BIOL10002
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
amyloids
if a protein changes the amino acid sequence, making hydrophobic regions that were inside are now outside, it will form flat sheets that act like fibrous proteins
homeostasis
physical and chemical composition must be maintained within a narrow range of physiological conditions that support survival and function
genes
specific segments of DNA that encode information about structure and function
genome
entire set of DNA instructions
ex. 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans
phylogenetic trees
portray the evolutionary histories of the different groups of organisms
able to find the closest living relatives
evidence comes from fossils, structures, metabolic processes, behavior, and molecular analyses of genomes
heat of vaporization
amount of heat needed to turn 1g of a liquid into a vapor
specific heat
amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius
dehydration reaction
every polymer formed from monomer, a water molecule is released
hydrolysis
breakdown of polymer to monomer
denatured protein
protein structured that is disrupted
heated slowly and moderately—disrupt weak interactions, causing secondary and tertiary structure to break down
larger volume, many shapes
all information needed to specify the unique shape of a protein is contained in its primary structure
some are reversible, some are irreversible (ex. when bond to the wrong molecule/egg)
chaperones
protein that protect the 3D structures of other proteins
bind to target protein when they just form or undergo denaturation
cage-like structure that allows denatured protein to enter and fold to its appropriate shape when the lid is on, and releases when it is in its correct shape
tumor makes chaperones to stabilize proteins essential for cancer growth
carbohydrate
4 biochemical role: store energy, transport energy, extracellular support (cellulose for cell wall), carbon skeleton
glycosidic bond form between each monomer
glucose
monosaccharides
blood sugar
breaking of glucose convert stored energy to chemical-bond energy and produce carbon dioxide
straight/ring formed (ring is more stable in water)
alpha and beta glucose where beta glucose has OH—group above the ring when attached to carbon 1
3 catabolic processes harvest energy in chemical bonds of glucose: glycolysis, cellular respiration, and fermentation
oligosaccharide
3-20 monomer forms a polymer
different human blood groups get their specificities from oligosaccharides chains
covalently bonded to proteins and lipids
starch
polysaccharide with alpha-glycosidic bond
energy storage for plants
binds with water
when there is no water, hydrogen bonds form between unbranched polysaccharides chains, which then combines to become starch grains
readily degraded—easily broken down to supply glucose
unbranched or moderately branched
glycogen
water insoluble
highly branched
alpha glycosidic bond
energy storage for animals
1000 glucose molecules would exert 1000 times the osmotic pressure of a single glycogen molecule, causing water to enter cells where glucose is stored, which needs a lot of energy to expel excess water from their cells
cellulose
structural support of cell wall
most abundant organic compound
beta glycosidic bond
amino sugar
form parts of glycoprotein in RER—keeping tissues together
amino group substitute hydroxyl group in carbohydrate
glycoprotein
one or more oligosaccharides chains covalently bonded to a protein
function in cell recognition and cell adhesion
proteoglycan
a class of glycoprotein that has more carbohydrates attached and longer carbohydrate chains
make up major parts of extracellular matrix
function in cell recognition and cell adhesion
