NURS 321: Lecture 3 - The Effective Nurse Councillor & Self-Awareness and Psychoanalytic Therapy
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Name five main types of mental health professionals?
General Practitioners (GPs), Psychiatrists, Psychologists, Social Workers, Nurses.
What demographic is more likely to have contact with social workers and nurses for mental health support?
Low-income and marginalized groups.
What characteristics define the ideal mental health professional?
Has an identity, respects and is open to change, makes life-oriented choices, appreciates themselves, has a sense of humour, is authentic, admits mistakes, has a sincere interest in the welfare of others, possesses good interpersonal skills, maintains healthy boundaries, is passionate, and derives meaning from their work.
What issues might beginning nurse counselors face?
Clients lacking commitment, anxiety, ambiguity, authenticity, countertransference, self-disclosure, perfectionism, humor, acknowledging limitations, advice giving, silence, shared responsibility, demanding clients, and role definition.
What is a SWOT analysis?
Analyzing your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Should mental health professionals be required to seek therapy before practicing?
Yes, as it can help them experience counseling, enhance interpersonal skills, manage work-related stress, confront personal issues, and develop patience with clients.
What is the purpose of therapy for counsellors?
Helps explore their beliefs and values, manage differences with clients, and avoid imposing their values on clients.
What is 'bracketing' in the context of counseling?
Managing personal values so they do not affect the therapeutic process.
What is 'value imposition' in counseling?
Occurs when a counsellor attempts to define the values and beliefs of their client.
Can religious counselors provide safe counseling to LGBTQ2+ individuals?
Yes, but they must first explore and challenge their own prejudices and biases about sexual orientation.
How can religious and spiritual values affect counseling outcomes?
They can enhance positive outcomes, but avoiding discussion of these topics can harm the therapeutic relationship.
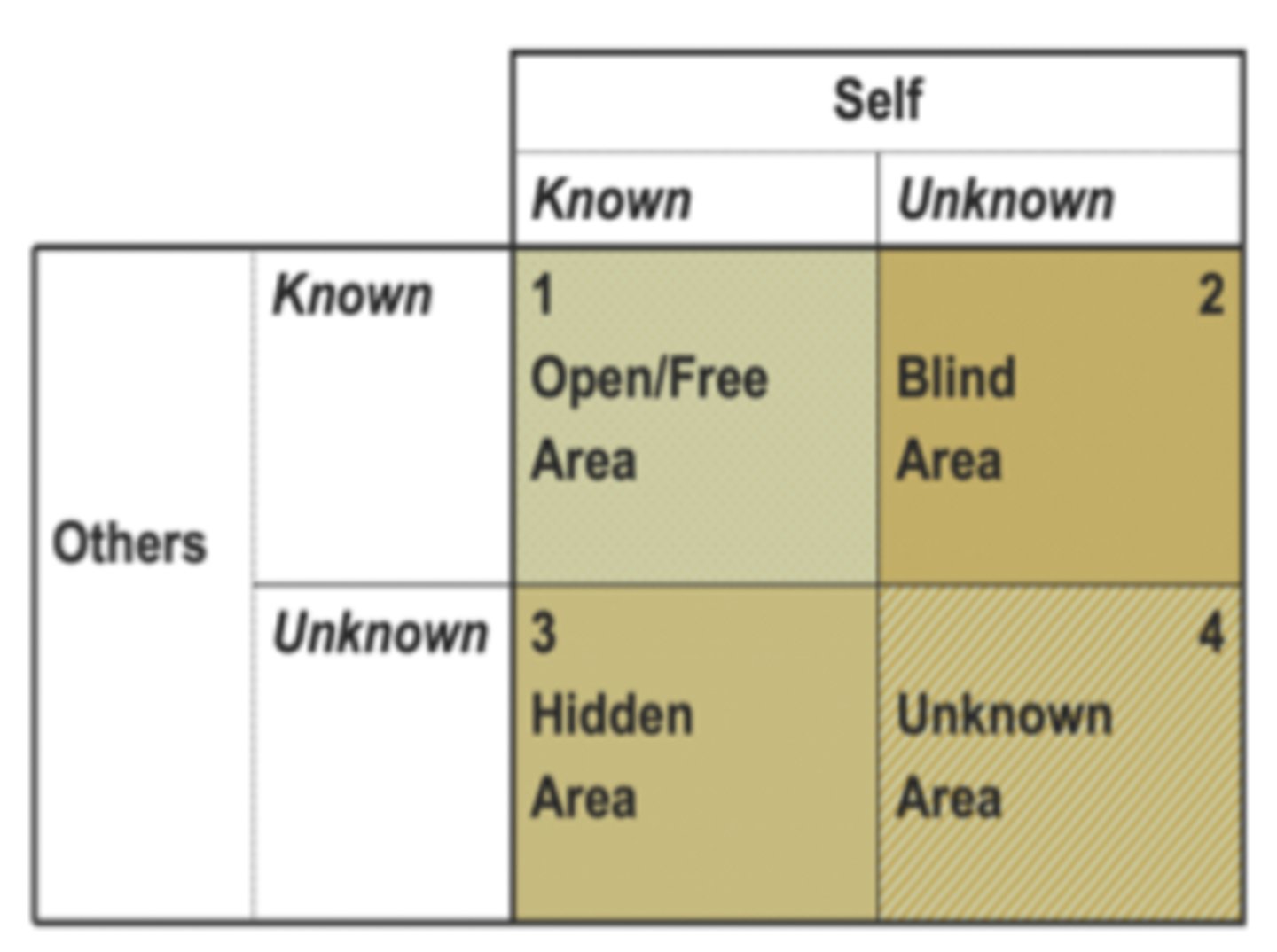
What is the Johari Window?
