STAT 164 - 3RD LE - CHAPTER 6.1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
CORRELATION ANALYSIS
It is a statistical technique used to determine the strength of the relationship between two variables, X and Y.
CORRELATION ANALYSIS
it provides a measure of strength of the linear relationship between two variables measured in at least interval scale.
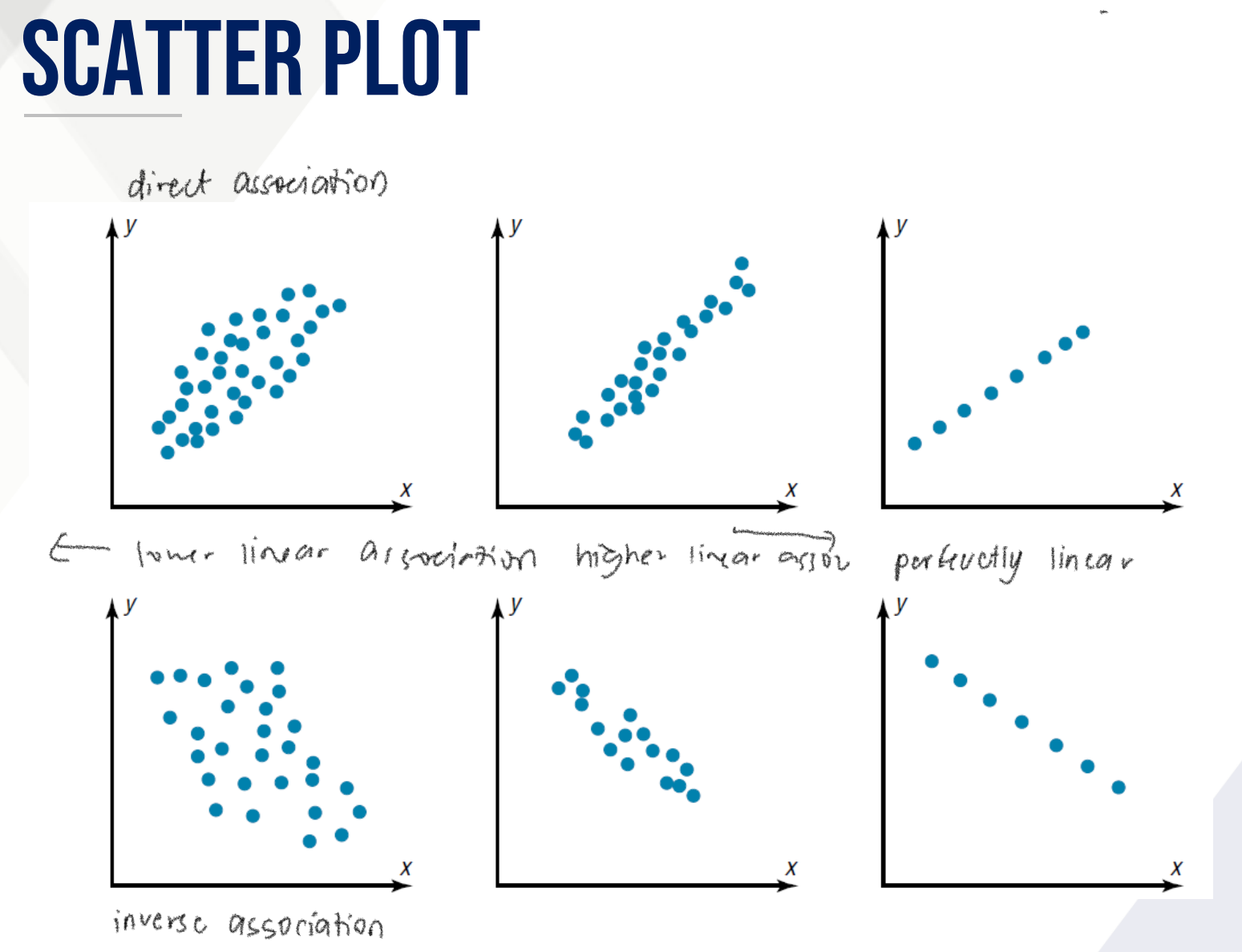
SCATTER PLOT
a graph of the ordered pairs of numbers consisting of variables X and Y
a visual way to describe the nature of the relationship between two quantitative variables

