Genetics Year 10
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
DNA name
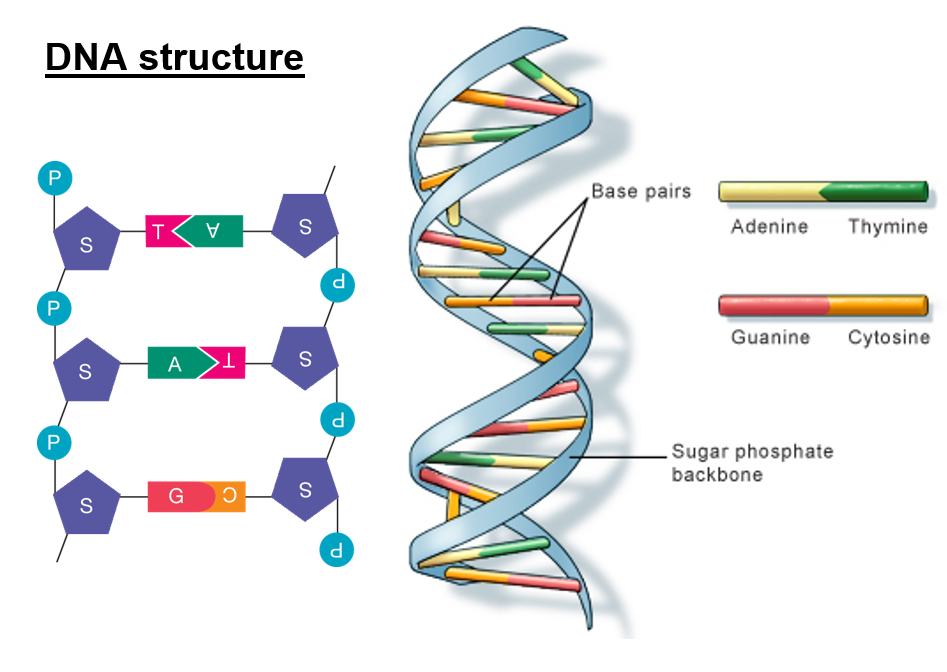
Building blocks of proteins. One amino acid is coded by 3 nitrogenous bases which makes one codon, e.g. AAC, or GCT.
Adenine with Thymine
Guanine with Cytosine
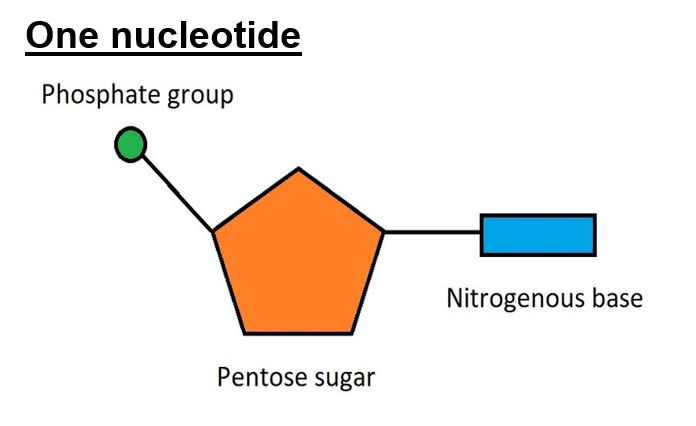
A phosphate group, pentose sugar and nitrogenous base.
Large bundled length of DNA that contains many genes. Large sections of DNA do not code for genes. Found in the nucleus of the cell.