A disclosure/feedback model of self-awareness that represents information known or unknown by a person and others, aiming to enlarge the 'OPEN' area to improve communication and relationships.
What is the 'Posture of Reciprocity'?
An approach that enables professionals to develop cultural awareness.
What are the 4 steps of cultural reciprocity?
Self-reflect, listen, validate, and compromise.
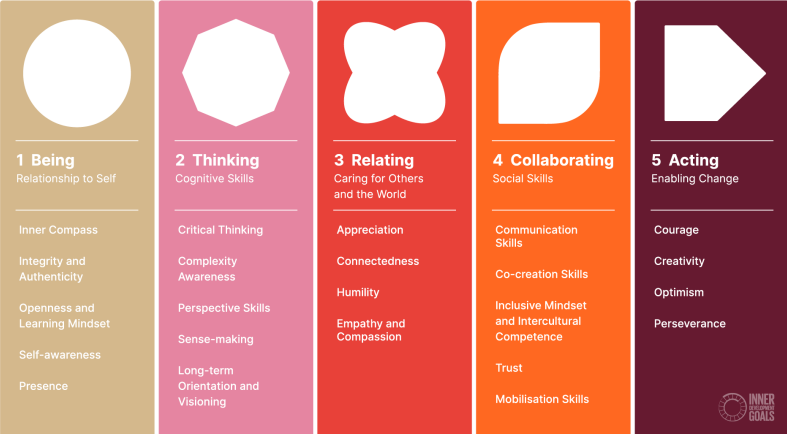
What are Inner Development Goals?
A framework of 23 skills and qualities that can be developed to live more purposeful and sustainable lives, emphasizing the connection between inner development and outer sustainability.
What are the 5 categories of skills in the Inner Development Goals?
Being, thinking, relating, collaborating, and acting.
What is professional burnout?
Occurs when work experiences negatively impact a person's vitality, leading to stress and decreased well-being.
What is the importance of self-monitoring for counselors?
Helps counsellors track their self-care, coping strategies, and management of work stressors.
Who is the founder of psychoanalysis?
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939)
What is psychoanalysis?
An approach to studying mental illness that assumes mental illness is caused by subconscious conflicts.
What are the two main instincts according to Freud's view of human nature?
Life instincts and Death instincts.
What are life instincts?
Instincts that serve the purpose of survival of the individual and the human race.
What are death instincts?
Instincts that manifest through our unconscious wish to die or to hurt ourselves or others.
What are 3 systems that make up our personality?
Id, ego, and superego.
What does the ID represent in Freud's structure of personality?
Impulses that are biologically driven and operate on the pleasure principle.
What is the role of the EGO in Freud's personality structure?
Mediates between the ID and reality, using logical thinking to create plans to satisfy needs.
What does the SUPEREGO represent in Freud's theory?
Protects us from the dangers of our impulses and includes internalized moral standards.
What is the goal of psychoanalytic therapy?
To make unconscious motives conscious, allowing for personal choice.
What is anxiety?
A feeling of dread that results from repressed feelings, memories, desires, and experiences that emerge to the surface of awareness
What are the three types of anxiety identified in psychoanalytic therapy?
Reality anxiety, Neurotic anxiety, and Moral anxiety.
What is reality anxiety?
A fear of real-world danger.
What is neurotic anxiety?
A fear of instincts getting out of hand and getting punished.
What is moral anxiety?
A guilt felt by acting outside of one's moral code.
What are some ego-defense mechanisms according to psychoanalytic theory?