found in sponge with 2 kinds of carbohydrate—one binds with membrane components to keep proteoglycan attached to cell, one help with specific recognition and adhesion
lipids
not polymer because individual lipid molecules are not covalently bonded
insoluble in water
hydrophobic—non-polar bonds
ex. phospholipid, triglyceride
triglyceride
simple lipid
contain 1 glycerol (small molecule with three hydroxyl groups) and 3 fatty acids (long non-polar hydrocarbon chain and an acidic polar carboxyl group, saturated/unsaturated)
ester linkage
form through 3 condensation reaction—carboxyl group of fatty acid binds to hydroxyl group of glycerol—ester linkage and release water molecule
ex. fats, oils
fatty acid
saturated—single bond, straight (ex. animal fat)
unsaturated—one or more double bond, kinks (determine fluidity and melting point) (ex. plants)
excellent storehouses for chemical-bond energy
amphipatic
a substance is part hydrophobic and part hydrophilic
ex. lipid (hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail)
phospholipid
2 phospholipid and 1 phosphate bound to glycerol
ester linkage
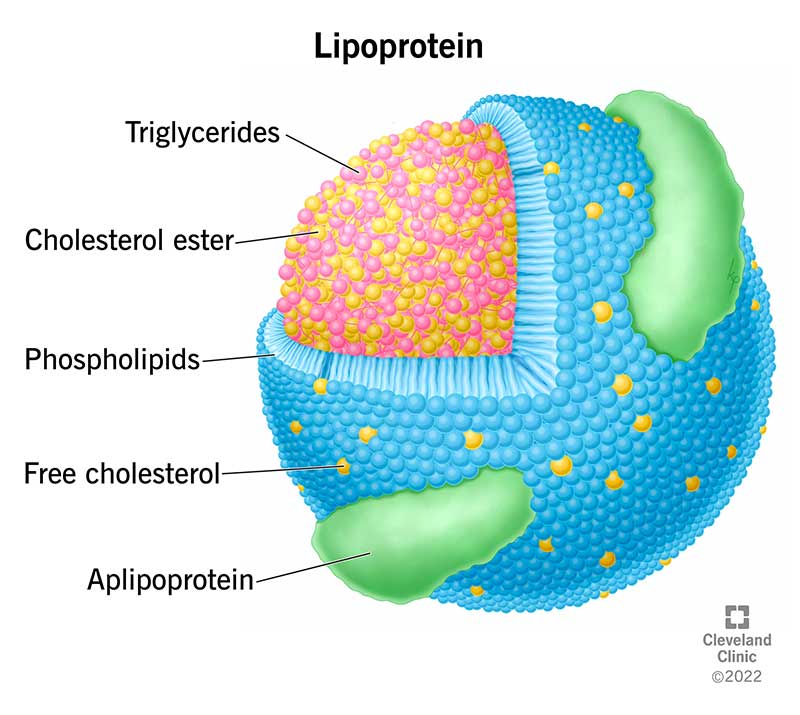
lipoprotein
phospholipid form a single-layered spherical with hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic interior
bind to cholesterol and transport it in the blood to various tissues in the body
nucleotide
3 components: nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, 1-3 phosphate group
nucleotide that make up nucleic acid is monophosphate
oligonucleotide has 20 nucleotide and include RNA molecules (primer, regulate expression of gene) and synthetic DNA molecules (analyze other longer nucleotide sequences)
polynucleotide are much longer and include DNA and some RNA
DNA: adenine with thymine, cytosine with guanine (hydrogen bond)
RNA: adenine with uracil, cytosine with guanine (hydrogen bond)
ex. ATP, GTP, cAMP
pyrimidine
6 member single ring structure
ex. cytosine, uracil, thymine
purine
double ring structure
ex. adenine, guanine
transesterification
formation of nucleic acid through the combination of monomers between third—OH on the sugar and the first phosphate of the incoming nucleoside triphosphate, forming phosphodiester bond
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
nucleotide
agent of energy transfer
energy source
drive endergonic reactions
convert into building block for nucleic acids
in eukaryotic cell, ATP is produced in mitochondria
in prokaryotic cell, ATP is produced on the cell membrane
use ATP to capture and transfer free energy
ATP synthesis occur through cellular respiration
formation and hydrolysis of ATP is energy-coupling cycle, because ADP picks up energy from exergonic reactions to become ATP, which then donates energy to endergonic reactions
energy is retained in P—O bonds of ATP in phosphate group
GTP (guanosine triphosphate)
energy source, especially in protein synthesis, and transfer information from environment to cells
cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
actions of hormones and transmission of information by nervous system
cell theory
cells are fundamental units of life
all living organisms are composed of cells
all cells come from preexisting cells
modern cells evolved from a common ancestor
implication: life is continuous (all cells come from a single cell which marks the origin of life)
surface-area-to-volume ratio
high ratio means diffusion is faster and more effective
high surface area but low ratio means it takes too long to transport materials across cells, so cells divide to increase ratio
some cells change shape through infoldings to maintain high ratio
resolution
minimum distance 2 objects can be apart and still be seen as 2 objects
ex. human eye is 0.2 mm
