Comprehensive Protein Synthesis: Transcription, Translation, and Regulation in Molecular Biology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
DNA makes RNA makes Protein.
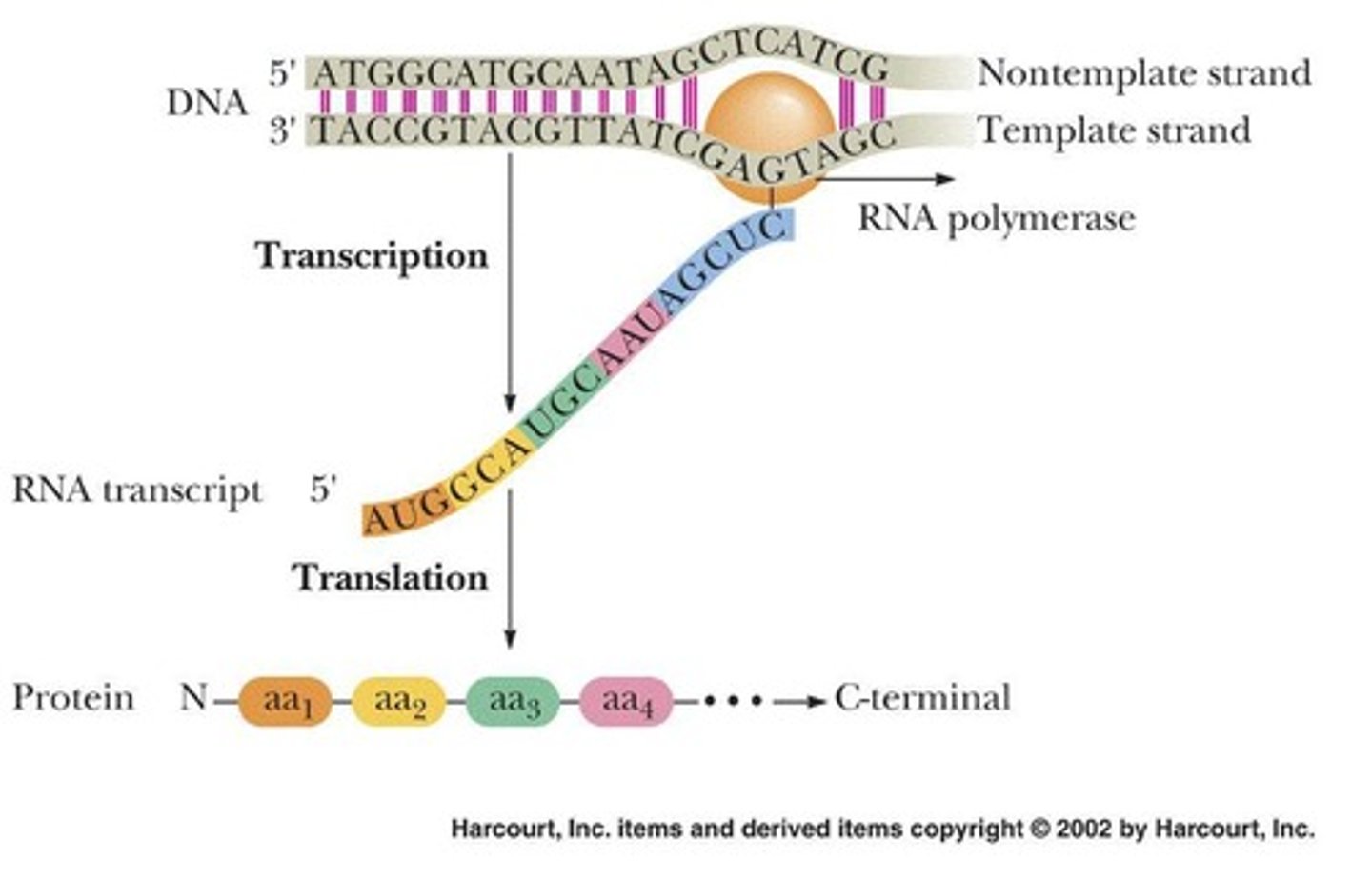
Transcription
Generates a single-stranded RNA directed by the sequence of DNA.
mRNA
The 4-letter language of DNA (ATGC) is transcribed into a similar language for mRNA (AUGC).
Hydrogen bonds in Transcription
H-bonded complementary base pairs are formed (A-U, T-A, G-C, C-G).
Translation
Converts nucleotide sequence of m-RNA into the sequence of amino acids comprising a protein.
Gene
DNA section that codes for one specific protein.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Consists of a reverse copy of the bases transcribed off the template strand of the DNA.
Ribosome
Translator and protein assembly site that reads the base sequence off mRNA codons.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
'Truck' used to pick up requested amino acid and bring it over to ribosome.
Transcription Steps
Transcription involves 3 steps: Initiation, Elongation, Termination.
