Bio 3218 Lecture 4 -- Fungus Like Organisms and Chytrids (basal Fungi)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the 3 Groups of Fungus-like Organisms
1. Kingdom Rhizaria
2. Kingdom Chromista
3. Kingdom Amoebozoa
What Classes Belong in Kingdom Rhizaria
- Plasmodiophoromycetes
What Phylum Belong in Kingdom Chromista
- Hyphochytriomycota
- Labyrinthulomycota
- Oomycota
What Classes Belong in Kingdom Amoebozoa
- Myxomycetes
- Dicytosteliomyctes
Kingdom Amoebozoa, Phylum Mycetozoa, Class Myxomycetes
- Plasmodial slime moulds
- Ex. Stemonitis fusca
What is a Plasmodium
- an acellular mass of protoplasm that glides around
- feeding by engulfing organic particles, bacteria, and other microbes
What is the Difference Between Stemonitales and Comatricha
- In Stemonitales the capillitium ("hair ends") are joined/ connected
- In Comatricha the capillitium ("hair ends") are free
What is the Function of the Capillitium
- Absorbs water
- Flings spores out so they can germinate
What is a Capillitium
- a mass of very fine threads interspersed among the spores of certain fungi
Do Spores Have a Cell Wall
- NO
Do Ameobas Have a Cell Wall
- No cell wall, only a cell membrane
- They will eventually lose 1/2 cell membranes
- Cell membrane has a pool of slime remains
Kingdom Amoebozoa, Phylum Mycetozoa, Class Dictyosteliomycetes
- The cellular slime moulds
- Ex. Dictyostelium discoideum