electron microscope has better resolution, but only see dead cells because it is investigated under vacuum
light microscope has resolution of 0.2 micrometer on living cells
cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer with proteins on them
maintain homeostasis
semi-permeable barrier
communicate with other cells and receive signals from environment
contribute and support cell shape
cytosol
fluid part of cytoplasm
cytoplasm
everything in the cell
not static—under constant motion
proteins move around and collide with other molecules
ribosome
sites of protein synthesis
on rough ER (endoplasmic reticulum), in cytoplasm, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
cell structure rather than organelle because it lacks membrane
consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
contain >50 different protein molecules
hydrophobic interaction
prokaryotic cells have ribosomes unattached in the cytoplasm
cell wall
support cell and determine shape
most bacteria’s cell wall contains peptidoglycan (amino sugars linked to short peptides at regular interval), and some as an outer membrane outside of peptidoglycan layer (polysaccharide-rich phospholipid membrane) or capsule (some protect bacteria from white blood cell and some help attach to other cells)
fractionation
allows cell organelles and other cytoplasmic structures to be separated from each other and examined using chemical methods
begins with destruction of cell membrane to allow cytoplasmic components to flow out into a test tube
biochemical analyzes are then done on the isolated organelle
microscopy and cell fractionation gives a complete picture of composition and function of each organelle and structure
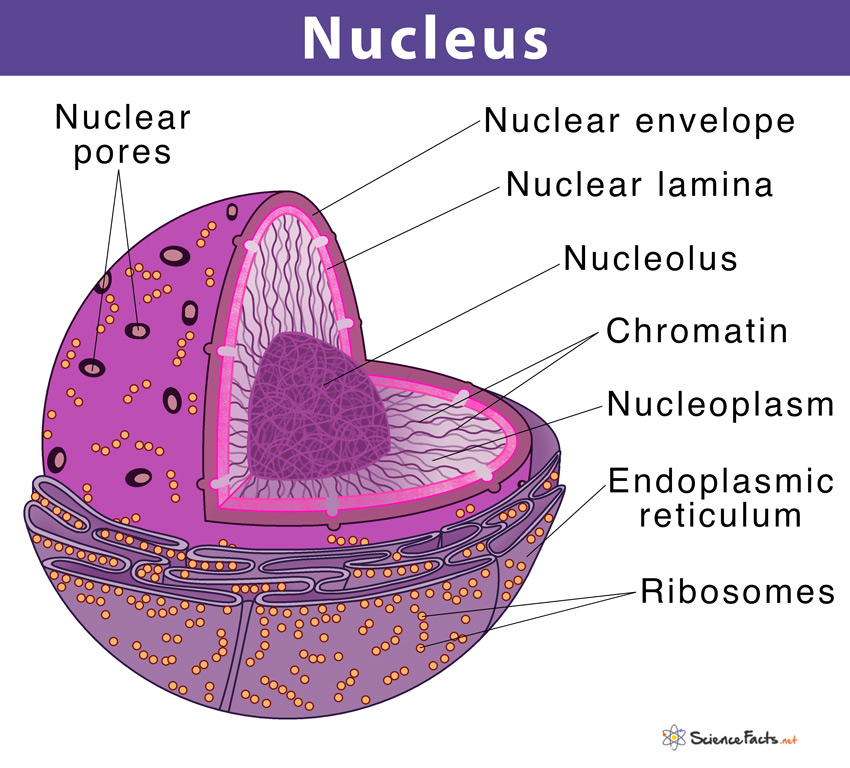
nucleus
storage of hereditary information in sequence of nucleotides in DNA
site of DNA replication
site where gene transcription is turned on or off
liquid content of nucleus and insoluble molecules is nucleoplasm
nuclear envelop enclose nucleus, which has thousands of nuclear pores (a protein channel that allows some molecules to pass and some not, also regulates its nucleus’s information-processing functions)
chromatin
fibrous complex that is a combination of DNA molecule with protein
during cell division, chromatin is tightly compacts and condensed so that chromosomes are visible
attached to nuclear lamina (protein formed by polymerization of lamin into intermediate filaments), which maintains shape of nucleus by attachment of chromatin and nuclear envelop
chromosomes
long, thin threads of chromatin
chromosomes near each other might swap DNA regions, causing abnormal cell reproduction and cancer
chromatids
held together by cohesin (protein complex)
at mitosis, cohesin is replaced by centromere
at the end of G2, condensins coats the DNA molecules to make them more compact
endomembrane system
interconnected system of membrane-enclosed compartments
include cell membrane, nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes
vesicles transfer substances between various components of the endomembrane system
static—constant motion
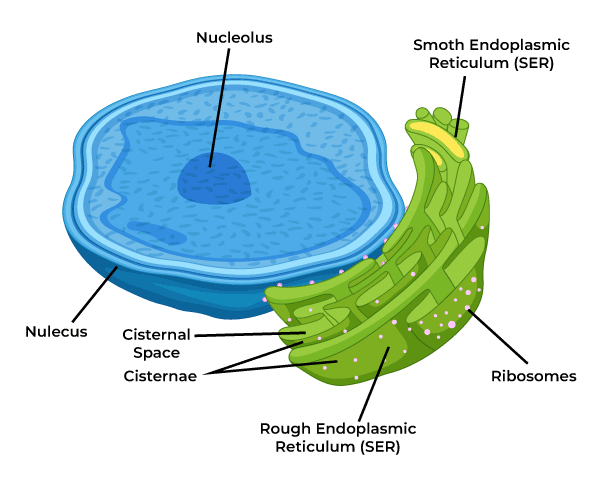
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
lumen is the space inside ER (10% interior volume) and when protein enter lumen, it undergoes several changes and folding into their tertiary structure
folds increase surface area, much greater than that of cell membrane
rough ER (RER): ribosomes attached and transport proteins to other locations in the cell
-most membrane-bound proteins are made in the RER
-cells involve in protein secretion contains a lot of RER (ex. antibodies for immune system, cells of pancreas/intestine)
