Lesson 80 - Introduction to Veterinary Reproductive Diagnostic Imaging
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What is ultrasonography commonly used in?
large and small animals
What is radiography commonly used in?
small animals
What is endoscopy commonly used in?
transcervical intrauterine artificial insemination to visualize the cervix and pass the insemination catheter into the uterus
What is radiography commonly used for in small animals?
litter size estimation
What are the limitations of radiography in pregnant small animals?
radiation exposure, not useful for early pregnancy diagnosis
What is endoscopy occasionally used for in large animals?
evaluate the uterus for cysts or foreign bodies in mares
What reproductive structures should be evaluated using ultrasonography for breeding management?
1. follicles
2. corpus lutea
3. uterus
4. fetus and fetal membranes
What are some pathological findings of ultrasonography of reproductive structures?
ovarian cysts, pyometra, cysts, masses, foreign bodies
A large animal veterinarian has two farm calls scheduled today. The first one is to a bovine farm to conduct herd pregnancy checks and the second is to evaluate a mare for breeding. What diagnostic imaging method will the veterinarian most likely use?
ultrasonography
What approach is commonly used for ultrasound in large animals to evaluate the reproductive system?
transrectal
What probe is commonly used for ultrasound in large animals to evaluate the reproductive system?
linear or convex rectal probe (5- 10mHz)
What is an important landmark for ultrasound in large animals to evaluate the reproductive system?
urinary bladder
What aspect of the reproductive tract is seen at the top of the screen with transrectal ultrasonography?
dorsal aspect
What are the normal ovarian structures that you can see in bovine ultrasonography?
1. follicles
2. corpus hemorrhagicum
3. corpus luteum
4. CL with a cavity
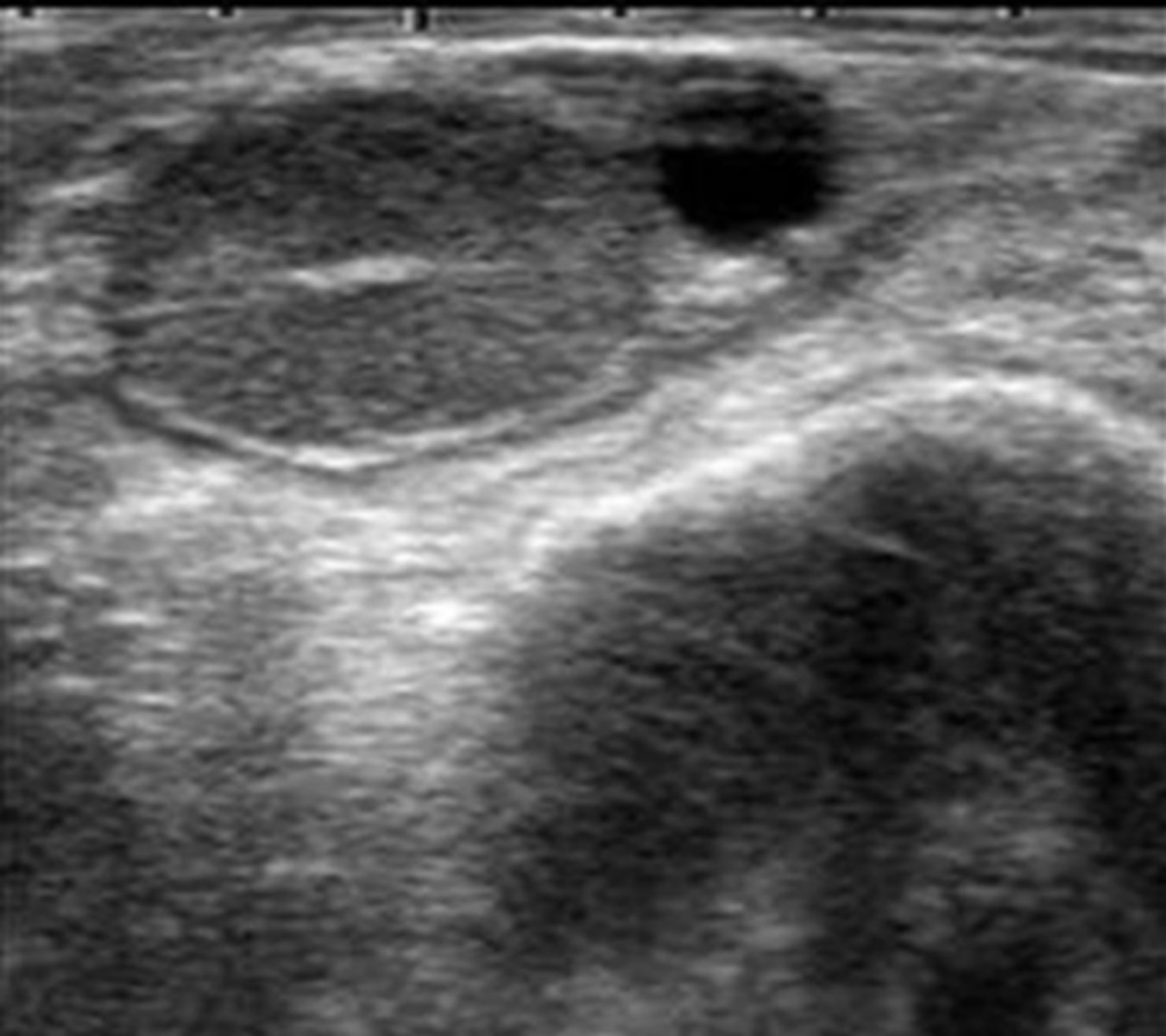
bovine ovary with a follicle and CL
bovine ovary with two follicles and a CL with a cavity
What can be visualized using color doppler ultrasonography?