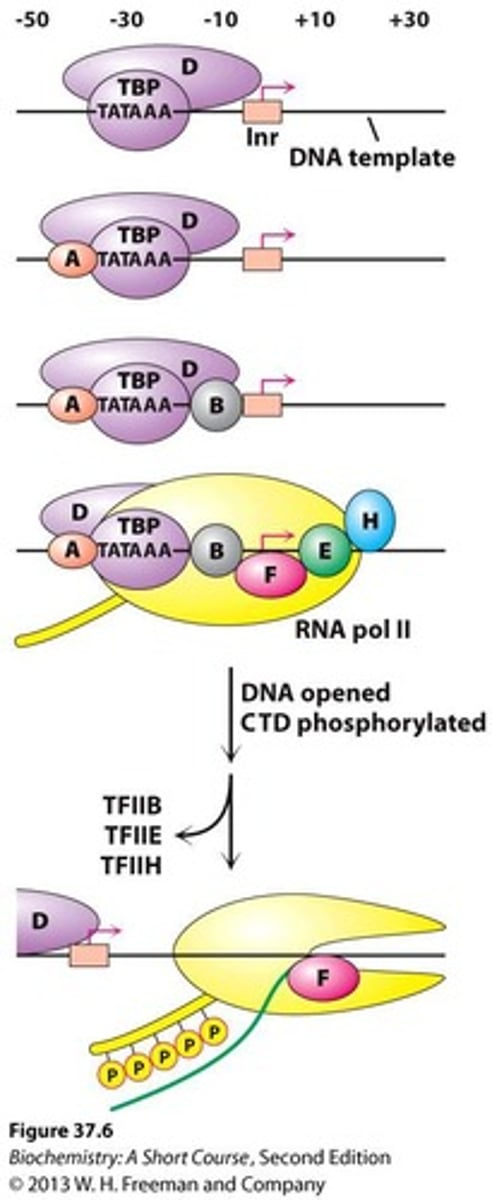
Initiation
Special DNA sequences called Promoters direct RNA polymerase to proper site to initiate transcription.
Open Promoter Complex
RNA polymerase unwinds about 17 base pairs of ds DNA to form the open promoter complex.
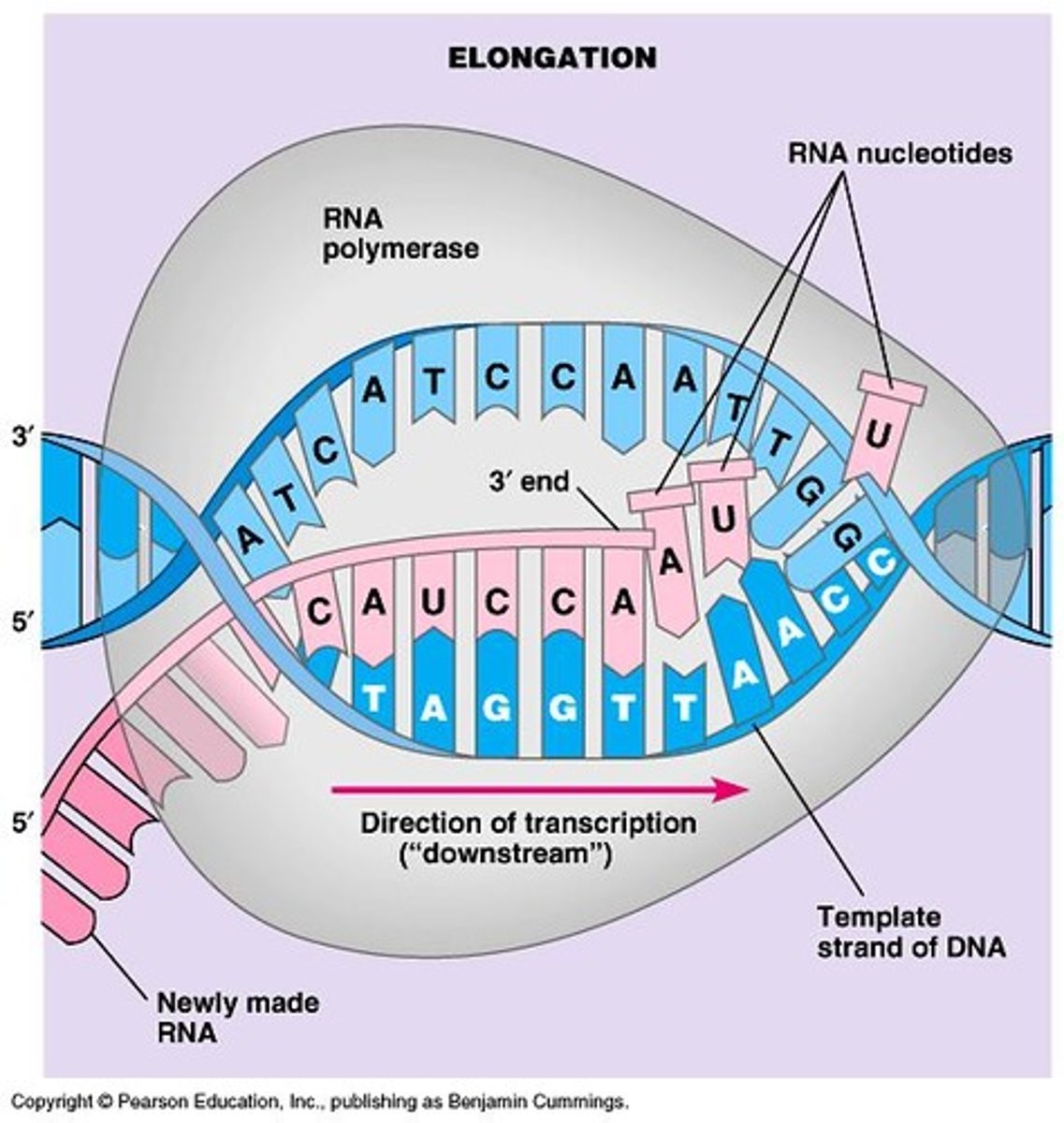
Transcription Bubble
Region containing RNA polymerase, DNA, and RNA product during elongation.
