Ocular Side Effects of Systemic Medications
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What does high clinicality mean?
Commonly encountered side effects.
What does high criticality mean?
Induce significantly detrimental and/or irreversible effects even if infrequent.
How do systemic drugs induce ocular side effects?
Systemic drugs that activate or block similar receptors in the eye (e.g. autonomic NS)
Direct toxic effects of medication to the ocular tissues once it’s absorbed through the bloodstream
Drug deposits that build up in an anatomical portion of the eye
Why is it important to know the ocular side effects of drugs?
Many ocular SE are induced by some systemic medications that are readily visible in ocular tissues during an ocular health assessment.
Do many of the side effects of these systemic medications have an impact vision or eye health?
No, just alter the anatomy. However, some ocular SE are significant and require drug discontinuation.
How does ocular effects from systemic meds affect the eyes?
Bilateral, always.
How do proton pump inhibitors, such as Prilosec, Protonix, Nexium, Prevacid, Dexilant, and AcipHex affect the eye?
They decrease tear production. High clinicality.
How does isotretinoin (an analog of vit A), such as accutane, zenatane, claravis, amnesteem, absorbica, for acne treatment affect the eyes?
Has a high criticality. Causes SEVERE dry eye and CL intolerance (often must D/C CL wear during the 3 mos course of treatment)
When should Isotretinoin not be given to a patient?
Contraindicated in any instance of pulmonary dysfunction: Asthma, COPD
How do oral anticholinergics affect the eyes?
They decrease all glandular secretions, including tear production, and gastric motility.
What are oral anticholinergics commonly used in?
Commonly used in GI disease to reduce nausea and for treatment of IBS.
How do oral antihistamines affect the eyes?
They have anticholinergic-like side effects
How do oral decongestants affect the eyes?
They decrease tear production.
Where are oral decongestants found?
In many OTC preparations for cold, sinus, and allergy
Stand alone agent in Sudafed
in Anti-Hist combo agents’ have a “D” in the name, such as Claritin-D, Tavist-D
Typical decongestant ingredients in pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine
What are other medication classes that have anticholinergic-like SE?
Tricyclic antidepressants: Elavil (amitriptyline)
SSRI: Paxil, Prozac, Zoloft, Celexa, Pexeva, Lexapro
Anti-Parkinson’s drugs: Levodopa, benztropine, benzhexol
How do oral B-blockers affect the eye?
They decrease the lysozyme and antibodies within the tears.
What are oral B-blockers used for? What are some examples?
The treatment of systemic hypertension and arrhythmia.
Examples: Tenormin (atenolol), Toprol, Lopressor (Metoprolol), generic propranolol
How do diuretics affect the eyes?
They decrease overall fluid available for tears.
Ex: Lasix (Furosemide), hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
How do oral contraceptives affect the eye?
They decrease tear production
How does methoxsalen affect the eyes?
Decrease tear production.
What is methoxsalen used for?
Treatment of psoriasis, a chronic, immune-mediated skin disease causing rapid skin cell buildup, resulting in red, scaly patches and potential joint pain
How does Salagen and Evoxac affect the eyes?
Prescribed in extreme cases of Sjogren’s to increase secretory functions, they are direct acting cholinergic agonists that bind acetylcholine receptors to increase exocrine secretions, which happens to also increase tear production.
When should Salagen and Evoxac not be prescribed to a pt?
Contraindicated in any instance of pulmonary dysfunction: Asthma, COPD.
What is the underlying mechanism and appearance of vortex (whorl) keratopathy?
Characterized by epithelial and subepithelial pigment deposits forming a classic whorl/vortex pattern across the cornea. Pattern results from migration of corneal epithelial cells.
Does vortex keratopathy affect vision? What symptoms may occur?
Typically does NOT reduce visual acuity, but may cause glare and halos.
How does vortex keratopathy progress, and what happens if the causative drug is stopped?
The conditions is reversible, deposits typically reverse, fade, or resolve after drug discontinuation
What are some drugs that can induce vortex keratopathy?
Amiodarone, used for cardiac arrhythmia
Plaquenil, an antimalarial drug also used for Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
Gold Salts, older drug taken for sever rheumatoid arthritis, not common
Why does amiodarone commonly cause vortex keratopathy, and how often does it occur?
Amiodarone deposits in corneal epithelial cells. Nearly all patients develop vortex keratopathy after ~3 months of therapy and is the most common drug cause of VK.
What other ocular finding occurs in ~50% of patients on long‑term amiodarone therapy?