Correlation Coefficient
It is a quantitative measure of the closeness or degree of relationship between two variables
It can be computed using a particular formula depending on the characteristic of the variable of interest
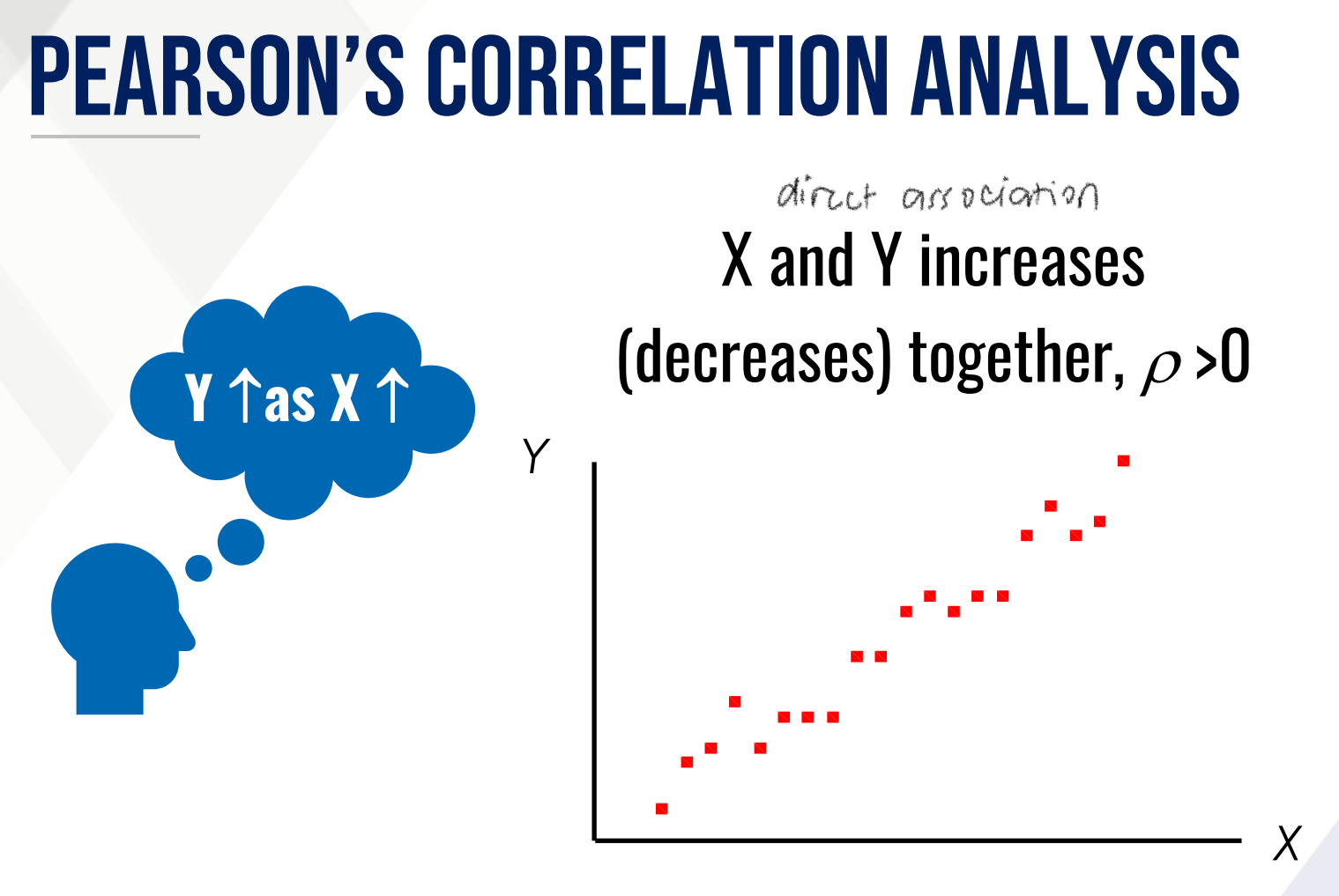
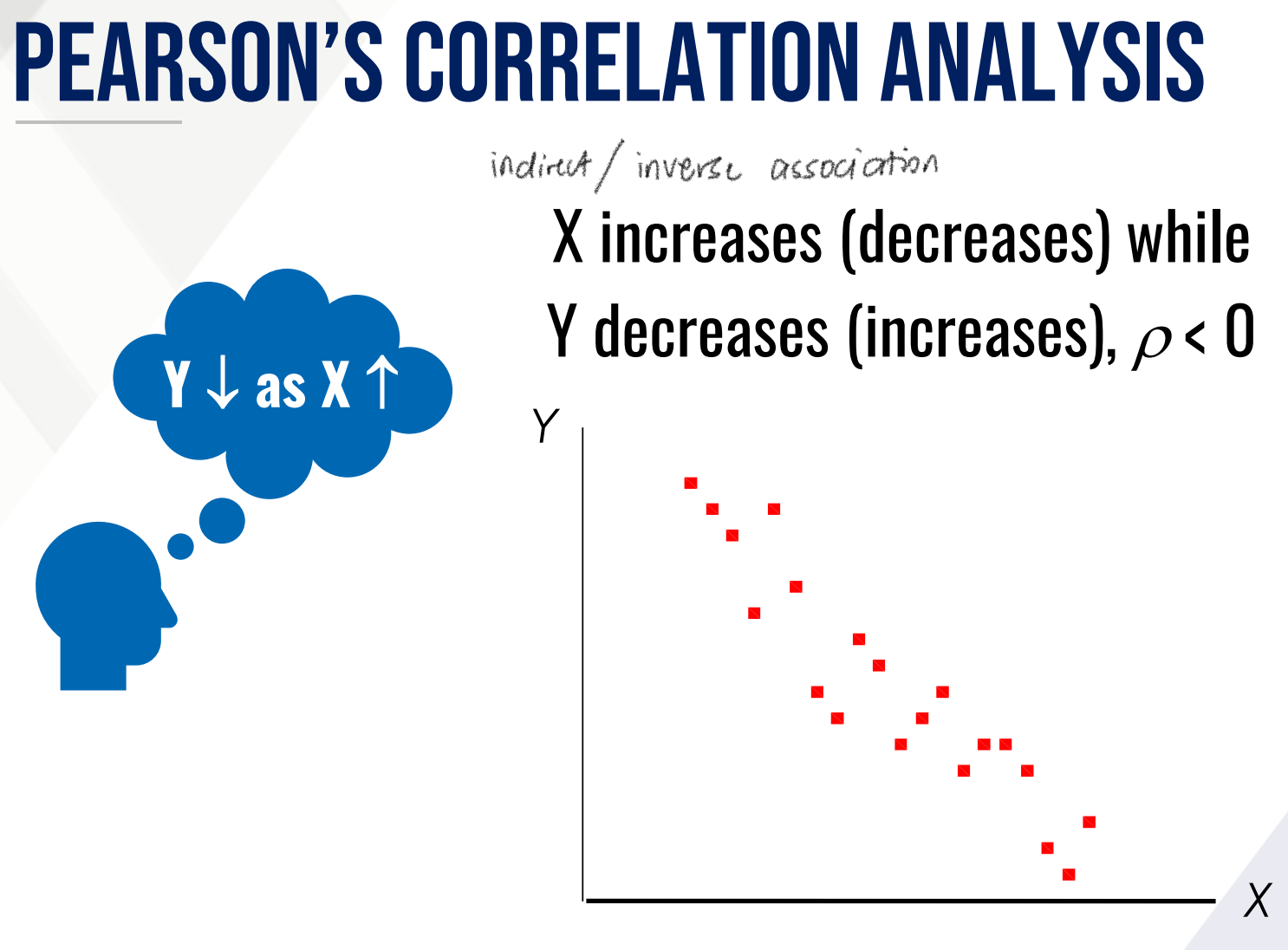
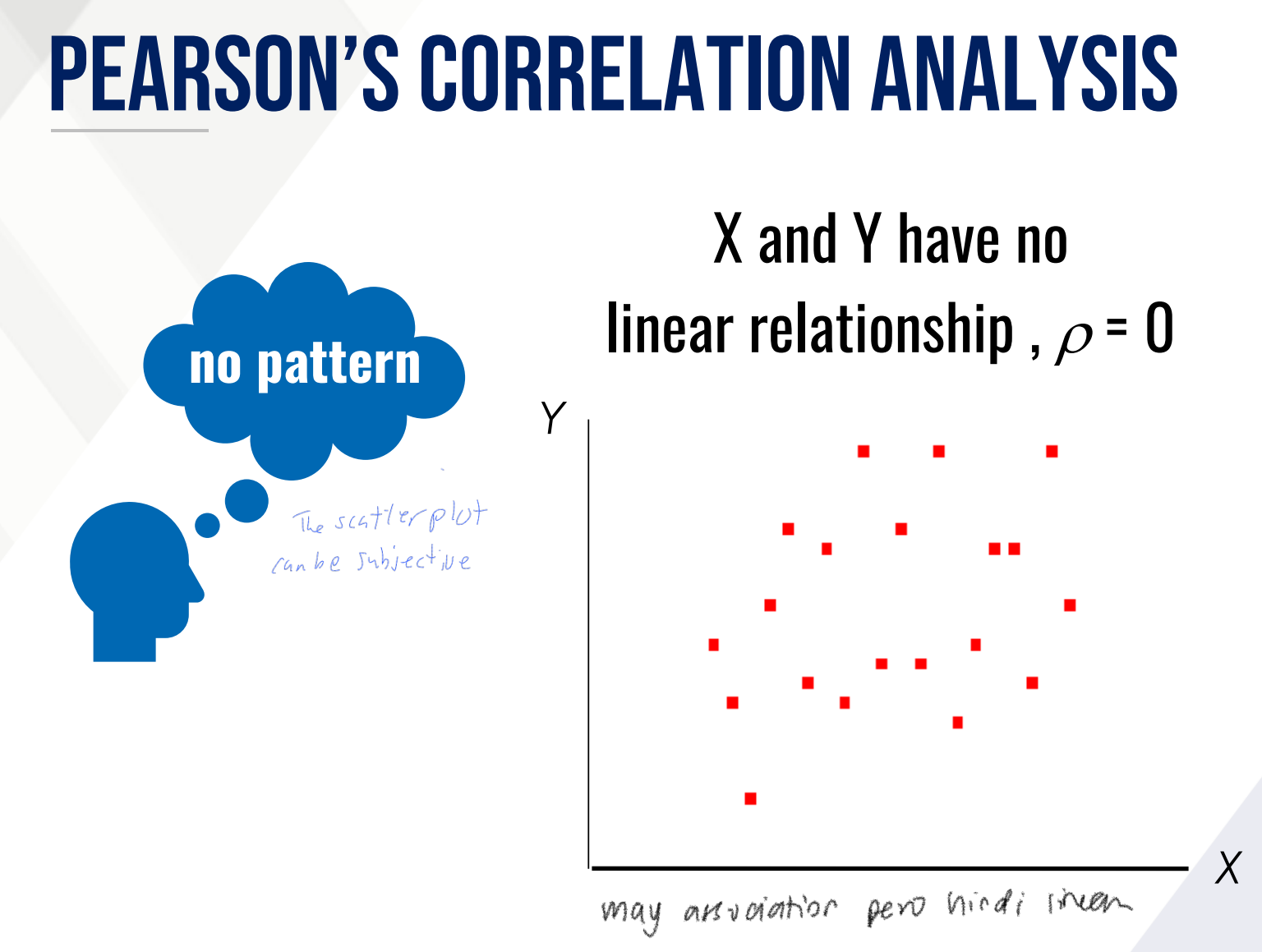
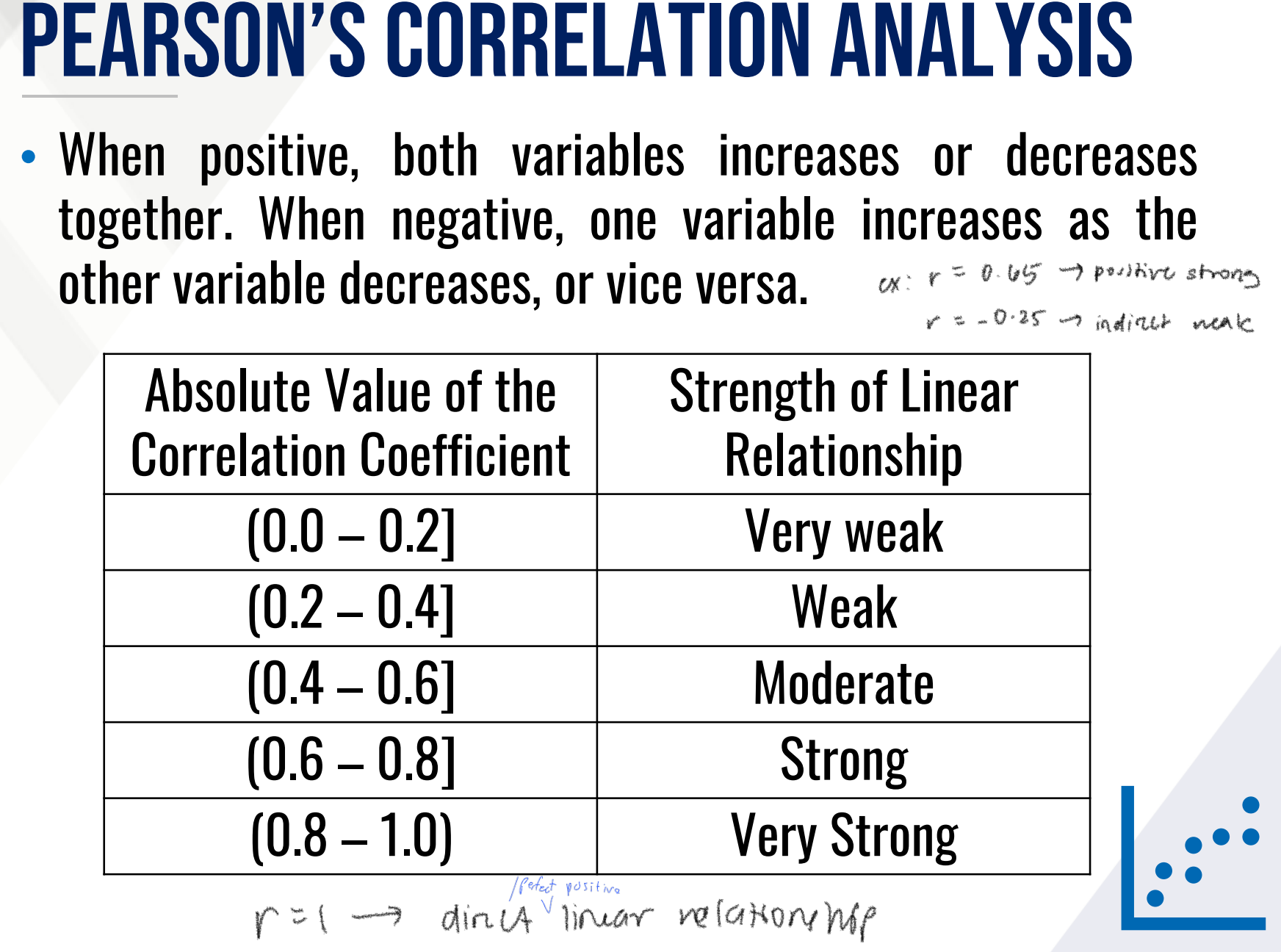
What do the following ρ ranges mean?
ρ > 0
ρ < 0
ρ = 0
How about the Strength of Linear Relationship?
Provide range and then interpretation for each.