smooth ER (SER) lacks ribosome but it is a continuity with portions of RER that is responsible for chemical modification of small molecules taken in the cell that may be toxic by making them more polar, which makes it more water-soluble and easily removed
-site for glycogen degradation in animal cells
-site for lipid and steroids synthesis and some polysaccharides
-store CA2+ which can trigger numerous cell responses
lysosomes
organelles that contain enzyme that are capable to break down all types of biological polymers
carbohydrate groups help to address the right protein to lysosome
primary lysosome are formed from Golgi apparatus, which contain digestive enzymes and sites where macromolecules hydrolyzed into polymers
-interior is more acidic (pH 5) than external cytoplasm (pH 7.2)
-breakdown food, other cells, or foreign objects through phagocytosis (cell membrane forms a pocket that engulf inward to enclose the material and forms a vesicle with the material called phagosome)
secondary lysosome forms when phagosome fuses with primary lysosome, where digestion occur
-waste are used to provide energy and raw materials for cellular processes
-second lysosome fuses with cell membrane and releases undigested contents into the environment through exocytosis
some cells are continually broken down and replaced through autophagy, which can engulf entire organelles
failure of lysosome to digest specific cellular components can lead to lysosomal storage disease (ex. Tay-Sachs disease when ganglioside (lipid) is not broken down and accumulates in brain cells)
plant cells don’t have lysosome, so vacuole hydrolyze macromolecules
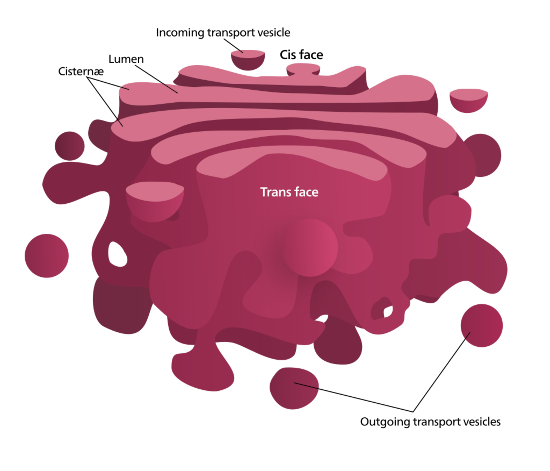
Golgi apparatus
consist of cisternae (flattened membranous sacs) and small membrane-enclosed vesicles
receives protein-containing vesicles from RER
modifies, concentrates, packages, and sorts protein before they are sent
add carbohydrates to modify
some polysaccharides for plant cell wall are synthesized
cuts certain precursor proteins to smaller functional fragments (ex. 241-amino acid polypeptide produce by pituitary gland)
cis face lies nearest to nucleus, where protein-containing vesicles fuse in and release their cargo into lumen
trans face lies closest to cell membrane, where vesicles exits to go to cell membrane or lysosome
medial face lies between cis and trans
each face contain different enzymes and perform different functions

mitochondria
transform chemical-bond energy into ATP
reproduce and divide independently of the central nucleus
cells that are active in movement and growth have the most mitochondria
2 membrane where inner membrane folds inward, leading to large surface area and give rise to cristae
inner membrane has many large protein complexes that participate in cellular respiration
mitochondrial matrix is the space within inner membrane that contains ribosomes and DNA used to make proteins needed for cellular respiration
chloroplasts
plastids that divide independently
contains green pigment chlorophyll
site of photosynthesis
2 membrane
folding forms lamellae , which is on the surface of thylakoid
stack of thylakoid lipids are granum
thylakoid lipids have 10% phospholipid and the rest is galactose-substituted diglycerides and sulfolipids (most abundant lipids)
-membrane contain chlorophyll and other pigments that harvest light energy for photosynthesis
grana is the site where light reactions occur
stroma is the fluid in chloroplast, which contains ribosomes and DNA
peroxisomes
accumulate toxic peroxides (H2O2) that are byproduct of some biochemical reactions
membrane enclosed—without mixing other parts of the cell
glyoxysomes
found only in plants, especially young plants
membrane enclosed
stored lipids are converted into carbohydrates for plant growth
vacuoles
