Trigonometry Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:13 PM on 9/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
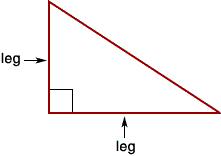
Legs of a right triangle
the two sides that form the right angle
2
New cards
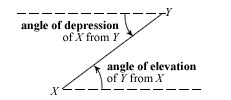
Angle of depression
the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight to an object below the horizontal line
3
New cards
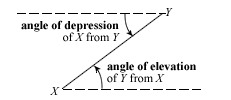
Angle of elevation
the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight to an object above the horizontal line
4
New cards
Cosine
ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
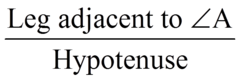
5
New cards
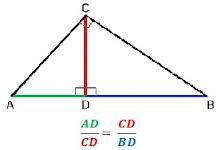
Geometric mean
the mean of n numbers expressed as the n-th root of their product
6
New cards
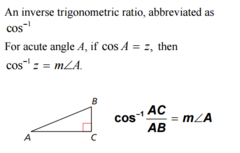
Inverse cosine
An inverse trigonometric ratio, abbreviated as cosˉ¹. For acute angle A, if cosA=z, then cosˉ¹z=m
7
New cards
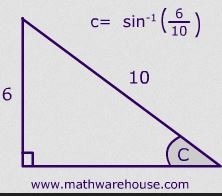
Inverse sine
An inverse trigonometric ratio abbreviated as sin-1
8
New cards
Inverse tangent
an inverse trigonometric ratio, abbreviated as tan-1
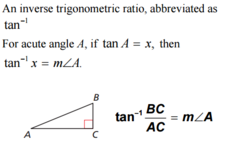
9
New cards
Law of cosines
a²=b²+c²-2bcCosA
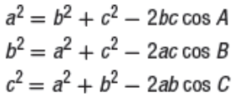
10
New cards
Law of sines
sinA/a=sinB/b=sinC/c
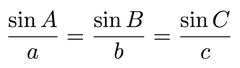
11
New cards
Pythagorean triple
a set of three positive integers that work in the pythagorean theorem
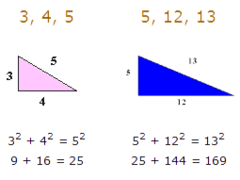
12
New cards
Sine
ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle

13
New cards
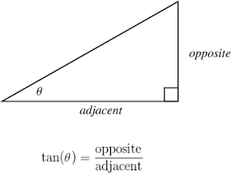
Tangent
ratio of the opposite to the adjacent side of a right-angled triangle
14
New cards
Trignometric ratio
a ratio of two sides of a right triangle

15
New cards
AA Triangle Similarity Theorem
If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar.
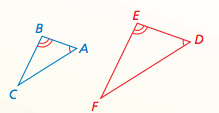
16
New cards
SAS Triangle Similarity Theorem
If two sides of one triangle are proportional to the corresponding sides of another triangle and their included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
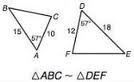
17
New cards
SSS Triangle Similarity Theorem
If the three sides of one triangle are proportional to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
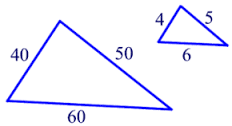
18
New cards
Corresponding parts of similar triangles
Two triangles are similar if and only if the corresponding sides are in proportion and the corresponding angles are congruent. There are three accepted methods of proving triangles similar: AA, SAS, and SSS.
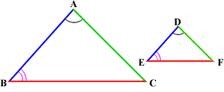
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)