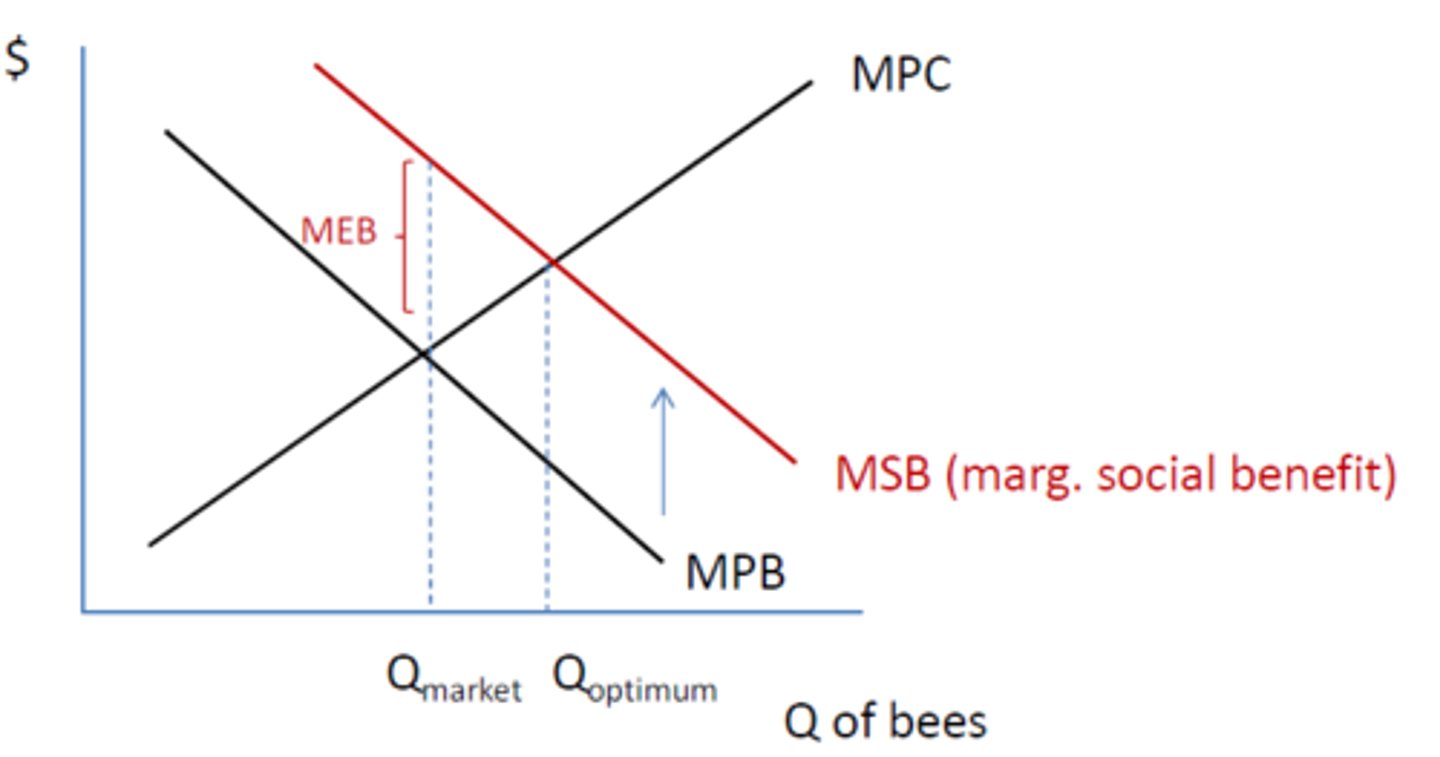
What is the only thing that causes the QUANTITY demanded/supplied to change?
Price
Factors that shift the demand curve
Tastes and preferences
income
availability and prices of related goods
beliefs about the future
Factors that shift the supply curve
Technology
Number and scale of sellers
beliefs about the future
How do we maximize revenue in terms of elastic/inelastic goods?
Raise prices on inelastic goods, and lower prices on elastic goods.
Why are profits zero in a perfectly competitive market
This is the term used to say that a company is "breaking even" meaning that they aren't losing money and are covering operating costs. --they're out of the red.
PCM
Perfectly Competitive Market
Sellers all sell identical goods/services. Buyers/Sellers are all price takers meaning they accept the market price and can't bargain for better prices.
How will a firm maximize labor hired?
Set VMPL=Wage
Nominal Exchange Rate
Units of foreign Currency/1 unit of domestic currency
If the Fed wanted to implement anti-recession monetary policy what would it do with each tool?
A: Open market operations: buy or sell?
B: Increase/decrease interest paid on reserves?
C:Increase/decrease lending from the discount window?
D:raise or lower the reserve requirement?
A: Buy
B:decrease
C:Increase
D: lower
If i just got a job paying $43,600 and inflation is 5%, what must my salary be in 9 years in order to keep the same purchasing power?
43,600*(1+5%)^9=$67,637.91
If i deposit $4200 and earn 10%, how much will i have in 25 years? 30 years?
4200*(1+10%)^25= 45505.76
30 years = 73287.49