Direction of RNA Synthesis
Direction of synthesis is 5' to 3'.
Phosphodiester Bond
New phosphodiester bond formed during RNA elongation.
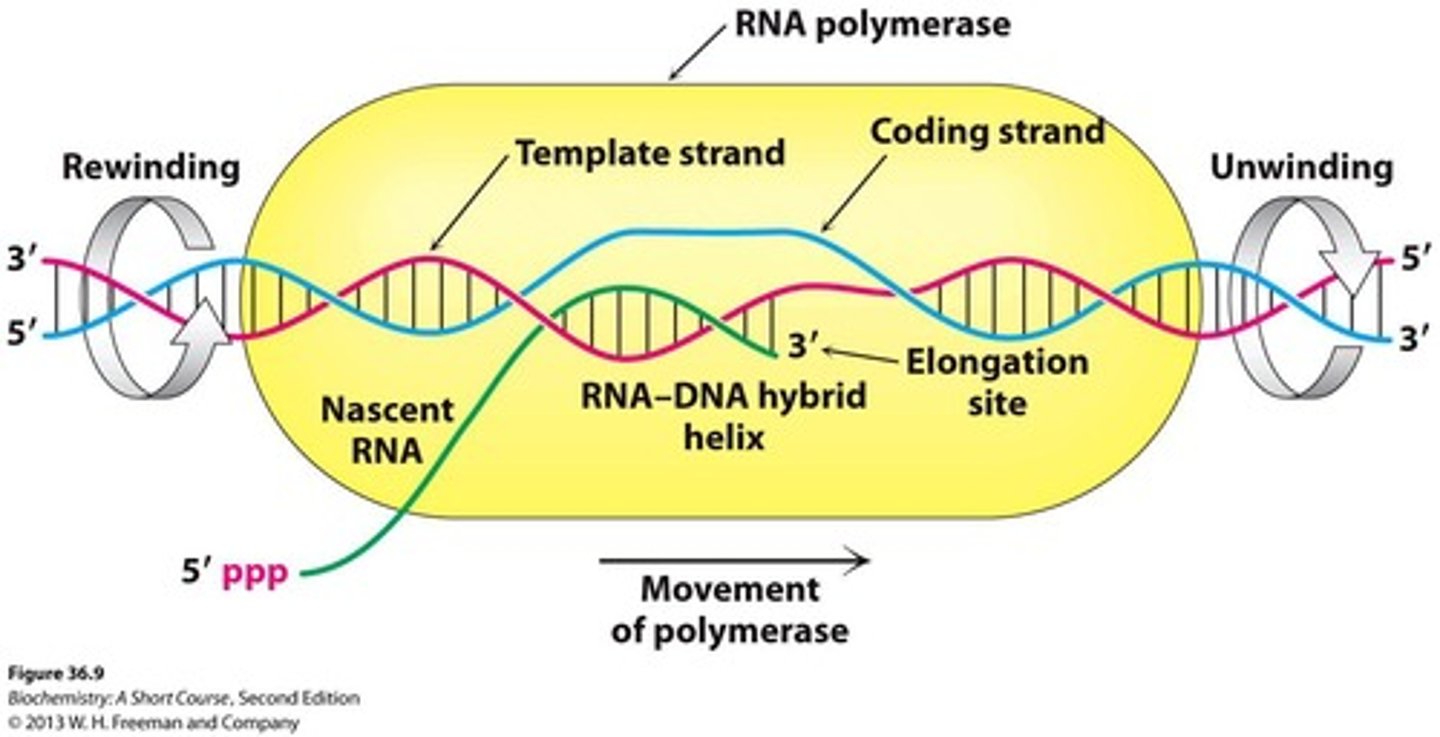
Coding Strand
The sequence of m-RNA is exactly the same as the coding strand (except T replaced by U).
Template Strand
The strand of DNA that is used as a template for transcription.
Transcription Factors
Regulatory proteins that bind the promoters & interact with RNA polymerase.
Closed Promoter Complex
Complex formed when the promoter is initially located by polymerase, with the DNA helix not unwound.
RNA Elongation Process
Once the DNA is unwound, elongation takes place.
Transcription Problem
Write the sequence of mRNA that corresponds to the given DNA sequence.
DNA-RNA hybrid helix
An intermediate in RNA synthesis consisting of approximately 8 nucleotides.
Termination of Transcription
Elongation continues until a termination signal is detected, which is a hairpin structure followed by several uracil residues.
Stop signal
A hairpin structure followed by several uracil residues that indicates the end of transcription.