About 50% develop pigmented deposits in the anterior subcapsular lens
Do corneal deposits from amiodarone reduce visual acuity, and why are they clinically important?
Corneal vortex deposits rarely affect VA, but they indicate increased drug concentration that could decrease vision via optic neuropathy.
Why is it difficult to determine whether optic neuropathy in an amiodarone patient is drug‑induced?
Patients on amiodarone often have vascular risk factors that match the profile for NAION, making it hard to distinguish drug‑induced optic neuropathy from a typical NAION event.
How common does plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine) cause vortex keratopathy?
Rare on the doses that are currently prescribed. Much more clinically significant for retinal toxicity rather than corneal changes.
What ocular changes can gold salts cause, and how do they resemble vortex keratopathy?
Gold salts can induce chrysiasis, gold particle deposition in ocular tissues, producing a vortex‑like appearance, but deposits are located in the posterior stroma, not epithelium.
What corneal layer is affected by chlorpromazine, and what type of drug is it?
Chlorpromazine is an antipsychotic that can cause corneal endothelial deposits, typically within the interpalpebral fissure.
These endothelial changes are rare compared to its lens effects. Anterior lenticular changes are much more common than the rare corneal endothelial findings.
What is Rifabutin used for and how does it affect the eyes?
It is used to treat tuberculosis. It can induce uveitis.
What is Keytruda and how does it affect the eyes?
Keytruda is used for cancer immunotherapy. It can induce uveitis.
What are bisphosphonates (such as Fosamax, actonel, boniva, reclast) used for and how dies it affect the eyes?
They are used to treat osteoporosis or Paget’s disease. They typically give pts self-limiting conjunctivitis for 2 days to 2 weeks after starting drug. Can rarely cause scleritis or uveitis and only resolved with drug discontinuation. Can also cause yellow/gold colored visual disturbance.
What is Flomax (tamsulosin) used for and how does it affect the eyes?
Tx of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
Helps maintain regular urinary flow by antagonizing alpha adreneric receptors to relax smooth muscles on urinary sphinceter.
Causes Floppy iris syndrom by blocking alpha receptors on iris dilator, preventing full pupillary dilation.
Causes complications during cataract surgery
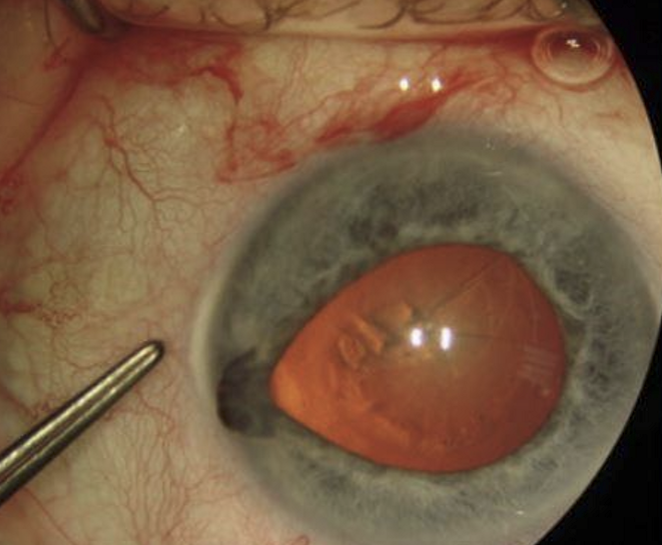
What must you ask all patients prior to cataract surgery?
Ask if they are on Flomax (tamsulosin).
What can surgeon do to minimize complications for a patient taking Flomax?
Employ small pupil intraoperative techniques.
How do anticholinergics affect the eyes?
They can cause pupillary mydriasis and cycloplegia, giving blurred vision. They also have the potential to increase IOP via angle closure.
How do antianxiety, antidepressants, and antihistamines affect they eyes?
They can cause pupillary mydriasis and cycloplegia, giving blurred vision. They also have the potential to increase IOP via angle closure.
What are some adrenergic agonists?
Amphetamines like Dexedrine (dextroamphetamine) for weight loss
Cocaine or Methamphetamines
Methylphenidate/amphetamine/dextroamphetamine derivatives and other for Tx of ADD/ADHD
Wellbutrin: an NDRI antidepressant
Oral decongestants
How do adrenergic agonists affect the eyes?
They can cause pupillary mydriasis without cycloplegia.
What are some drugs that can cause pupillary miosis?