- Important in biochemical studies of development and intercellular communication via c-AMP
What is a Pseudoplasmodium
- A multicellular mass of protoplasm that glides around
- Feeding by engulfing organic particles, bacteria, and other microbes
Why is Dictyostelium discoideum Used for in Research
- Because of how it interacts with cells using c-AMP
Life Cycle of a Spore
1. Spore
2. Germinating Spore
3. Amoeba
- engulf bacteria and other small particles of food
4. Bacterial colony
- aggregates to form a larger structure
5. Aggregation
- there is genetic variation here
- amoeba aggregates with other amoeba to form this structure
6. Slug
7. Young Sporangium
8. Mature Sporangium
- made up of stalk cells: cells which make up a stalk for other cells to climb up
- were once amoeba that got left behind when fruiting bodies were formed
- group of spore cells form a ball ontop of stalk cells
9. Cycle REPEATS
Kingdom Rhizaria, Phylum Cercozoa, Class Plasmodiophoromycetes
- The plant slimes
- Have an acellular plasmodium within plant tissues
How do Plant Diseases Infect Fungi
- Infect via swimming zoospores (flagellete stage)
- Form a plasmodium and eventually resting spores within the plant tissues
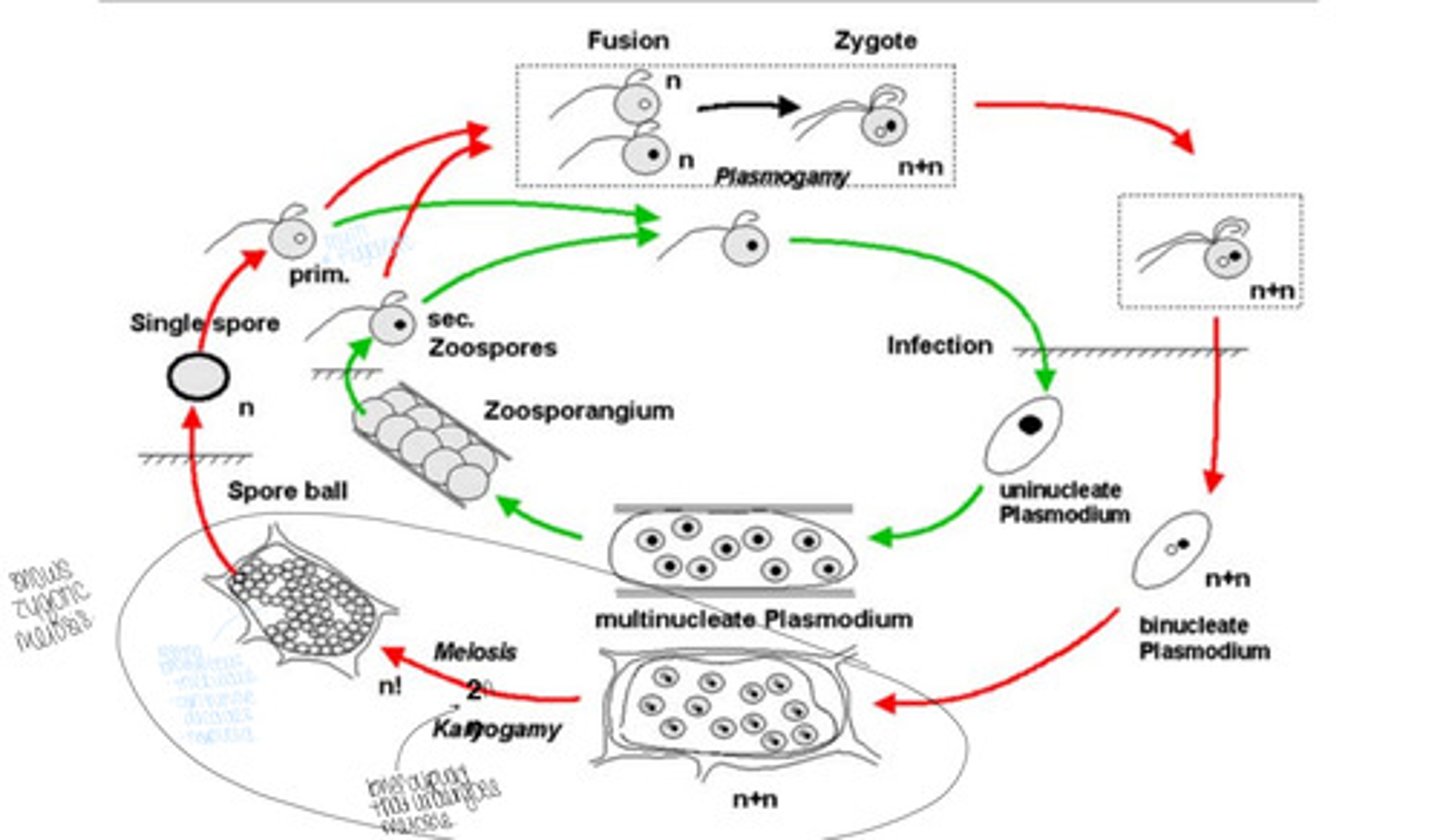
What is the Zygotic Meiosis Life Cycle of Spongospora subterranea
Kingdom Chromista, Phylum Hyphochytriomycota