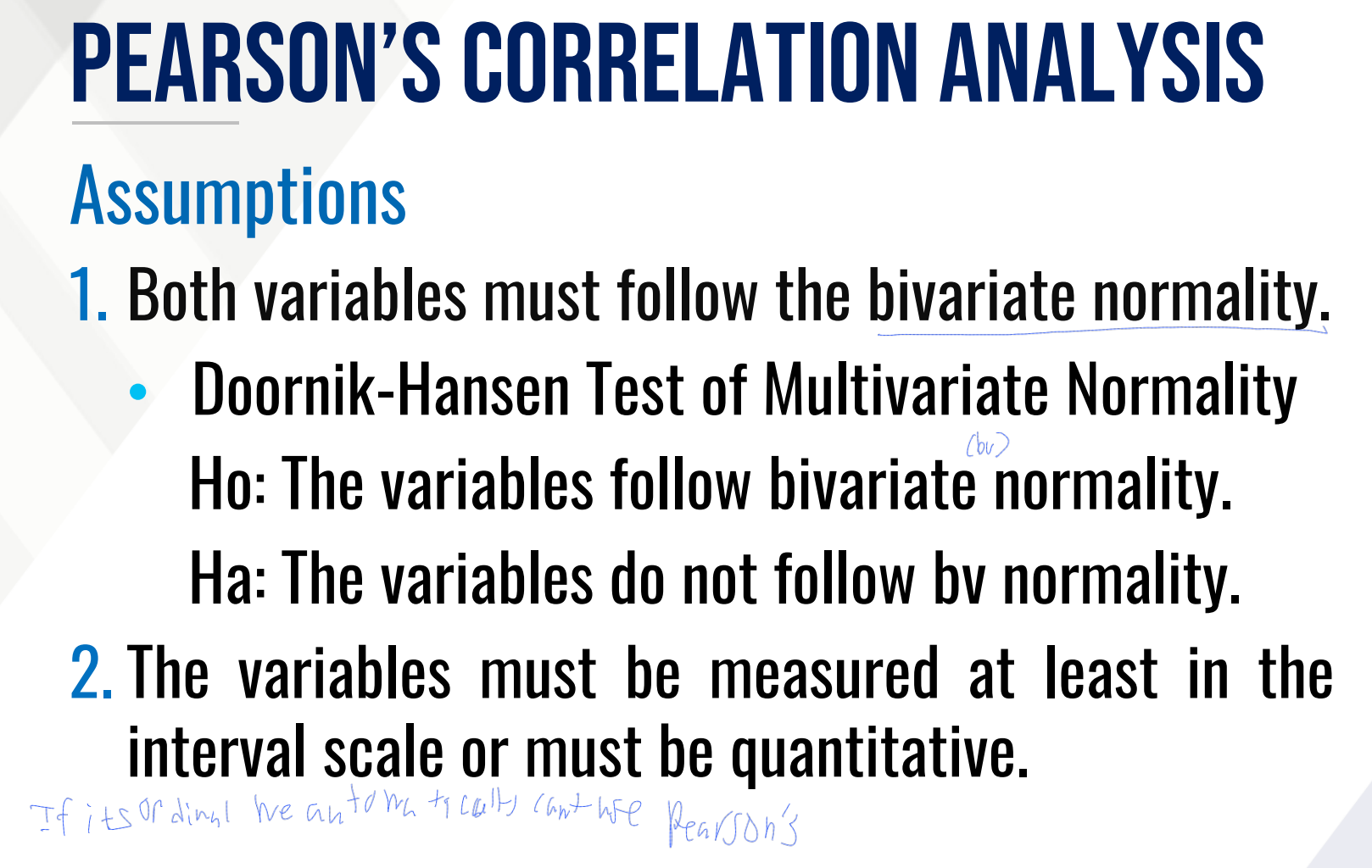
If its ordinal we automatically cant use Pearson’s
What are the assumptions for PEARSON’S CORRELATION ANALYSIS?
Both variables must follow the _______________.
What test?
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
The variables must be measured at least in the ______________ or must be ______________.
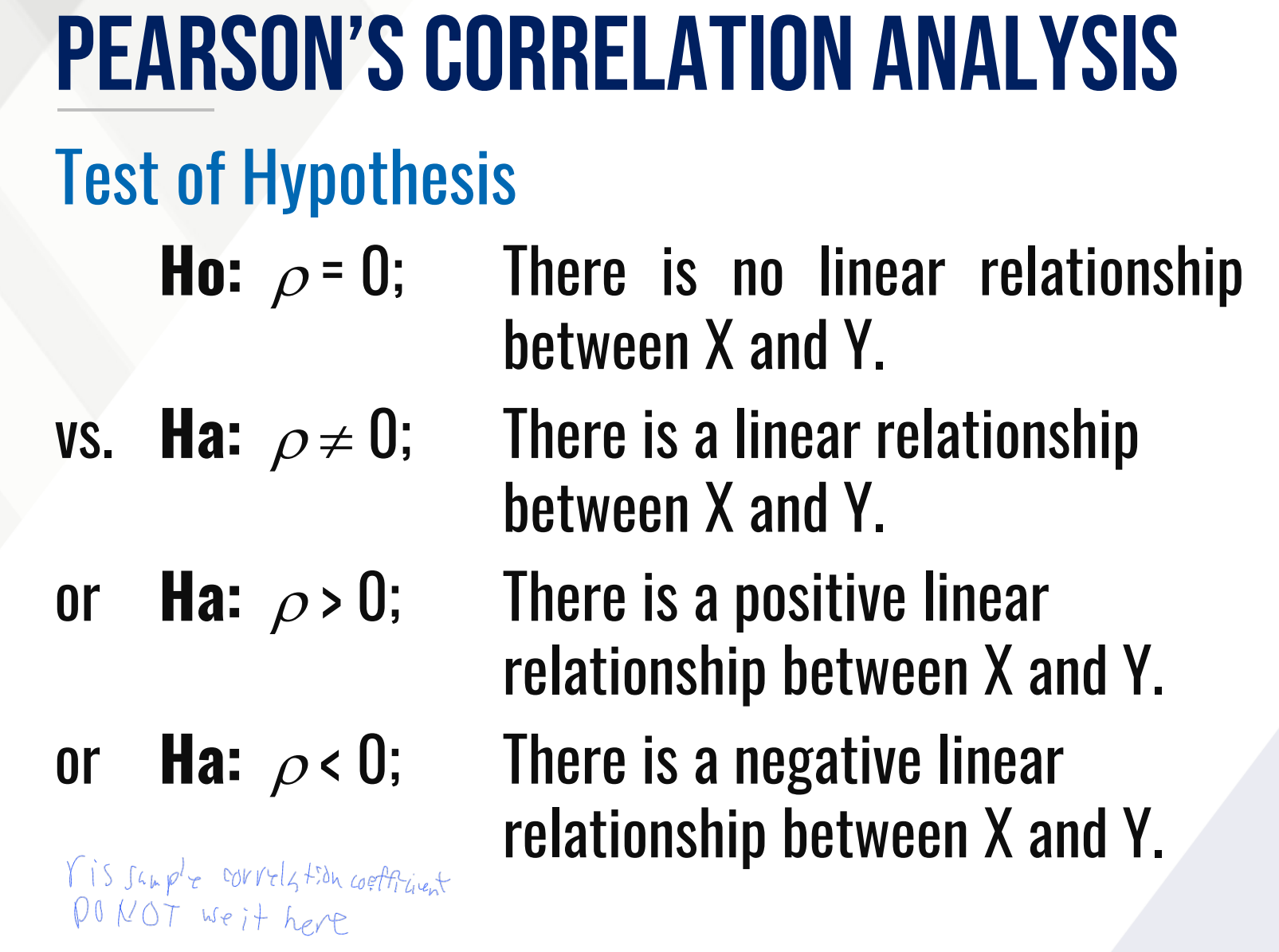
What is the Test of Hypothesis for PEARSON’SCORRELATION ANALYSIS?
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
or Ha (in words): >
or Ha (in words): <
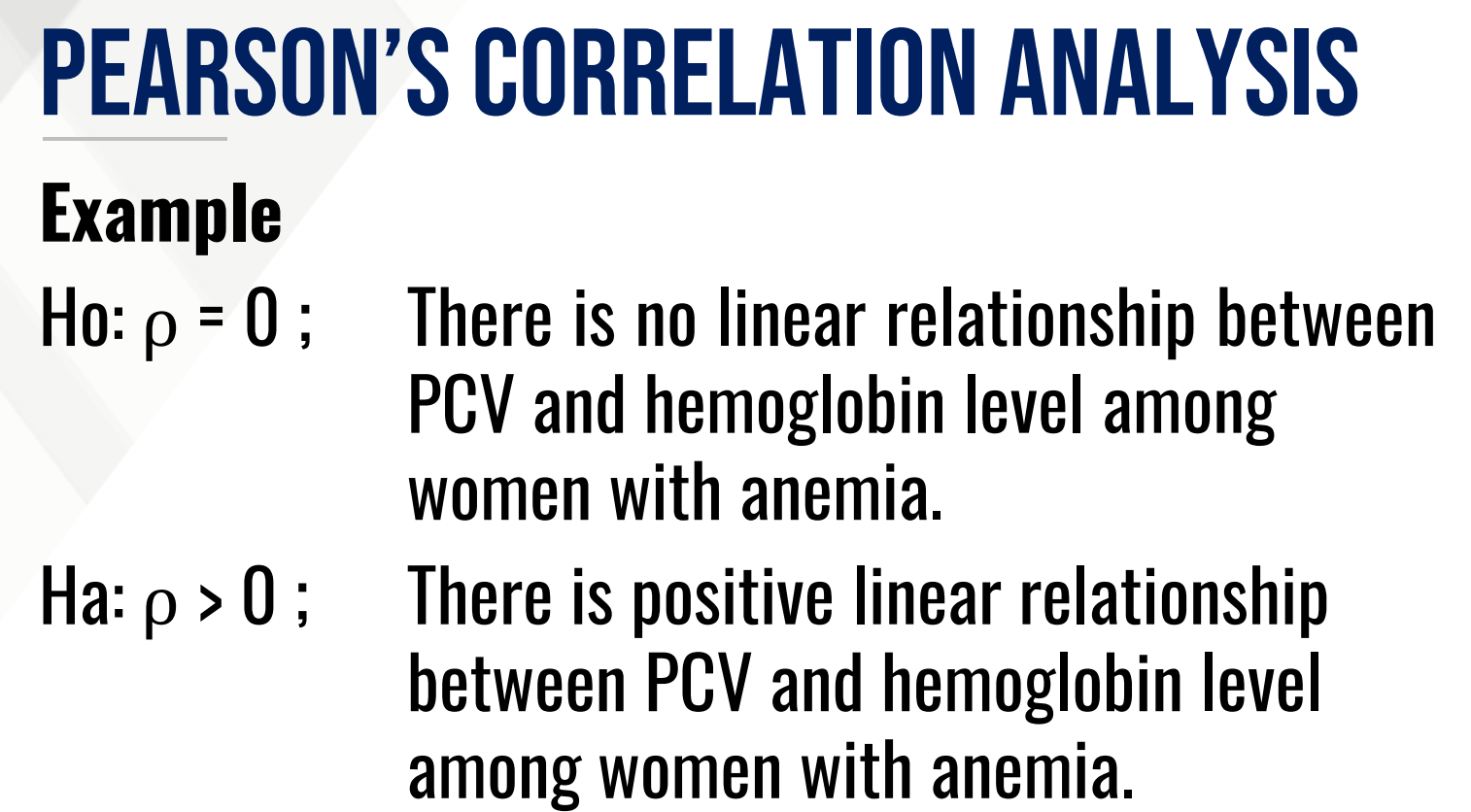


There is a positive (direct) strong linear association between PCV and hemoglobin level among women with anemia.