blood flow
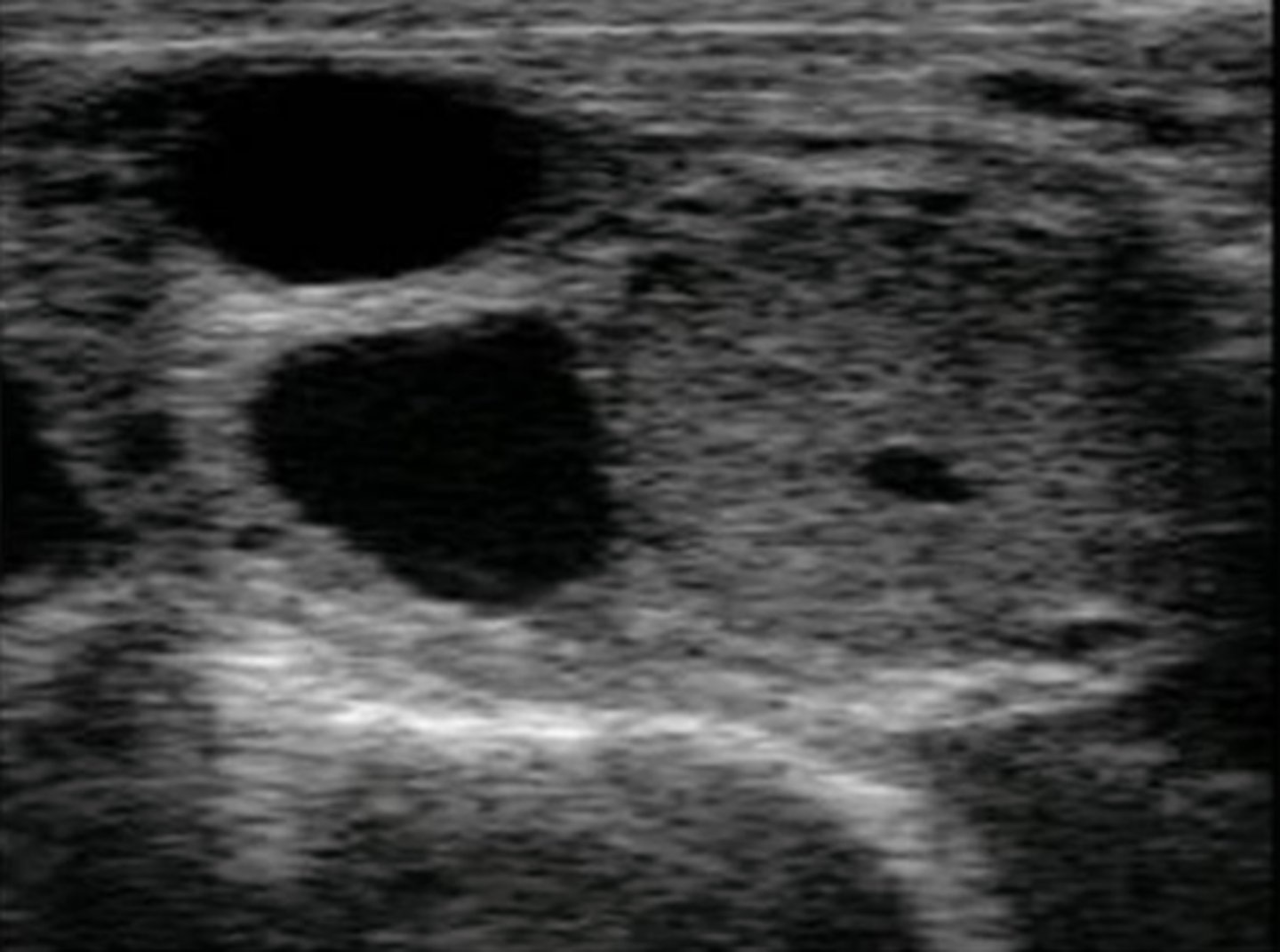
What are the normal ovarian structures that you can see in equine ultrasonography?
