Chemical bonding - year 10 IGCSE chemistry
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Ionic bonding
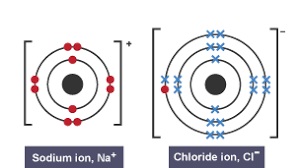
A chemical bond formed when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom between a metal and non-metal
Ion
An electrically charged atom or group of atoms that are formed by the loss or gain of electrons
Dot and cross diagram for ionic bonding
Properties of ionic compounds
Solid at room temperature
Have high melting and boiling points
Not an electricity conductor when solid, only in an aqueous
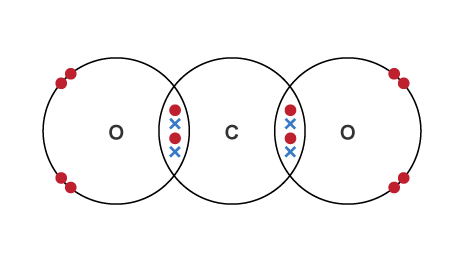
Covalent bonding
A chemical bond that forms when 2 non-metal atoms share a pair of electrons on the outer shells of the atoms
Dots and cross diagram for covalent bonding
Properties of covalent structures
Low melting and boiling points
Cannot conduct electricity
Giant covalent structures
Contains many atoms each joined adjacent atoms by covalent bonds and arranged into giant regular lattice
Properties of giant covalent structures
Very high melting points
Variable electrical conductivity
Allotropes
Different structural forms of the same element under the same element
Fullerene
An allotope of carbon that are connected by single and double bonds
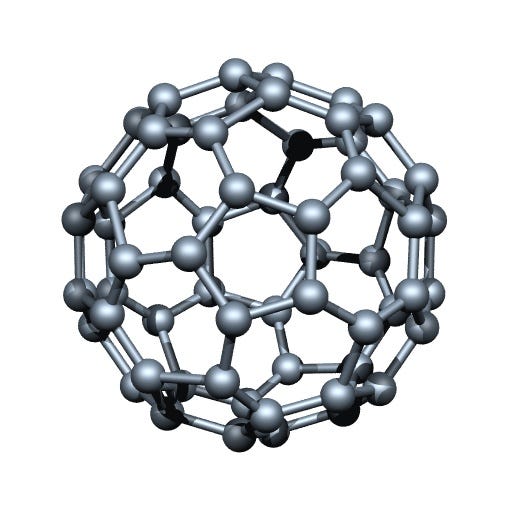
Carbon’s allotropes
Diamond, graphene, graphite
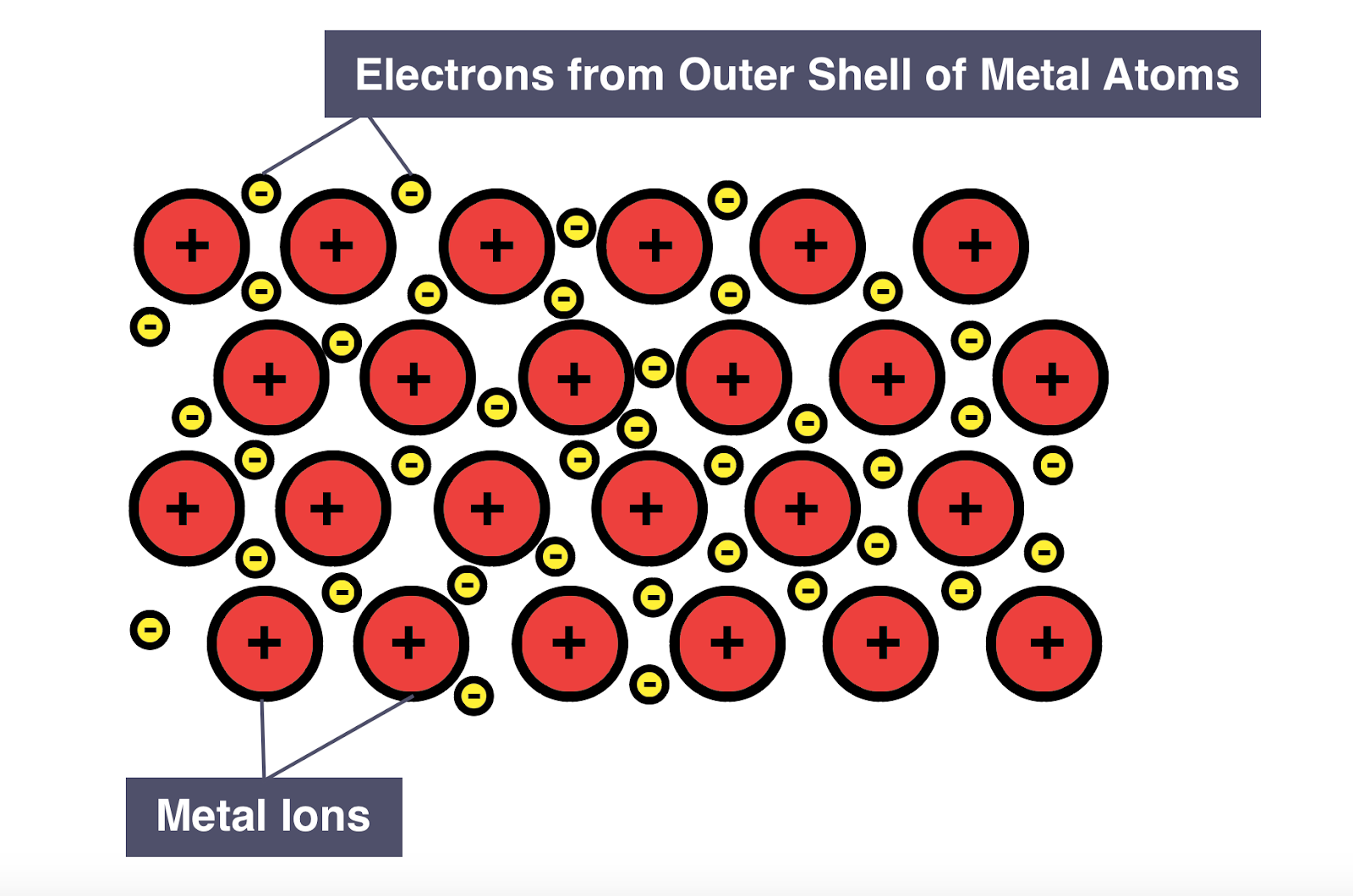
Metallic bonding
The attraction between the positive ions and delocalized electrons that keep the ions together
Metallic lattice
Giant 3-dimensional lattice structure of positive ions (cation) surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons
Properties of metallic bonding
High melting and boiling points
Conducts electricity
Malleable and ductile
Alloy
2 or more different elements mixing together 2 different metals
Cation
An ion with a positive charge
Anion
An ion with a negative charge