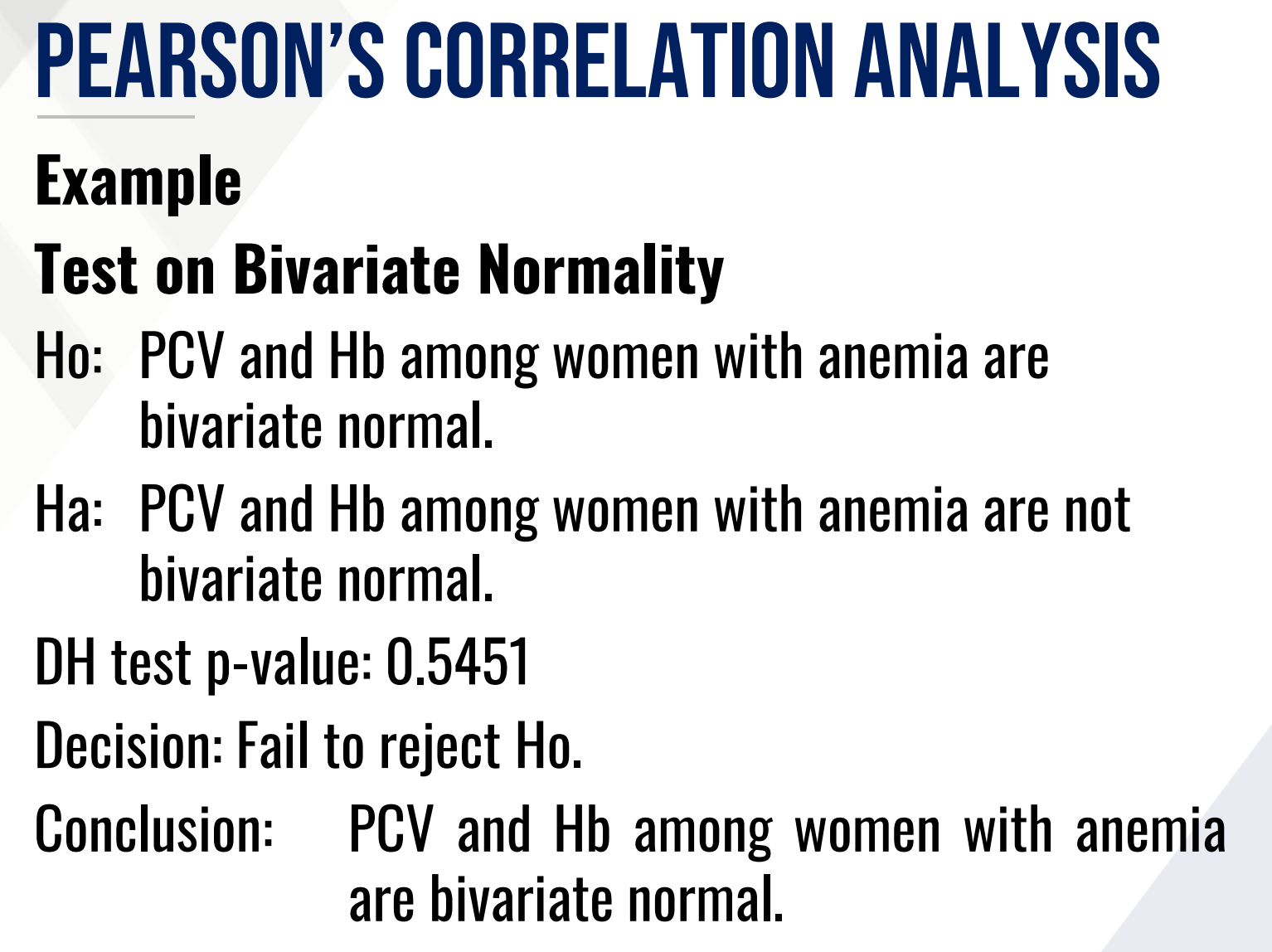
Test on Bivariate Normality, provide the following:
DH test p-value: 0.5451
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
Decision:
Conclusion:
Test of Hypothesis, provide the following:
p-value = 0.0011
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
Conclusion:
SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS
Uses the ranks X and Y
measures the degree of correspondence between rankings
SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS
measures how well one variable is monotonically associatd on the other variable
variable are at least ordinal in scale
the statistic rs is used to estimate the true correlation, p
SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS
Its coefficient, ρs, measures the strength and direction of monotonic association between two ranked variables.
Assumption: X and Y are at least ordinal in scale.
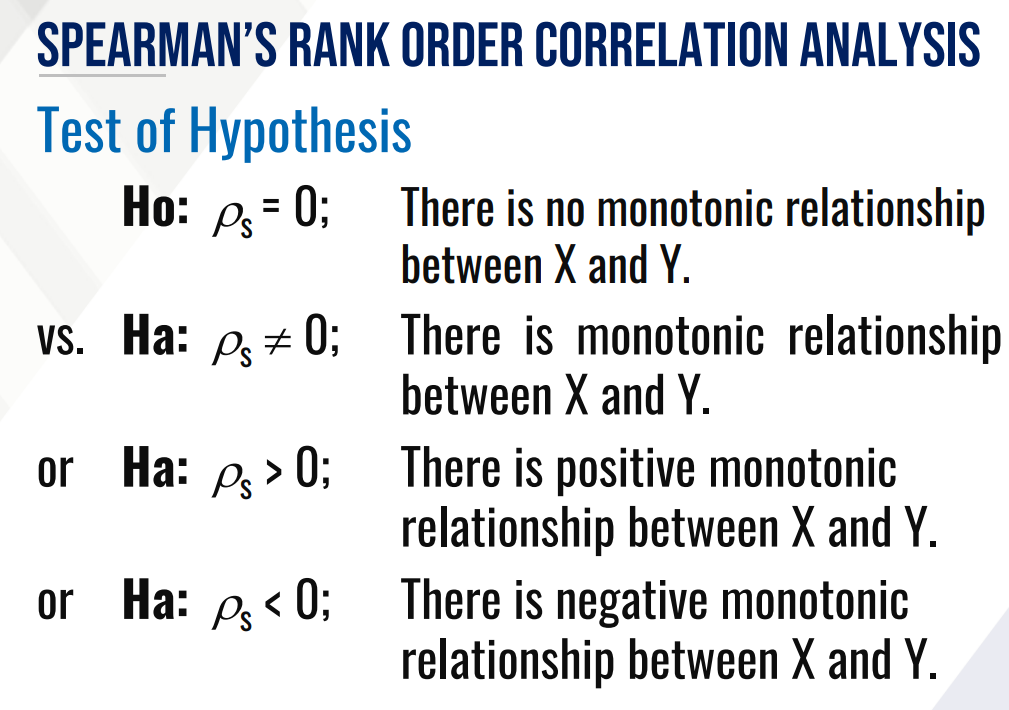
What is the Test of Hypothesis for SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS?
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
or Ha (in words): >
or Ha (in words): <
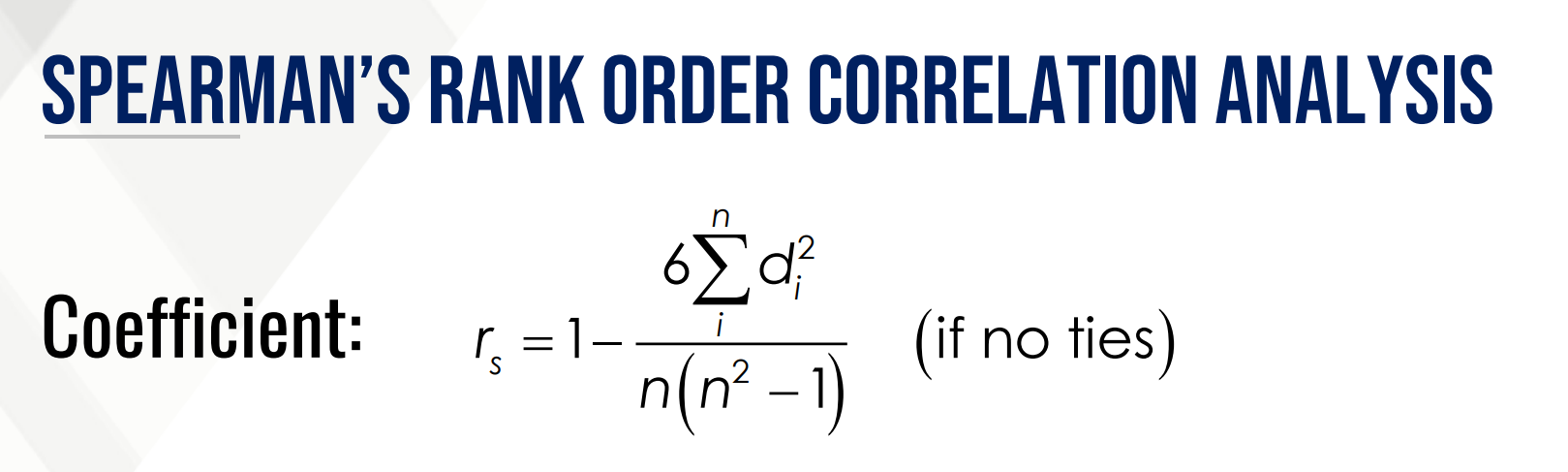
SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS Coefficient formula?