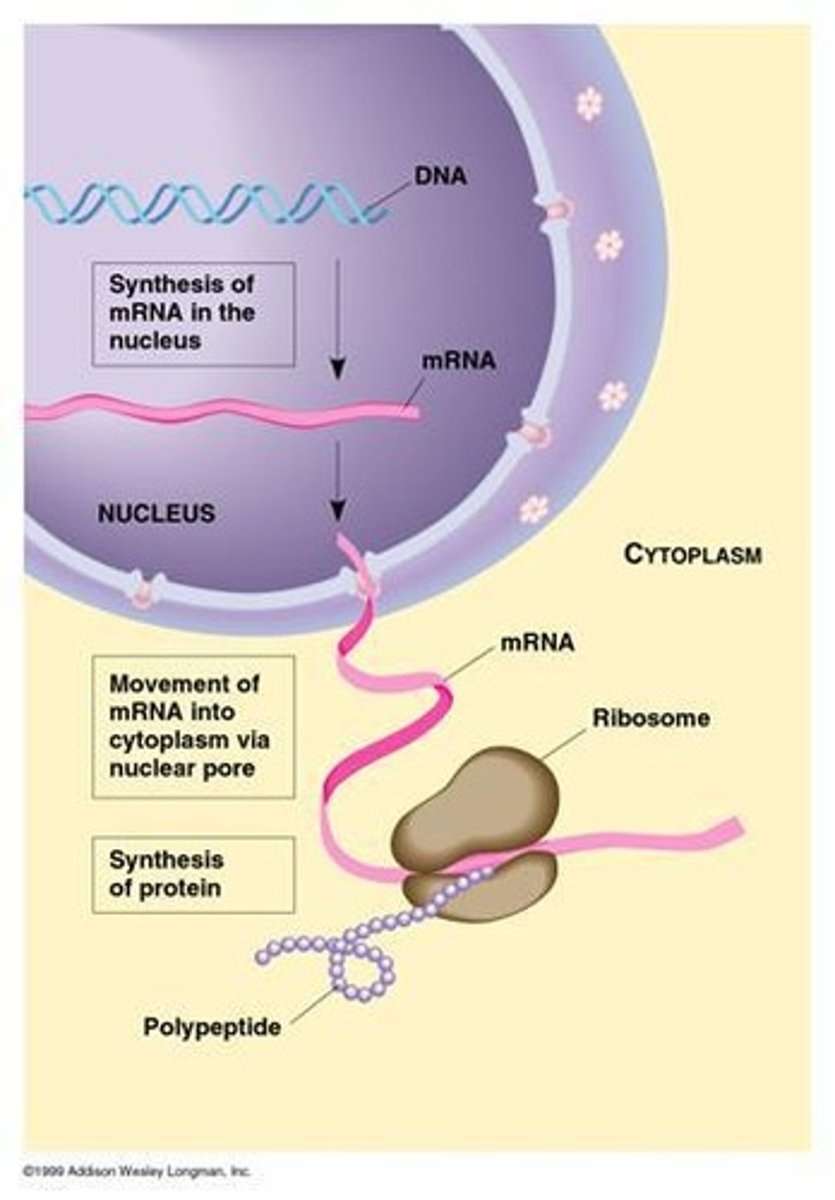
Nascent mRNA
mRNA that travels out of the nucleus through nuclear pores to find a ribosome.
Gene Expression & Regulation
The control of the process of gene expression influenced by various factors.
Regulation of Gene Expression
Influenced by regulation of transcription, RNA processing, and the nuclear membrane.
Promoter
A DNA sequence that initiates transcription of a particular gene.
TATA box
Located between positions -24 and -32 bp upstream of the initiation site, it is essential for RNA polymerase binding.

Initiator element (Inr)
Located between base pairs -3 and +5, often paired with the TATA box.
Downstream core promoter element (DPE)
Located between base pairs +28 and +35, it plays a role in transcription initiation.
CAAT box
A regulatory element located between -40 and -150 bp upstream of the gene.
GC box
Another regulatory element located between -40 and -150 bp upstream of the gene.
Steroid hormones
Powerful regulatory molecules that control gene expression, such as estradiol.
