Chaoters 1,2,4, and 8 3D art - Test 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Three Dimensional
those having height, width, and depth.
What happens when photographing three dimensional work?
in photography it cannot convey surface texture, weight, and balance of peace nor it can sapture sound, smell, or motion.
Point of view
a set distance and angle from which the piece is viewed.
Two dimensional
having only height and width but no depth.
Values
gradation from lights and darks
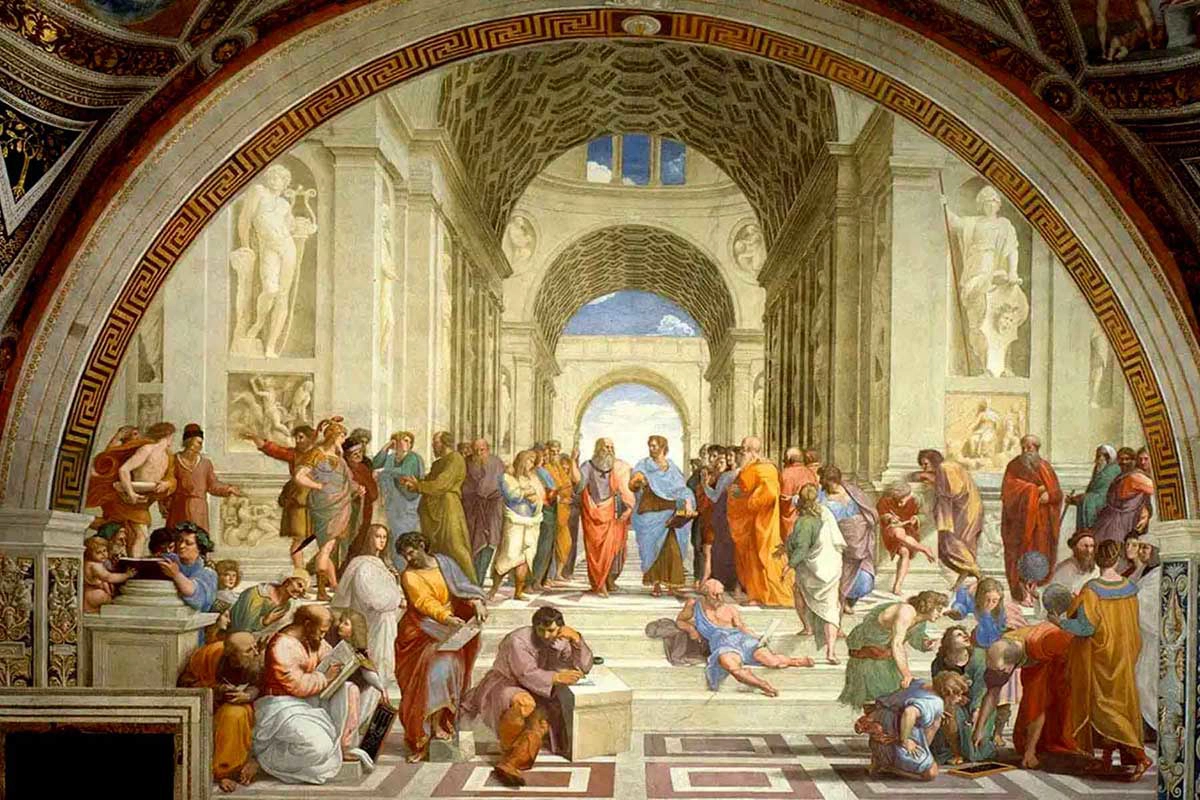

Linear perspective
The convergence of parallel lines toward a distant vanishing point
Virtual realities
utilizes immersive technology to create interactive, three-dimensional digital environments that blend imagination with reality
What does virtual mean?
is a computer term reffering to anything that exists only as digital memory in computer than in physical.
Scale
the relative size of pieces.
Does photography give good idea of the scale of art piece?
no. many photographs give no clues to weather the object pictures is very small or very large.
How do artists then potray scale in photography?
They often include in the photograph something of known size-such as a bench or a human being, to serve as a standard of comparison.

Conceptual art
work or events exsiting as ideas in the artists mind but not necessarily presented or maintained in tangible form
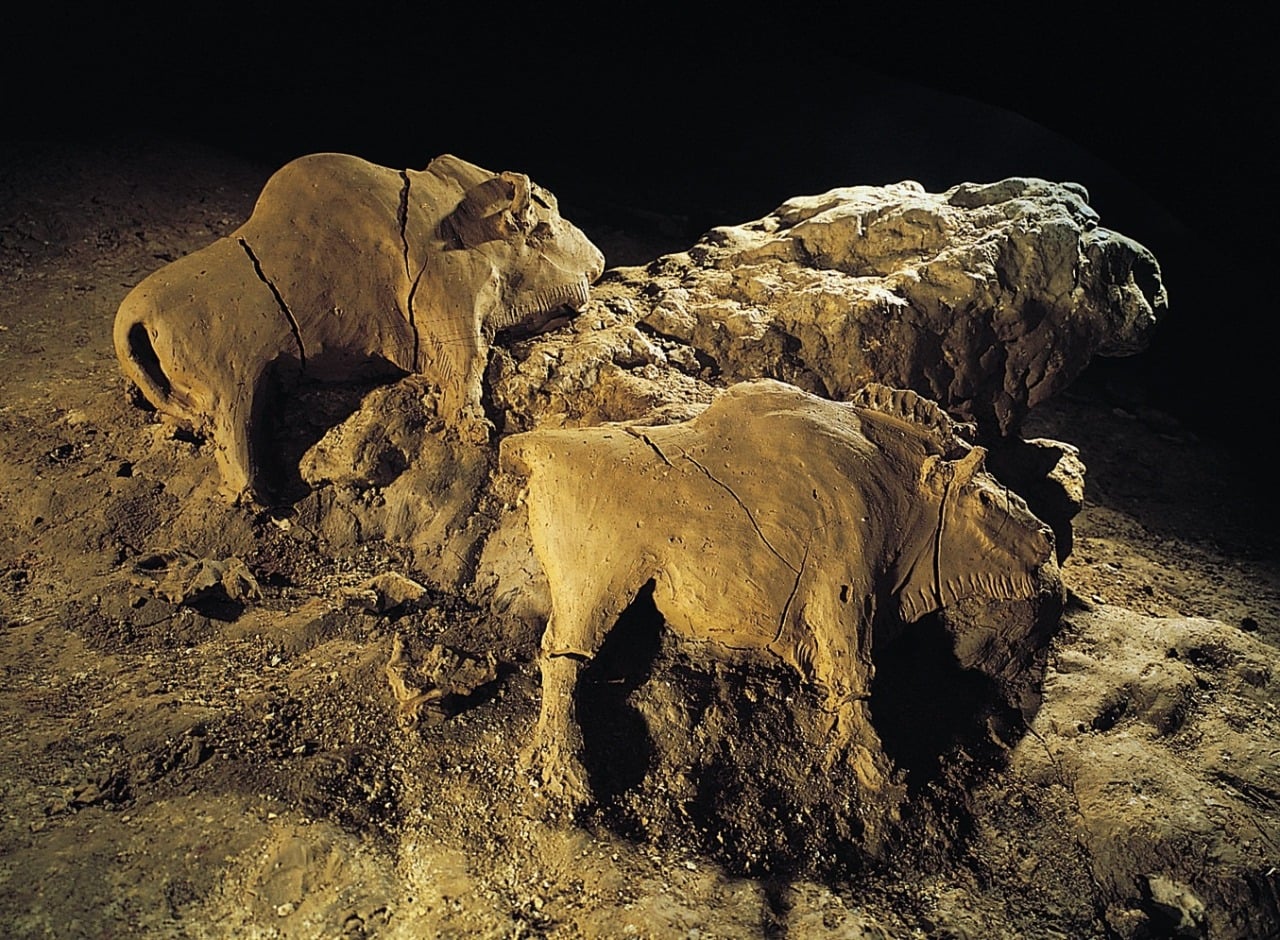