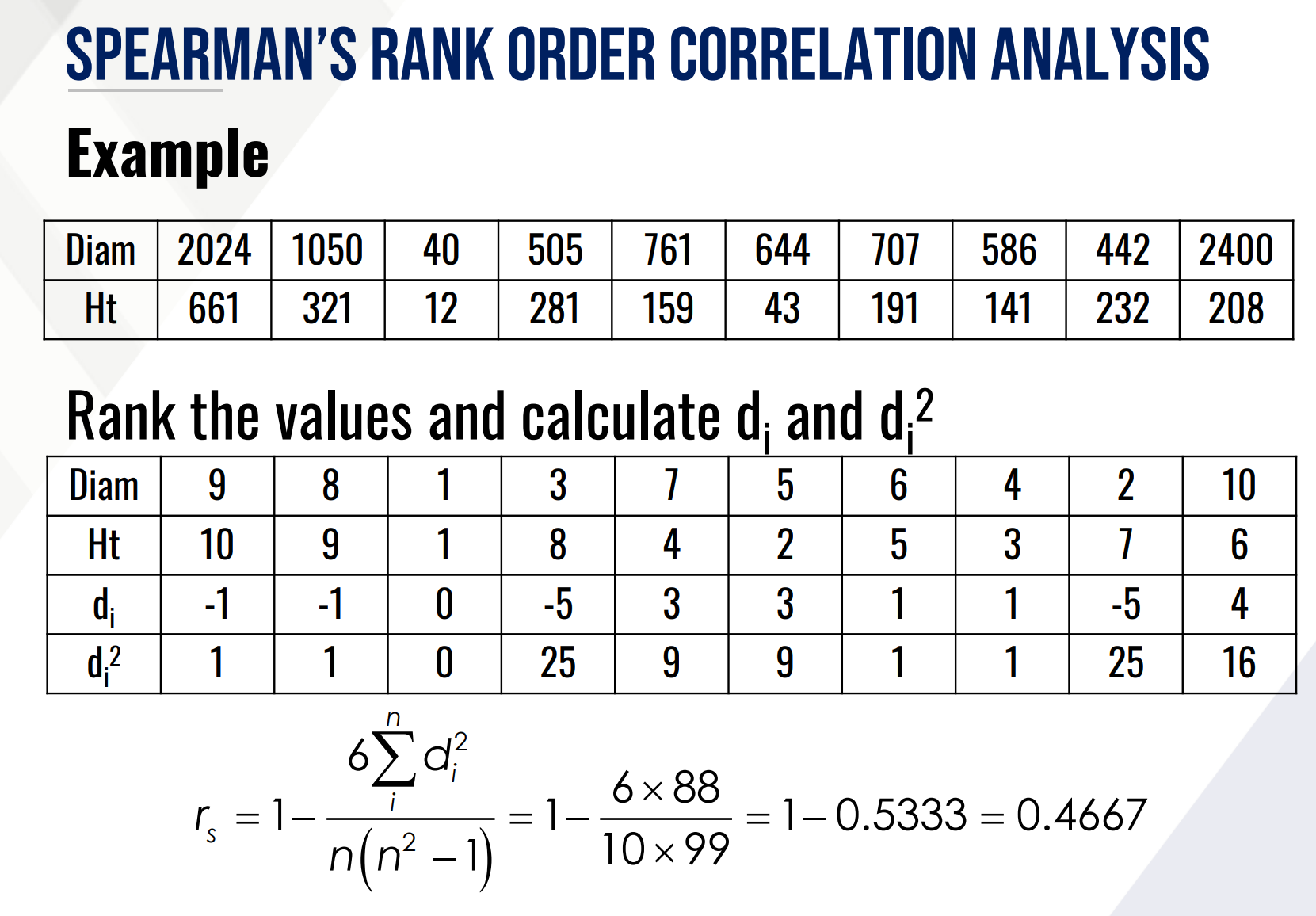
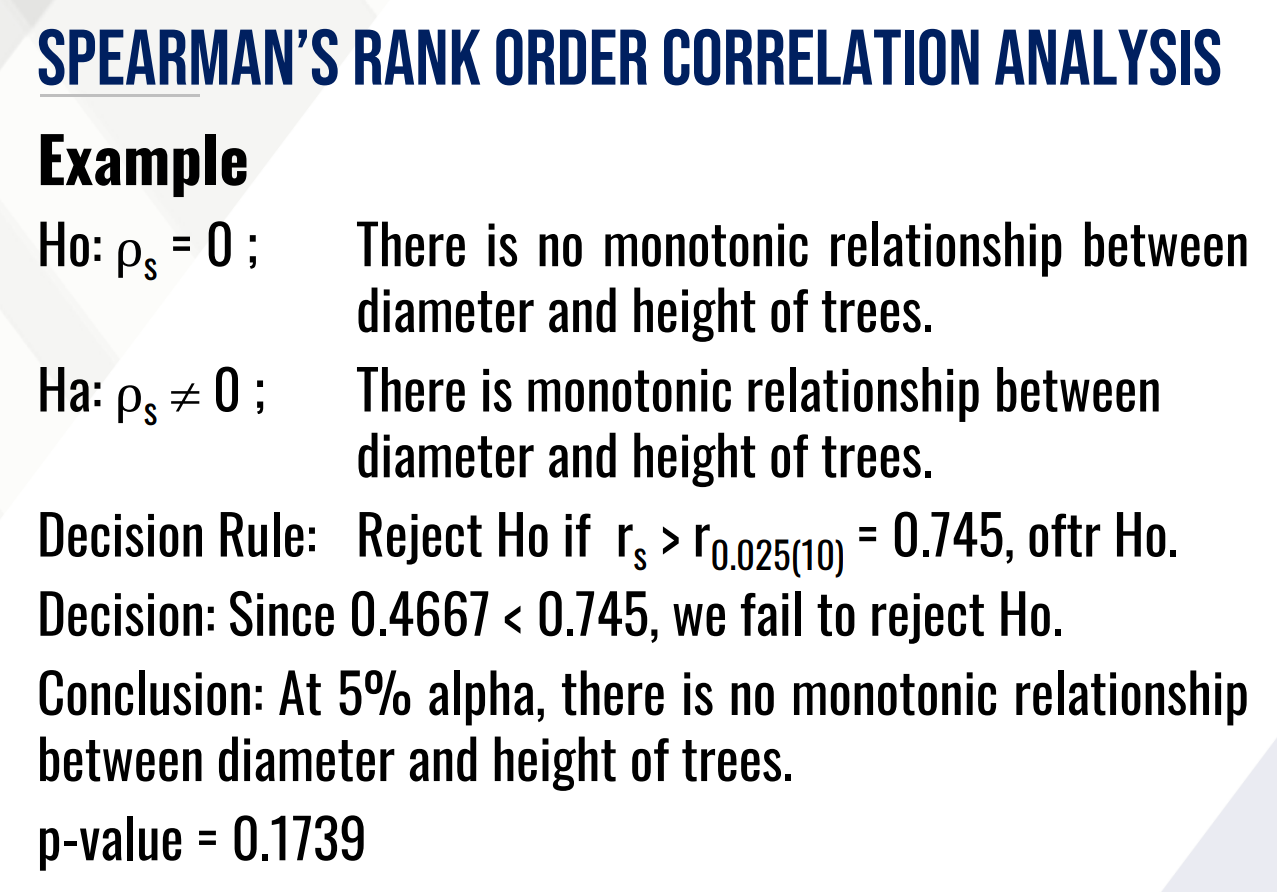
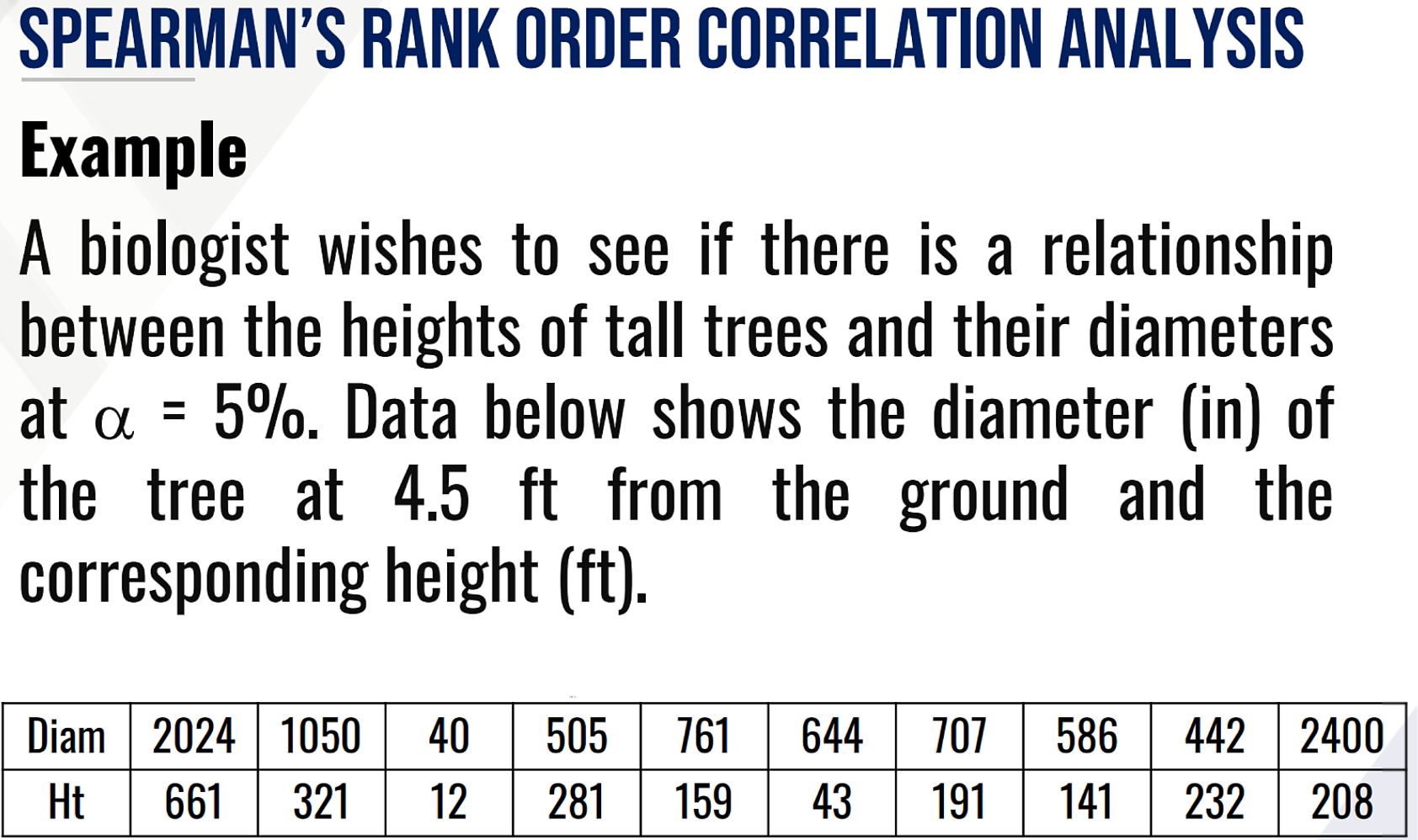
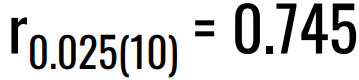
SPEARMAN’S RANK ORDER CORRELATION ANALYSIS, provide the following:
Test statistic:
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
Decision:
Conclusion:
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Quantitative
Variable 2 - Quantitative
Condition - Bivariate Normality - Yes
Measure of Association - Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient
Corresponding Test Procedure - t-Test for Correlattion Coefficient (Pearson’s Correlation)
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Quantitative
Variable 2 - Quantitative
Condition - Bivariate Normality - Yes
Measure of Association - ____________________
Corresponding Test Procedure - ____________________
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 -
Variable 2 -
Condition - Bivariate Normality - No
Measure of Association - Spearman’s Rank Order Correlation Coefficient
Corresponding Test Procedure - Spearman’s Rank Order Correlation Analysis
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 -
Variable 2 -
Condition - Bivariate Normality - No
Measure of Association - ____________________
Corresponding Test Procedure - ____________________
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Categorical
Variable 2 - Categorical
Measure of Association - Phi Coefficient (2×2 continegncy table), Contingency Coefficient, Cramer’s V
Corresponding Test Procedure - Chi-Square Test, G-Test, Fisher’s Exact Test (2×2)
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Categorical
Variable 2 - Categorical
Measure of Association - ____________________
Corresponding Test Procedure - ____________________
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Ordinal
Variable 2 - Quatitative
Measure of Association - Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient
Corresponding Test Procedure - t-Test for Correlattion Coefficient (Pearson’s Correlation)
