exam 3 pt 10 (ecological succession -> vectors)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
ecological succession
sequence of community + ecosystem changes after a disturbance → primary + secondary
primary succession
occurs where NO SOIL exists when succession begins
→ I.e. plants that begin to grow out of a glacier
secondary successeion
begins in an area where soil REMAINS AFTER a disurbance
→ after fire, species growing on soil that REMAINED
biogeography
where life occurs over the continents
what factors determine where you find diversity in a community?
1) latitude
2) area
species area curve
quantifies a larger geographic area has more species
→ north american breeding bird supports this idea
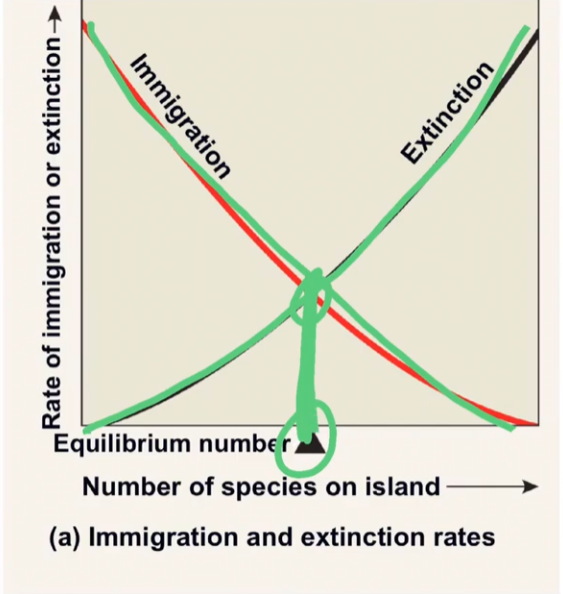
island equilibrium model
species richness on island depends on island size + distance from the mainland, immigration, and extinction
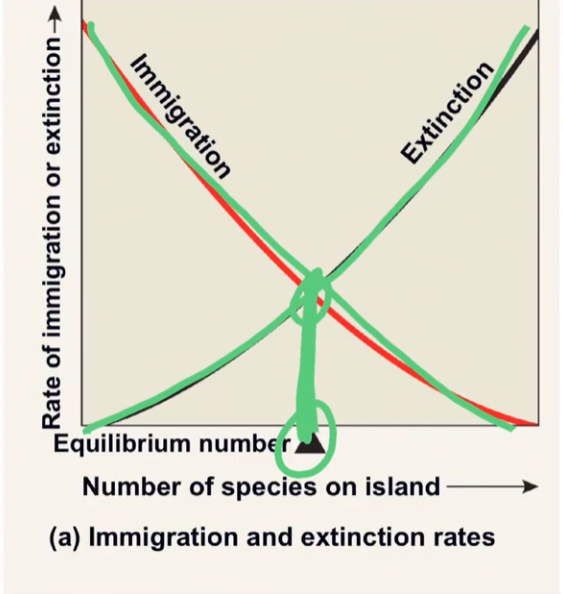
equilibrium number
carrying capacity on islands
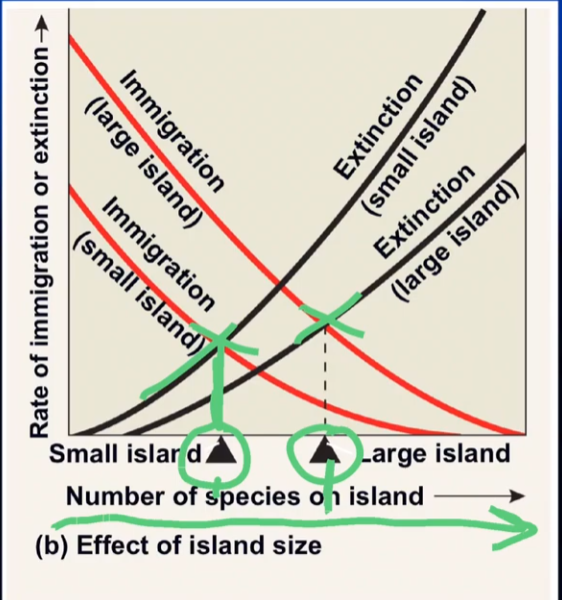
what is this telling you?
large island, holds more species
small islands, holds less species
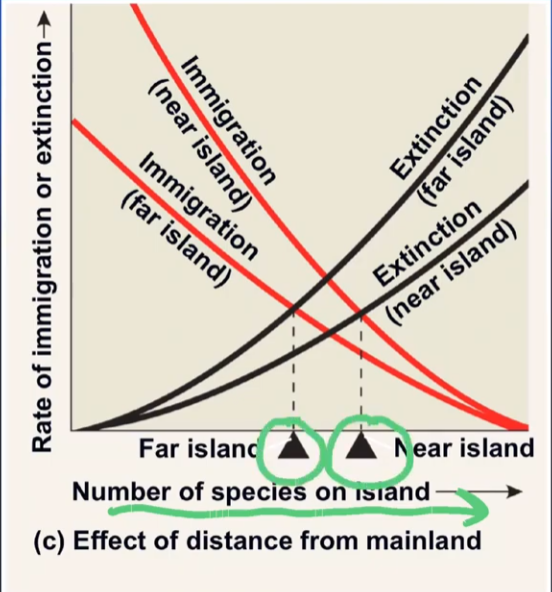
what is this telling you?
islands FAR from the main land support less species
islands CLOSE to the main land support more species
pathogens
disease-causing microorganisms, viruses, viroids, and prions
→ ecological communities are universally affected by this quickly and extensively
zoonotic
pathogens have been transferred from animals to humans
the transfer of pathogens can be direct or through an intermediate species called a _____
vector
→ i.e. mosquitos are the vector that transmit malaria; ticks are the vector for lymes