Anticholinesterase: insecticides, nerve gases
Opiates (Heroin, morphine, exycodone, hydrocodoen, codeine)
Salagen (oral pilocarpine) and Evoxac (cevimeline): direct acting cholinergic agonists
How do anticholinesterases cause pupillary miosis?
They prevent breakdown of natural acetylcholine which more actively binds mucarinic receptors.
How do opiates cause pupillary miosis.
They affect the central nervous system, causing sphincter pupillae contraction and create pinpoint pupils.
How does Salagen and Evoxac cause pupillary miosis?
They are direct acting cholinergic agonists, stimulating M3 receptors on the iris sphincter muscle.
Why is Salagen and Evoxac prescribed?
To treat extreme cases of Sjogren’s to increase secretory functions.
What is Dilantin (phenytoin) and how does it affect the eyes?
Anti-seizure meds
Can cause: Gaze evoked nystagmus or Downbeat nystagmus
What are some dopamine D2 antagonists and their uses?
Chlorpromazine as an antipsychotic
Seroquel (quetiapine) for bipolar disorder
How does dopamine D2 antagonists affect the eyes?
Anterior lenticular opacities in stellate appearance
Corneal endothelial deposits in interpalpebral fissure: rarely seen
Can give conj and sclera bluish hue
irreversible opacity, but little to no decrease in VA
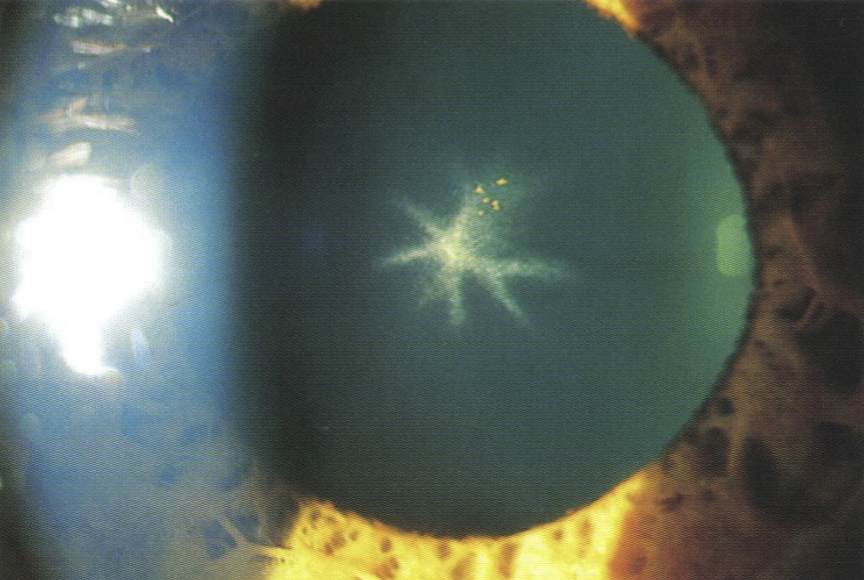
What are the effects of corticosteroids on the eyes?
Causes Posterior Subcapsular cataract (PSC), which looks exactly like age-related PSC
It is irreversible and dramatically effects VA
Occurs from prolonged use, including nasal sprays for allergies and inhalers for asthma
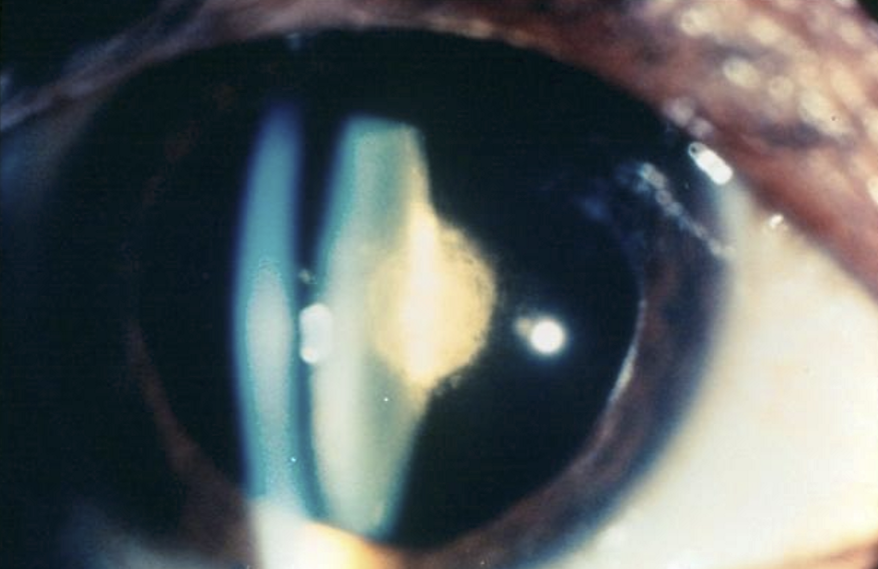
What is topamax and what effects does it have on the eye?