mostly in plants, fungi, protists
from ER or Golgi apparatus
take up 90% of cell volume and grows as cell grows
water enter vacuoles from cytosol, making it swell, but not in mature plants due to the cell wall
contain some pigments to attract animals that assist pollination or seed dispersal
vacuoles of seeds contain molecules that hydrolyze stored proteins into monomers (used for food for plant growth in germination)
store toxic molecules and waste products for defense and survival
cytoskeleton
support cell and maintains its shape
holds and moves cell organelles and other particles in position within the cell
movement of cytoplasm—cytoplasmic streaming
interacts with extracellular structures, helping cell anchor in place
3 components: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
microfilaments
7nm in diameter
help entire cell or cell parts move
maintain cell shape—tension-bearing
changes in cell shape
polymerization of monomer actin (protein)—reversible
form long, double-helical chains
cytoplasmic streaming
pinch when dividing animal cell—form cleavage furrow
formation of pseudopodia (false feet)—extensions that enable some cells to move
muscle contraction
intermediate filament
6 molecular classes that share same general structure
form from fibrous protein keratin
8-12 nm
anchor nucleus and some other organelles
maintain shape—tension-bearing
formation of nuclear lamina
microtubules
long, hollow, unbranched cylinder (25nm)
wall consists of 13 columns of tubulin molecules
protein tubulin (alpha and beta)—reversible
form rigid internal skeleton for some cells
allow motor protein to move organelles
maintain shape—girder
capable to change length rapidly—adapt to new cell purposes
framework for formation of cellulose and help orient cellulose fibers of cell wall
2 types of motor proteins that move chromosomes during cell division: kinesin (positive end that allow movement of vesicles inside neurons) and dynein (negative end that allow microtubule doublets to slide past one another in cilia and flagella)
cilia and flagella contains microtubules (9 fused and 2 unfused), which nexin holds them together and forces from dynein causes it to bend rather than move
cilia
0.25 micrometer
hair-like structure covering the cell
move fluid
movement is through sliding of microtubules doublets past one another, driven by dynein
flagella
100-200 micrometer
singly or in pairs
tail like structure
cell wall
contain cellulose fiber with other complex polysaccharides and proteins
provide rigid support but still flexible to bend
barrier to infection
cell wall on leaves have porous, but not for vascular system
plasmodesmata
20-40 nm
plant cell wall channels
allows diffusion of water, ions, small molecules, RNA, proteins
extracellular matrix
composed of collagen (fibrous protein), proteoglycans (matrix of glycoproteins), and a third group of protein that link collagen and proteoglycans matrix
hold cells together in tissue
contribute to physical property of tissue
filter materials—important in kidney
orient cell movement during embryonic development and during tissue repair
chemical signaling between extracellular matrix and cytoplasm
theory of endosymbiosis
some organelles arose by one cell ingesting another cell, giving rise to a symbiotic relationship
ingested cell loses its autonomy and some function
gene of ingested cell were transferred to host’s DNA
ex. mitochondria, plastids (ex. chloroplast), nucleus
nucleus—starts from membrane of bacterial cell folding around nucleoid, then nucleoid became nuclear envelope
primary endosymbiosis of a purple bacteria—mitochondria
primary endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic cyanobacteria