Relief
refers to the raising of three-dimensional forms rom flat background.
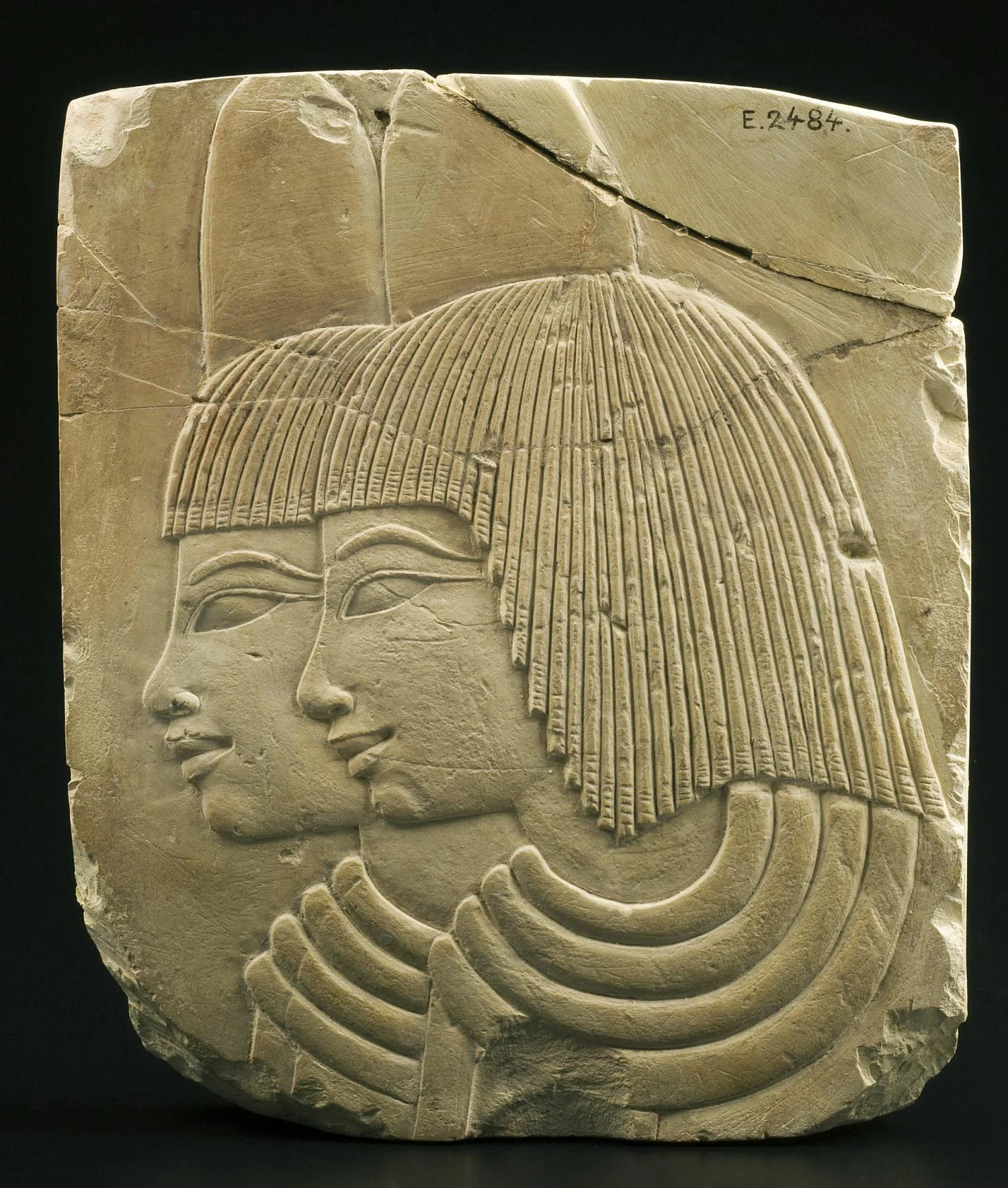

Low relief
the shallowest form of relief.
Bas relief
it is the same os low relief. is derived from the Italian basso-rilievo, meaning "low relief".

