BIOSC-130 Exam 5: Key Biology Terms & Definitions
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Types of Body Plans
- single-celled
- simple multicellular
- complex multicellular
Single-celled body plan
direct exchange with environment ex. amoeba
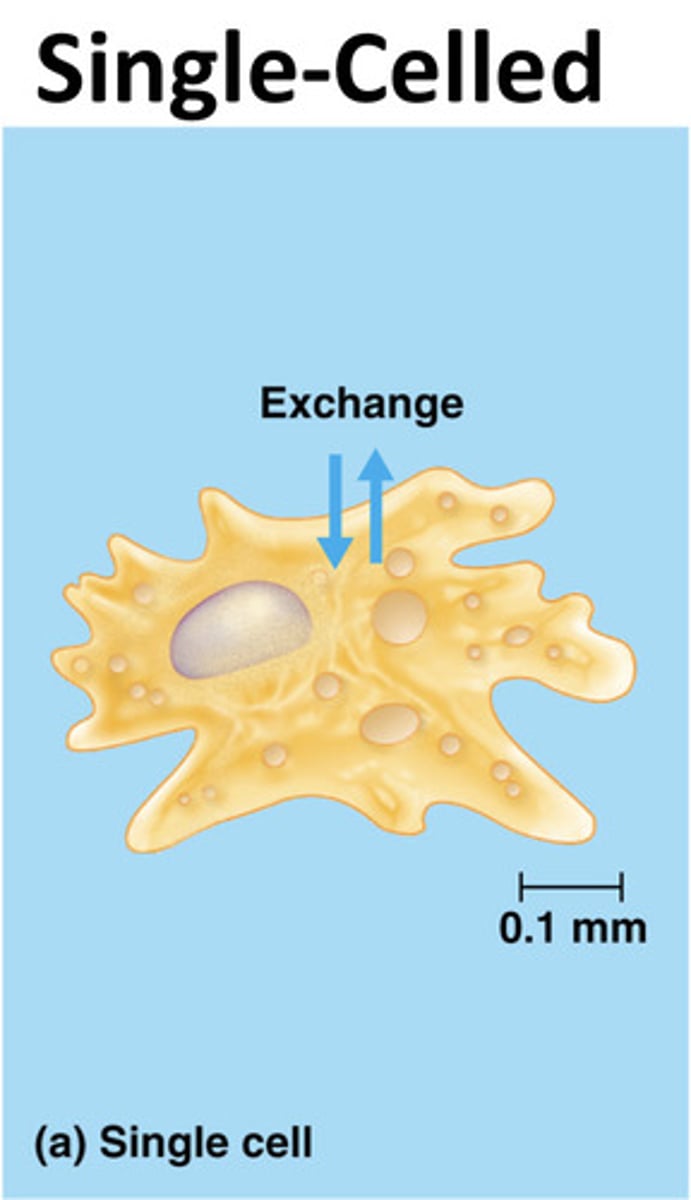
simple multicellular body plan
most cells contact environment ex. hydra
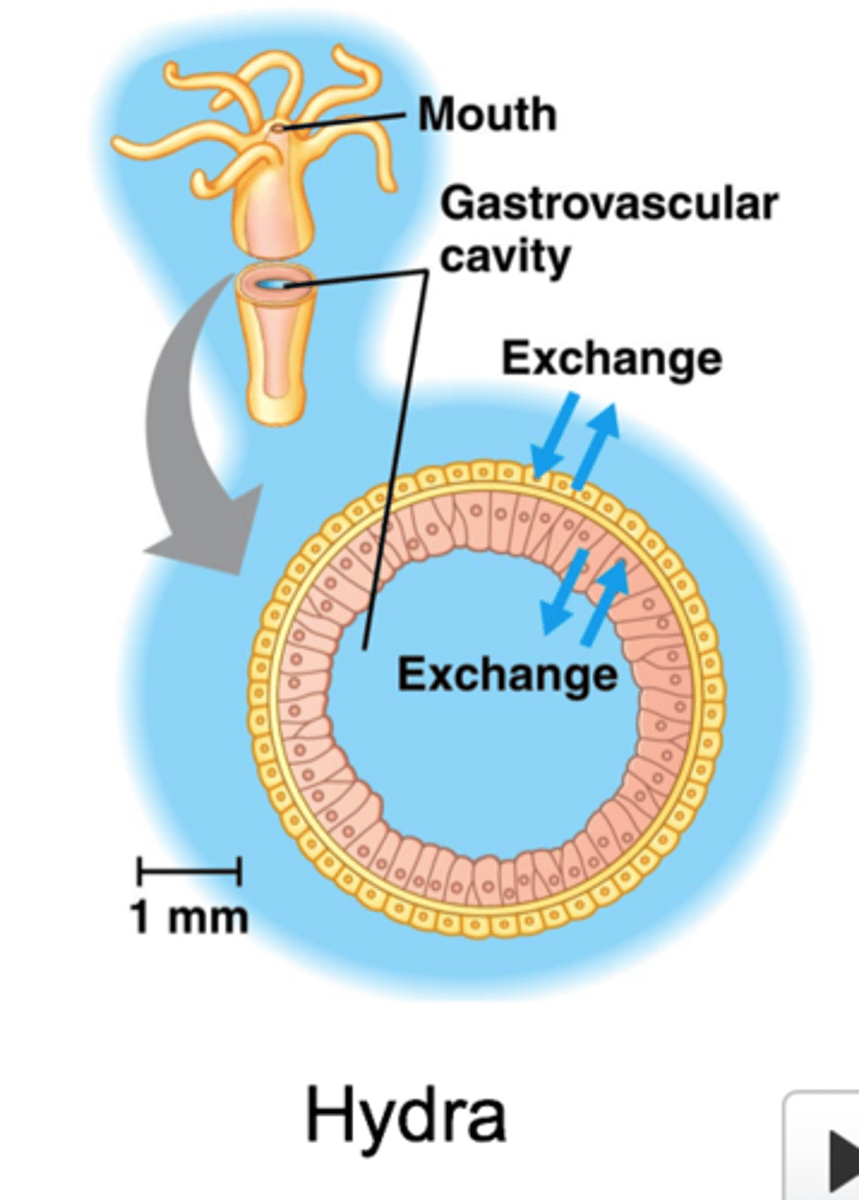
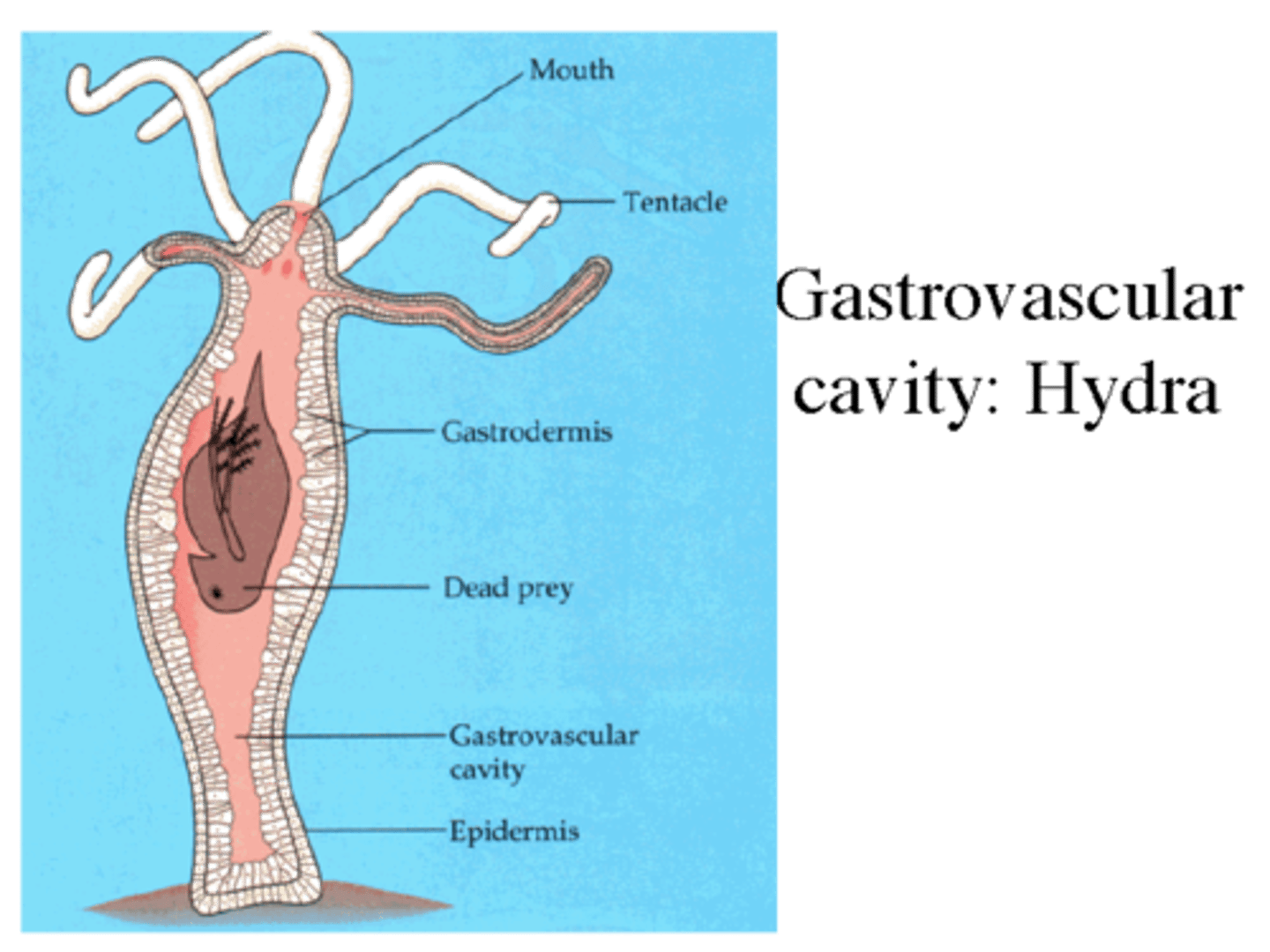
gastrovascular cavity
enables exchange of internal cell layer in simple body plan
complex body plan
exchange surfaces with internal fluids (interstitial and circulatory fluids)
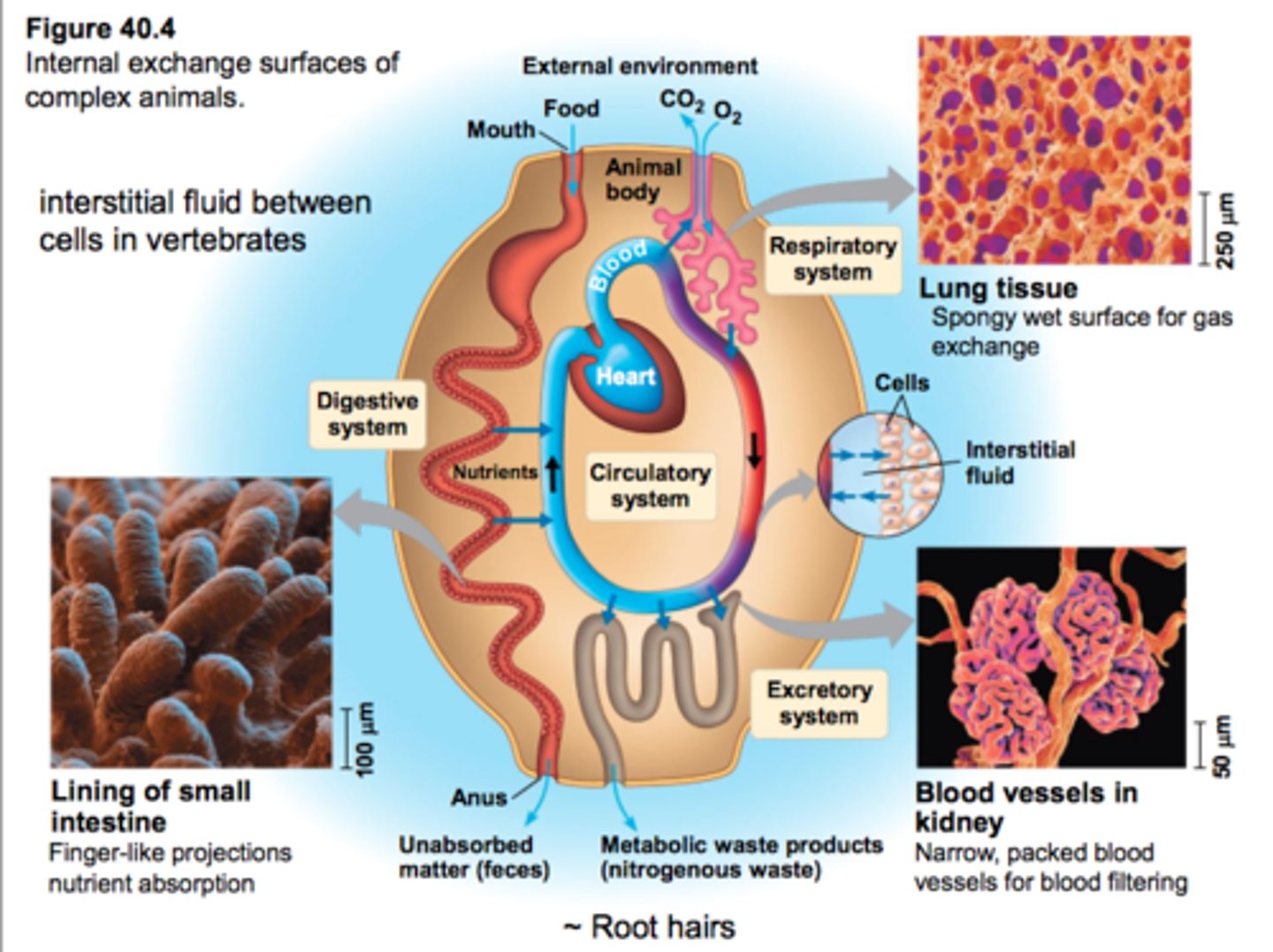
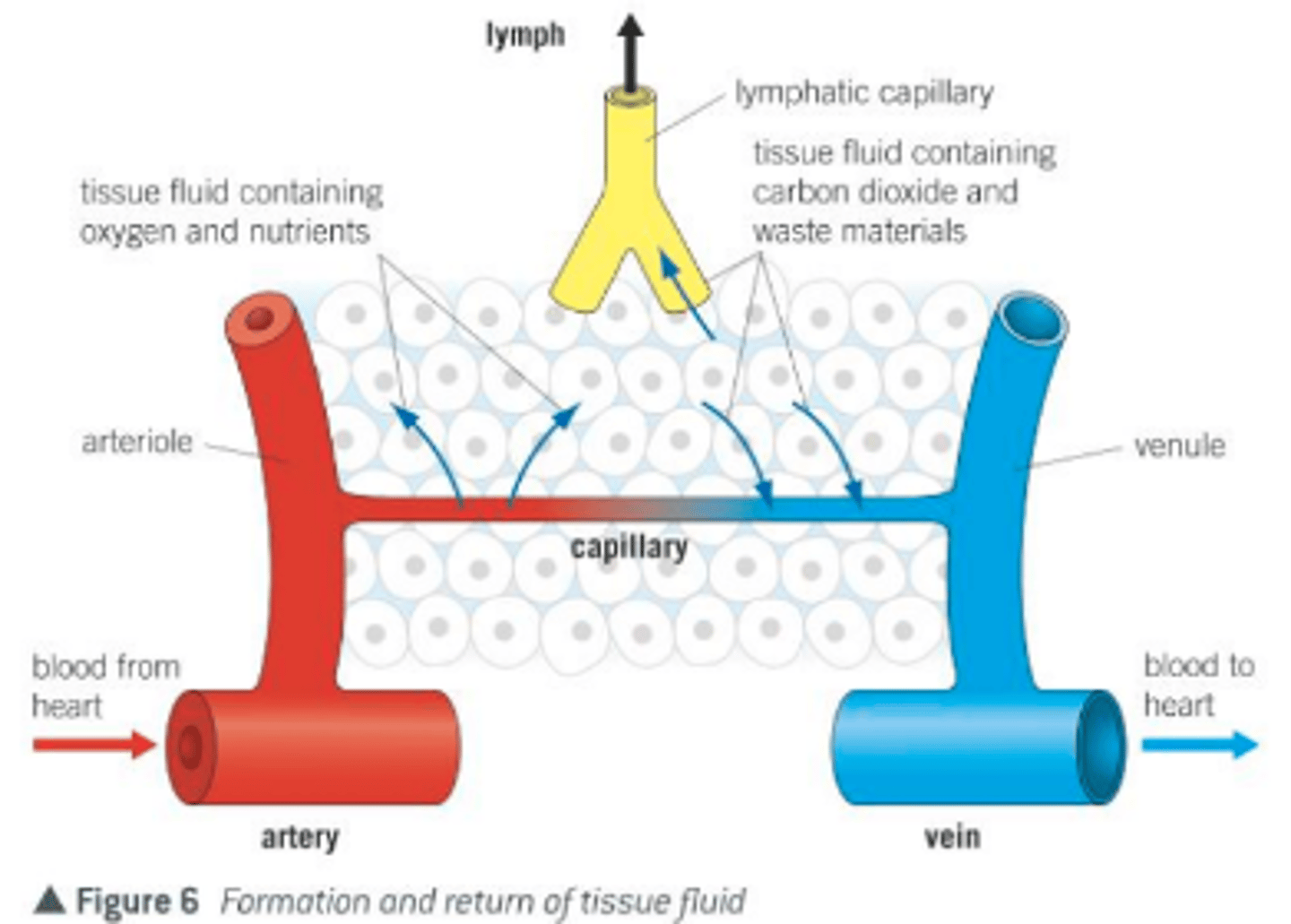
Interstitial Fluid
fluid in the spaces between cells; buffers cells
Circulatory Fluid
moves material throughout body ex. blood
Cardiovascular System
transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes
Components of Cardiovascular System
- pump = heart
- tubes = vessels
- fluid = open (hemolymph); closed (blood)
Open Circulatory System
fluids called hemolymph bathes the organs, equivalent to interstitial fluid. ex. cricket
Closed Circulatory System
circulatory system in which the oxygen-carrying blood cells never leave the blood vessels; interstitial and circulatory fluids kept separate
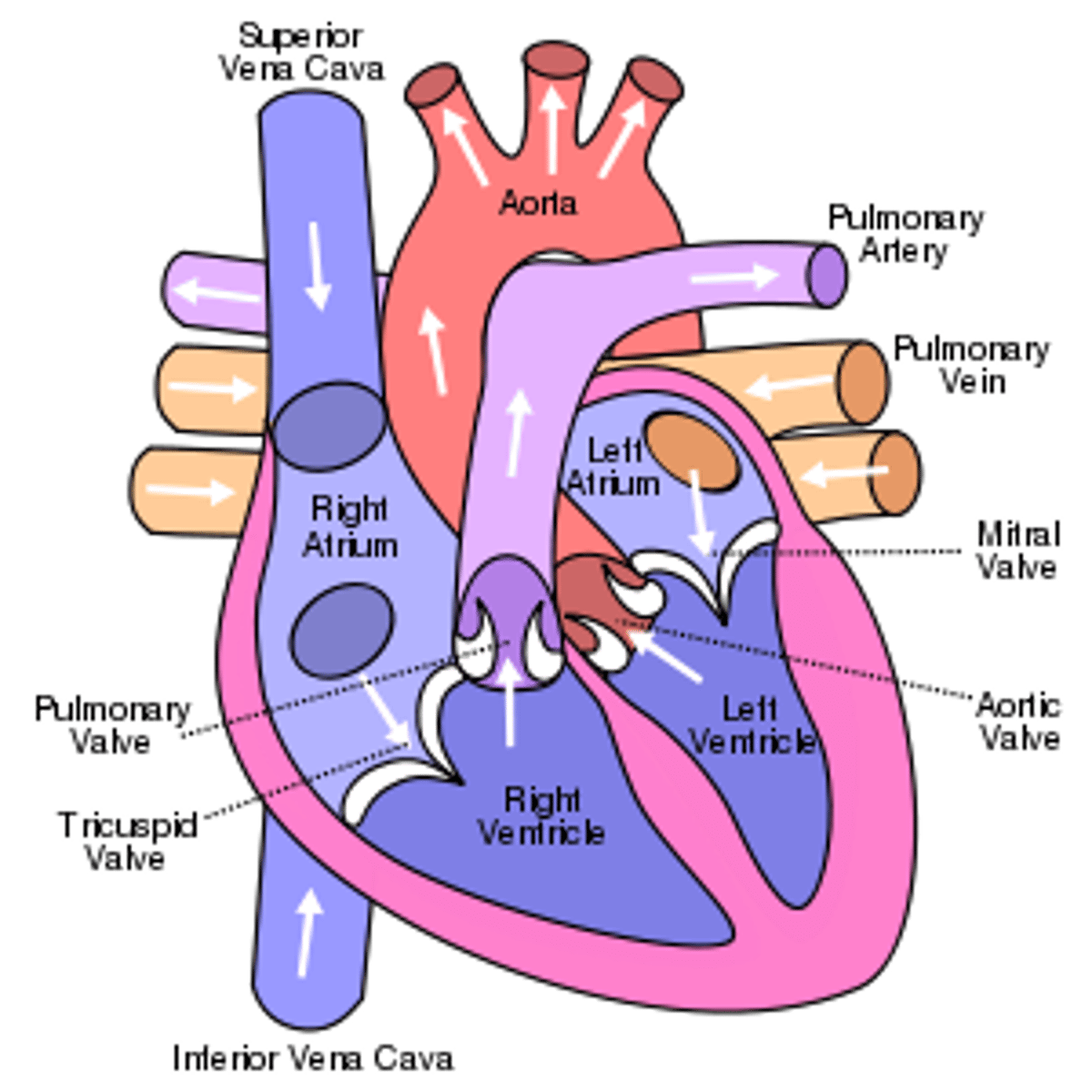
Heart Chambers
atria and ventricles
Atria
upper chambers of the heart that receive bloods from veins
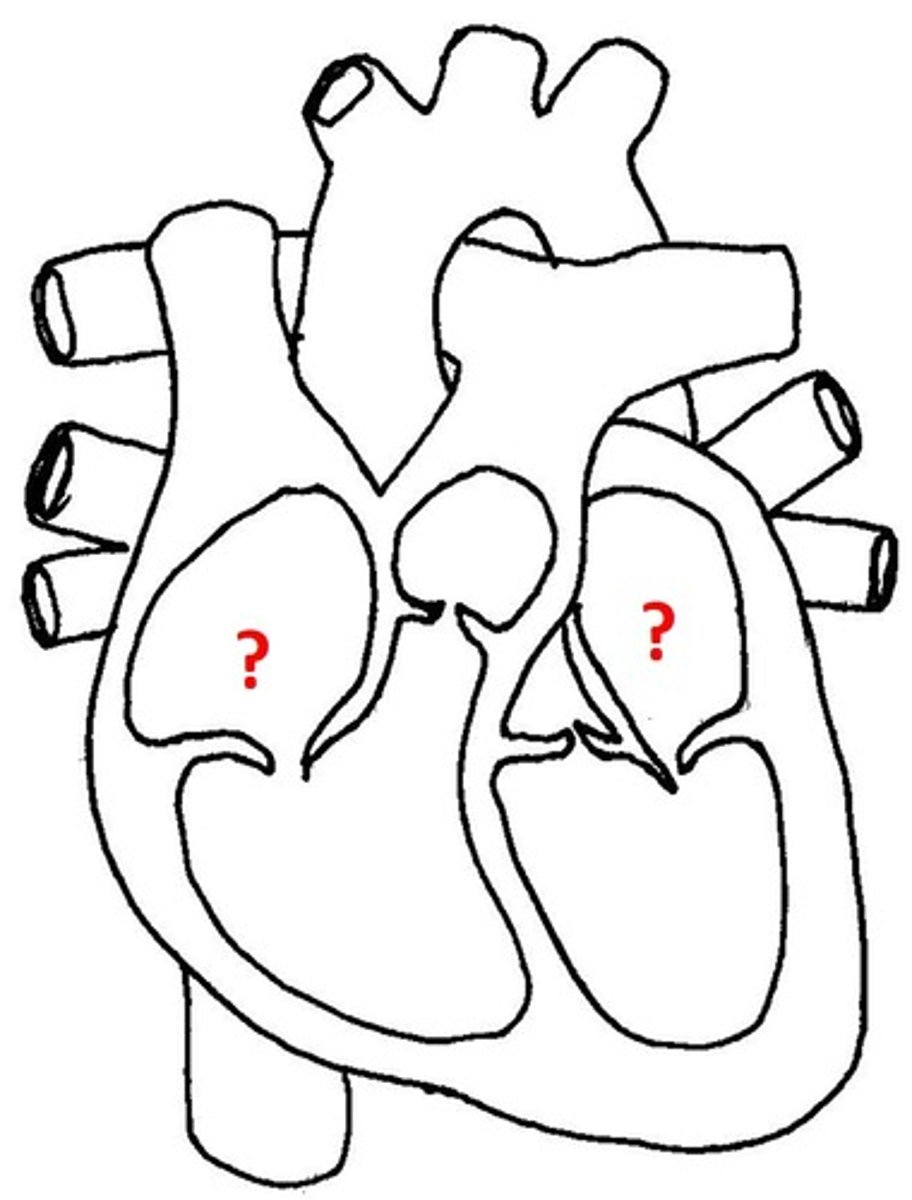
Ventricles
lower chambers of the heart that pump blood to arteries
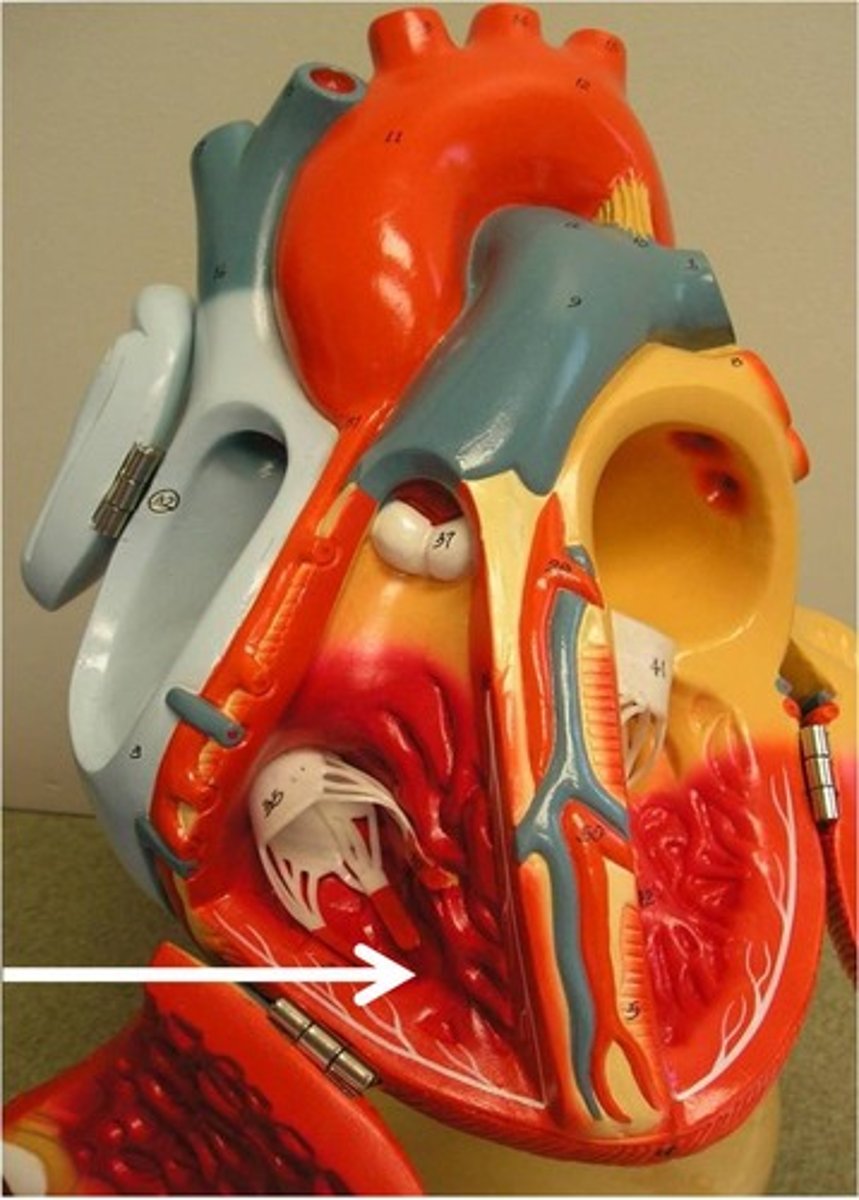
Valves
Flaps of tissue that open and close to allow the flow of blood in one direction only
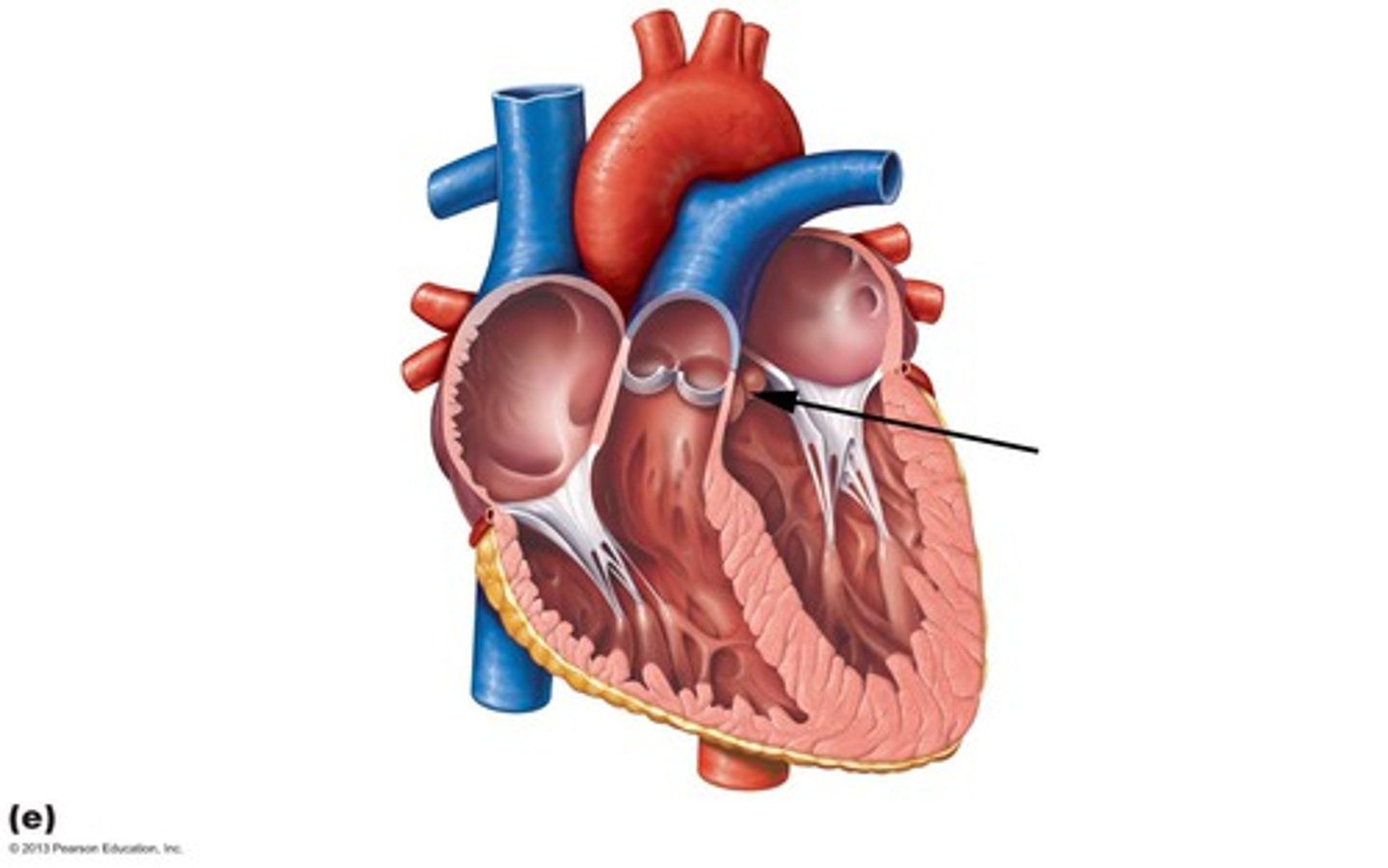
atrioventricular valves
valves located between atrium and ventricles
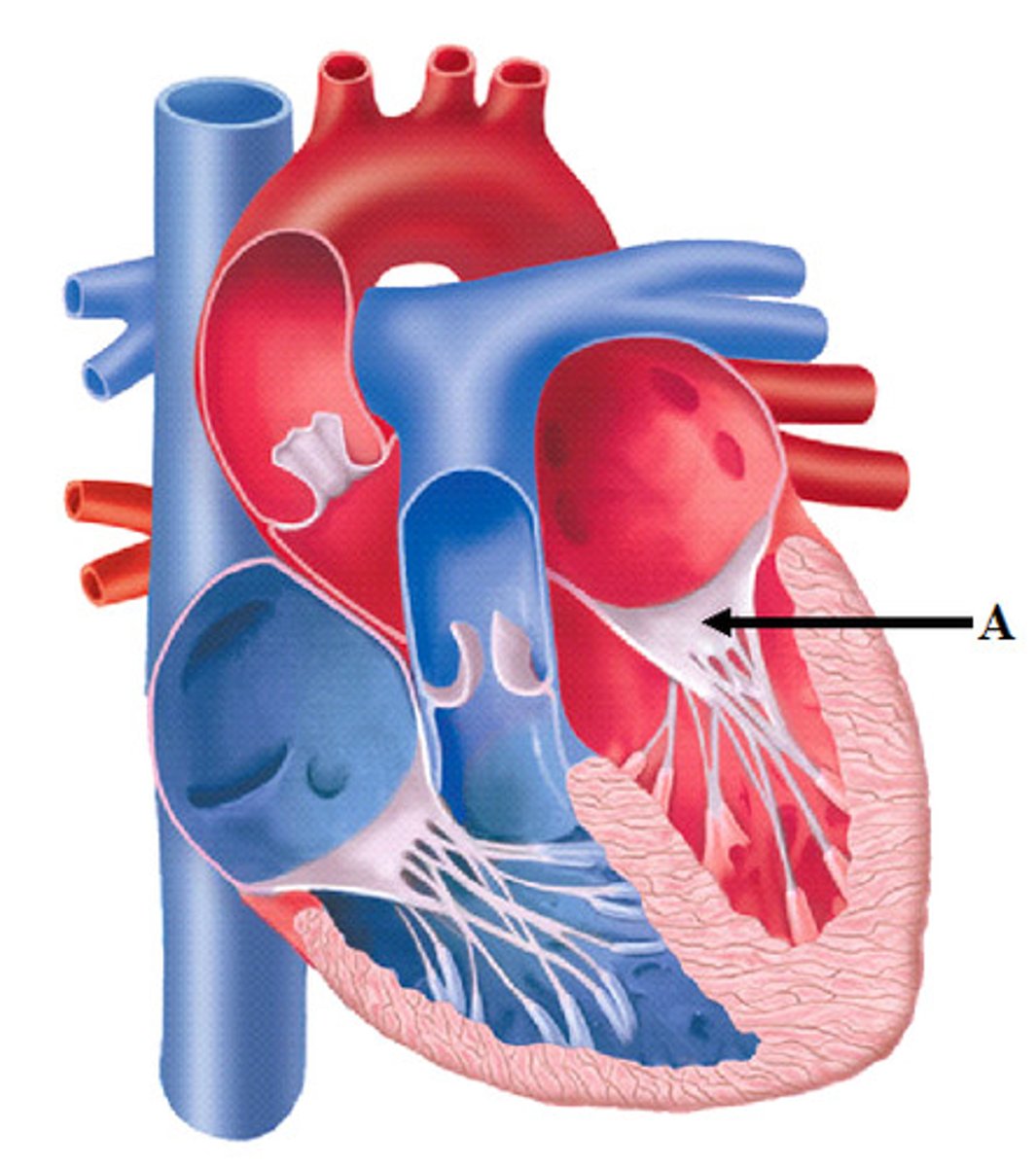