- Tinsel tailed water moulds
- Contain a single flagellum but it is tinsel flagella
- Asexual
- Small minor group in terms of # of species
- important in regulating numbers of freshwater plankton algae, chytrids, and oomycetes
Kingdom Chromista, Phylum Labyrinthulomycota
- Net slimes
- Have a pseudoplasmodium, but take the form of a net or reticulum
- Marine and have cellulose cell walls
Kingdom Chromista, Phylum Oomycota
- Two-tailed water moulds
- Have a cellulose cell wall and 2 different flagella:
1. Whiplash Flagellum
2. Tinsel Flagellum
- Includes many important plant pathogens
- including Phytophthora infestans --> cause of late nlight of potato
What Happens to Potato Leaves Under Warm/Dry Conditions
- Most of the field will survive
What Happens to Potato Leaves Under Cool/ Moist Conditions
- Most of the field will not survive
What is a Phytopthora
- Goes through the plant, kills it, and digests it for its nutrition
What is the First Part of a Plant to Die
1. Leaves
2. Stem
What Does the Oomycota Have
- cellulose cell wall
- biflagellette zoospores
- this tells us that it is not a unikont
What is a Deciduous Zoosporangium
- another word for spore
- drops and gets blown by wind
- can either land on a leaf in cool/ moist conditions or it lands on a leaf in warm/dry conditions
Cool/Moist Conditions:
- spore hatches and releases zoospores
Warm/ Dry Conditions:
