BSN 3084- Midterm
1/228
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
229 Terms
How does the WHO define mental health?
A state of well-being in which an individual is able to realize his or her own potential, cope with the normal stresses of life, work productively and fruitfully, and make a contribution to the community
Public Health Agency define mental health as?
The capacity of each of and all of us to feel, think, and act in ways that enhance our ability to enjoy life and deal with the challenges we face.
Can a person be healthy without considering mental and physical health? (WHO 2014)
NO
What influences mental health?
Support systems
spirituality, religious influences
family influences
developmental events
personality traits and states
demographics and geographical locations
negative influences
cultural beliefs and values
health practices and beliefs
hormonal influences
biological influences
inherited factors
enviromental experiences
Mental Illness
Refers to all mental disorders with definable diagnoses (definable by DSM-5)
DSM-5
The diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Classifies disorders people have (Ie. major depressive disorder)
Consequences of mental illness stigma
limiting opportunities (housing, friends, employment, etc), two-thirds of people don’t seek treatment, people often conceal illness, creates barriers to care
Rights of a person with mental illness
Right to medical care
right to be treated with humanity and respect
equal protection right
right to be cared for in the community
right to provide informed consent before recieving any treatment
right to privacy
freedom of communication
right to voluntary admission
What is the aim of the mental health strategy for Canada
the aim of the strategy is to improve the mental health and well-being for all Canadians
Mental health for Canadians striking a balance goals?
Reducing inequalities
increasing prevention
enhancing coping
Where were mentally ill before mid-1800s
at home with family or in jail
1839 legislation of upper canada resolution
authorizing the building of the first asylum, used an old jail abandoned as unfit for prisoners
Why were asylums built?
industrialization increased need for institution
no medications or treatments at this time
mentally ill seen as nuisance
Mental health care spaces today
psych units in community hospitals
4 psych hospitals in Ontario
most MH clients served outside inpatient units
community-based MH services developed what?
day hospitals
crisis management teams
outreach services
primary care psychiatry (ACTT)
Fundamental premise of psychiatric nursing care is?
goal of nursing care is to promote wellness, maximize integrated function. Care is based on determined needs and expected treatment outcomes.
MH in community settings
assessment, case management, promoting continuation of treatment
MH in hospital
Managing behaviroal crisis, safety, suicide risk
Canadian MH act
Law that describes what should happen when someone who is living with a mental illness needs treatment and protection for themselves
Purpose of Canadian MH act
protect clients rights and freedom, keep client free from unlawful detainment, protect the public
Voluntary Patient
person agreed to be admitted to the psychiatric facility for care, observation, and treatment
Involuntary Patient
assessed by a psychiatrist and found to exhibit signs of mental illness and or impaired judgement
Informal patient
has been admitted with the consent of another (POA) who has the legal authority to give this consent
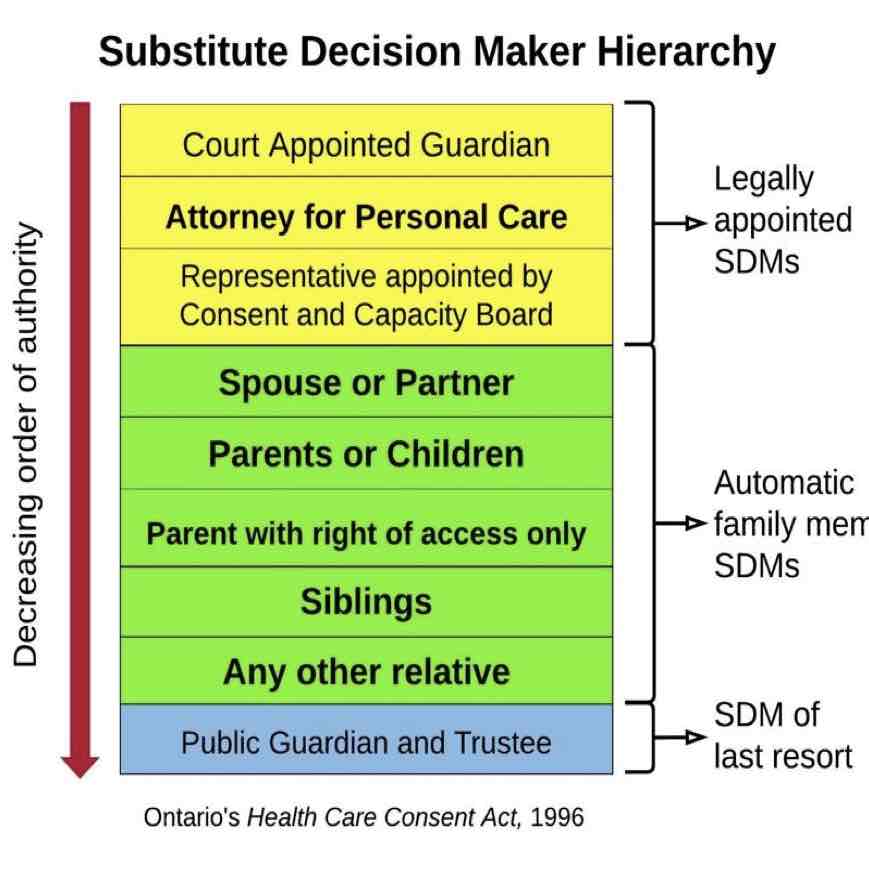
Substitute Decision Maker (POA)
a person who is authorized by law to make decisions on behalf of another (can be for care, property, or finance)
Public Guardian and Trustee (PGT)
an independent agency that can be given responsibility for making decisions on behalf of person who has been declared incapable. ward of the state
