Photosynthesis+Respiration Blue Questions
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
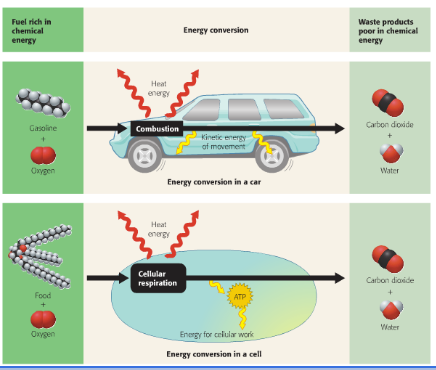
How is combustion in a car similar to cellular respiration? Use the diagrams to explain.
Combustion in a car and cellular respiration are similar because both processes convert fuel into usable energy through oxidation. In a car engine, gasoline reacts with oxygen in combustion to release energy, producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. Similarly, in cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to produce ATP (energy), along with carbon dioxide and water. Both processes rely on oxygen, generate heat, and produce waste products that must be expelled (exhaust in cars, CO₂ in respiration).
Where do the calories in your food come from?
The calories in food come from macronutrients: carbohydrates (4 kcal per gram), proteins (4 kcal per gram), and fats (9 kcal per gram). Alcohol also provides energy at 7 kcal per gram. These macronutrients store chemical energy, which the body converts into ATP through metabolic processes like cellular respiration.
How does ATP power your muscles?
ATP powers muscles by breaking down into ADP and phosphate, releasing energy for muscle contraction. This energy allows myosin to pull actin filaments, causing contraction. ATP is replenished through cellular respiration.
Explain how energy flows and carbon cycle through an ecosystem
Energy flows through an ecosystem from the sun, with plants capturing solar energy and passing it along the food chain to herbivores and predators, while releasing heat during respiration and decomposition. Carbon cycles through the ecosystem as plants absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, converting it into organic matter. Consumers release carbon dioxide through respiration, and decomposers break down organic matter, returning carbon to the soil and atmosphere, completing the cycle.
How is energy released during respiration? Where does it go?
Energy is released during respiration when glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water. This process occurs in the mitochondria of cells, and the energy is stored in molecules called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is then used by cells to perform various functions, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and active transport.
Why do we exhale CO2?
We exhale CO2 because it is a waste product of cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy, and carbon dioxide is produced as a byproduct. This CO2 is transported through the bloodstream to the lungs, where it is expelled from the body when we exhale.
Why do you breathe?
We breathe to take in oxygen (O2) and remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from our bodies. Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration, the process by which our cells produce energy (ATP). Breathing allows oxygen to enter the lungs, where it is transferred to the bloodstream and delivered to cells. It also helps remove carbon dioxide, a waste product produced during respiration, preventing it from building up in the body.
What is required for respiration? How do we get it?
Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration, where it helps produce ATP (energy) in cells. We get oxygen from the air when we breathe it in through our lungs.
Glucose is a sugar that comes from the food we eat, especially carbohydrates. After digestion, glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells for energy production.
What is the connection between breathing respiration and cellular respiration?
Breathing brings oxygen into the lungs, where it diffuses into the bloodstream and is transported to cells.
Cellular respiration occurs in the cells (specifically in mitochondria) where oxygen is used to break down glucose into ATP, which powers the cell's activities. During this process, carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced as a waste product, which is carried back to the lungs and exhaled when we breathe out.
Why is fermentation beneficial to humans?
Fermentation is used in food production to create products like bread, yogurt, cheese, beer, and wine. The process enhances flavor, texture, and preservation, making these foods enjoyable and longer-lasting because of lack of oxygen.
How do organisms control body temperature and blood sugar?
Endotherms (like humans) regulate their body temperature internally by balancing heat production and heat loss. This is done through mechanisms like sweating, shivering, and altering blood flow. Insulin is released when blood sugar is high (after eating) and helps cells absorb glucose for energy or storage as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
What is our gut microbiome and what does it do?
The gut microbiome refers to the community of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that live in our digestive tract, primarily in the intestines. Digestion: Many microbes help break down food that the body cannot fully digest on its own, such as fiber, turning it into short-chain fatty acids that provide energy.
Where does the mass in a tree come from?
The mass in a tree comes from carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the air. Through photosynthesis, trees absorb CO₂ and convert it into glucose using sunlight. This glucose helps the tree grow and forms cellulose, which makes up the tree's biomass. Water (H₂O) also plays a role, but most of the tree’s mass comes from CO₂.
How does climate change affect plants?
Climate change affects plants by changing temperature, rainfall, and growing seasons. It can cause water shortages, droughts, or flooding, and affect plant growth. Extreme weather and temperature shifts harm plant health, while increased CO₂ may boost some growth.
Why do plants need fertilizer
Plants need fertilizer because it provides essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which help with growth, root development, and reproduction. However, these nutrients are often depleted in soil and must be replenished for healthy plant development.
Explain the flow of materials in a tree
Xylem: Transports water and minerals absorbed by the roots up to the leaves.
Phloem: Carries sugars and nutrients made in the leaves through photosynthesis to other parts of the tree for growth and energy storage.
Where does the oxygen we breathe come from? Where does the carbon dioxide we exhale go?
Oxygen: The oxygen we breathe comes from plants and algae through the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants and algae take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, and using energy from sunlight, they produce glucose and release oxygen as a byproduct.
Carbon Dioxide: The carbon dioxide we exhale is a waste product of cellular respiration, which occurs in our cells to produce energy. Once exhaled, CO2 enters the atmosphere and is used by plants and algae during photosynthesis, continuing the cycle. Some CO2 is also absorbed by oceans and soil.
Why do cacti grow slower?
Cacti grow slower because they are adapted to survive in dry, harsh environments where water is scarce. To conserve water, cacti have developed thick, fleshy tissues that store water, a feature that limits their growth rate. Additionally, cacti often have fewer stomata (pores) to reduce water loss through transpiration, and their metabolism is slower to minimize energy use. The limited availability of water and nutrients in their desert habitats also slows their growth compared to plants in more nutrient-rich environments.
What is one benefit to being a C4 or CAM plant? What is one drawback?
Benefit: C4 and CAM plants conserve water, making them ideal for hot, dry environments.
Drawback: They use more energy than C3 plants, which can limit their growth.
Relationship between photosynthesis and respiration
The products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the reactants for cellular respiration. The products of cellular respiration (carbon dioxide and water) are the reactants for photosynthesis. This forms a cycle of energy and matter.