semilunar valves
valves located between the ventricles and arteries
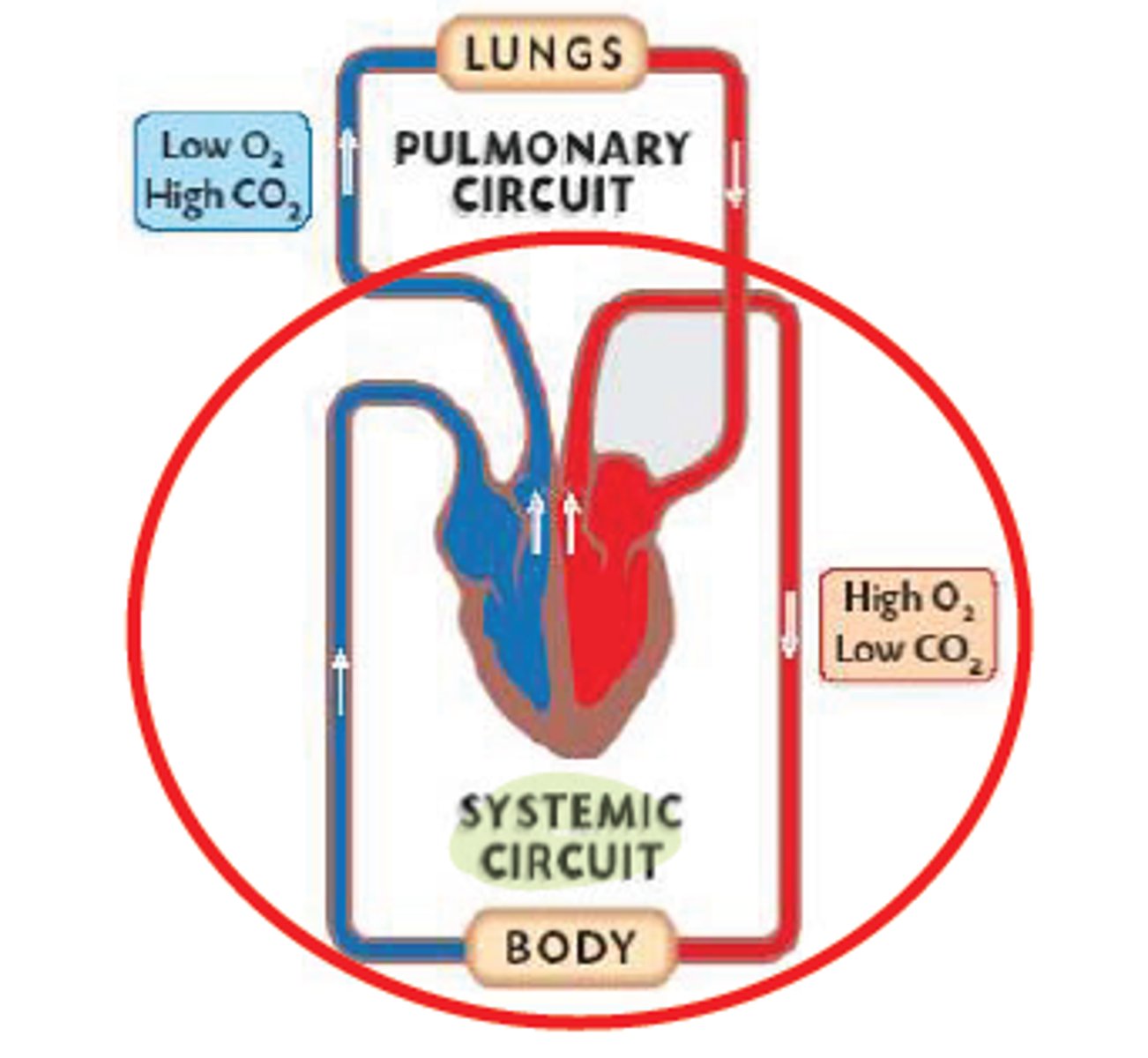
Pulmonary Circuit
carries blood to the lungs from right heart for gas exchange and returns it to the left heart --> oxygenates blood
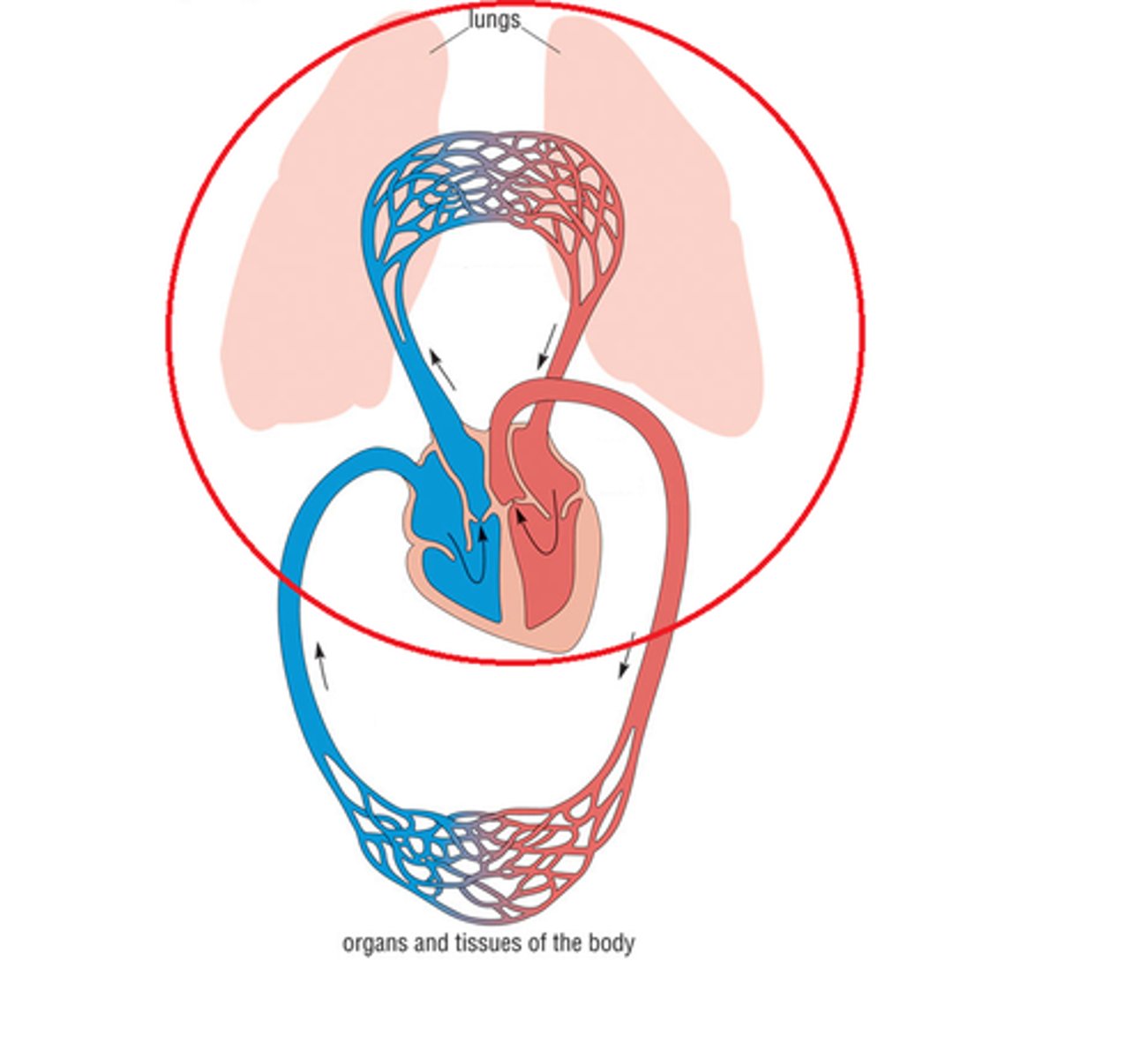
Systemic Circuit
carries blood between the left heart towards the body and back to the right heart --> delivers oxygenated blood to body
Cardiac Cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles
Step 1 of Cardiac Cycle
atrial, ventricular diastole --> relaxed heart lets blood into atria and ventricles
Step 2 of Cardiac Cycle
atrial systole, ventricular diastole --> atria contracts to push blood into ventricles
Steps 3 of Cardiac Cycle
atrial diastole and ventricular systole --> ventricles contacts to push blood from ventricles to arteries, atria relax to let blood flow from veins into atria
diastole
relaxation of heart that allows blood to fill