Antiepileptic/antiseizure medication also used for migraine prophylaxis.
Causes choroidal and ciliary body effusion → forward displacement of lens–iris diaphragm.
Can induce large acute myopic shift (often up to 5–8 D; reversible).
Reduces accommodative amplitude due to ciliary body edema.
Shallow anterior chamber, which can trigger secondary angle‑closure glaucoma (non–pupillary block; potentially sight‑threatening).
What can topamax (topiramate) cause?
Angle closure crisis. Requreing IOP therapy or PI.
How do corticosteriods affect the eye?
Increases IOP by reducing outflow through deposition of polysaccharides in the TM. It is the most common drug responsible for drug induced IOP spike
What other drugs can cause a myopic shift?
Sulfonamides
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Hydrochlorothiazide
Rare and only mildly increases myopia by 1D or less
What are other drugs that can increase IOP?
Anticholinergics
Antihistamines
Antidepressants
Phenothiazines (antipsychotics)
Sympathomimetics
Work by decreasing outflow by narrowing angle through pupillary dilation
What are some examples of beta blockers and how do they affect the eyes?
atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (toprol, lopressor), propranolol
They decrease IOP
If pt is already on a systemic beta blocker, then need a glaucoma med of a diff category since many of these receptors are already bound
How do cardiac glycosides, such as Lanoxin (digoxin) affect the eye?
They inhibit Na pumps in the production of aqueous → lowers IOP
What do Cannabinoids such as THC in marijuana do to the eye?
They cause a slight decrease in IOP, but not enough for medicinal purposes.
What is plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine) and how does it affect the eye?
It is an antimalarial drug now used in chronic inflammatory conditions such as SLE and RA.
Se: resides in tissue with high melanin and thus can cause Plaquenil or Bull’s-eye maculopathy
Vision loss is permanent and may still progress despite drug discontinuation
How can we prevent vision loss from plaquenil?
Early detection with OCT can prevent vision loss with drug discontinuation.
What baseline eye exams are required before starting hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)?
Full ocular exam including visual acuity
Macular OCT
10‑2 automated visual field
Establishes baseline to detect early retinal toxicity.
When should annual screening begin for hydroxychloroquine retinal toxicity?
Dose > 5 mg/kg/day
Renal disease
Concomitant tamoxifen use
If not high‑risk, annual screening begins after 5 years of use
What is the risk for Bull’s-Eye maculopathy with time?
Risk up to 5 years of use < 1%
Risk up to 10 years of use < 2%
Risk up to 20 years of use < 20%
What is Tamoxifen (Soltamox) and how does it affect the eye?
Anti-estrogen for Tx of breast cancer
White-yellow refractile opacities in the perimacular area, often present after decreased VA symptoms
Visual field abnormalities with reduced VA
Rare if does is less than 20mg/day (which is normal dose). Typically only occurs at high doses of 120 mg/day
How often do you follow up pt taking tamoxifen?
Every 6 months
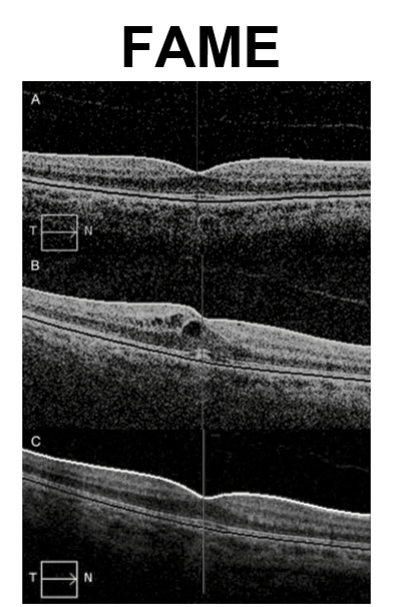
What is Fingolimod (Gilenya) and how does it affect the eyes?
Tx of Multiple Sclerosis
FAME: fingolimod associated macular edema
Higher risk of FAME for diabetics
Resolves after discontinuation of meds. Quicker with topical NSAID treatment.