Estradiol
A hormone that controls genes involved in the development of female secondary sex characteristics.
Progesterone
A hormone involved in mammary gland development, a secondary sex characteristic.
Pre-mRNA
Messenger RNA precursors synthesized by RNA polymerase II that undergo processing.
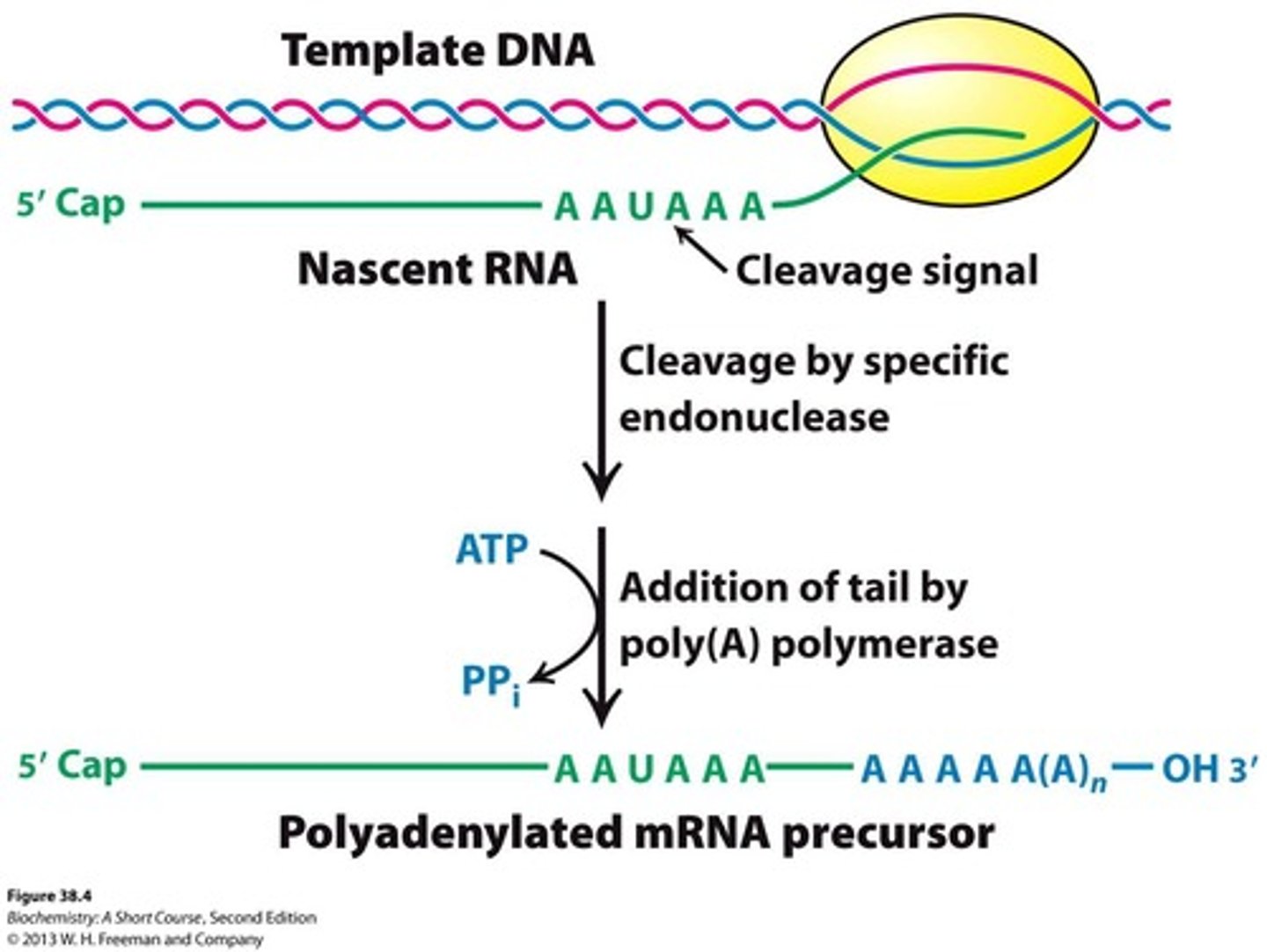
5' cap addition
Modification of the 5' end of pre-mRNA by adding a GTP.
Poly A tail addition
A stretch of polyadenylate added to the 3' end of pre-mRNA, typically about 250 nucleotides long.
Splicing
The process of removing noncoding stretches of RNA (introns) and ligating the remaining exons to form mature mRNA.
Defects in Splicing
Can cause diseases in humans due to improper processing of mRNA.
Gene expression in prokaryotes
The primary transcript serves as mRNA and is used immediately as a template for protein synthesis.
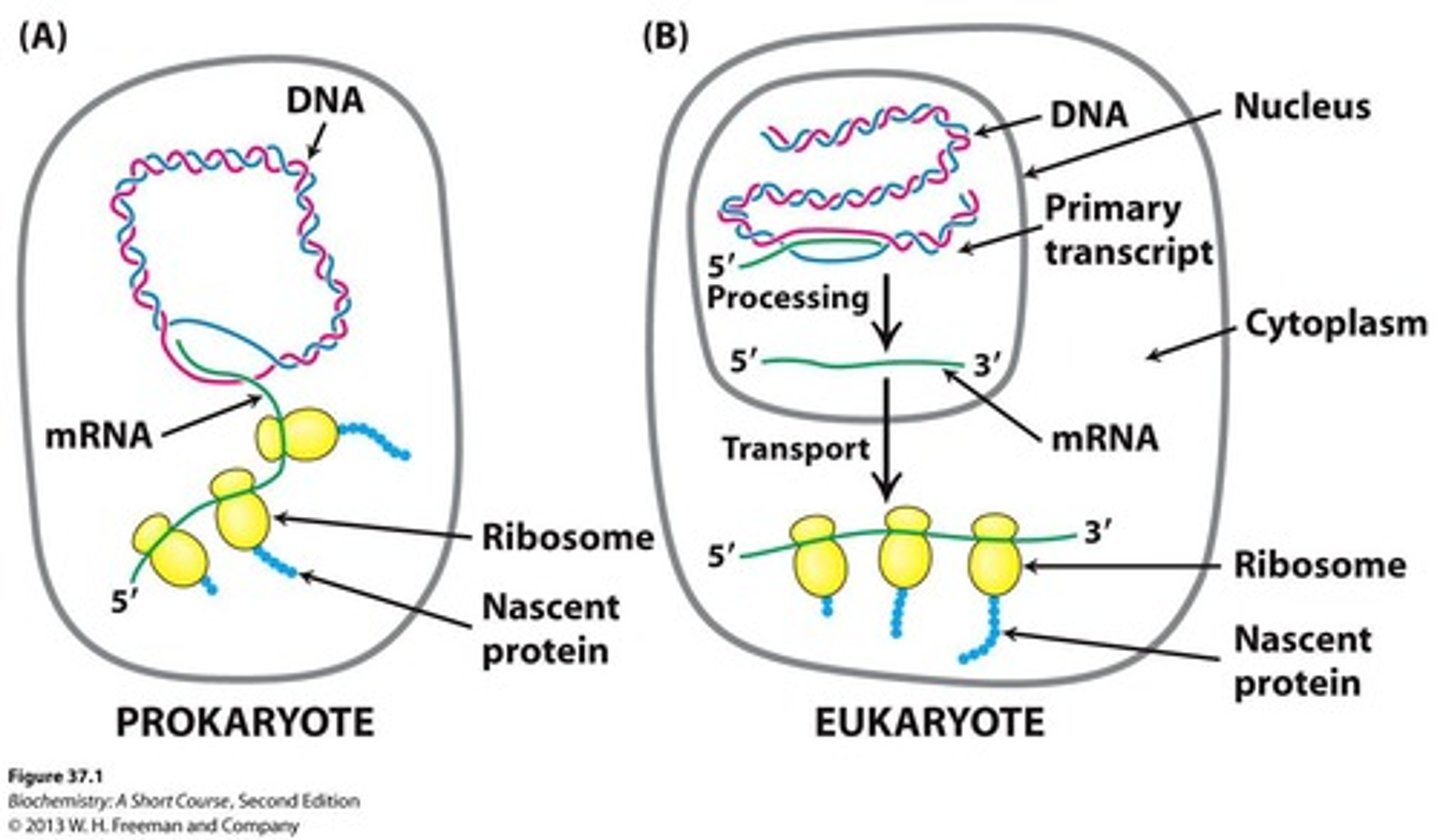
Gene expression in eukaryotes
mRNA precursors are processed and spliced in the nucleus before being transported to the cytoplasm for translation.