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Ordinal
Variable 2 - Quatitative
Measure of Association - ____________________
Corresponding Test Procedure - ____________________
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Ordinal
Variable 2 - Ordinal
Measure of Association - Kendall’s Rank Correlation Coefficient
Corresponding Test Procedure - Kendall’s Rank Correlation Test
Given the variables 1 and 2, provide the measure of association and the corresponding test procedure:
Variable 1 - Ordinal
Variable 2 - Ordinal
Measure of Association - ____________________
Corresponding Test Procedure - ____________________
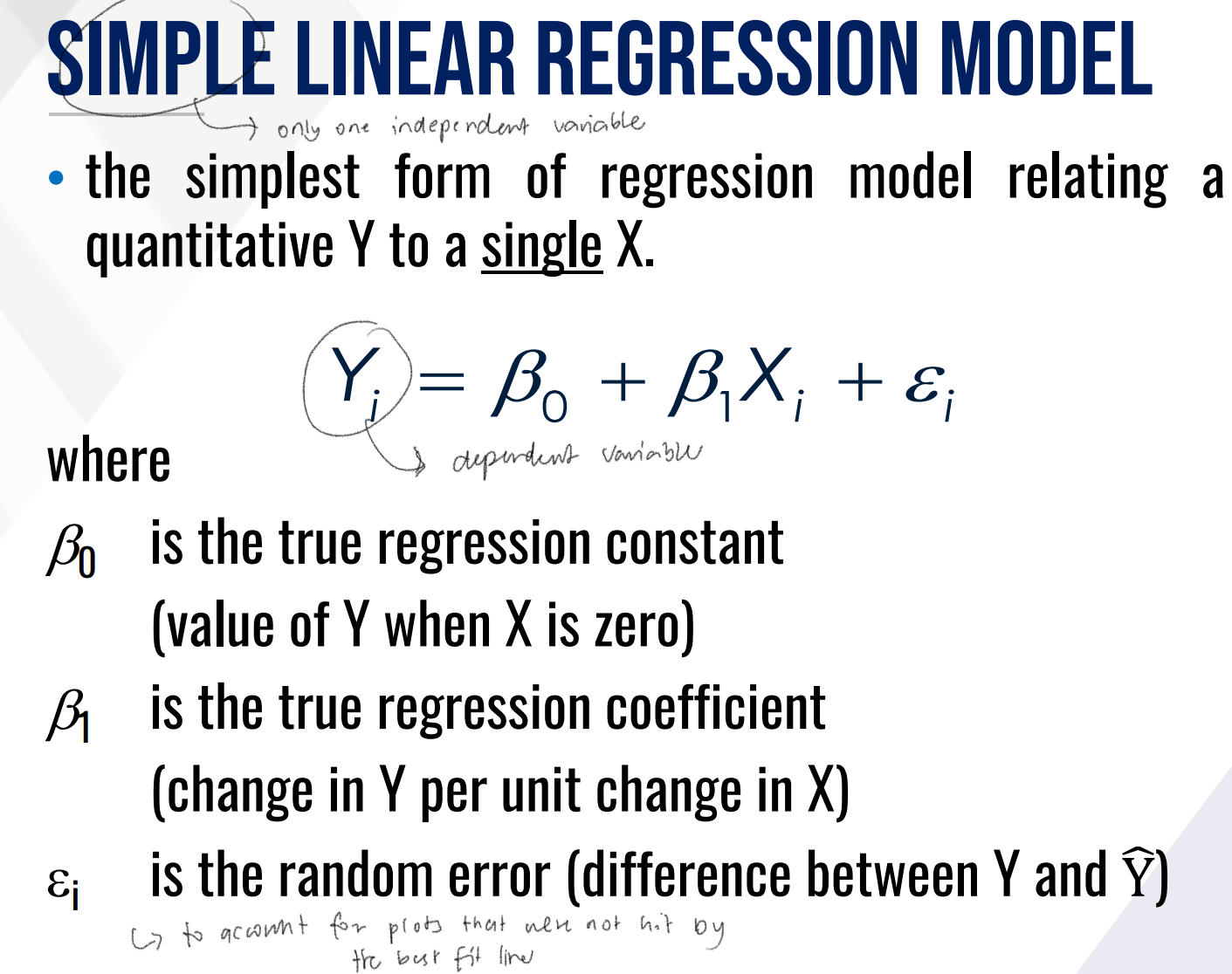
REGRESSION ANALYSIS
It is a statistical technique used to study the functional relationship between variables which allows predicting the value of one variable, say Y (dependent, outcome, or response variable), given the value of another variable, say X (independent or explanatory variable).
REGRESSION ANALYSIS
It is assumed in this technique that a change in X will lead directly to a change in Y.
LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL
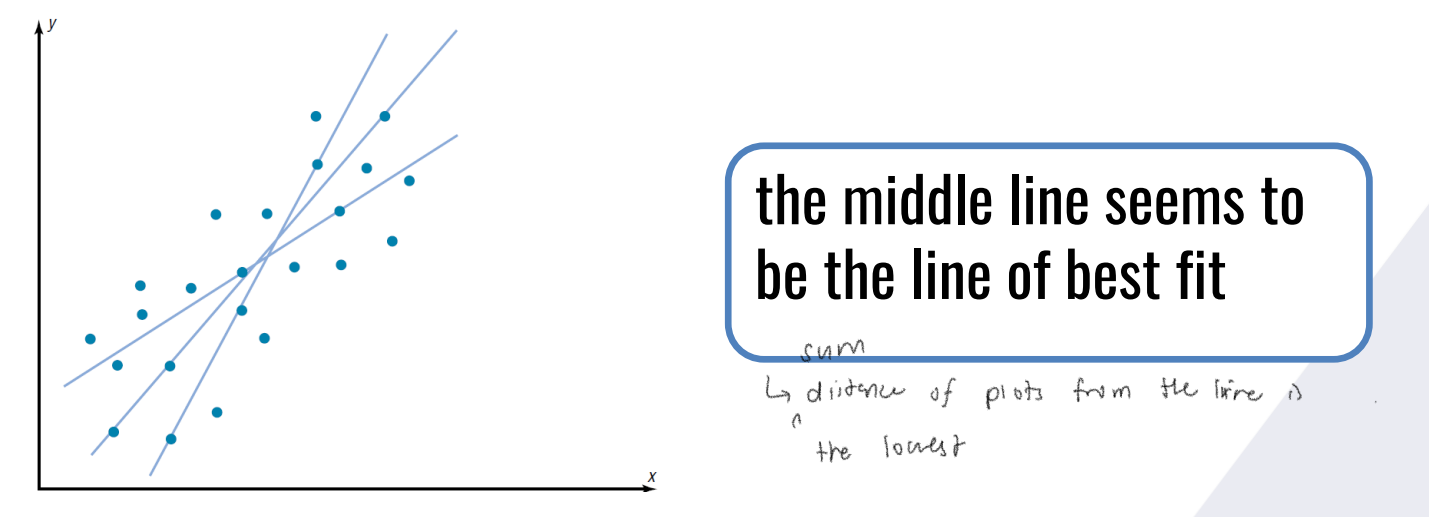
provides a linear equation representing the best fitted regression line between a quantitative Y and a set of X.
LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL

used to see the trend of association and make predictions or estimates of Y based on the data
error
independent
normally distributed
homoscedastic
LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL ASSUMPTIONS
The values of X are measured without ________.
The values of Y are statistically ______________.
For each value of X, there is a subpopulation of Y values that is _____________.
The variances of the subpopulations of Y are _____________.
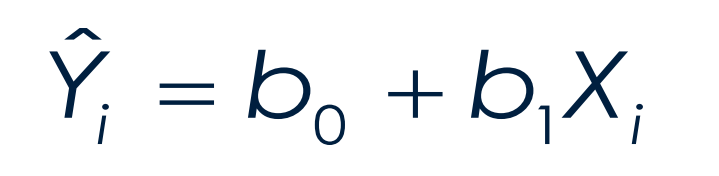
What is the formula to solve for the value of the dependent variable in a SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL?
Also what is the formula for the estimated regression model?