primary endosymbiosis: cyanobacterium/purple bacterium have 2 membrane, not one. cyanobacterium/purple bacterium enters host eukaryote via endocytosis and gets surrounded by a food/phagocytic vacuole. instead of being eaten, it stays within the cell. over time, the outer membrane of vacuole breakdown leaving an endosymbiont with its original 2 membranes. it transfer its genetic information to the nucleus
secondary endosymbiosis: a eukaryote eats another eukaryotic cell that has a chloroplast through phagocytosis. vacuole membrane breakdown over time, leaving a triple-membrane chloroplast. eaten cell’s genetic material is transferred to pirate’s nucleus. it will have 3 sources of genomes in the nucleus: mitochondrial, chloroplastic, nuclear (ex. chloroplast of brown algae)
cholesterol
20-50% of animal cell membrane
locate inside membrane
hydroxyl group of cholesterol interact with polar end of phospholipid
important for membrane unity and fluidity
not hazard to health
cholesterol with long chained, saturated fatty acid are pack tightly, so it is less fluid
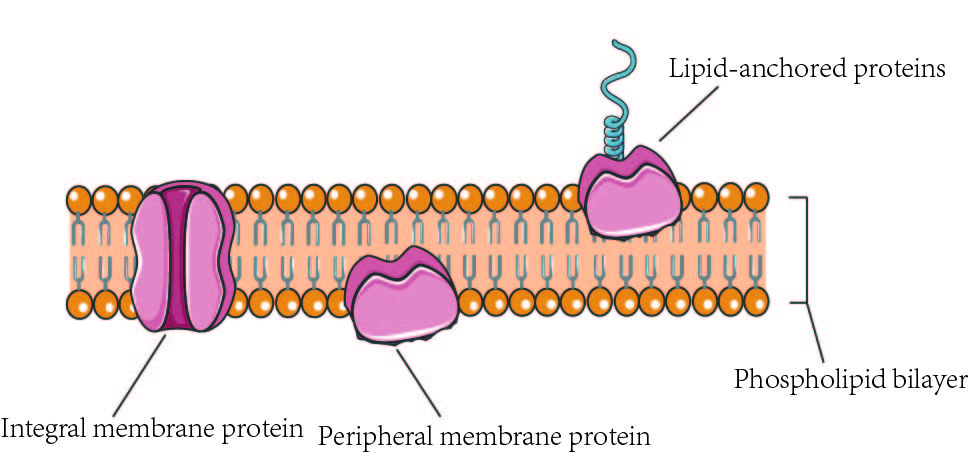
integral membrane proteins
membrane protein
hydrophilic—amino acids on R group is polar
hydrophobic—other amino acids on the R group is nonpolar
cross through membrane or embedded in bilayer
ex. transmembrane protein cross through
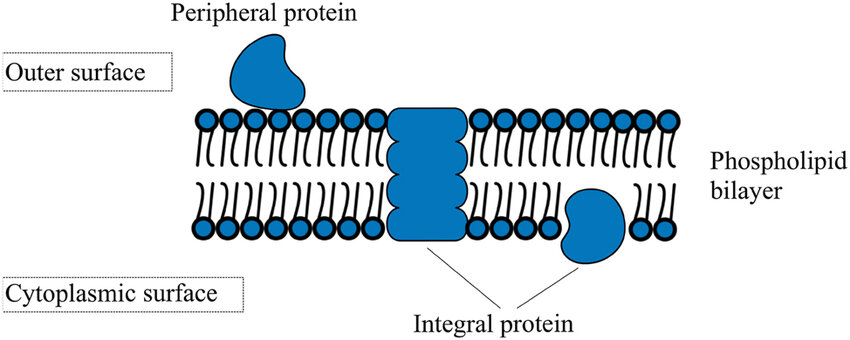
peripheral membrane protein
polar region interact with exposed integral membrane protein’s polar head
non-covalently bond to either membrane surface
locate on one side
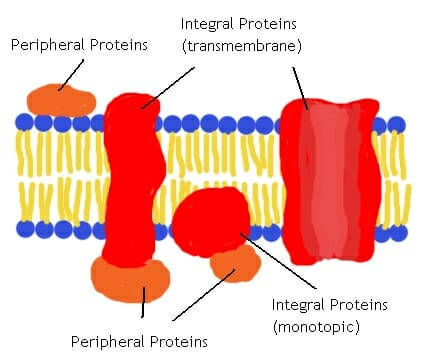
anchored membrane protein
covalently bind to hydrophobic lipid group
insert into phospholipid
homotypic
binding of cells in a tissue
same molecule binding with each other
keep skin cells together in a sheet of cells
heterotypic
binding between different molecules on different cells
ex. sperm and egg
glycolipid
carbohydrate covalently bonded to lipid
serve as recognition signal
ex. carbohydrates changes when cells become cancerous, which allows white blood cells to target cancer cells for destruction
cell junctions
additional membrane structure that connect 2 cells
seal intercellular space
reinforce attachments to one another
communication
3 types: tight junction, desmosomes, gap junctions
tight junction
prevent substances from moving through the space between cells
ex. cells lining the bladder have tight junction so urine cannot leak out
maintain a cell by restricting migration of membrane proteins
-ex. endocytosis
desmosomes
hold neighboring cells firmly together
materials move in the extracellular matrix
stabilize tissues that receive physical stress
ex. skin
gap junctions
channel that run between membrane pores in adjacent cells
allow substance to pass between cells
ex. rapid spread of electric current in the heart so heart muscle cells beat
integrin
transmembrane protein
maintain cell structure via interaction with cytoskeleton
noncovalently binds to extracellular matrix—reversible
passive transport
no require input of chemical-bond energy
energy comes from concentration gradient
ex. simple diffusion (phospholipid bilayer), facilitated diffusion (channel or carrier protein)
active transport
driven by chemical-bond energy
often through ATP, produced in mitochondria
directional
3 kinds of membrane protein that carry out active transport: uniporter (move one in one direction, ex. calcium-binding protein), symporter (move 2 in same direction), antiporter (move 2 in opposite direction, integral membrane glycoprotein, ex. sodium—potassium pump Na+ in, K+out)
coupled transporter: symporters and antiporters
2 basic type of active transport: primary and secondary
primary active transport
direct hydrolysis of ATP—form ADP, phosphate group, and energy