systole
contraction of heart muscles to pump blood
Cardiac Output
volume of blood ejected from the left side of the heart in one minute
Stroke volume
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction (mL/beat)
Heart Rate
number of beats per minute
Cardiac Output Formula
CO = SV * HR
Resting Cardiac Output
70mL/beat * 70 beats/min = 4900 mL/min
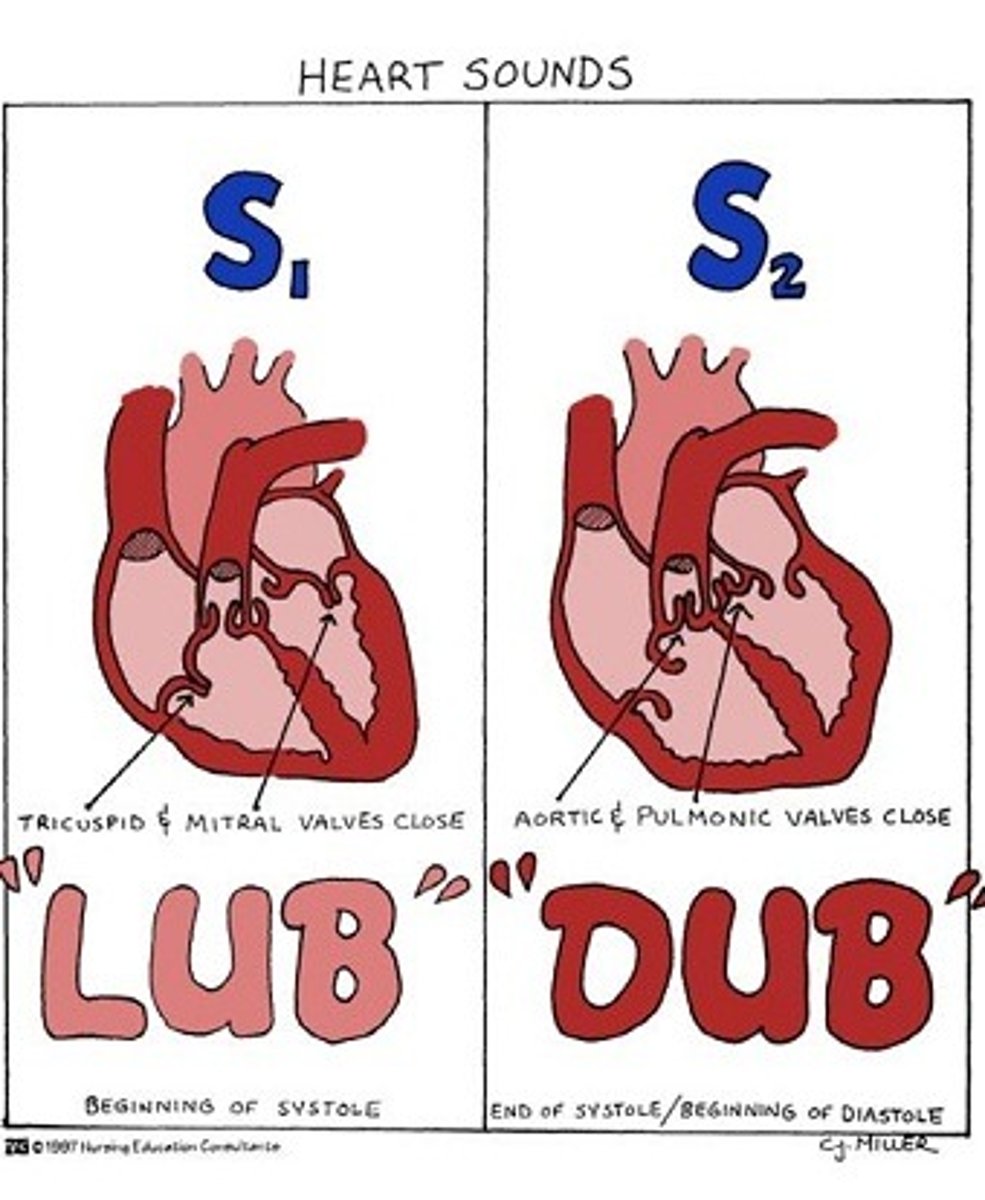
Heart Sounds
"lub" = AV valves close --> ventricular systole closes AV valves
"dub" = SL valves close --> ventricular diastole, aterial pressure closes SL valves
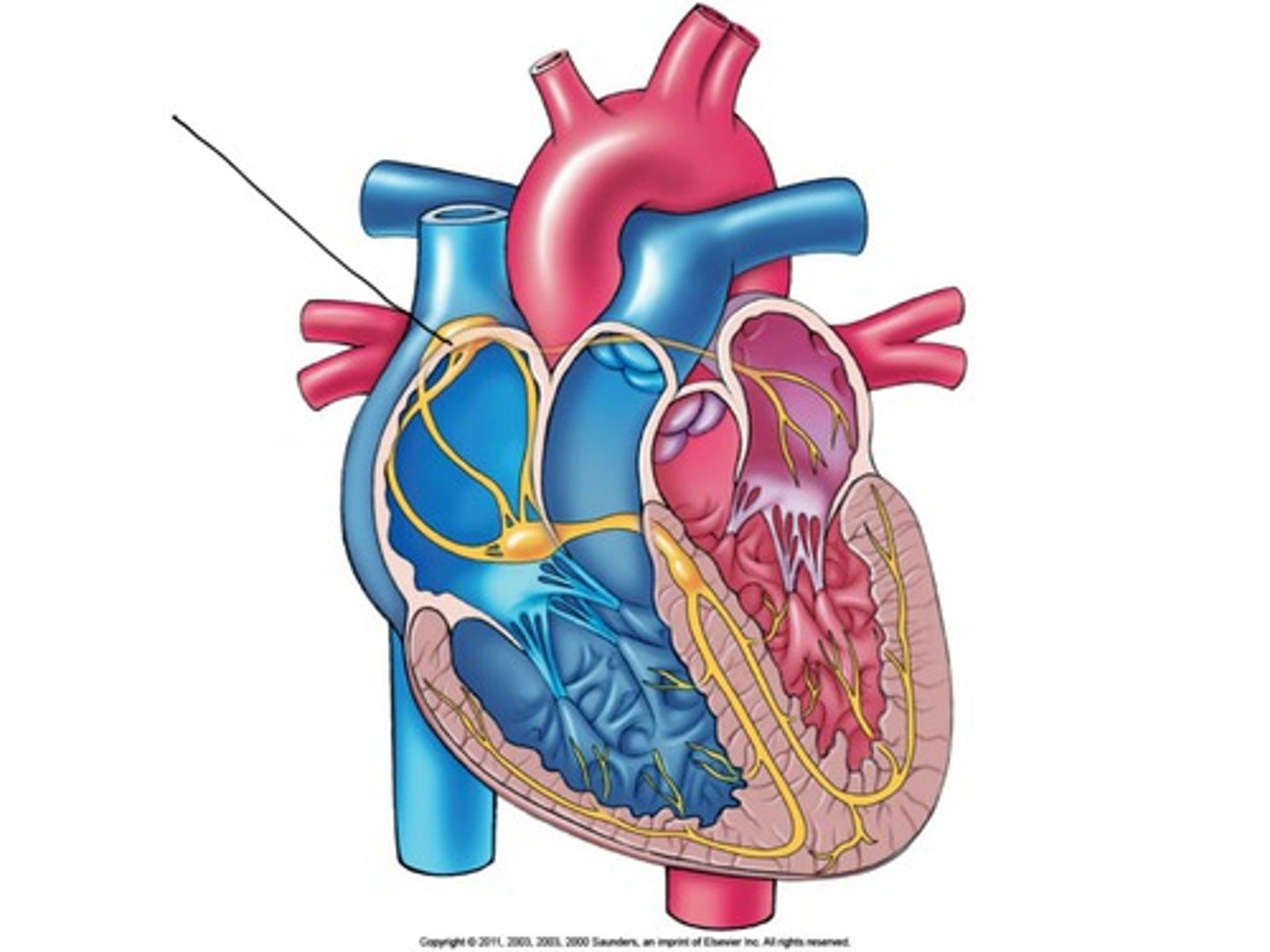
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
the pacemaker; highly specialized, neurological tissue impeded in the wall of the right atrium; responsible for initiating electrical conduction of the heartbeat, causing the atria to contract and firing conduction of impulses to the AV node
SA Node Regulators