Repression
Denial
Reaction formation
Projection
Displacement
Rationalization
Sublimation
Regression
Introjection
Identification
Compensation
Undoing
What is repression?
Unconsciously pushing negative thoughts away.
What is denial?
Refusing to believe or even perceive painful realities.
What is reaction formation?
Actively expressing the opposite impulse when confronted with a threatening impulse.
What is projection?
Attributing to others one's own unacceptable desires and impulses
What is displacement?
Directing energy toward another object/person when the original object/person is inaccessible.
What is rationalization?
Making excuses for behaviours that are considered unacceptable.
What is sublimation?
Diverting sexual/aggressive behaviour into other channels.
What is regression?
When you go back to an earlier phase of development, where there were fewer demands.
What is introjection?
Taking in the values and standards of others.
What is identification?
Identifying yourself with successful causes, people, or organizations in the hopes that you will be perceived as worthwhile.
What is compensation?
Covering up a real or perceived weakness by emphasizing a trait one considers more desirable.
What are the psychosexual stages?
The Freudian chronological phases of development.
What are the 3 early stages of the psychosexual stages?
Oral stage, Anal stage, and Phallic stage.
What characterizes the oral stage?
Inability to trust and a fear of love.
What characterizes the anal stage?
Inability to recognize or express anger and a lack of autonomy.
What characterizes the phalic stage?
Inability to accept sexuality or sexual feelings.
What are the psychosocial stages?
Erikson's chronological phases of development requiring basic tasks to be mastered throughout life.
What is classical psychoanalysis grounded on?
Id psychology.
What is contemporary psychoanalysis grounded on?
Ego psychology.
What is the significance of childhood experiences in psychoanalytic therapy?
Childhood experiences are examined to help clients gain insight and self-understanding.
What is the therapist's role in psychoanalytic therapy?
To create a transference relationship and help clients achieve self-awareness and control over impulses.
What is the blank screen approach?
When analysts typically assume an anonymous, non-judgmental stance.
What are the 6 basic techniques of psychoanalytic therapy?
Maintaining the analytic framework, free association, interpretation, dream analysis, and analysis of resistance and transference.
What does maintaining the analytic framework involve?
Maintaining neutrality/objectivity, and consistent sessions, fees, and environment.
What is the purpose of interpretation in psychoanalytic therapy?
To explain and teach clients the meanings behind their behaviours and experiences.
What technique involves encouraging clients to say whatever comes to mind?
Free Association.
What is Dream Analysis in the context of psychoanalytic therapy?
A technique that uncovers hidden motives and meanings behind dreams.
What are the 2 levels of content of a dream?
Latent and manifest.
What does the latent content of a dream consist of?
Hidden, symbolic, and unconscious motives, wishes, and fears.
What is the manifest content of a dream?
The dream as it appears to the dreamer.
What is dream work?
The process by which the latent content of a dream is transformed into the less threatening manifest content.
What is resistance in the context of psychoanalytic therapy?
The client's reluctance to discuss awareness of repressed experiences.
What characterizes psychodynamic therapy?
Short, limited objectives, uses more supportive interventions, and focuses on the present and practical concerns.
According to Carl Jung, what must we do at midlife?
Let go of values and behaviours that guided us to that point and confront the unconscious.
What is individualization?
The harmonious integration of the conscious and unconscious aspects of personality.
What is the collective unconscious?
The deepest and least accessible level of the psyche.
What are the archetypes?
The images of universal experiences contained in the collective unconscious.
What is a persona?
A mask or public face that we wear to protect ourselves.
What are the animus and anima?
The biological/physiological aspects of masculinity and femininity.
What is the shadow?
Our dark side, representing the thoughts, feelings, and actions that we tend to disown.
What does Object-Relations Theory focus on?
Attachment and separation in relationships.
What is Self Psychology concerned with?
How interpersonal relationships contribute to the development of the self.
What is the relational psychodynamic model?
A therapy approach that emphasizes the interactive process and the therapist-client relationship.
What are some shortcomings of psychoanalytic therapy?
Costly, based on Western values, therapist ambiguity, and does not always address all factors that cause client challenges.
What is the importance of empathy in the client-therapist relationship?
Empathy is central to developing a sense of self in Self Psychology.
What should clients avoid during the therapeutic process?
Making radical life changes.
What does the term 'transference' refer to in psychoanalytic therapy?
The client's projection of feelings and attitudes from past relationships onto the therapist.
What does the term 'countertransference' refer to in psychoanalytic therapy?
The therapists' unconscious emotional response to a client based on their own past, resulting in a distorted perception of the client's behaviour.