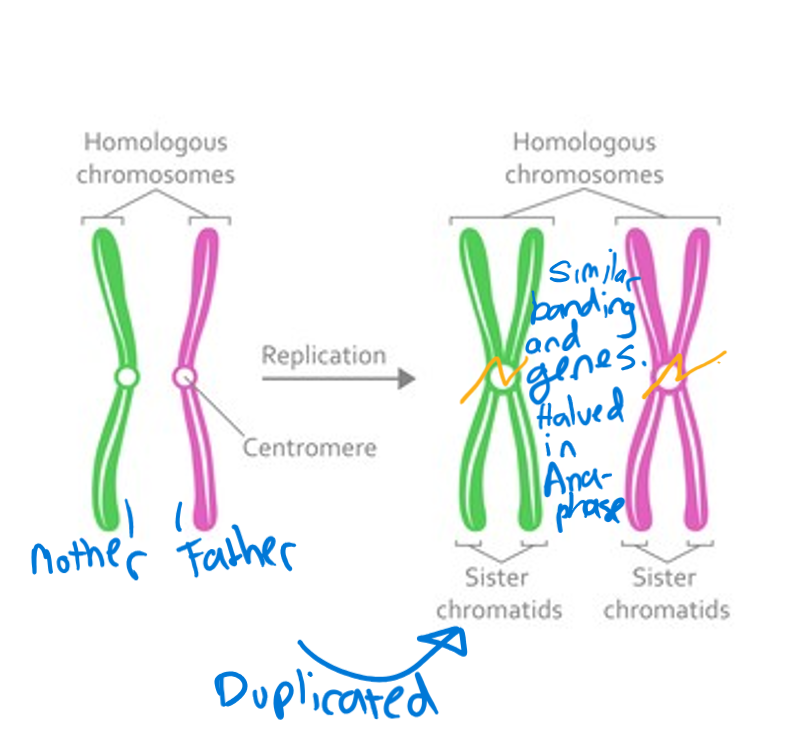
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and have the same genes. One from mother, one from father.
Explanation: Get duplicated before cell division, so i and I (i and l are homologous chromosomes) become ii and ll. They are still homologous chromosomes, just doubled. These doubled chromosomes are each sister chromatids (i is a sister chromatid to i). They are then halved the opposite way (cutting chromatids each in half) during anaphase.
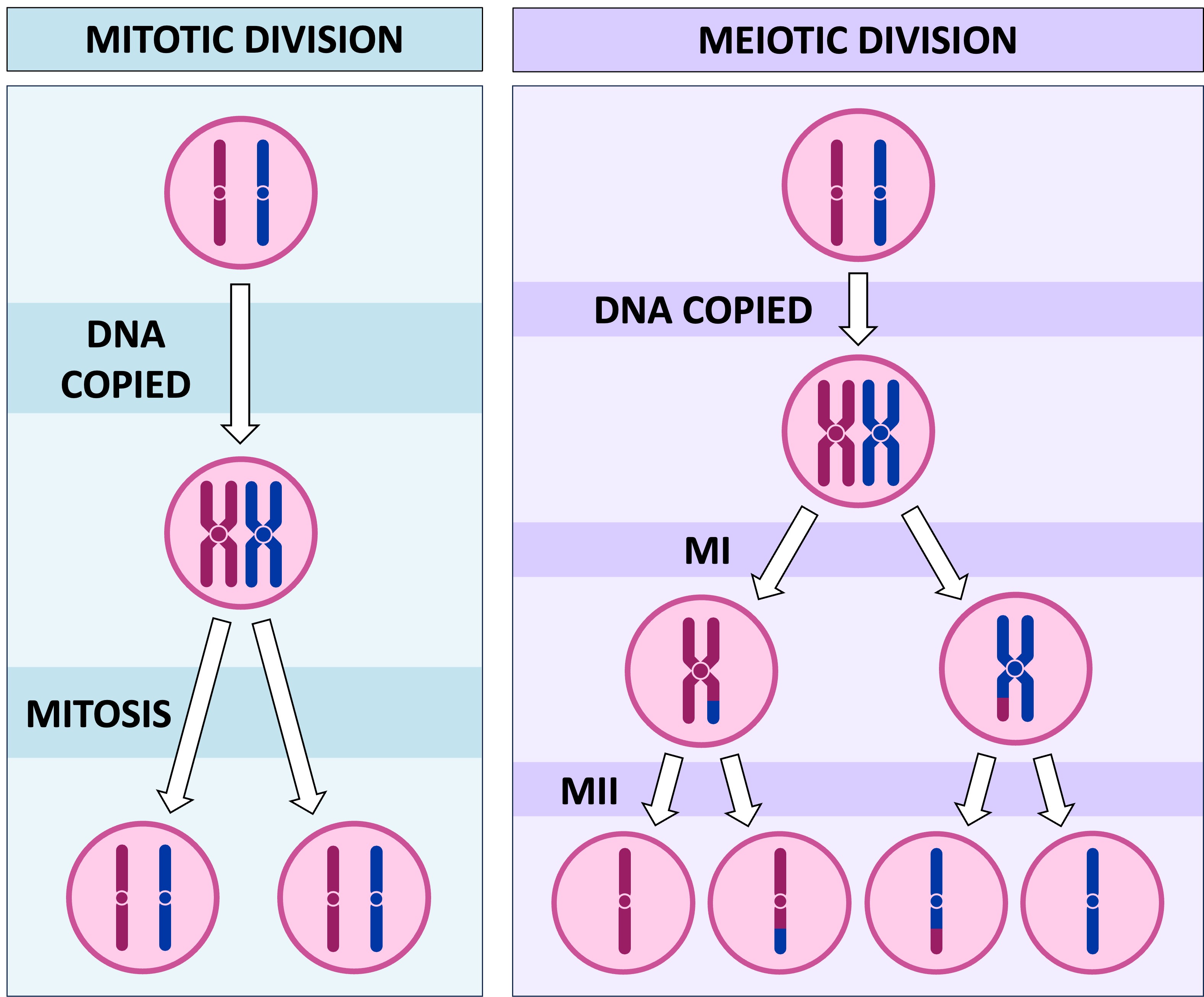
Mitosis
Begins with one duplication of DNA/chromosomes. Cell division in somatic cells, resulting in 2 identical daughter cells. Used for growth and repair.
