2.29 Apply Coulomb’s law to explain periodic trends in atomic radii and ionization energies.
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
How does Coulomb's law explain periodic trends in atomic radii and ionization energies?
Coulomb’s Law describes the force between two charged particles
Where F is the force, q1 and q2 are the charges of the particles, and r is the distance between them.
Attractive force between the positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons is explained by Coulomb’s law.
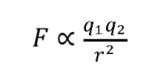
How does Coulomb’s law explain trends in atomic radii across and down the periodic table?
Across a Period (→):
As protons are added to the nucleus, the nuclear charge (positive charge) increases, strengthening the attractive force between the nucleus and electrons.
Electrons stay in the same energy level, and as a result, the atomic radius decreases due to stronger attraction.
Down a Group (↓):
Electrons are added to higher energy levels, farther from the nucleus, increasing the distance (rrr) in Coulomb’s law.
Even though nuclear charge increases, the effect of shielding from inner electrons reduces the overall attractive force, leading to an increase in atomic radius.
How does Coulomb’s law explain trends in ionization energy across and down the periodic table?
Across a Period (→):
As nuclear charge increases, electrons are more tightly bound to the nucleus due to the stronger attractive force, making it harder to remove an electron.
This leads to an increase in ionization energy.
Down a Group (↓):
Electrons are farther from the nucleus (larger rrr), and shielding by inner electrons reduces the nuclear attraction on the outermost electron.
As a result, it is easier to remove the outer electron, leading to a decrease in ionization energy.
.
.