What is Pentosan polysulfate sodium (PPS or Elmiron) used for and how does it affect the eyes?
Tx of interstitial cystitis of the bladder (mostly Females)
Induces bilateral symmetrical paracentral hyperpigmentation with pale yellow deposits
Often misdiagnosed as dry AMD (but lacks drusen) or pattern dystrophy of the RPE
Nodular thickening of the RPE on OCT
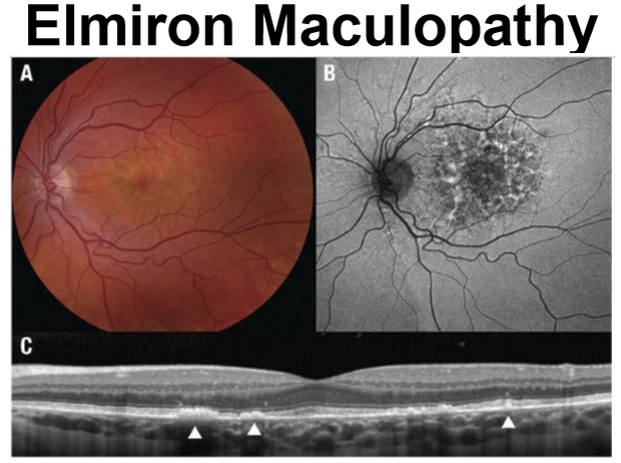
What are symptoms of Elmiron maculopathy?
Difficulty reading
Prolonged dark adaption
Cumulative dose induced after 500g, or approximately 5 years of use
Changes are usually irreversible, and may even continue to progress after stopping drug
What is Niacin used to for and how does it affect the eyes?
Med used to reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels
Can induce macular edema → dulled central vision and metamorphopsia
Changes can be 100% reversed within 4-8 wks of drug discont
What is Lanoxin (digoxin) used for and how does it affect the eyes?
Tx of cardiac arrhythmias and CHF
Can induce impaired vision and color vision perception
pts complain of snow vision: objects appear covered with frost or snow with a yellow or green tinge to objects
Visual effects completely reversible
What is Vigabatrin used for and how does it affect the eyes?
Seizure disorder
Can induce irreversible VF loss in 30-50% of those treated for over 1 year
VF usually not noticed until encroaches central field → Permanent tunnel vision
What is Interferon alpha used for and how does it affect the eyes?
Hepatitis C
Forms cotton wool spots and flame-shaped hemes in post pole
Rarely of visual significance
Will resolve after treatment is completed
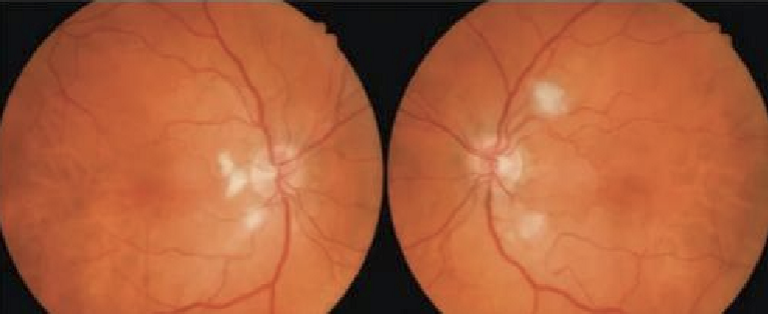
What is Thioridazine and how does it affect the eyes?
Tx Schizophrenia/anti-psychosis
Pigmentation changes in periphery, but progresses towards macula
Diffuse RPE/choriocapillaris loss with focal areas of RPE hyperplasia
Can occur 30-90 days of drug Tx
Is does dependent, if <800mg, little to no effect
Pigmentary changes are permanent but can recover most visual loss
What does Talc Retinopathy indicate?
Drug abusers crushing tables and mixing them in water to inject intravenously to get a higher high. Talc, an inert filler, becomes embolus in the retinal vasculature. Most have no effect on vision, but can lead to macular ischemia and retinal neovasc
What are some medications that are used for erectile dysfunction and how does that affect the eyes?
Viagra (sildenafil), Levitra (vardenafil), Cialis (tadalafil)
MOA: inhibits PDE5 which enhances the effects of NO → vasodilation of corpus cavernosum.
Also inhibits PDE6, used in phototransduction and color vision perception.
Creates episodes of Blue vision
What diseases are erectile dysfunction drugs contraindicated for?
Anyone with a history of NAION or monocular patients.