- autonomic nervous system = sympathetic increase; parasympathetic decrease
- hormones = epinephrine
- body temperature
Electrical Conduction in Heart
SA node --> atria, AV node, fibers (bundle branches) --> apex (bottom), ventricles
Blood Flow
arteries --> arterioles --> capillaries --> venules --> veins
Arteries
deliver blood away from the heart
- stores systolic pressure --> slowly release
- maintains driving pressure during relaxation (diastole)
Arterioles
direct blood flow
- change diameter (vasoconstriction and vasodilation) --> resistance --> impacts blood pressure and directs flow
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing or constricting of blood vessels decreases blood flow to vessels
Vasodilation
widening of blood vessels increases blood flow to vessels
Capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
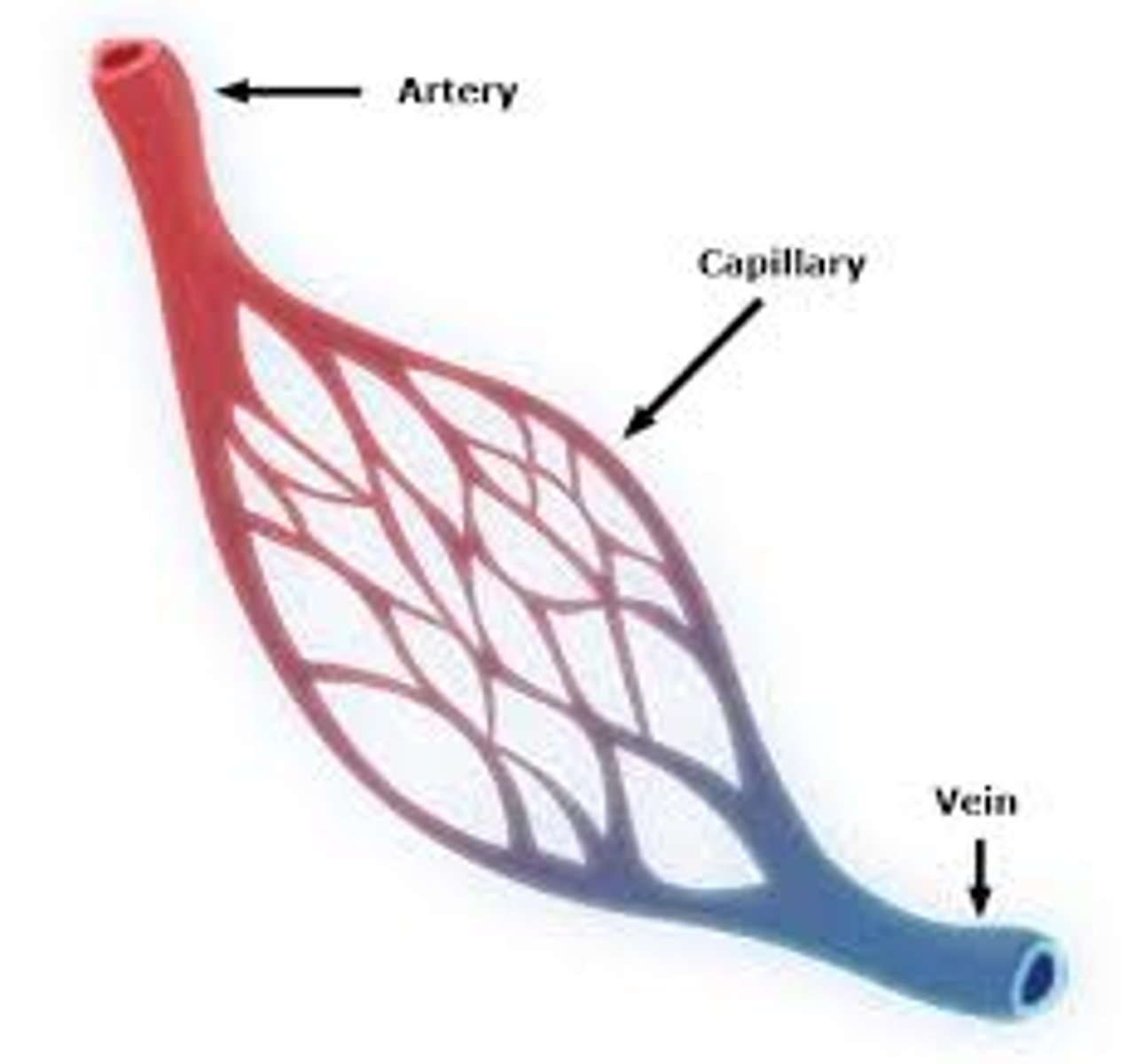
What is capillary flow controlled by?