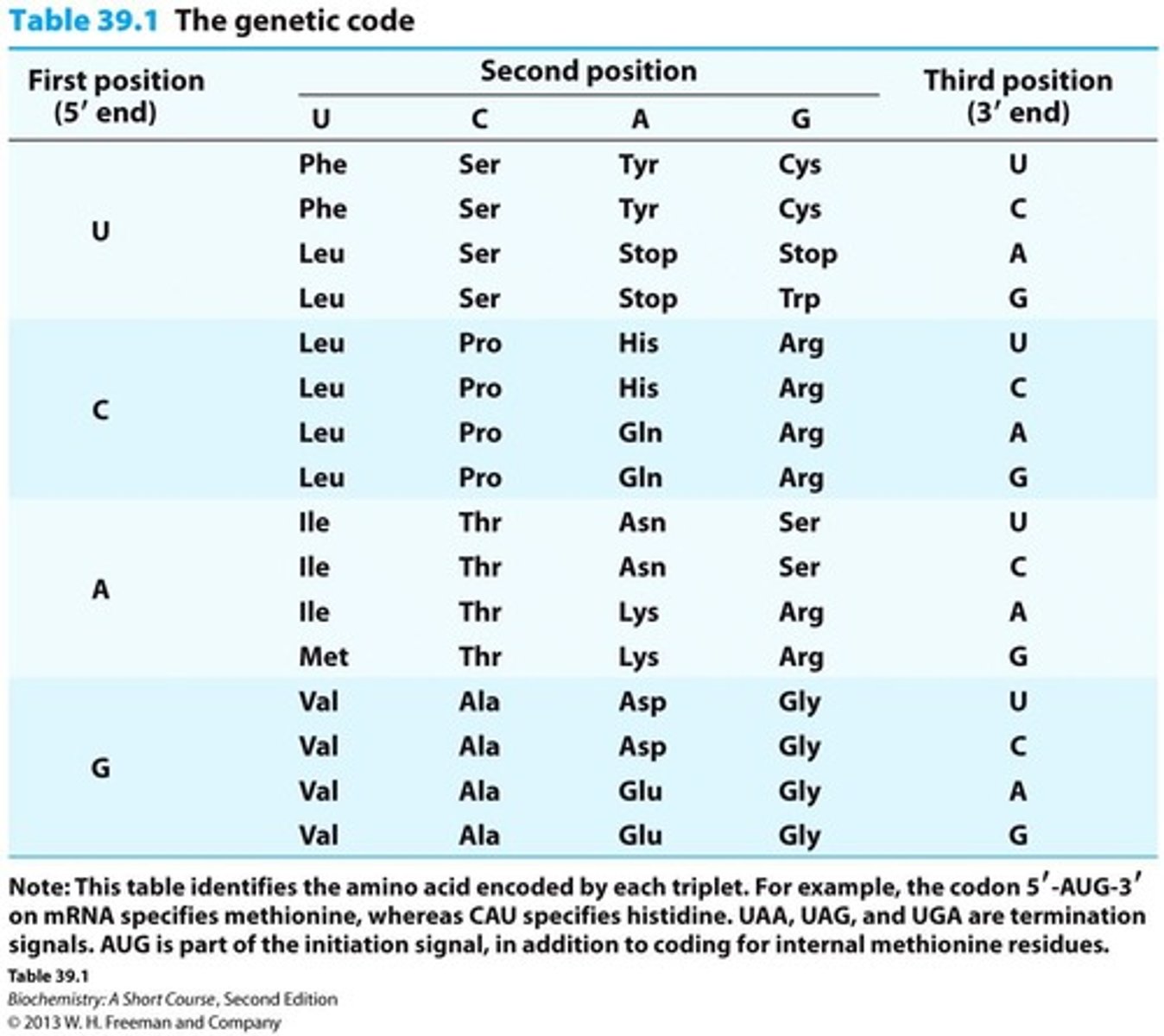
Genetic Code
Protein synthesis is a process of translation. Nucleic acid sequence information in DNA is translated into amino acid sequence information.