Coefficient of Determination (R2)
This estimates model adequacy
proportion of the total variation in Y that is explained by X, usually expressed in %
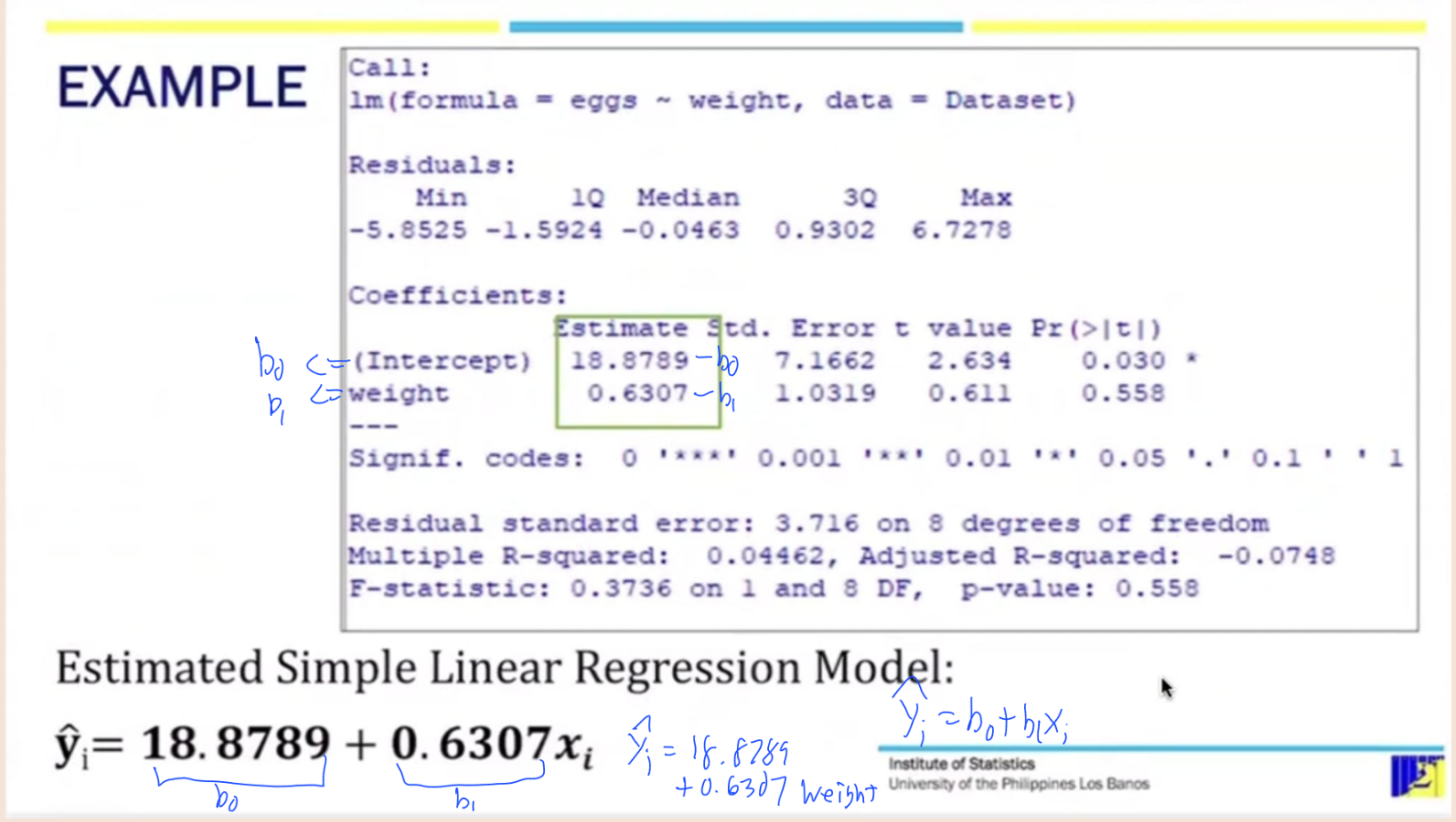


SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL

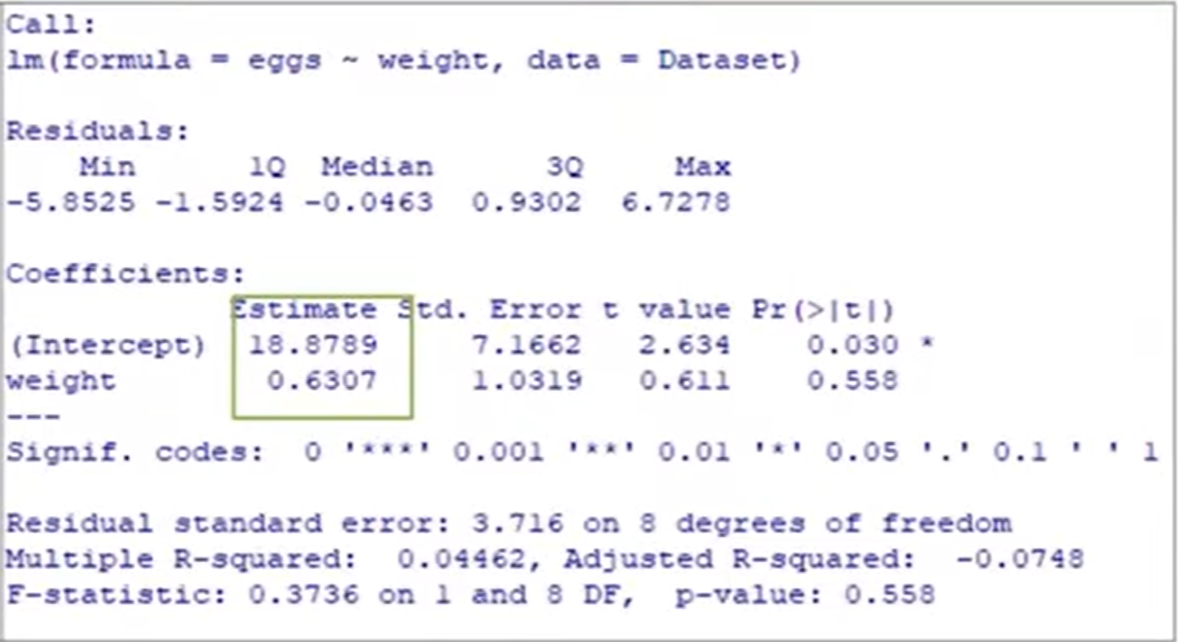
Provide the following:
Estimated Simple Linear Regression Model:
Interpretation of each Regression coefficient
R2
Interpretation of R2


What is the estimated MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL formula?


Provide the following:
Estimated Linear Regression Model
Interpretation of the Regression Coefficients
Interpretation of the Regression Constant

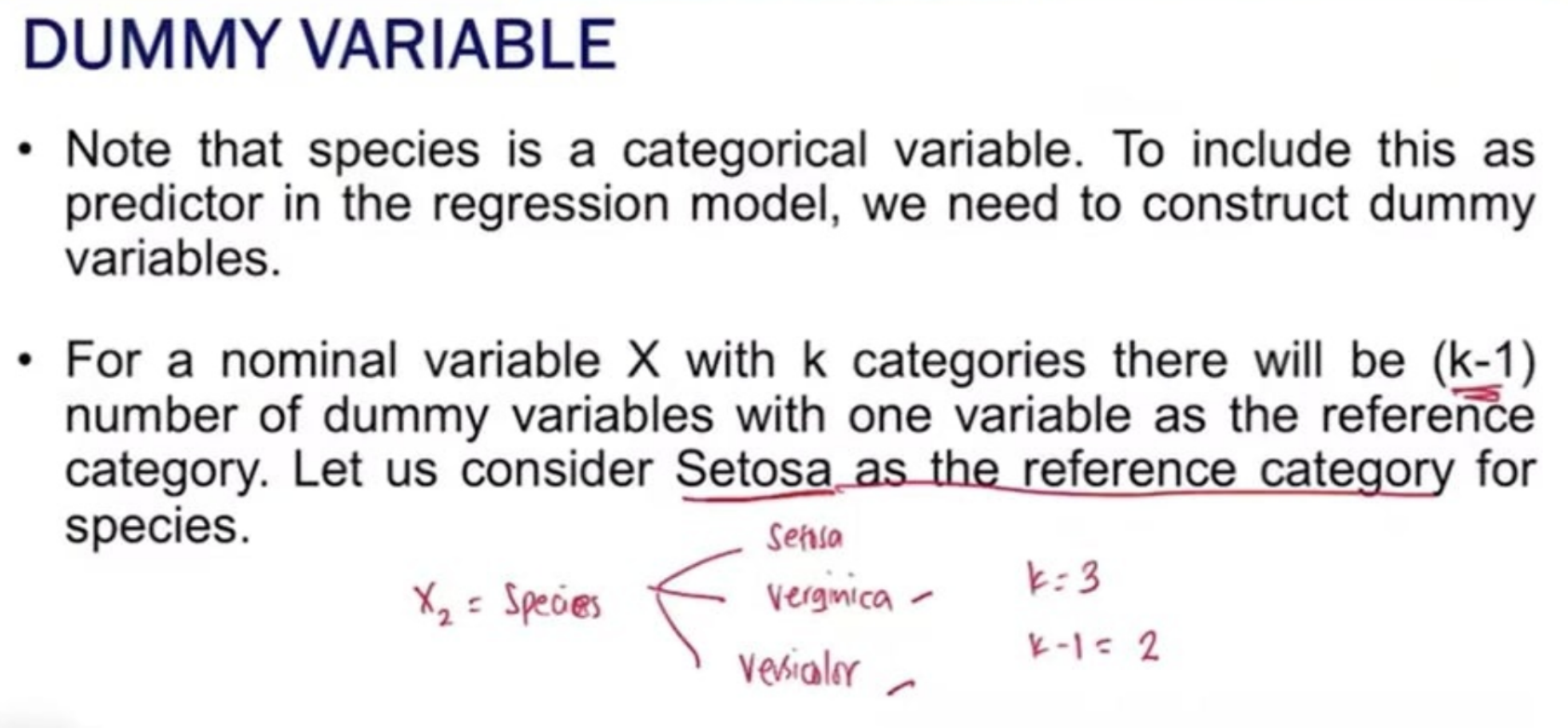
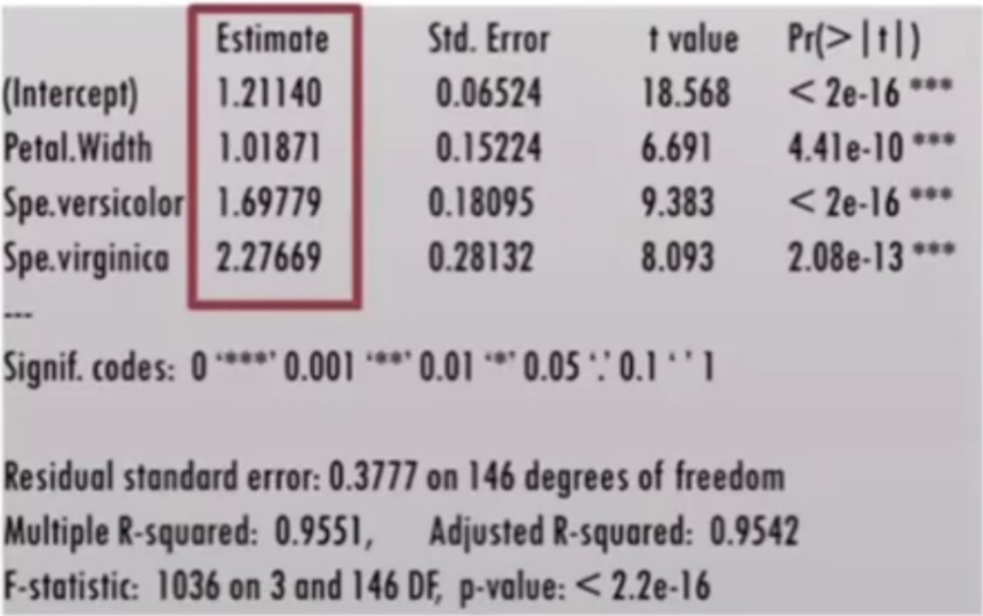

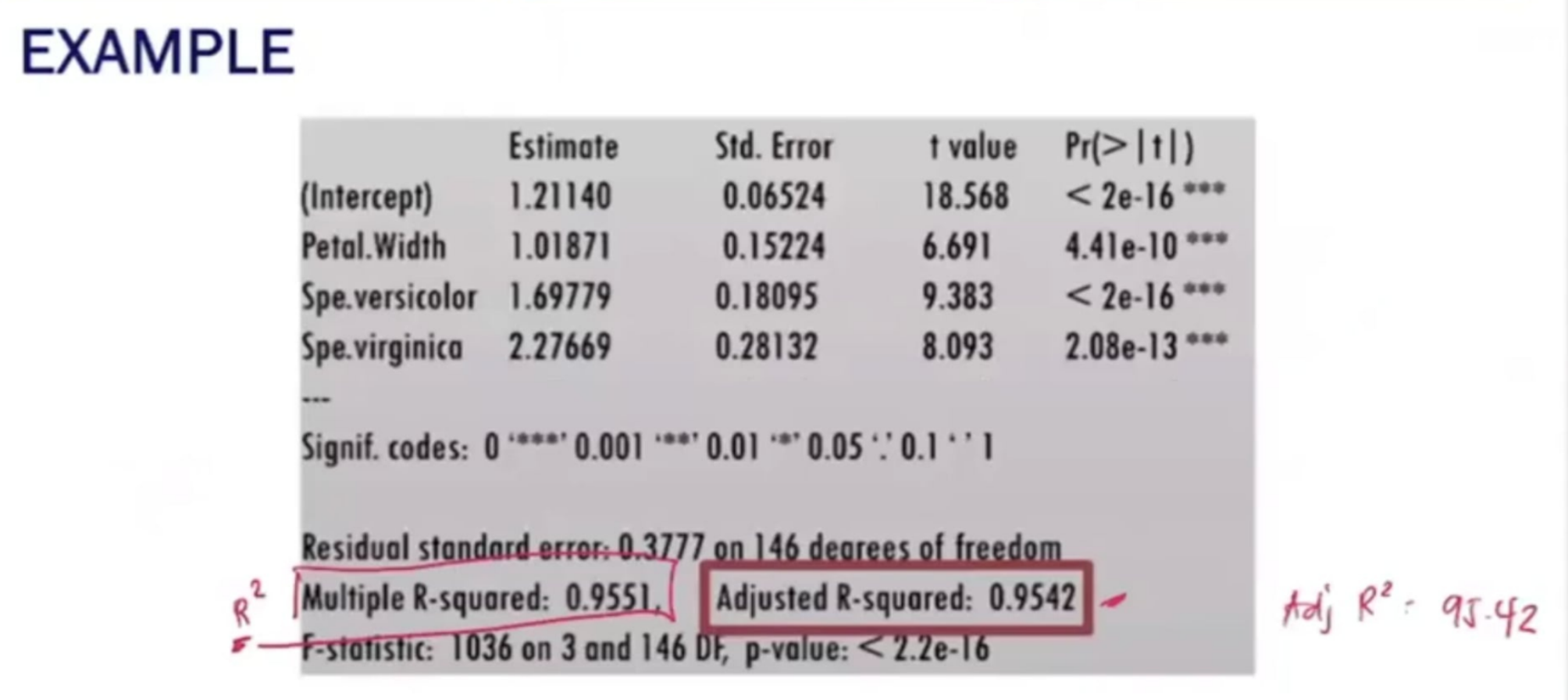
To assess the fit of the multiple linear regression model constructed, we use the Adjusted R2 instead of the R2.