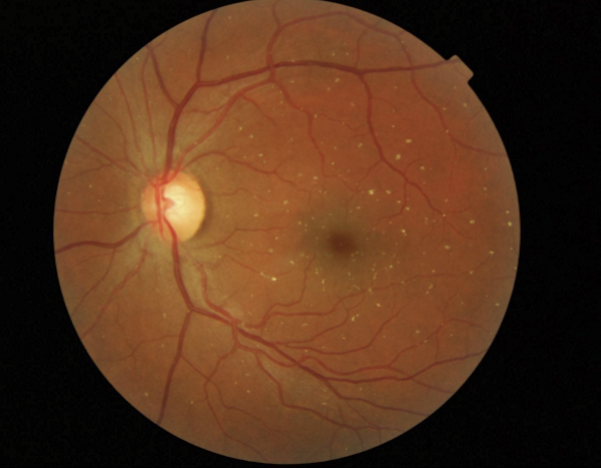
What is Ethambutol and how does it affect the eyes?
Treat Tuberculosis
Bilateral progressive optic neuropathy in 2-8 months after starting drug
Causes decreased VA, color vision, and centrocecal field defects
Effects can be reversible if caught before optic atrophy set in
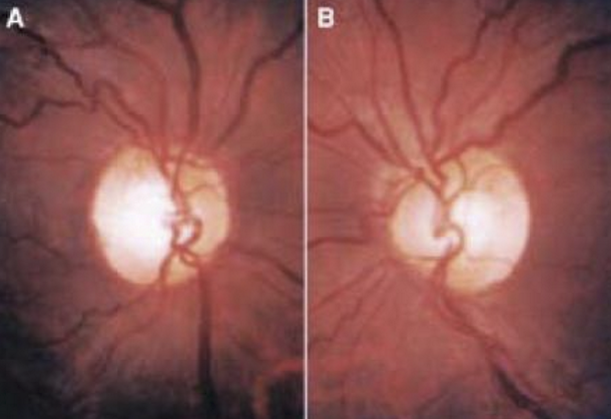
What is amiodarone and how dies it affect the eyes?
Anti-arrhythmic drug
Rare at1.76% of users, but can cause bilateral disc swelling d/t blockage of axoplasmic flow
Develops within first year of med use
Slowly resolves over months after drug D/C
Vision can restory
Causes vortex keratopathy
What is Topamax used for and how does it affect the eye?
An epilepsy/antiseizure med that is also sued for migraine prevention
Suspicions about its effect on the optic nerve
Same med that can cause dramatic increases in myopia and angle closure glaucoma
What drugs can induce idiopathic intracrainial hypertension (IIH)?
High dose Vit A or Isotretinoin (an analog of vit a)
Tetracyclines *all varieties)
Nalidixic Acid (1st gen fluoroquinolone)
Hormone-based birth control (oral or implants)
As well as pregnancy itself
Withdrawal of systemic steroids (if not tapered correctly)
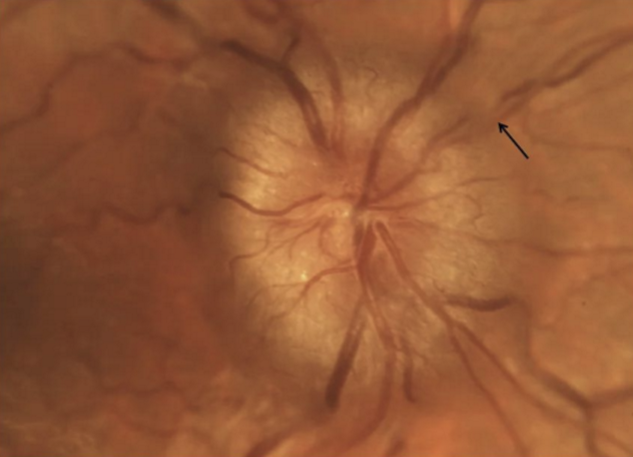
How do drugs cause IIH?
MOA: blockage of arachnoid vila that inhibits drainage of CSF into superior sagittal sinus.
How can you tell if there is an increase in intracranial pressure?
Bilateral optic nerve edema. But IIH is a diagnosis of exclusion.
What must be ruled out before the pt is diagnosed with IIH?
Space occupying lesions: intracranial mass, hemorrhage. AND meningitis.
How is IIH confirmed?
Imaging, typically with MRI with contrast
Lumbar puncture with a high opening pressure (>20 cm CSF)