Codon
Three nucleotides, called a codon, encode an amino acid.
Nonoverlapping Code
The genetic code is nonoverlapping.
No Punctuation Code
The genetic code has no punctuation.
Direction of Code Reading
The genetic code is read in the 5' to 3' direction.
Degenerate Code
The genetic code is degenerate.
Universal Code
The genetic code is universal.
Start Codon
AUG codon signals the start of translation.
Stop Codon
UAA, UGA, UAG signals termination.
Reading Frame
It is one of the 3 possible ways to read off the bases of mRNA in triplets.
Open Reading Frame (ORF)
Sequence of mRNA (or corresponding DNA) that can be translated to a protein.
Transfer RNA (t-RNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules function as an adaptor molecule between a codon and an amino acid.
Cloverleaf Shape of tRNA
All tRNA molecules have a cloverleaf shape.
Acceptor Stem
AA-accepting region is called acceptor stem.
Amino Acid Attachment
Amino Acid is attached to a -OH group of A in the CCA region of the acceptor stem.
Phosphorylated 5' End
The 5' end is phosphorylated and the 5' terminal residue is G.
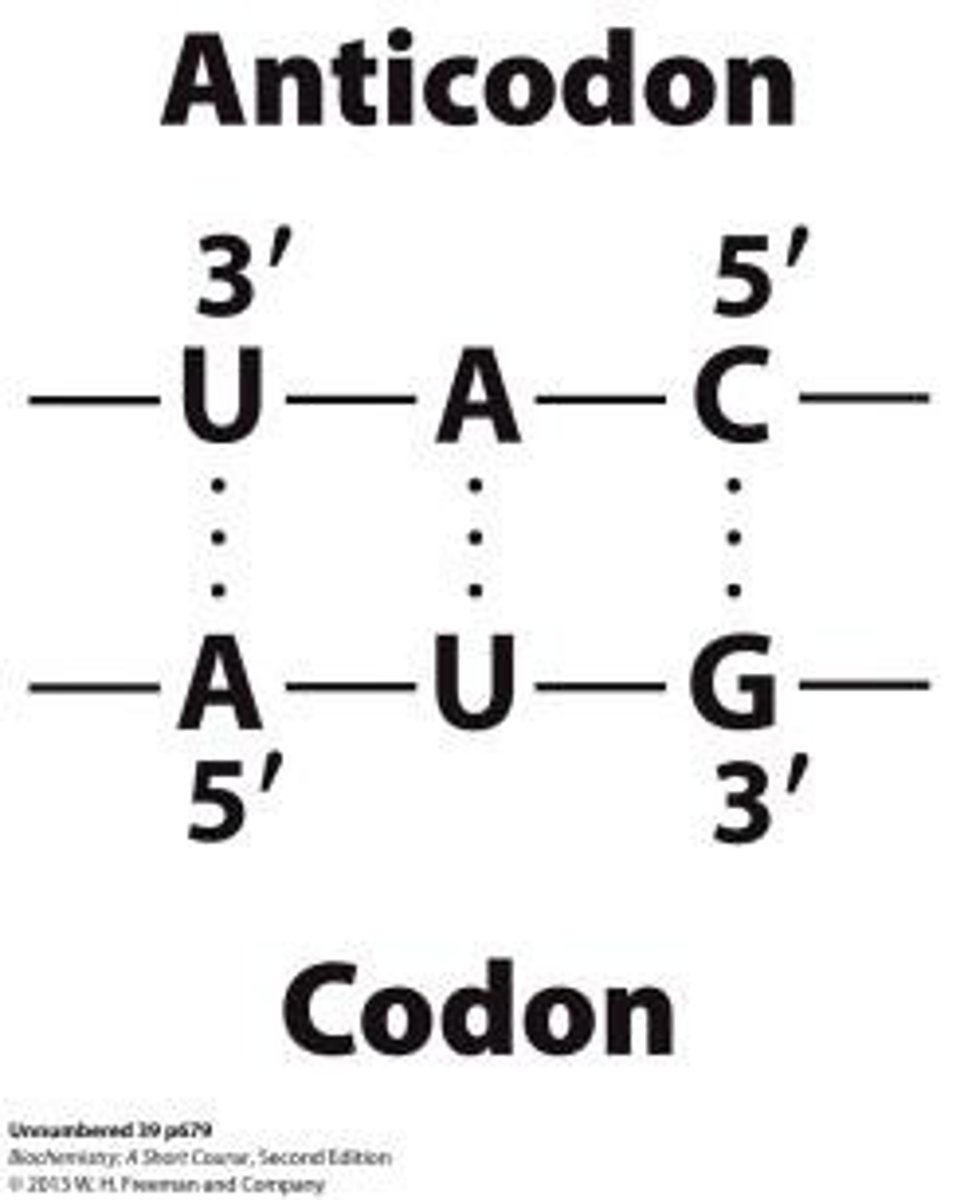
Anticodon
The anticodon is in a loop near the center of the sequence.
Codon-Anticodon Interactions
The code is read off m-RNA base sequence H-bonding between codon (mRNA) and anti-codon of specific t-RNA.
t-RNA Synthetase
Each aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is specific for a particular amino acid.
Loading-Up Reaction
Analogy: Twenty different colored trucks = 20 specific t-RNAs.
Ribosome Size
70S in size and is composed of two subunits, a large 50S subunit and a smaller 30S subunit.