ex. sodium—potassium pump
second active transport (co-transport)
doesn’t use ATP
supply energy by an ion concentration gradient established by primary active transport
ex. sodium—potassium pump establish concentration gradient that provide energy for secondary active transport of glucose
simple diffusion
more lipid-soluble, more rapid diffusion across membrane
hydrophobic
electrically charged/polar doesn’t pass through (ex. amino acid, sugar, ions) because they form hydrogen bonds with water
osmosis
movement of water molecules across the membrane
passive
isotonic: equal solute concentraiton
hypotonic: lower concentration than others
hypertonic: higher concentration than others
water moves from hypotonic to hypertonic
cell wall limits intake of water, so water build up turgor pressure, enlarge vacuoles/plant cells, which is why plants are upright when hydrated
facilitated diffusion
passive transport
aid by channel proteins (integral membrane proteins) or carrier proteins (binds substances and speed up diffusion)
ion channels
channel proteins for particular ions
gated channel: open when stimulus (ligand) causes a change in 3D shape
other channels open in response to physical stimuli, such as sound waves, voltage
aquaporins
protein channels that allow water to cross
cellular plumbing system
water molecules move through the channel, excluding ions, which maintain electrical properties of cells
glucose transporter
binds to glucose, which changes the 3D shape of protein and release glucose to the other side of the membrane
have strong concentration gradient that favor glucose entry
cells that require large amounts of energy have high concentration to maximize diffusion rate, such as muscle cells and human brain
endocytosis
brings small molecules, macromolecules, large particles, and small cells
only in eukaryotes
3 types: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis
phagocytosis
engulf large particles or entire cell
unicellular use phagocytosis to feed
white blood cells use phagocytosis to defend the body by engulfing foreign cells and substances
food vacuoles/phagosomes—lysosome for digestion
relatively nonspecific
pinocytosis
form smaller vesicles
bring fluids and dissolved substance into the cell
relatively nonspecific
receptor-mediated endocytosis
molecules at the cell surface recognize and trigger uptake of specific material
capture specific macromolecules
depends on receptor proteins (integral membrane proteins) that bind to specific region called coated pits
when ligand binds to receptor proteins, coated pits invaginates and forms a coated-vesicles and clathrin (protein) strengthen and stabilize the vesicles to travel away to cytoplasm
ex. cholesterol: LDL receptors on the cell surface binds to LDL, and the clathrin-coated pits engulf and become a vesicle. vesicle is fused with a lysosome, in which LDL is digested and cholesterol are available for cells to use. in healthy individuals, liver takes up unused LDLs for recycling
exocytosis
process of packaging materials in vesicles and secretes from a cell
release vesicle contents into the environment
2 ways: vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and release the vesicle content or vesicle touches the cell membrane and a pore forms, releasing the vesicle contents
cell division of prokaryotes
cell division signal (inside or outside of the cell) is usually environmental conditions and nutrient concentration
-nutrient, pH, and temperature has to be optimal
DNA replication starts at the ori and ends at the ter
-most prokaryotes have one main chromosome
DNA segregation is when each daughter cell receives a copy of every chromosome. once replicated, ori regions move toward opposite ends of the cell. protein bind to the DNA sequences, which hydrolyze ATP