High relief
forms are brought more fully off the flat surface, for nearly sculptural effect.
Frontal works
three dimensional work designed to be seen from only one side but not confined to a flat background.
Frontal
organized for being viewd from the front. EX: jewlery
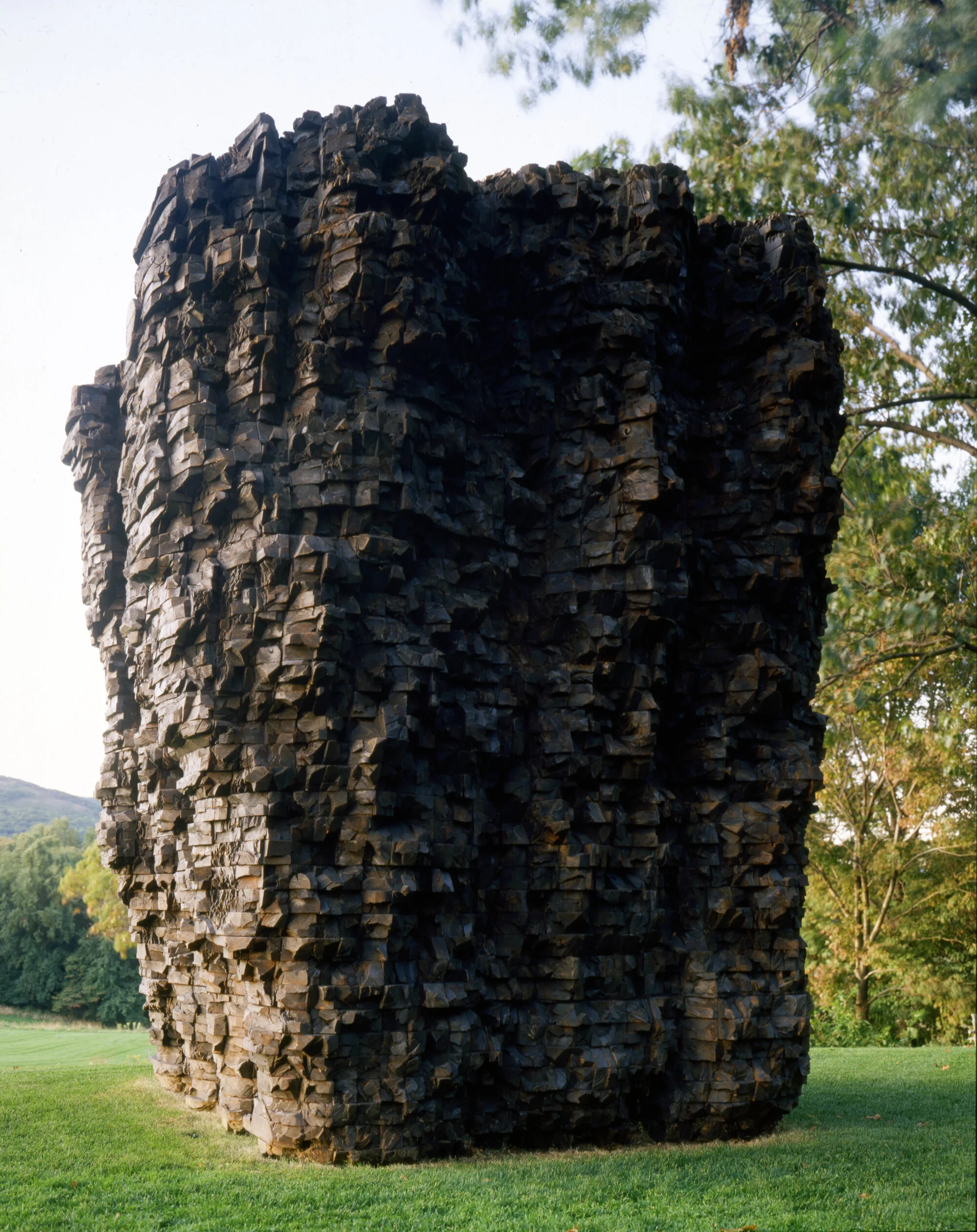

Full round
fully dimensional piece. designed to be seen from all sides. 360 degrees
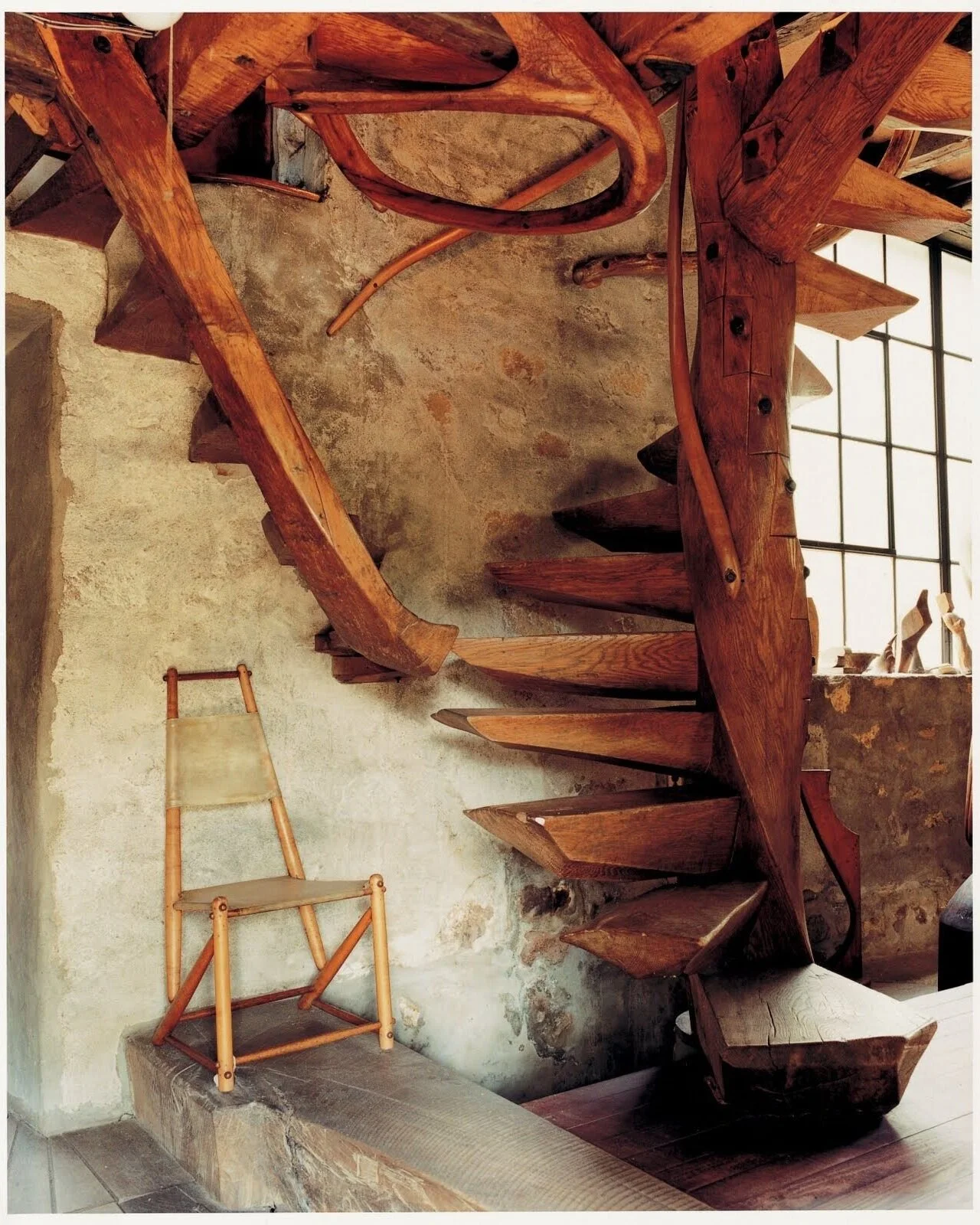