Polyribosomes
Several ribosomes can translate an mRNA molecule at the same time, forming polyribosomes or polysomes.
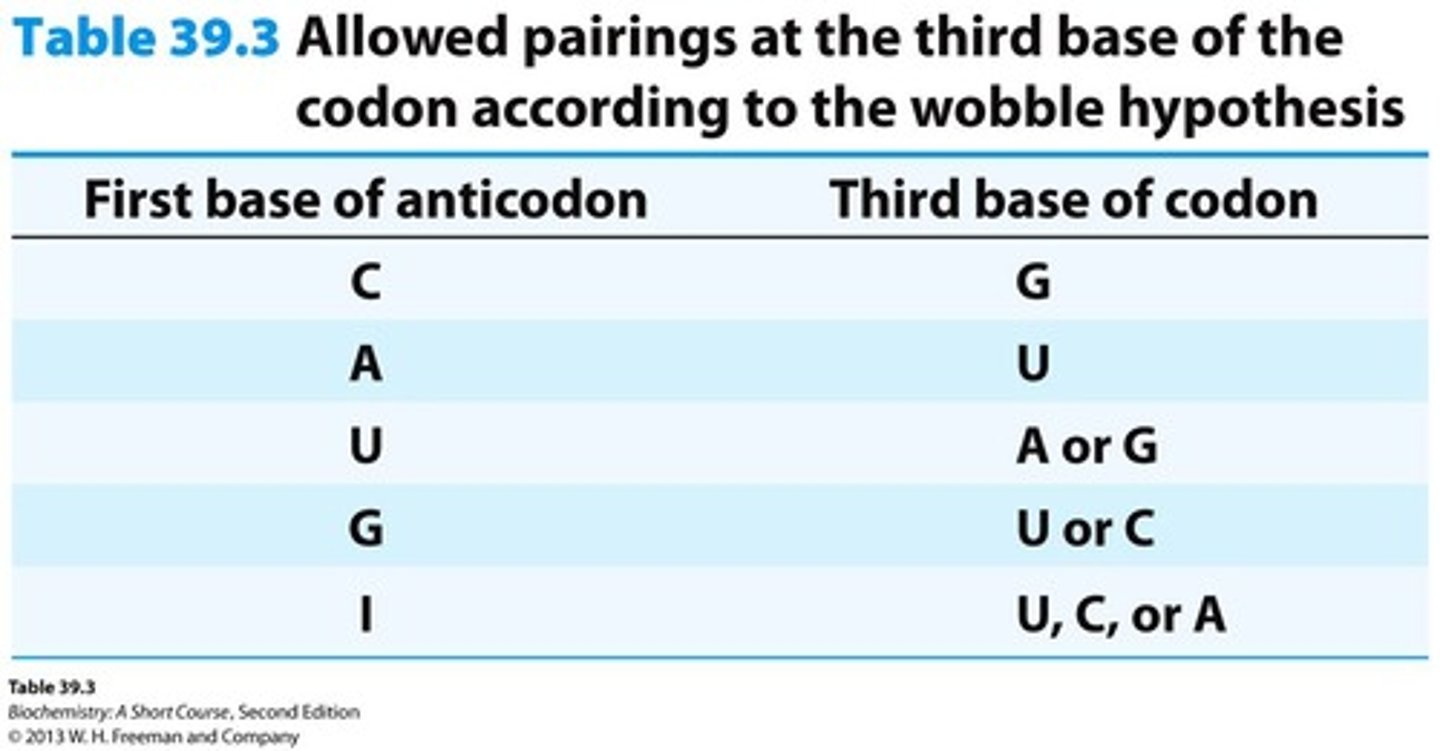
Wobble Hypothesis
Some tRNA molecules can recognize more than one codon.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs, containing three tRNA binding sites: A, P, and E.
A site
The aminoacyl site on the ribosome that binds the incoming tRNA.
P site
The peptidyl site on the ribosome that binds the tRNA with the growing peptide chain.
E site
The exit site on the ribosome that binds the uncharged tRNA before it leaves the ribosome.
30S initiation complex
The initial complex formed during the initiation phase of translation.
70S initiation complex
The complex formed at the end of the initiation phase of translation.
Elongation
The second step of translation where the polypeptide chain is extended.
Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu)
A protein that delivers the appropriate aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site.
Elongation factor Ts (EF-Ts)
A protein that induces the release of GDP from EF-Tu, allowing another cycle to begin.
Peptide bond formation
An exergonic process catalyzed by the enzyme Peptidyl transferase.
Translocation
The process where the mRNA moves through the ribosome by a distance corresponding to one codon.
Elongation factor G (EF-G)
Also called the translocase, it uses GTP hydrolysis energy to translocate the mRNA.
Termination
The final step of translation where the polypeptide chain is released upon encountering a stop codon.
Release factors (RF)
Proteins that recognize stop codons and facilitate the release of the complete protein.
Stop codons
Codons (UAA, UGA, UAG) that signal the termination of protein synthesis.
GTP hydrolysis
The process that provides energy for translocation and other steps in translation.
Polypeptide chain growth
The process of synthesizing a protein chain by the successive addition of amino acids.
N-terminal
The end of a polypeptide chain that has a free amino group.
C-terminal
The end of a polypeptide chain that has a free carboxyl group.
Genetic code problem
An exercise involving transcription and translation of a given DNA sequence.