Substitute decision maker hierarchy (Highest to lowest)
requirements for admission
going voluntarily, police under MHA (section 17), Form 1, Form 2
grounds for detainment
danger to self
danger to others
displaying impaired judgement likely to result in harm to self
Form 1
By physician
can be held for 72 hours
person will receive a form-42 outlining why
person can refuse treatment *remember involuntary status is separate from treatment decisions
Form 2
an order for examination (signed by justice of peace) to be examined by doctor
Form 2 is based on
sworn statements from loved one
evidence of mental illness
danger to self or others
failure to care for own needs
Form 3
held for 2 weeks minus one day
cannot be initiated by same person as form 1
must be given a form 30 (the why)
patient has right to contest
pt recieves a rights advisor
Rights advisor
consults pt about rights within 24 hours of form 3, pt has right to refuse this
contesting form 3
if contested referred to consent and capacity board
Form 4
Renewal of form 3
first renewel: 30 days
second renewel: 60 days
third: 90 days
Can appeal each one
Form 5
discontinuation of forms or upon discharge
Informed consent
to give a informed consent a person must be capable of making decisions and be given information about their condition, recommended treatment, likely outcomes and risk of either accepting or refusing treatment
Competency
is the capacity to understand the consequences of ones decisions. pt are considered competent until legally declared incompetent
Capacity to consent Form 33
legally declared incapable to make treatment decisions for themselves. SDM will then make treatment decisions until (if) the person becomes capable
Community Treatment Order (CTO)
an order from physician which allows the pt to receive care in the community. it specifies exaxtly what dr, what meds, follows etc
Unintentional Tort
unintended acts that cause harm. Negligence and malpractice
intentional tort
causing harm on purpose
assault, battery, false imprisonment, invasion of privacy, defamation of character
Chemical restraints
antianxiety, antipsycotic, antidepressant, sedative-hypnotic
Physical restraints
hand mitts
lap belts
four side rails
geriatric chair
chest/vest
extremity (ankle or ankle)
Enviromental
seclusion
Physical alternatives to restraints
1:1 supervision
bed alarm
placing the client close nursing station
use of protective equipment or devices for IV sites
Psychosocial alternatives to restraints
reorientation
reassurance
de-esacalation
pet-therapy
distraction
activites
distraction
reducing stimulation
familiar objects
Legalities and ethics with restraints
supervision
documenataion
quick-realease tie to bed frame
2 finger spacing between wrist and extremity
HCP renew prescription Q 12 h
obtaining consent SDM
HCP seeing client to renew
What are the three most common cognitive disorders in adults?
delirium, dementia and depression
What is delirum?
altered LOC
disorientation
anxiety
agitation
poor memory
delusional thinking
hallucinations
is delirum a medical emergency?
yes
Etiology of delirum
always secondary to another condition
if other condition is corrected delirium should correct
Common causes of delrium
post-op
infections (uti)
metabolic disorders
intoxication or withdrawal
nervous system disease
tumor
systemic disease
psychosocial stressors
Four cardinal features of delirium
acute onset and fluctuating course
reduced ability to direct, focus, shift, and sustain attention
disorangized
disturbance of consciousness
Nursing implementation delirium
prevent harm from confusion, aggression, or fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Drug therapy delirium
haldol for severe agression
What is dementia?
a collection of symptoms caused by various diseases affected brain
Is dementia a normal part of aging?