- arteriole diameter/vasoconstriction/vasodilation
- precapillary sphincters that adjust flow into capillaries
Characteristics of capillaries
- narrow and numerous --> large surface area that decrease blood velocity and increase exchange
- thin, porous walls good for exchange
- no muscles
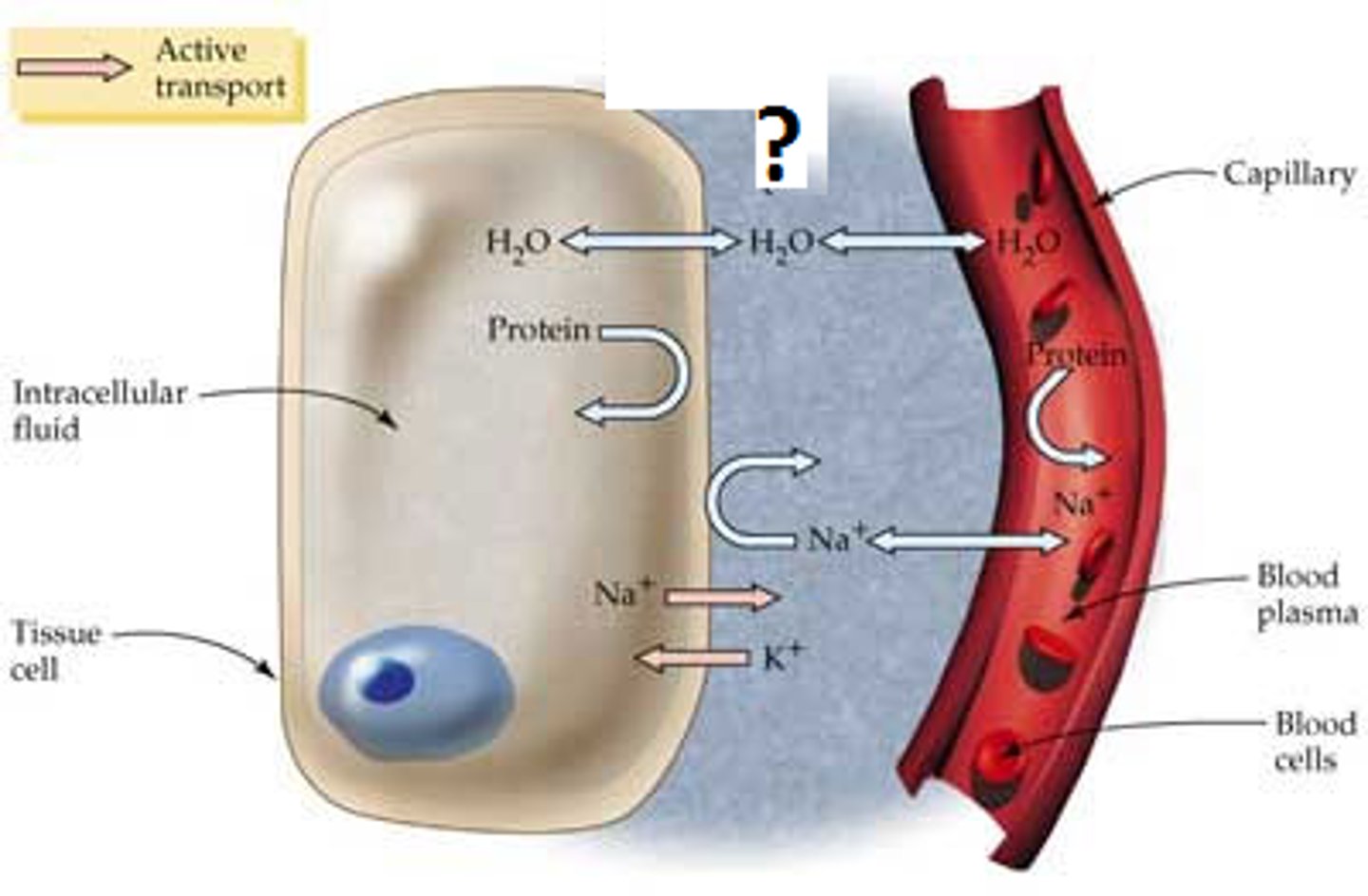
Capillary Exchange
large molecules (cells/proteins) --> most stay in blood/plasma, small number move via exo/endocytosis
small molecules (gases, ions, nutrients) --> through cells/diffusion/membrane transport; around cells via pores in capillary walls
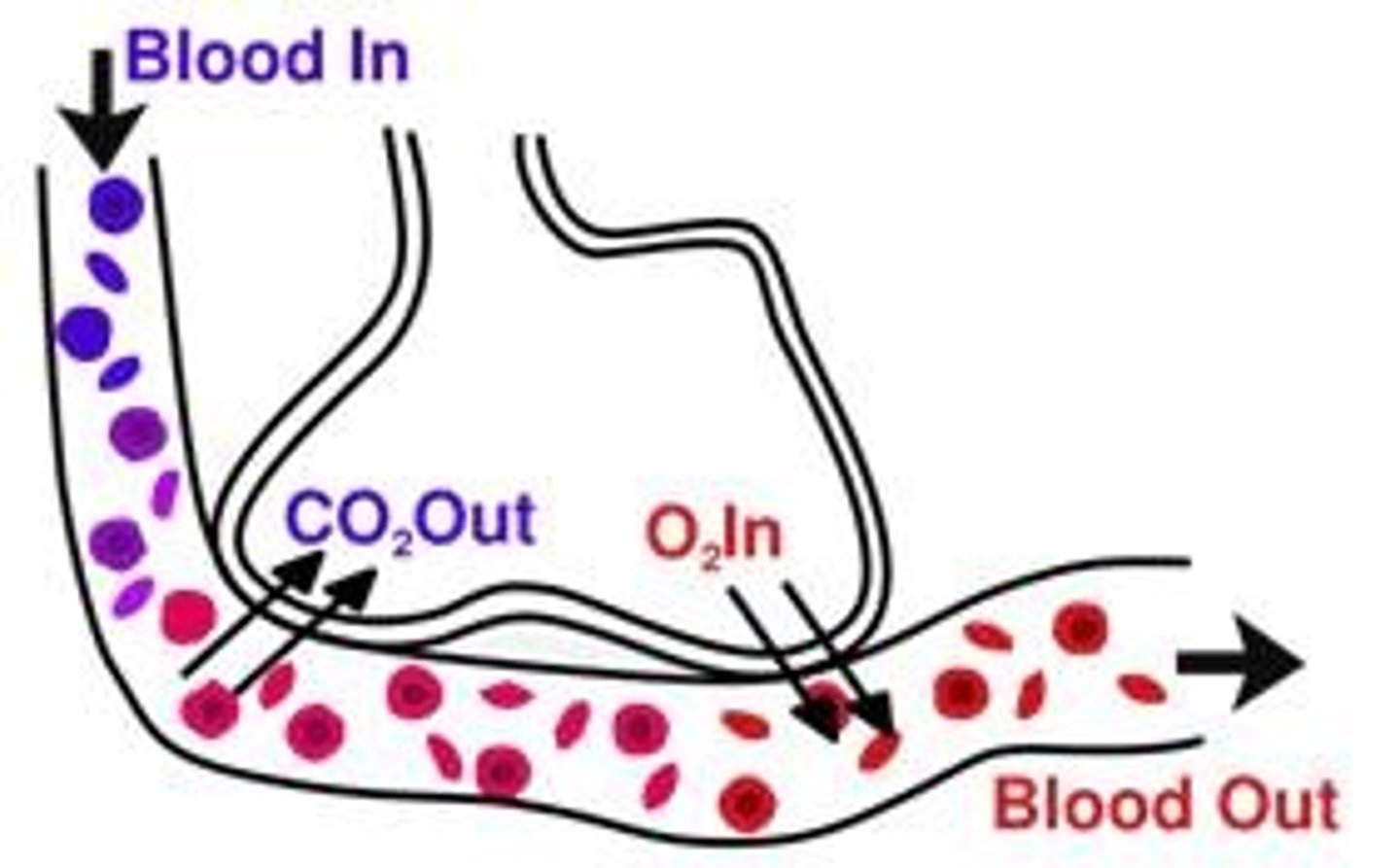
Capillary Exchange Pt. 2
fluids move through pores in capillary walls
- filtration (OUT): circulatory --> interstitial due to blood pressure
- reabsorption (IN): interstitial --> circulatory due to osmotic pressure pulls proteins back in
How fluids are returned into circulatory system
if filtration > absorption --> net loss of fluid. fluids collected and returned by lymphatic system
What is the impact of capillary porosity on blood pressure?
reduces blood pressure
Venules/veins
return blood to the heart that have one-way valves to ensure unidirectional flow
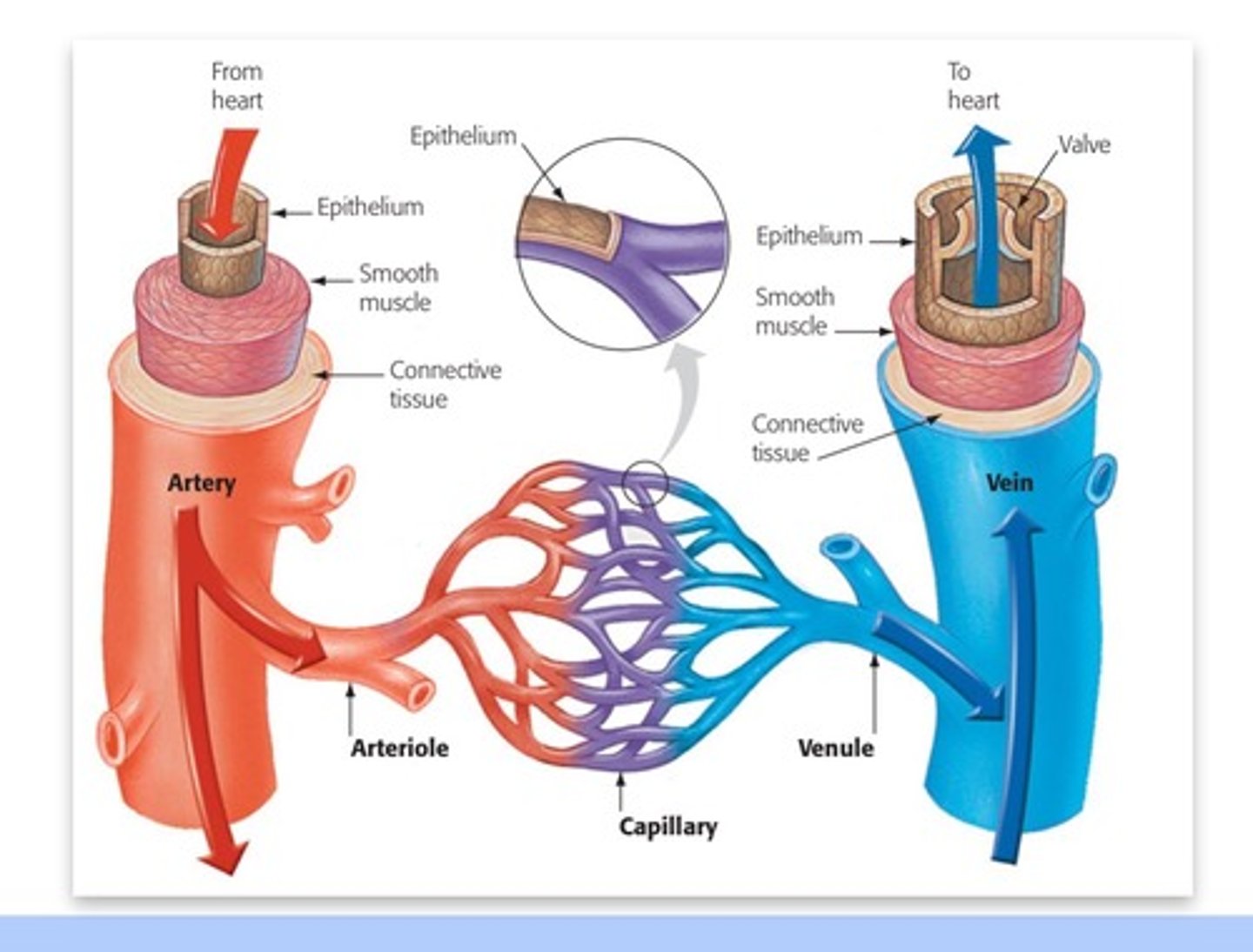
Venous Return
volume of blood returned to the heart hindered by gravity
How is blood aided in returning despite gravity?