- spore germinates with a hyphae
What is a Necrotrophic Pathogen
- a pathogen that feeds on dead stuff
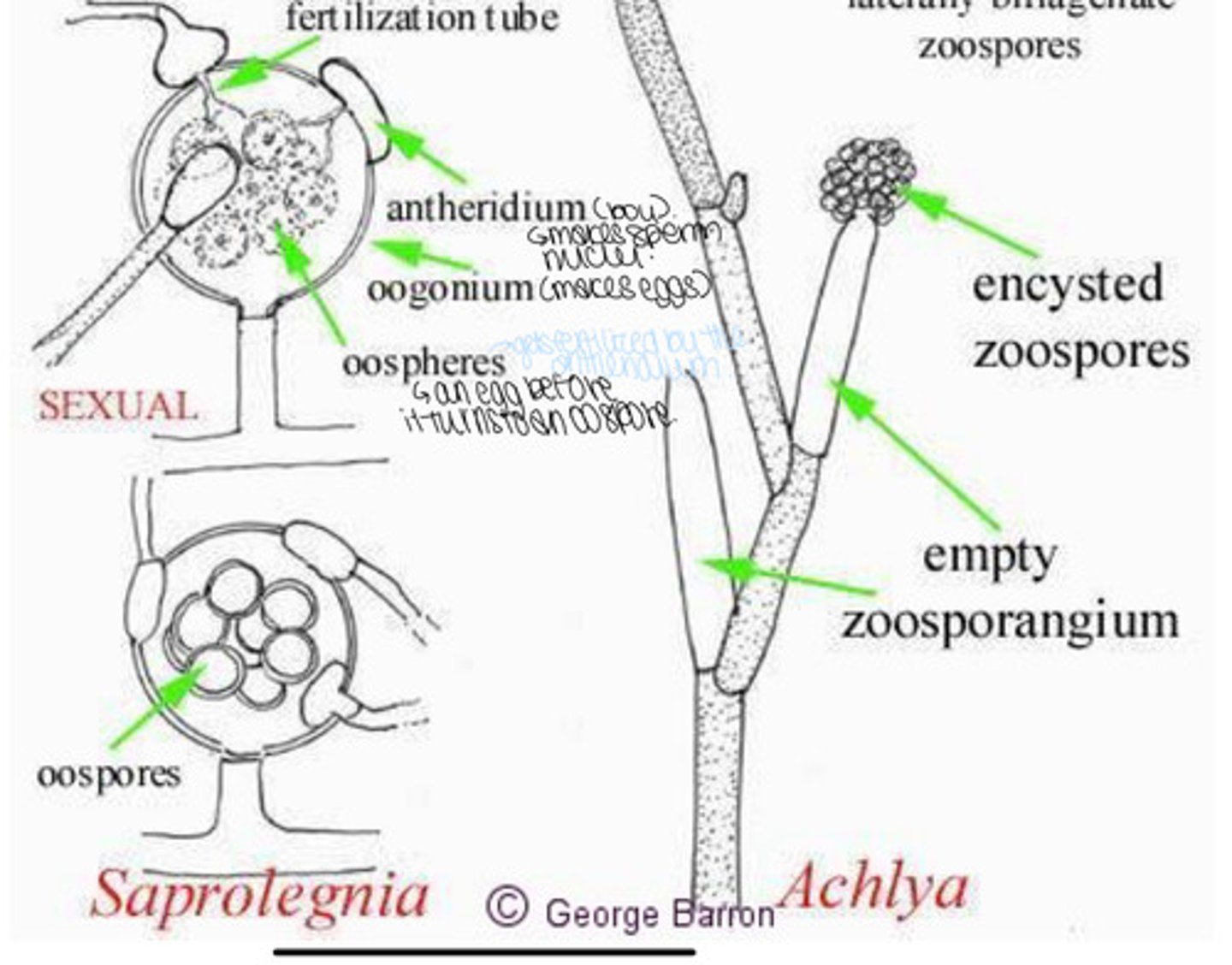
What do Antheridium Make
- makes sperm nuclei
What do Oogonium Make
- makes eggs
What are Oospheres
- aka. an egg before it turns into an oospore
- gets fertilized by the antheridium
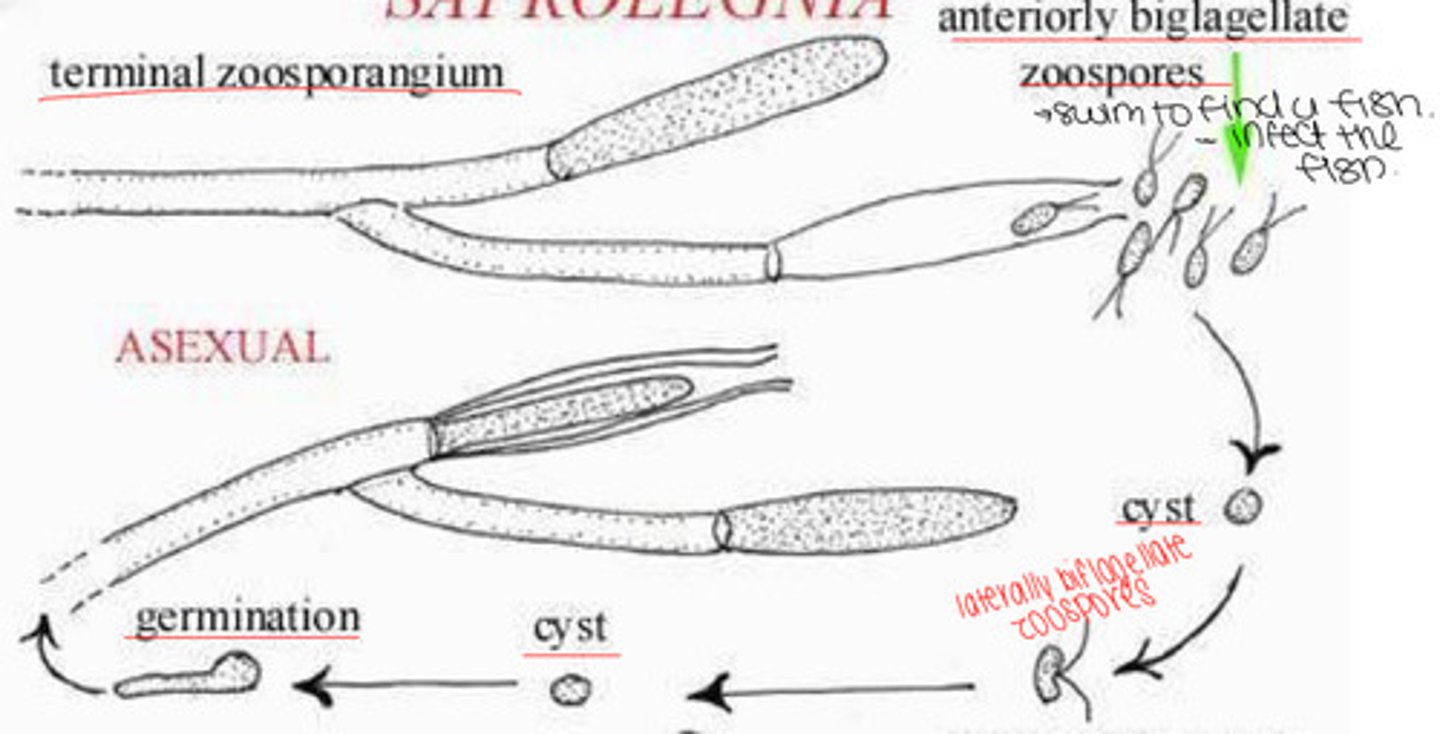
Asexual Life Cycle of Saprolegina
Sexual Life Cycle of Saprolegina
What is Albugo
- white rust of crucifers
- pustules that are white in colour
What is Myzocytiopsis
- an oomycete nematode parasitoid
- zoospores find a nematode and form an infection
- organism digests the nematodes internal organs
What is Phytophthora Sojae
- development of oospores
- plant pathogen
- sweet pea disease
What is NeocallimastixN
- has multiflagellete zoospores
- an exception to the Chytridiomycota group considering the number of flagella
- is able to digest cellulose
What is Batrachochytrium
- a member of the Chytridiomycota group
- interferes with cell membranes and the uptake of nutrients and water
- causes the extinction of many amphibians such as frogs
What is a Blastocladiomycota
- zoospores contain one flagellum
- zoospores swim out of the zoosporangium
- zoospores follow chemical gradients to find a nematode
- once zoospores find a nematode, it sticks, and eventually zoospores will digest the inside of the nematode