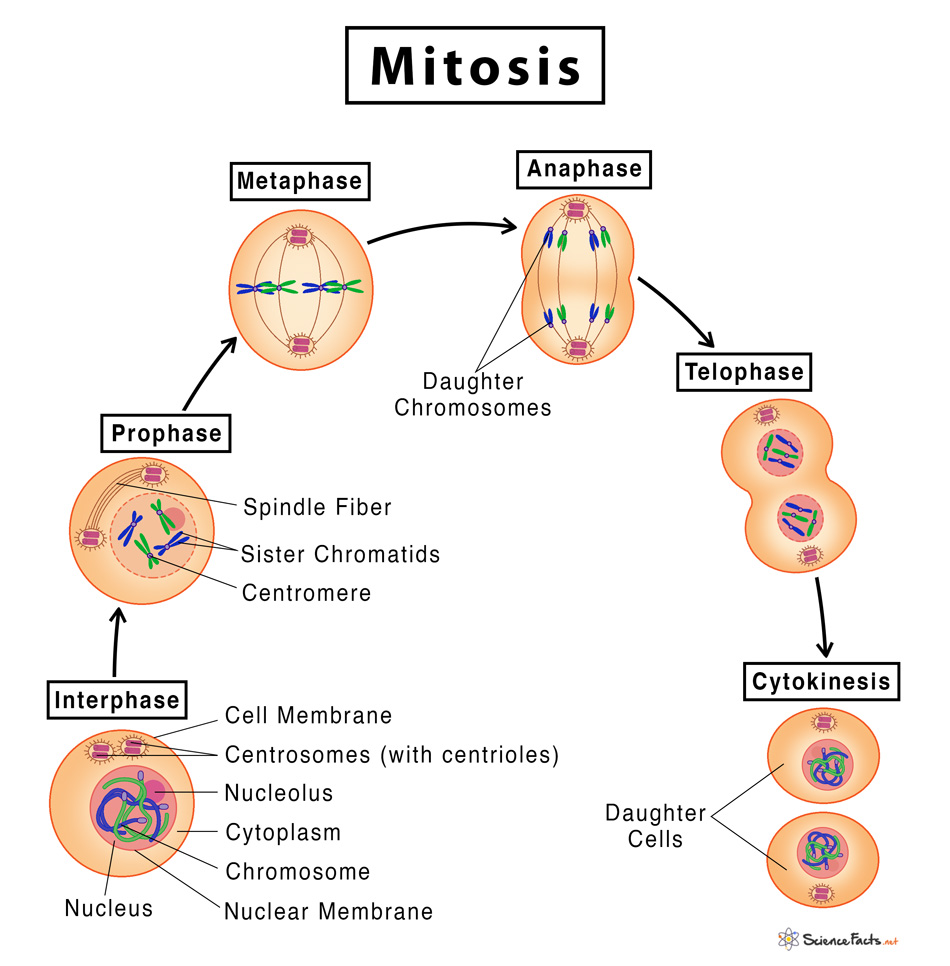
Prophase - chromosomes condense and become visible
Metaphase - chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase - sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
Telophase - new nuclear membranes form around the separated chromosomes, creating two new cells
mutation in a gonads that produces gametes, can be passed on to children
Point mutations
Change in nitrogenous bases, possibly changing the amino acid order. Each point mutation usually only affects 1 gene. Types are substitution, insertion and deletion.