Walk through works
This process places you at the center of the work; rather than your circumnavigating its circumference, it encircles you.This feeling of being surrounded by a 360-degree experience
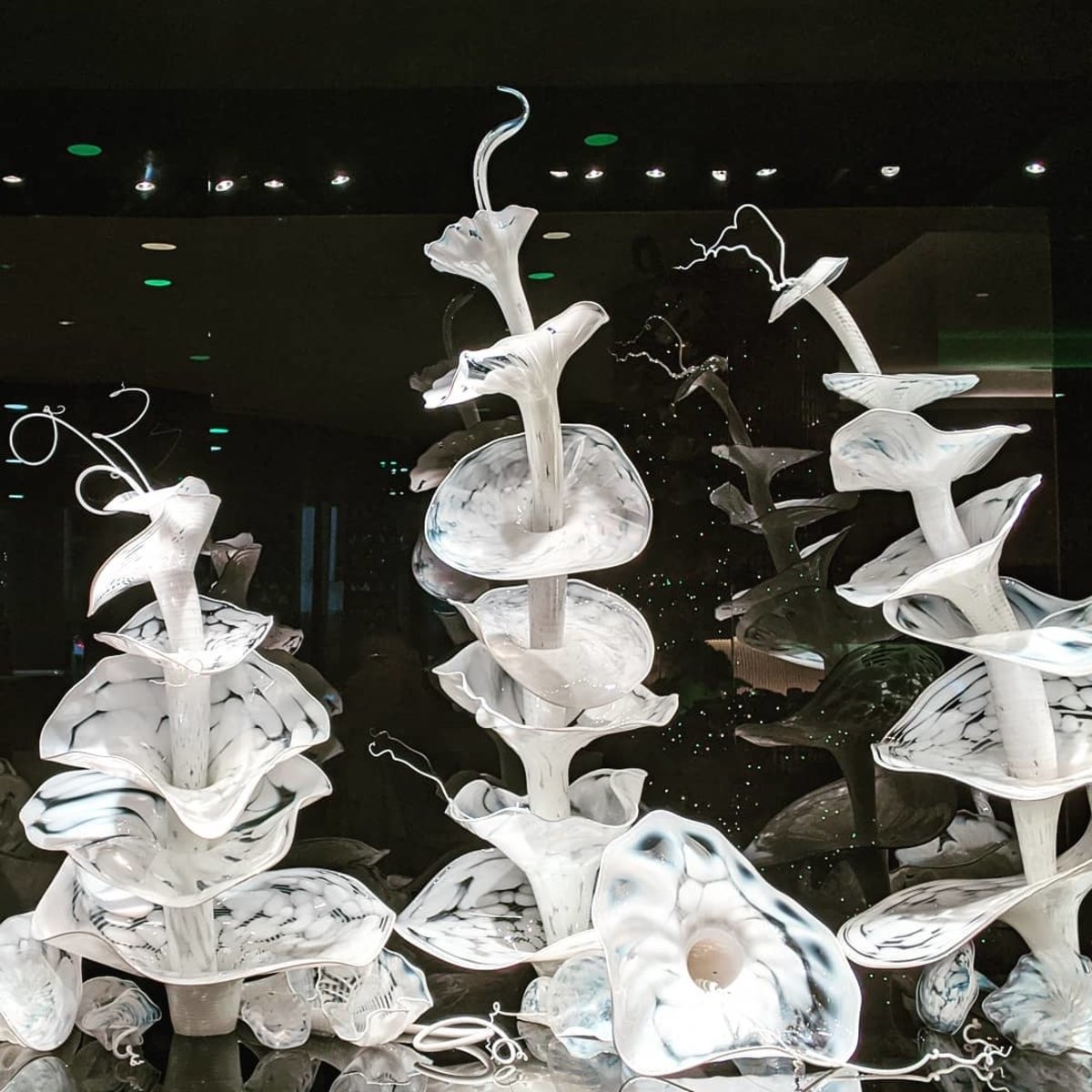

what are two ways one can draw viewers attention to their own sculpture?
by Tactile/ visual appeal. if the viewer has a need to touch the sculpture their eyes will will look around it as if feeling it.
and by engaging curiosity. “how did the artist do that” “what keeps it from falling?”
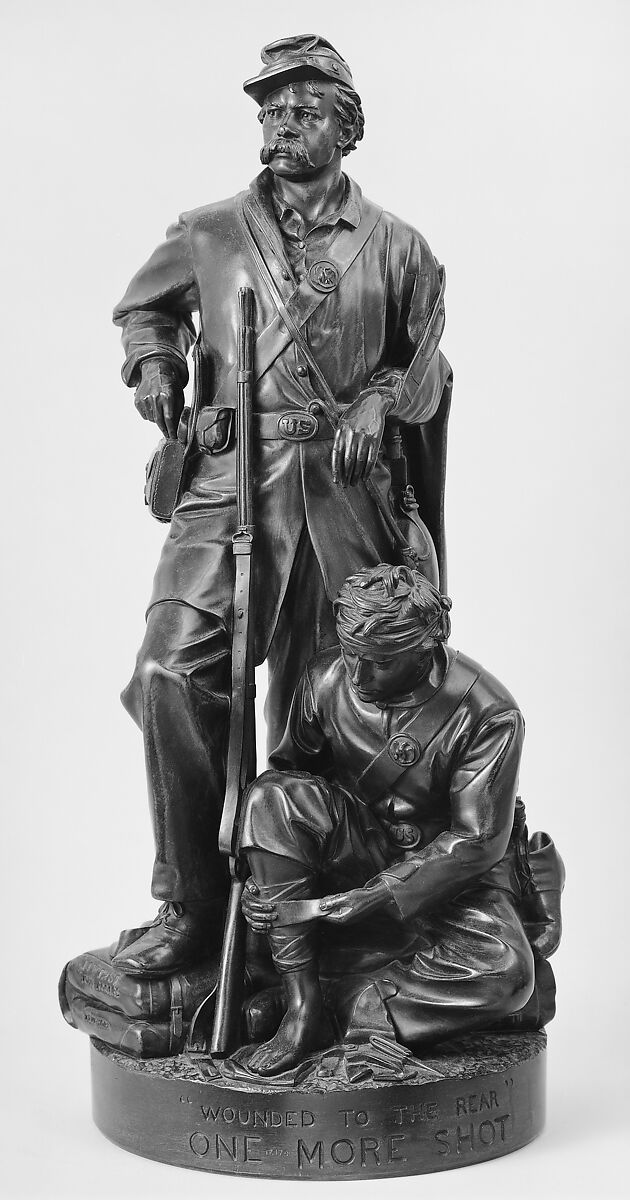

