ex 2 fetal spine, hips, and 3D US
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
A normal baby has how many thoracic ribs?
12
How does the spinal cord appear sonographically?
hypoechoic
A hip that is in normal position at rest, has abnormal movement with stress, but remains within the confines of the acetabulum is which of the following?
lax hip
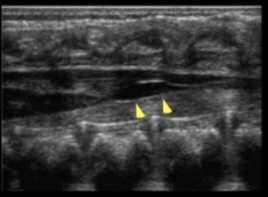
What is demonstrated on the spine image?
filar cyst
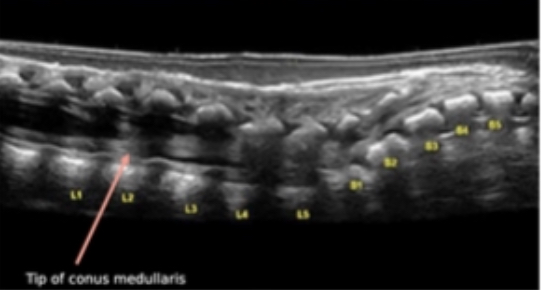
At what level does the conus end?
L2
Conus terminating at L4 with no movement is indicative of?
Tethered cord
At what level is conus abnormally low?
L3
Until what age can US be used to evaluate the spine?
6m
What location is the thickness of the filum terminale measured at?
L5-S1
What is the best patient position?
prone
Volume acquisition has what two types?
manual and automatic
Manual or freehand is the method used for 3D imaging using 2D probe?
true
The greater the alpha angle, the greater the subluxation?
false
The angle that describes the greater the angle, the greater degree of subluxation is?
beta
What type of rendering is best used for fetal face?
surface mode
What type of rendering mode generates only the brightest echoes?
Maximum
What type of rendering mode generates only anechoic or low echoes?
Minimum
Maximum mode is good for visualizing the bladder?
false
What is the fourth dimension in 4D US?
time
4D US acquires 40 volumes per second and only used with MANUAL acquisition?
false
Which type of volume acquisition has a long acquisition time but allows for assessment of the fetal heart?
STIC
What view is the “ball on a spoon”?
coronal
Which of the following is not an indication for a hip US?
they are all indications
The barlow maneuver has hips flexed 90 degrees and ____?
adducted
At what age should hip US not be done?
3-4 weeks
Where does the spinal cord terminate?
conus medullaris
Subluxation is complete dislocation?
false