Point mutations - Substitution
One nucleotide is swapped for another, only changes DNA code for one amino acid. Example is sickle cell anaemia.
monosomy- missing chromosome
Point mutations - Insertion
Extra nucleotide/s are inserted, changing the DNA sequence for all following amino acids. This is called a frameshift mutation. Example is fragile X syndrome
Point mutations - Deletion
A nucleotide is deleted from a sequence, changing all following amino acid coding. Another frameshift mutation. Example is Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Chromosomal mutation types
Duplication - part copied (increases gene expression)
Inversion - a segment is removed, then replaced within the chromosome in reverse order
Deletion - part deleted
Insertion - A portion of one chromosome is removed and replaced in another chromosome.
Translocation - Segments of two chromosomes are exchanged
•Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
•Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
•Klinefelters syndrome (trisomy XXY)
•XYY syndrome (trisomy XYY)
•XXX syndrome (trisomy X)
•Turners syndrome (monosomy XO)
Other mutations don't make it past the embryo
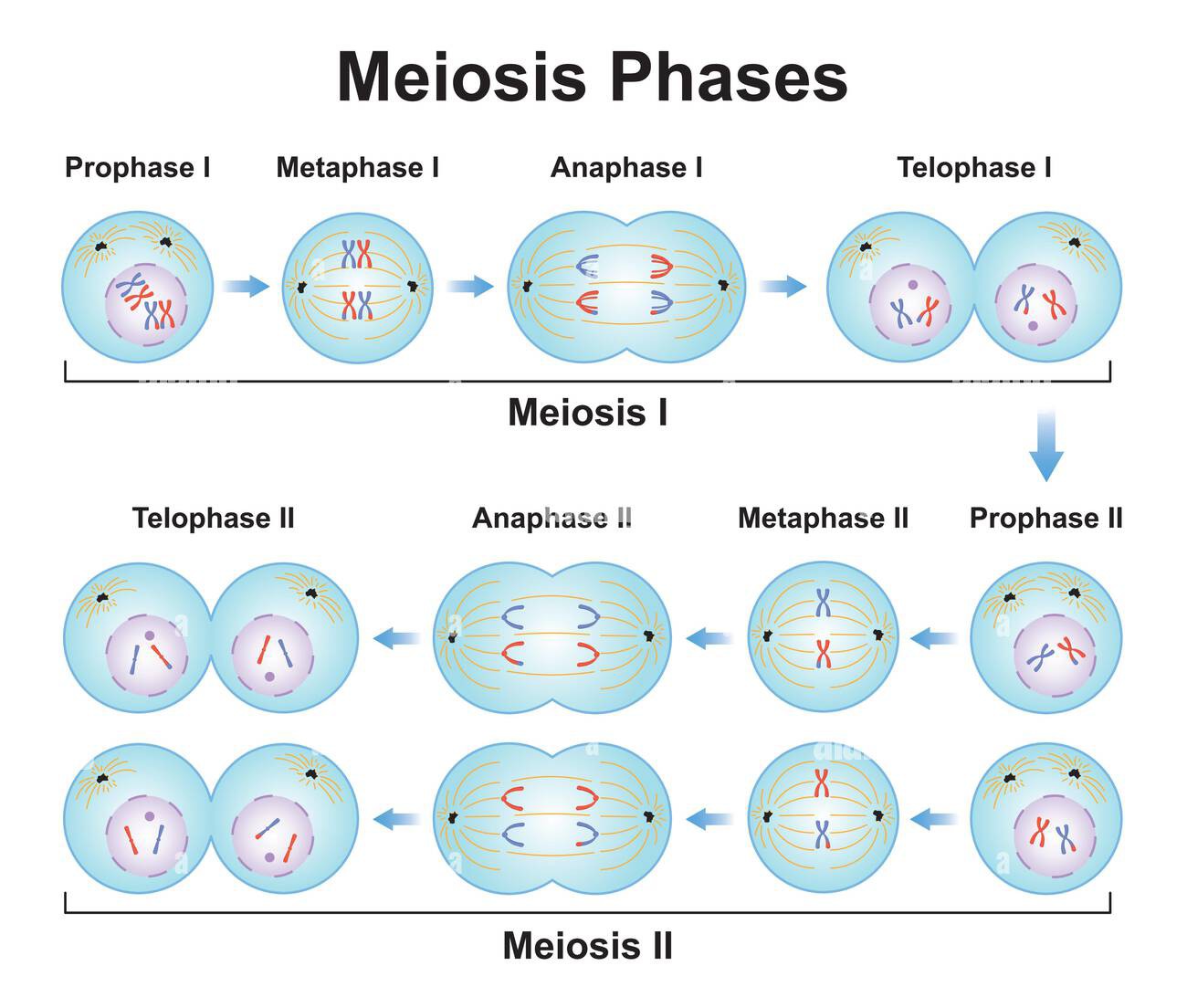
Meiosis
A type of cell division that occurs in gonads. Starts with one duplication of DNA/Chromosomes. Results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes. Used for reproduction.
Alleles
Alternative forms of a gene. In a homologous pair, the 2 chromosomes each have one variation of specific genes.
Due to a heterozygous individual; a blend of both alleles appears in the phenotype in heterozygous individuals
Pedigree genders
Circle is female
Square is male
Autosomal dominant
Every generation; each affected individual has affected parent
Autosomal recessive
Not every generation.
if unaffected parents and affected child, it must be recessive
if both parents affected, all children must be too
X-linked dominant