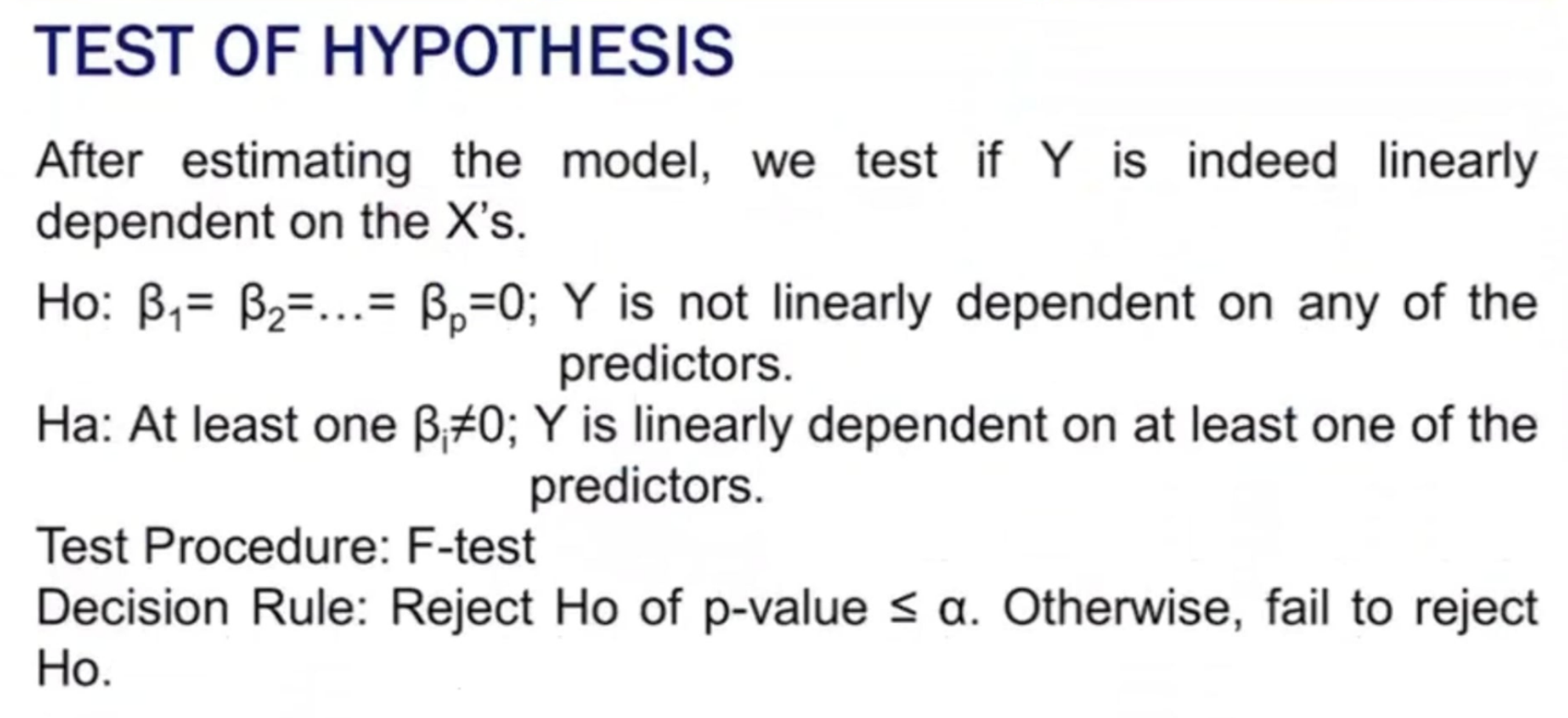
MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL
Provide the following:
Ho (in words):
Ha (in words):
Test Procedure: F-test
Decision Rule:
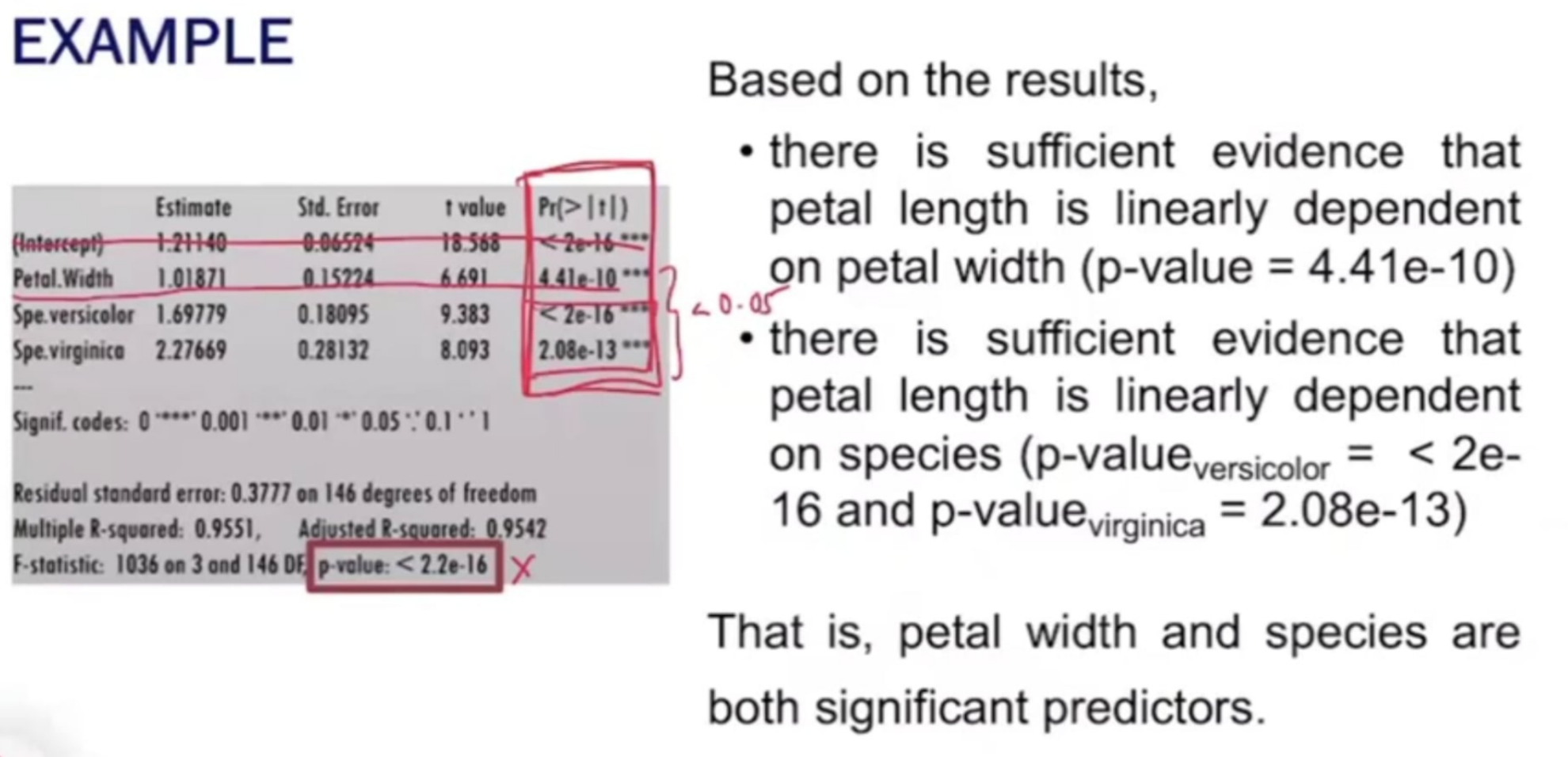
MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL

What is the conclusion for each predictor? Overall?