- muscles in walls of veins (venoconstriction)
- peripheral pumps (skeletal and respiratory)
- diastolic suction
Starling's Law of the Heart
"pump what you get" --> influences stroke volume, cardiac output
Arteriosclerosis
"hardening of the arteries" due to lipid deposits/plaques that reduce elasticity --> narrow arteries and reduce flow --> heart attack when there is a blockage
Myocardial Infraction
"heart attack" due to blockage in coronary artery due to blood clot causing inadequate O2 to cardiac muscle that damages cardiac muscle
Treatments for Heart Attack
bypass surgery, stent, stem cells
Parts of the Respiratory System
upper = mouth, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx (conditions air and provides protection)
lower = trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli (exchange due to big surface area)
What drives breathing?
negative pressure breathing
- inhale = Pout > Pin, air moves in
- exhale = Pin > Pout, air pushed out
Tidal Volume
normal breath
Vital capacity
maximum inhale, maximum exhale
Residual volume
air remaining following exhale --> "used air mixes with "new" air
How does altitude impact breathing?
Altitude reduces pressure differences --> slows diffusion
What drives partial pressure gradients?
drives O2 from lungs into tissues and CO2 from tissues into lungs
Partial Pressure
Pgas = Ptotal *%gas
Hemoglobin (Hb)
tetramer protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds O2 in blood stream --> four O2 per Hb --> binding at one site influences binding at others
How does carbon dioxide influence Hb and O2 affinity?
increased CO2 production lowers pH, induces increased O2 release from Hb --> increased metabolic activity matched in increased O2 delivery
forms of CO2 transport
hemoglobin = Hb
plasma = 7%
bicarbonate = 70%
What are our bodies "lines of defense"?
- physical barriers = block entry
- internal innate responses = rapid, broad specificity
- adaptive immunity = slower, highly specific, develop through life
Two Major Branches of Immune System
Innate and adaptive immunity
Innate immunity
Immunity that is present before exposure and effective from birth. Responds to a broad range of pathogens.
Adaptive immunity
the ability to recognize and remember specific antigens and mount an attack on them
Surface Barriers
- skin
- mucous membranes (trap = mucous; inactive and wash away = tears, saliva; create hostile enviro = low pH of stomach, urinary tract, and skin)
- commensal bacteria
Leukocyte
white blood cells, which protect the body against disease
Innate Immune Responses
- First line of defense
(Fast, but nonspecific)
- Cellular and non-cellular innate defenses
Cellular Innate Defenses
- toll-like receptors (TLRs)
- phagocytosis (neutrophils, macrophages)
- targeted death of infected host cells (natural killer cells/lymphocytes)
Non-cellular Innate Defenses
- complement proteins (membrane attack complexes)
- anti-microbial peptides
Inflammatory Response
nonspecific defense reaction to tissue damage caused by injury or infection
Histamine
increased blood flow (vasodilation), makes capillaries more leaky
Cytokines
attract/activate other immune cells
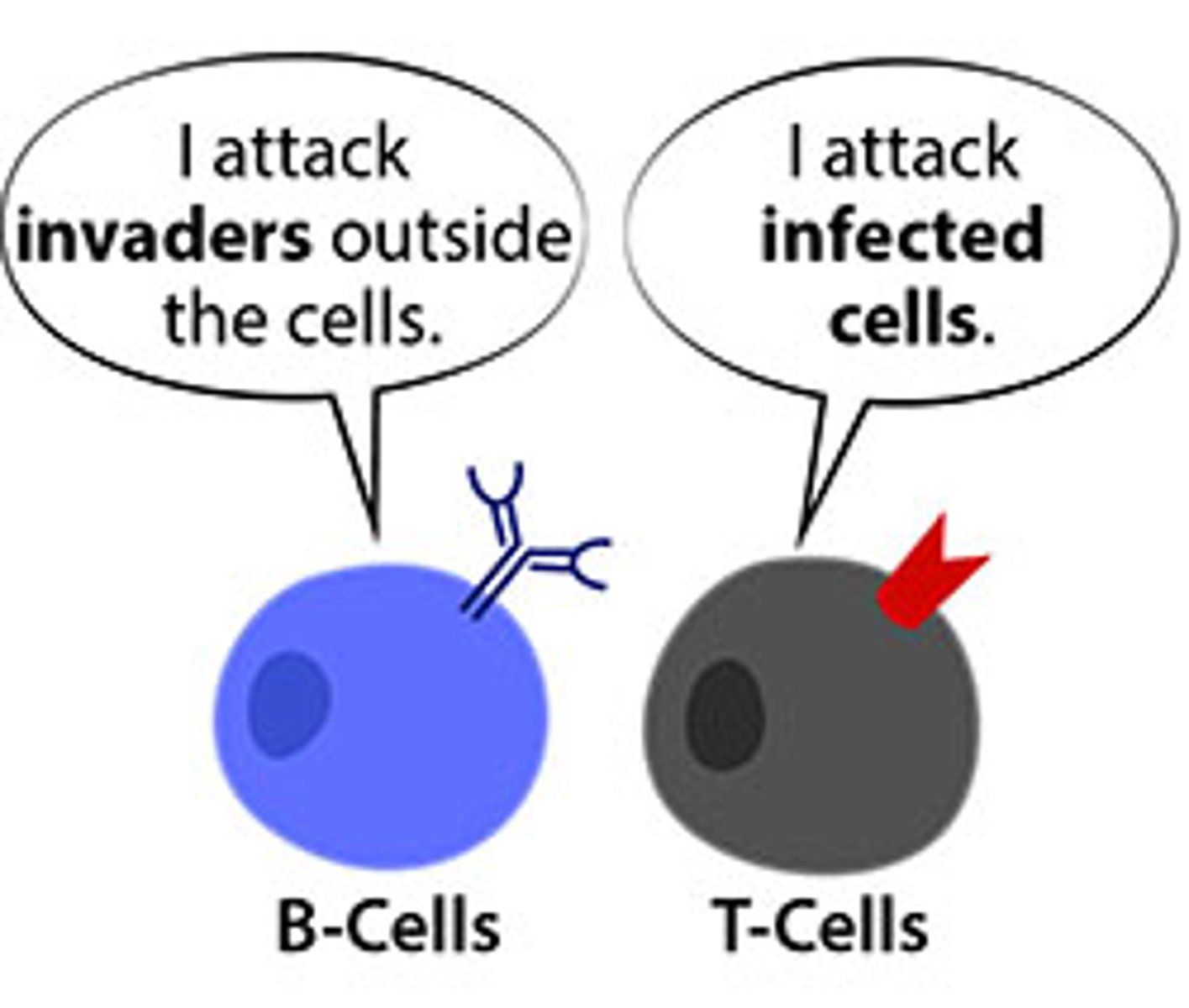
Lymphocytes
type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections
B-cells
cells manufactured in the bone marrow that create antibodies (antibody-mediated response) for isolating and destroying invading bacteria and viruses in blood --> antigen interaction stimulates antibody production
Humoral response
antibodies defend against infection in body fluids
T-cells
Cells created in the thymus that produce substances that attack infected cells in the body --> requires host cell presentation of antigen that is presented in MHC molecule
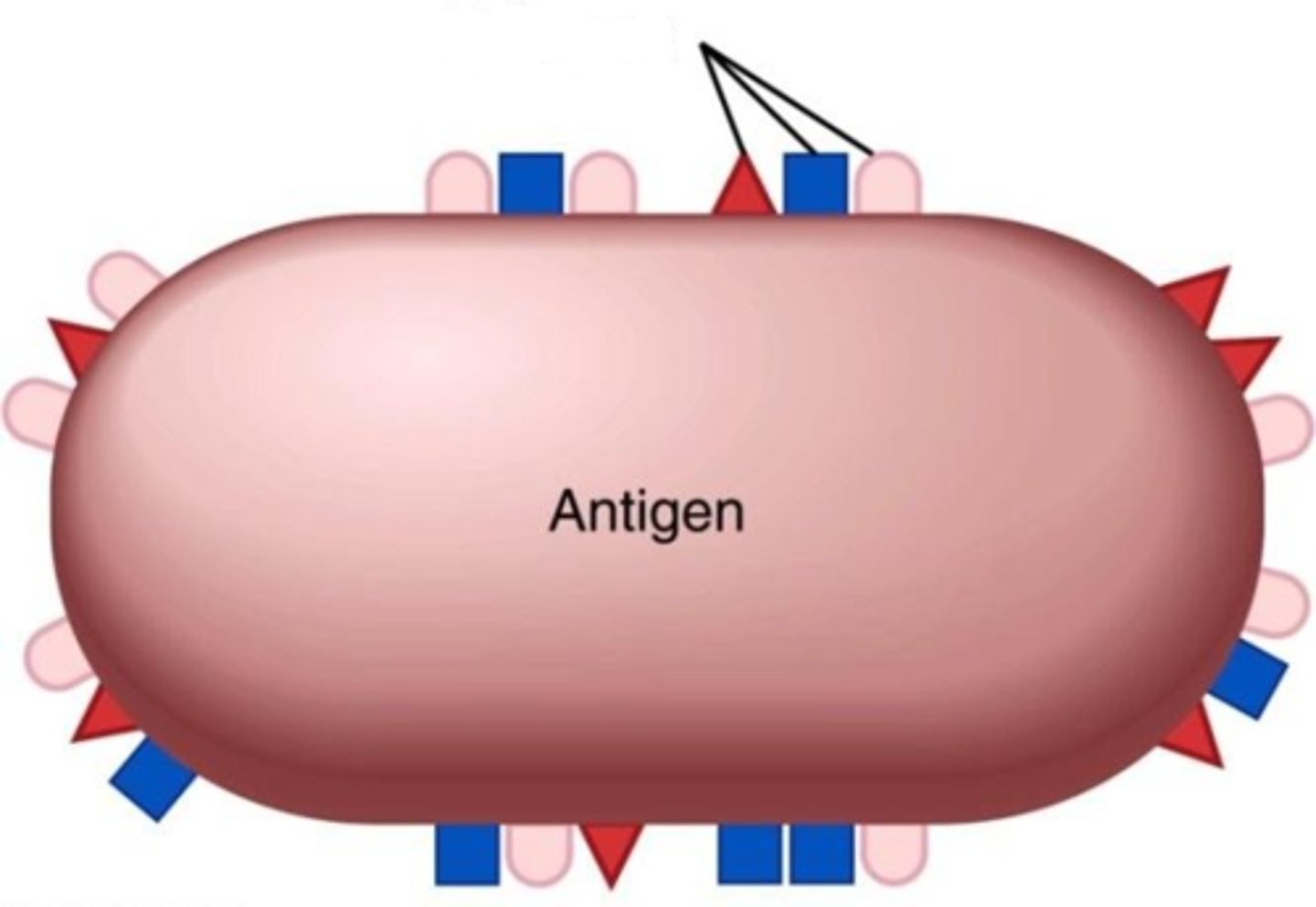
Antigen
any molecule that elicits a response from B or T cells using epitopes
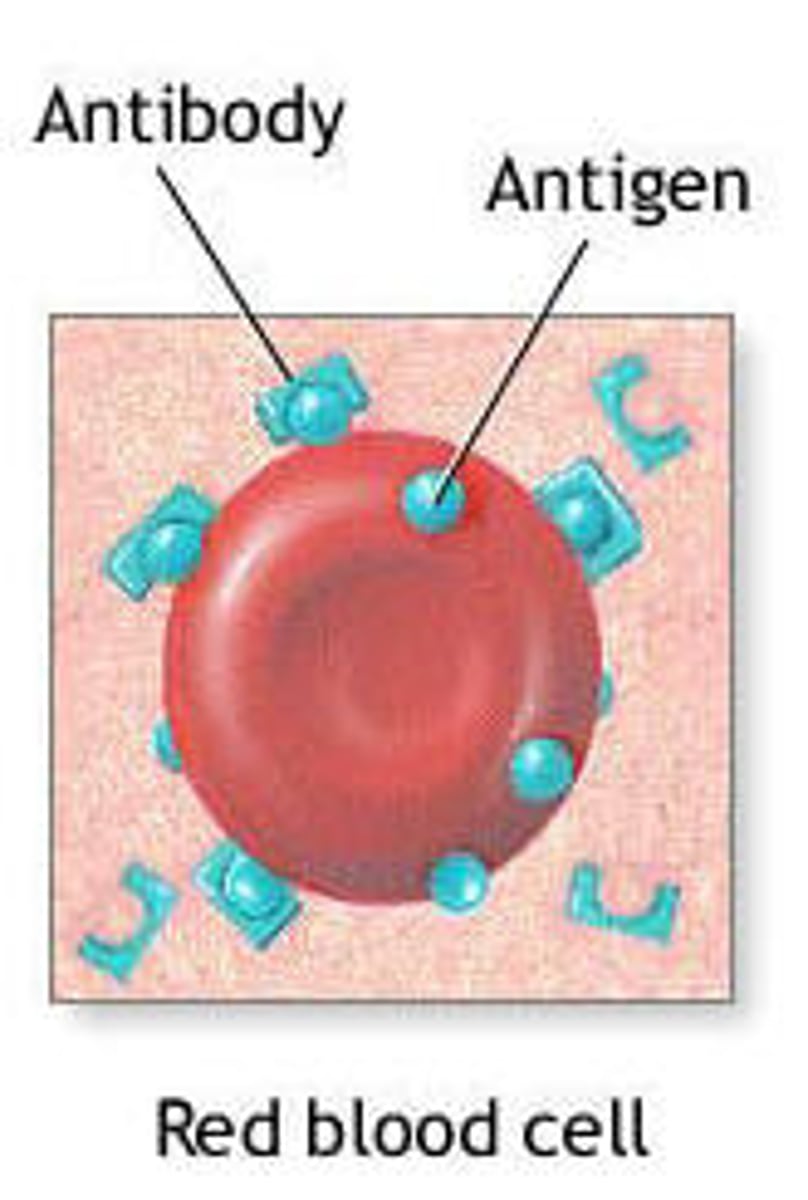
Epitopes
portion of antigen that binds the antigen receptor (receptor epitopes per antigen)
How is receptor diversity possible?