Representaional art
visual accuracy in artistic representation of objects from our three dimensional world.
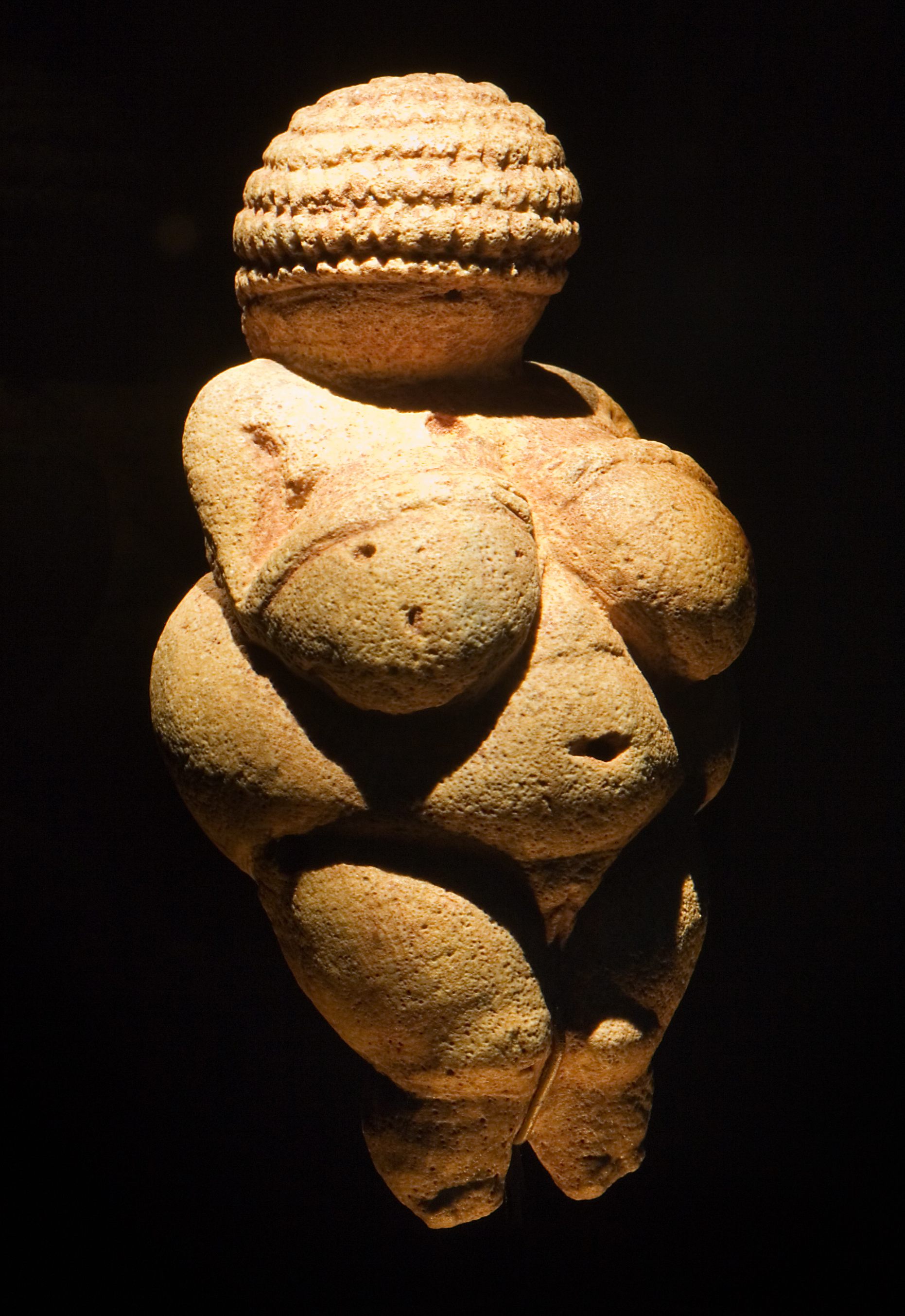