cytokinesis is when cytoplasm divides to form 2 new cells with cell membrane/cell wall
results in reproduction of entire single-celled organism, and they are identical
ex. binary fission
cell division of eukaryotes
cell division signal for single-celled is appropriate environmental conditions, while for multicellular is suitable internal environments that relate to function but it doesn’t mean it is necessary to occur
DNA replication contain more chromosomes and starts at numerous origins of replication
DNA segregation—mitosis, which involves spindle (special cytoskeletal structure composed of microtubules)—produce identical cells
cytokinesis—plant cells form cell plates (multiples vesicles that contain pectin, cellulose, and hemicellulose) while animal cells form cleavage furrow that pinch off
cell (division) cycle
4 phases: G1, S, G2, M
M phase include mitosis and cytokinesis
cell spends most of the time in interphase, which includes G1, S, G2
G1 phase: single, unreplicated DNA molecule with associated proteins
S phase (DNA replication): chromosome is duplicated, which consists of 2 sister chromatids (remained join until mitosis)
G2 phase: cells get prepared for mitosis
G0 (resting phase), where there is no cell division, but sometimes cells can reenter G1 under certain environmental conditions (growth factor)
mitosis
spindle in mitosis is formed by microtubule structure
centrosome determines orientation of spindle and it consist of a pair of centrioles
in prophase, chromatids are visible and kinetochores (protein) develop in the centromere region
prophase and prometaphase: microtubule link the poles and chromosomes to make up spindle
-polar microtubule form framework of spindle and run from one pole to another, while kinetochore microtubule attach kinetochores on chromosomes
prometaphase: nuclear envelope breaks, spindle is formed
metaphase: chromosomes line up at the equator
anaphase: separation of chromatids, which activates anaphase-promoting complex (APC) when cohesin is hydrolyzed by separase
telophase: spindle disappears, nuclear envelope forms
cytokinesis: contractile ring (composed of microfilaments of actin and myosin) pinches the cell for animal cell, while membranous vesicles from Golgi apparatus fuse to form cell plate for plant cell
CDK (cyclin-dependent kinases)
enzyme that controls the transition from one phase to another, which is the restriction point
CDK is always present, but inactive, until cyclins binds (protein) to it
binding of cyclin changes the shape of CDK and expose its active site to substrates. a protein substrate and ATP binds to CDK. protein substrate is phosphorylated, which regulates cell cycle.
G1/S cyclin—CDK catalyze phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein (RB), which is an inhibitor at the restriction point. cyclin—CD changes 3D structure of RB, so the resulting product is ADP and RB-P. this inactivates the RB protein, and the cell cycle proceed
ex. if DNA is damaged by radiation during G1, p21 (protein) binds to G1/S—CDK, preventing cyclin binding, which keeps it inactive and cell cycle pauses until DNA is repaired, in which p21 breaks down and cyclin binds to CDK. if DNA is unable to repair, the cell undergoes cell death
growth factors
external chemical signal that brings cells from G0 to G1
ex. platelets produce platelet-derived growth factor that help heal the wound
ex. interleukins are growth factors for white blood cell
ex. erythropoietin are growth factor for red blood cell
phosphorylation
addition of a phosphate group
ex. reaction from ADP to ATP
cell fusion experiment
reveal existence of internal signals that control the transitions between stages of the cell cycle