during development, segments of receptor genes are combined randomly (Pick 1 V, 1 J, add C, and combine)
Self-tolerance
the body lacks mature lymphocytes that can react against its own components
Autoimmune disease
immune system attacks self
clonal selection
antigens bind to specific receptors, causing a fraction of lymphocytes to clone themselves
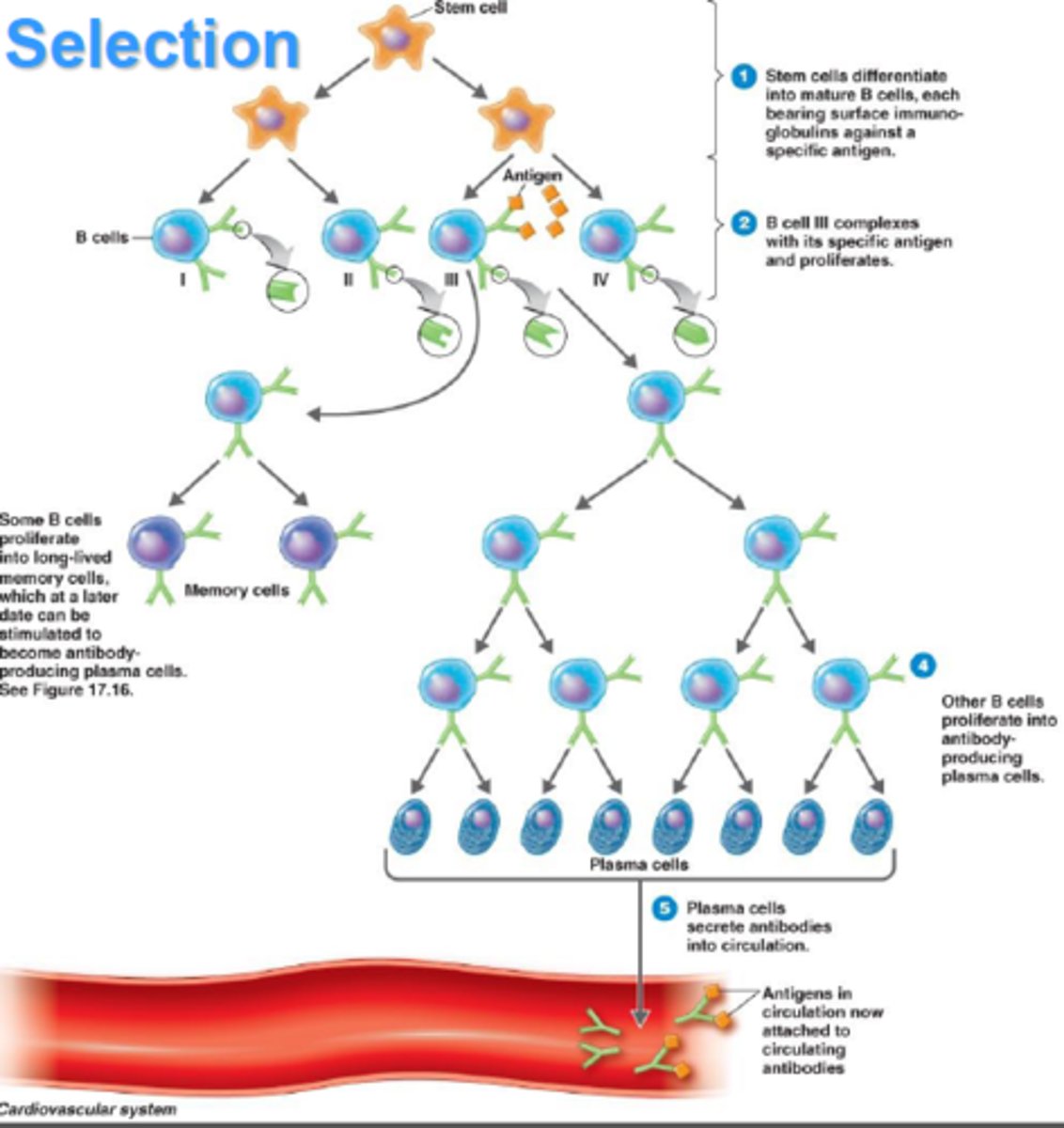
Step 1 of Clonal Selection
selection
Step 2 of Clonal Selection
clonal expansion
- mitosis
Step 3 of Clonal Selection
Differentiation
- effector cells = immediate action short-lived
- memory cells = persist for subsequent exposure
Antibody mechanisms of action
- neutralize pathogen directly
- facilitate phagocytosis
- activate other defenses
What are allergies?
exaggerated responses to antigen
MHC molecule
major histocompability complex
What is required to activate T-cells?
simulatenous interaction with antigen (via antigen receptor) and MHC molecule
What do activated T-cells release?
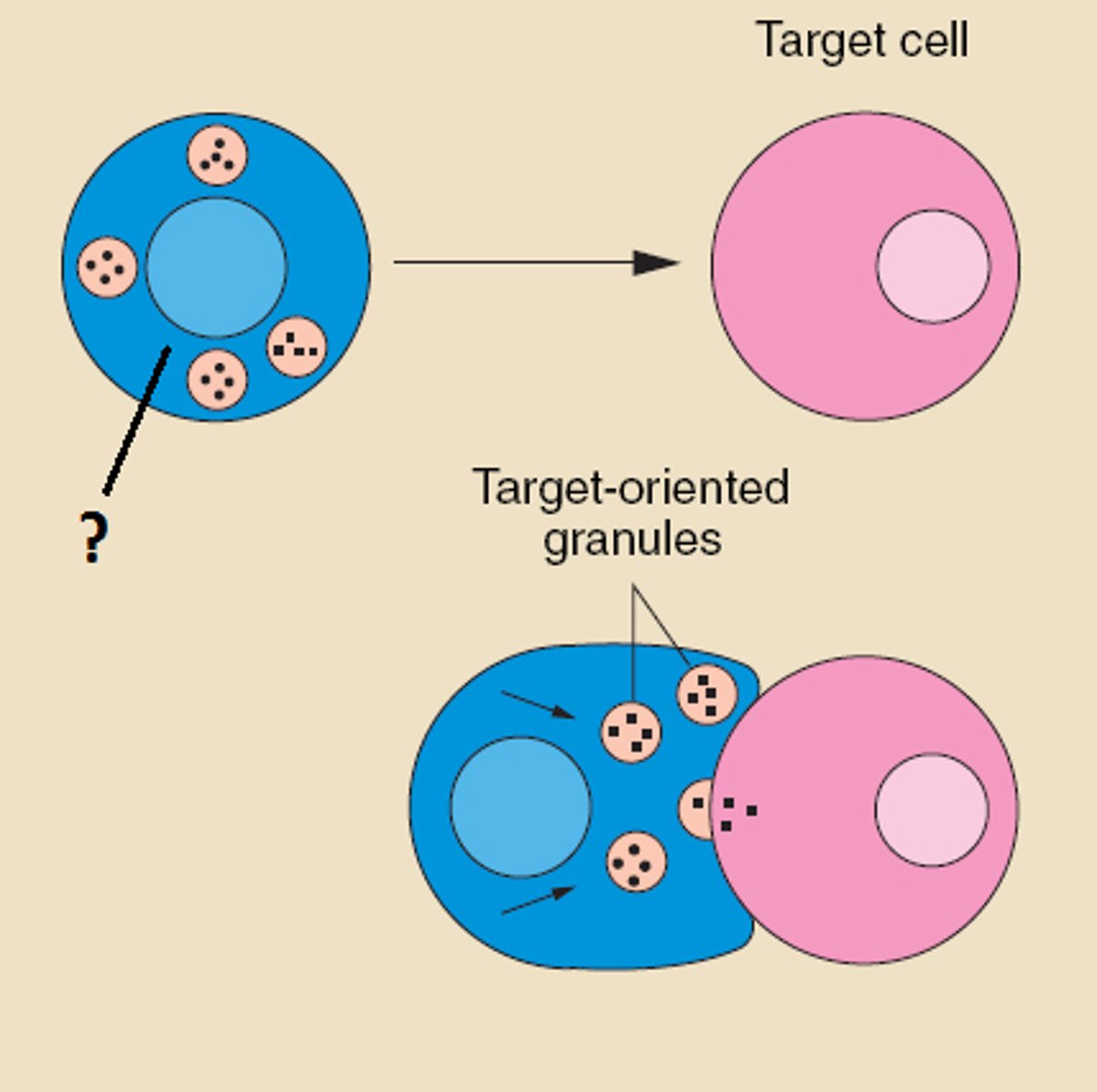
chemical to kill infected host cell (perforins that makes pores, granzymes which induce suicide)
Cytotoxic T-cell
activator = infected somatic cell
receptor = MHC-1
Helper T-Cell
activator = antigen-presenting WBC (dendritic cell, macrophage, B-cell)
receptor = MHC-2
What is unique about helper T-cells?
activates both branches of adaptive immune response (humoral and cell-mediated)
Active immunity
defenses derived from response to infection
- vaccination
Memory cells
B lymphocytes that do not become plasma cells but remain dormant until reactivated by the same antigen
Passive immunity
the short-term immunity that results from the introduction of antibodies from another person or animal.