Abstraction
reduction of details in order to focus on a thing's essence. In the ancient Woman of Willendorf
stylize
a way to draw or depect what we see. or the manner in which the work is executed.
content/ subject matter
that which is being depicted
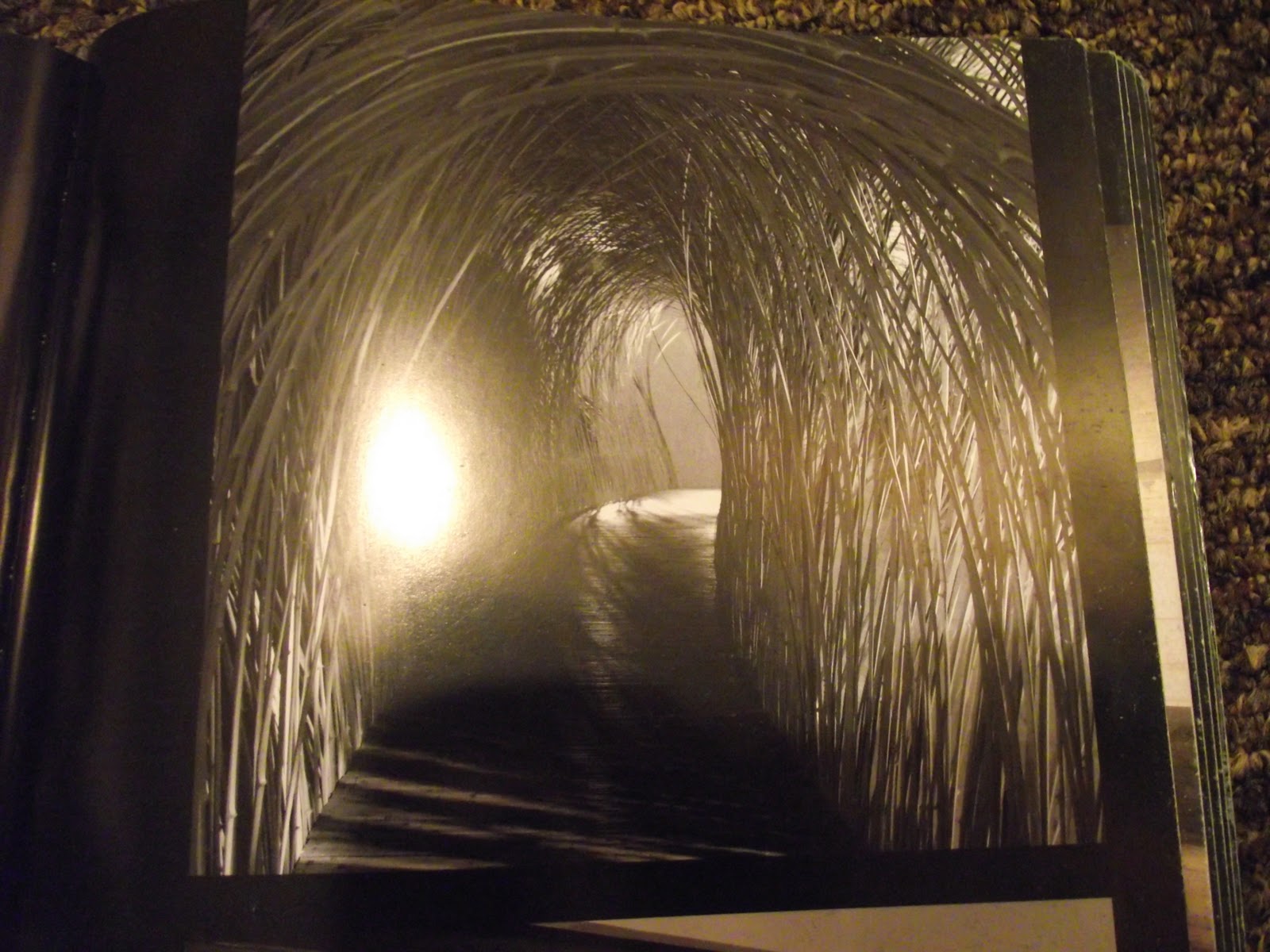

installation pieces
designed enviroments installed in muesums, soetimes temporarily.
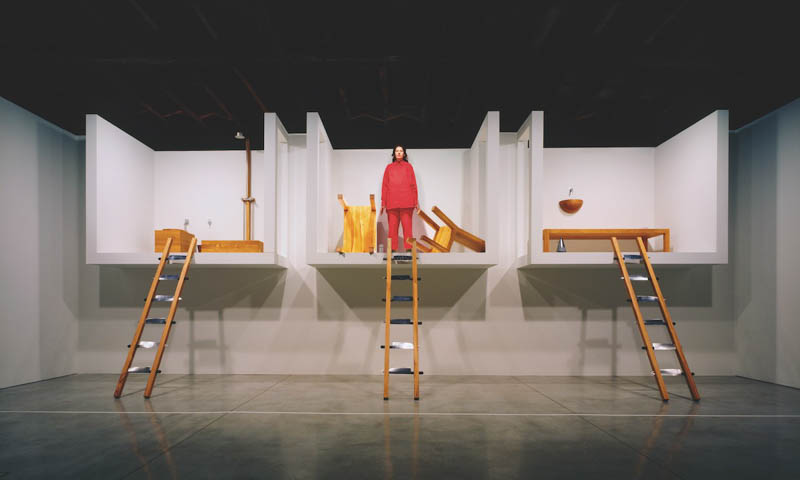

performance piece
involve viewers in a live expirence conducted or set up by the artist. often these are statged as theater.
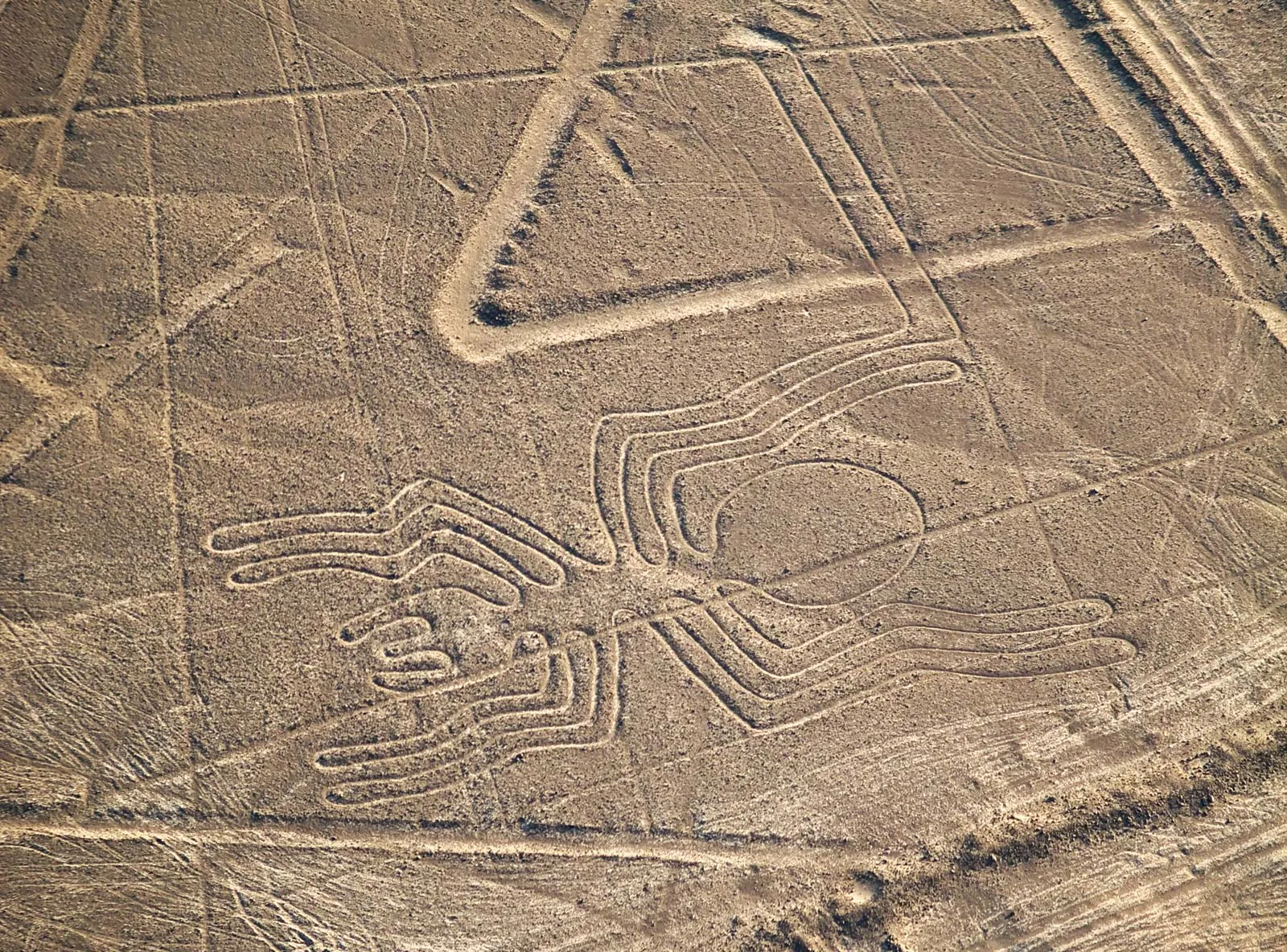