FDD - Affected father = all affected daughters (and mother).
Unaffected mother cannot have affected sons or father as she can’t be a carrier and husband can only pas to daughters
mostly affects females
X-linked recessive
MSR - Affected mothers = all affected sons (and father, and mother must at least be a carrier)
Unaffected mother can have affected sons (she can be a carrier)
More common in males
Karotype
Complete view of chromosomes in homologous pairs
Heterozygous vs homozygous
Heterozygous - One dominant and one recessive allele (Bb)
Homozygous - 2 dominant or 2 recessive alleles (BB or bb)
Different dominance types
Simple dominant/recessive, sex-linked, co-dominance, incomplete dominance.
Sex-linkage
While the Y chromosome determines gender, it is small and therefore has few equivalent genes with the X chromosome. The X chromosome therefore often has full ‘decision’ over certain characteristics, as there is no overriding genes (in males). Represented like: XBXb and XBY-
Red blood cells (RBCs)
Have antigens (proteins) on their surface to determine our blood type. Types are A, B, AB, and O. Also either does or doesn’t have Rh proteins to determine positivity or negativity.
What are the 3 alleles for the ABO blood type gene?
•IA – Antigen A, (type A blood), dominant
•IB – Antigen B (type B blood), dominant
•i – No antigen (type O blood), recessive
IA and IB are dominant over i but have equal dominance over each other.
Why does the body produce antibodies for certain blood types and not others?
Depending on the blood type that your body is familiar with (the blood type you have), your body creates antibodies for the blood type it does not know.
A blood - B antibodies
B blood - A antibodies
AB blood - No antibodies
O blood - A and B antibodies
Rhesus factor
Another antigen that either is or is not on your RBCs. Also known as the D antigen, written as Rh+ or Rh-. If you have the D antigen, your blood type is positive, if you don’t, it’s negative.