no
dementia affects who
mostly older adults, 700000 + canadians
Four most common types of dementia
alzheimer’s disease
vascular dementia
dementia with lewy bodies
frontotemporal dementia
alzheimer disease
cause unknown
age is most important risk fact
changes in brain structure and function amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, loss connections between cells and cell death
plaques
alzheimers symtoms mild
mild forgetfullness
short-term memory impairment
difficulity recognizing what numbers mean
loss of intiative and intrests
poor judgement
difficulty finding the right word
confusion about location of familiar places
Anxiety
7 a’s of demenita
amnesia: memory issues
aphasia: communication deficient
apraxia: loss of motor skills
agnosia: difficulty cognizing intended use of items
altered perception: can’t judge
apathy: malaise, depression
anosognosia: unaware of neurological deficit
Late stages alzheimers symptoms
long-term memory loss
unable to communicate
cannot perform ADLs
the client may be unresponsive and require total care
Diagnosing Alzheimers
diagnosed by ruling out everything else
through comprehensive analysis
Alzheimers drugs acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
improve or stabilize cognitive decline by blocking cholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine
donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine
Alzheimers drugs NMDA
protects nerve cells against excessive amounts of glutamate
mematine
Alzheimers drugs SSRI
treat associated depression
may help with sleep
sertaline, fluvoxamine, citalopram
Alzheimers drugs anticovulsants
maange behaviour, stabilize mood, improve cognition
levetiracetam
Alzheimers behavioural problem
occur in 50-60%
all actions are purposeful expressing a need
Alzheimers sundowning
a specfic type of agitation client becomes more confused and agitated in late afternoon and evening
Alzheimers safety concerns
injury from fall
wandering
injury to others and self
fire or burns
impaired judgement or descion
sundowning interventions
drugs
exposure to daylight
limit naps and caffeine
maintain a quiet calm environment
Alzheimers eating and swallowing (late and middle)
loss of interest in food, decreased ability to self feed
when chewing and swallowing becomes difficult use pureed food, thickening, nutritional supplements
Dementia with lewy bodies
characterized by presence of lewy bodies in brain stem, amygdala, and cortex
Have parkinsons and Alzheimers symptoms
Vasuclar demenita
may have sudden onset after cerebrovascular event
frontotemporal dementia
degeneration of the frontal lobe, temporal lobe or both
nerve cells die because of the accumulation of proteins in neurons
Creutzfeldt-jakob disease
rare and fatal
caused by prions
what is parkinson’s disease
disease of basal ganglia characterized by
slowing down of initation and execution of movement
increased muscle tone
tremor at rest
impair postural reflexes
pathology of parkinson’s disease
degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons, disrupts dopamine-acetylcholine in basal ganglia
Classical triad of parkinson’s disease
tremor
rigidity
bradykinesia
Begining stages vs Later stages of parkinson’s disease
beginning stages involve only mild tremor, slight limp arm swing
later stages may have shuffling, propulsive gait with arms flexed and loss of postural reflexes
what is rigidity parkinson’s disease?
increased resistance to passive motion when limbs are moved
typified by a jerky quality,
cogwheel
caused by sustained muscle contraction (pt may be sore tired and achy)
what is bradykinesia parkinson’s disease?
slowing down inintiation and execution of movement
evident loss of autonomic movements PD (bradykinesia)
blinking
swing arms while wlaking
swallowing of salvia
self-expression
minor movements of postural adjustment
tremor PD
minimal initially
prominent at rest
pill rolling
benign essential tremor (during voluntary movement)
how is PD diagnosed?
no specfic test
diagnosed based on hx and clinical features
diagnosis can be made when two of three of classic triad are present
Levodopa with carbidopa (sinmet)
precursor of dopamine coverted to DA in basal ganglia
carbidopa inhibits enzymes from breaking down levodopa
Anticholinerigics PD
decrease acticity of acetylcholine
Drugs for tremors
antihistamines with anticholinergic or beta blockers
What does entacapone do?
prolonges the effects of sinemet
Sugical care PD
ablation surgery
deep brain situation (electrode in the brain delvers current to specific location)
Nutrition PD
easy to swallow
cut small
several small meals
levodopa can be impaired by protein and B6
Consider mobility PD
remove rugs (shuffling)
back of the chair on blocks
think about stepping over a line on the floor
walk with toes up
What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
chronic progressive degenerative disorder of the CNS, demyelination of nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord, women more than men, onset around 30
Cause of MS
cause unknown, multiple genes confer susceptibility, could be related to external factors
Pathophysiology of MS
characterized by chronic inflammation, demyelination, and gliosis in the CNS, autoimmune by T-cells
Disease process of MS
loss of myelin
disappearance of oligodendrocytes
proliferation of astrocytes
plaques scattered throughout the CNS
myelin replaced by scar tissue
Symptoms of MS
weakness or paralysis of limbs, trunk, and head
diplopia
scanning speech
spasticity of muscles
numbness and tingling
patchy blindness (scotoma)
blurred vision
vertigo and tinnitus
decreased hearing
neuropathic pain
lhermitte’s sign (electric shock down spin moving neck)
nystagmus
ataxia
dysarthria
dysphagia
constipation
spastic bladder
flaccid bladder
sexual dysfunction
anger
depression
euphoria
Diagnosis of MS
Multiple lesions on MRI
CSF analysis