how does the unexpected draw viewers attention?
Some artists evoke viewer involvement by surprise. Certain pieces are deliberately designed to be shocking-to draw sudden attention to something that people normally do not see or do not want to see. Or, something may suddenly be perceived in an unexpected place.
Applied design
interior projects such as interior design, landscape design, and industral
Line
A mark made by a moving point; can be straight, curved, thick, thin, implied, etc.
Shape
A 2D enclosed area (circle, square, triangle)
Form
A 3D object with volume (height, width, depth)
Value
Lightness or darkness of a color.
Texture
How a surface feels or looks like it feels (rough, smooth)
Color
Created by light; includes hue, value, and intensity.
Space
The area around, between, or within objects.

Why is size important in art or in 3D work?
not only important in scaling work to its surroundings but also managing the practical details of creating, transporting, and displaying it
Ergonomics
The study of how people relate physically to their environment. has led to the designing of office furniture that minimizes fatigue and improves work effecency by suporting the human body.
Layouts
two dimensional plans viewed from overhead
fabricated
constructed using industrial techiques by someone other than the artist may require mechanical drawings to scale for precise duplication.
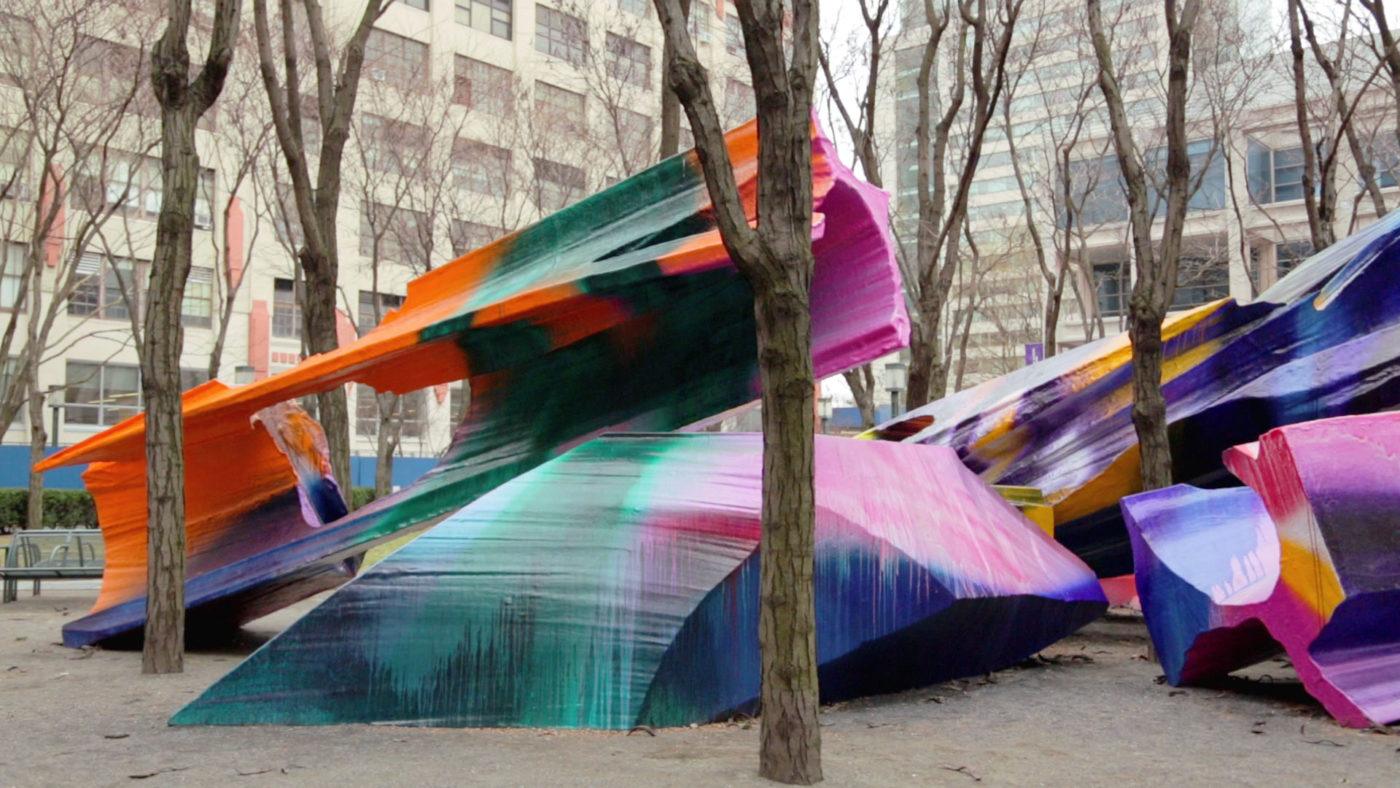

site specific works
those to be installed in a particular location drawings of the piece in place as the viewer will see it are usually necessary. works are created in dialogue with their surroundings—the location of their installation is a part of the work itself.
maquette
small scale model
Balance
Visual stability in an artwork (symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial).
Contrast
Difference between elements to create interest.
Emphasis
The focal point of an artwork.
Movement
How the viewer’s eye travels through the piece
Pattern
Repetition of elements.
Rhythm
Repeated elements that create visual tempo.
Unity
A sense that all parts belong together.
Variety
Differences that add interest.
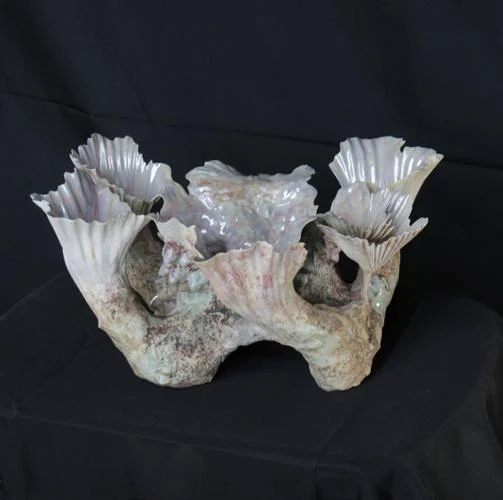

Exterior form
the external, visible, or tangible outline and structure of an object, defining its shape in both 2D and 3D. It represents the outer boundary (contour) and, in sculpture or architecture, the three-dimensional volume (height, width, and depth)
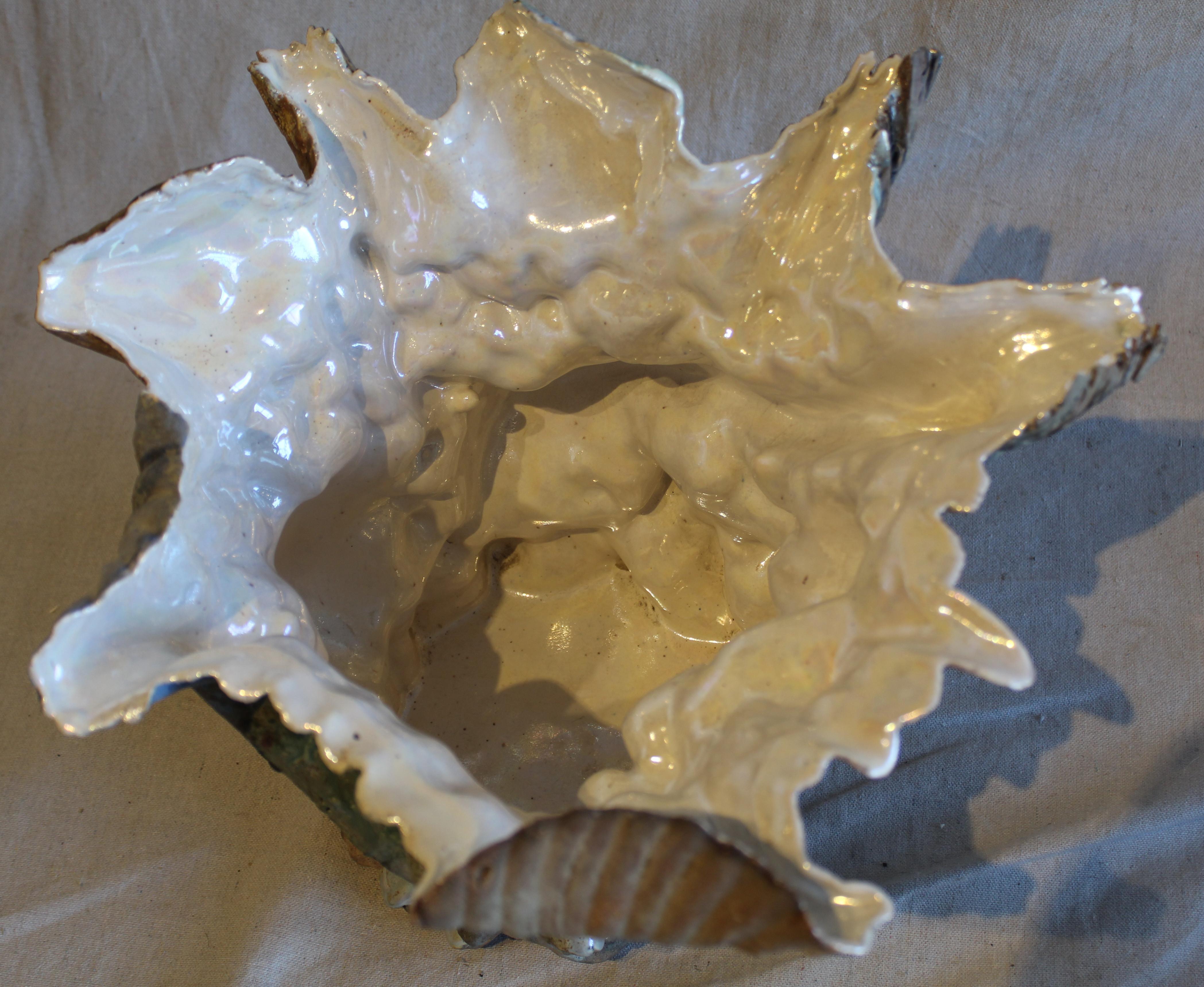

interior form
These works often feature an outer, protective shell that encloses a smaller, more delicate, or complex form within.
Primary countour
the shape of its outermost extremity
secondary countors
the forms developed on its surface
positive forms
solid areas that occupy space
Negative space
the shapes of spaces that are enclosed or delineated by positive forms.
Static
in the sense of appearing stationary, non-moving.

dynamic
forms are those characterized by motion and change or energy that will lead to motion and change
representaional/figurative
forms are those that refer directly to an object from the three-dimensional world of our ecpreience
superrealism
highest degree of representational.
Idealism
depicting an object accoriding to an accepted standard of beauty

nonobjective
a type of abstract or nonrepresentational. it tends to be geometric and does not represent specific objects, people, or other subjects found in the natural world.
Sculpture
A three-dimensional artwork that occupies real space.
Additive process
Creating form by adding material (ex: clay modeling).
Subtractive Process
Creating form by removing material (ex: carving).
Casting
A process where liquid material is poured into a mold and allowed to harden.
Mold
A hollow form used to shape materials.
Freestanding Sculpture
A sculpture meant to be viewed from all sides.