1. follicles
2. corpus hemorrhagicum
3. corpus luteum
equine ovary with preovulatory follicle
equine ovary with a corpus hemorrhagicum
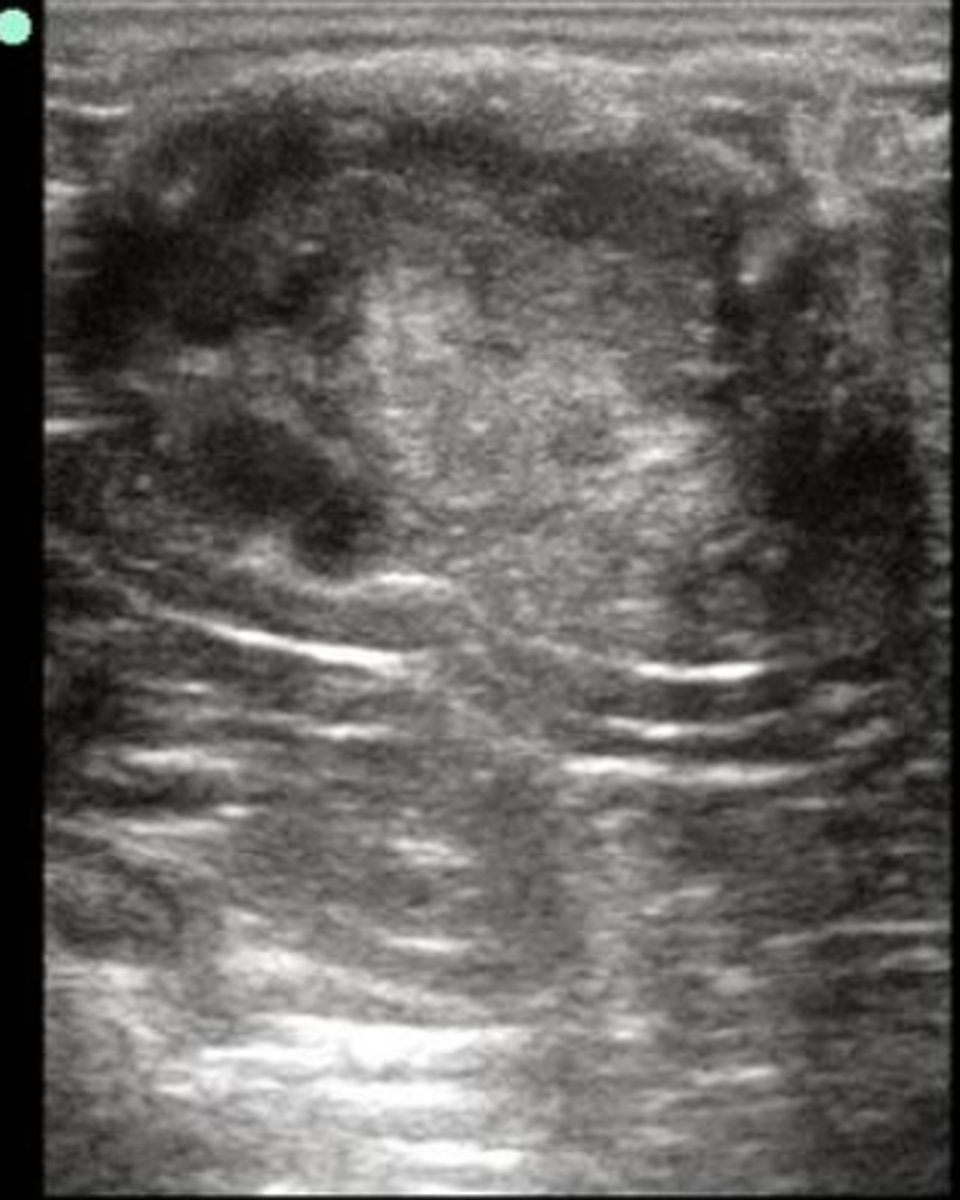
equine ovary with a corpus luteum
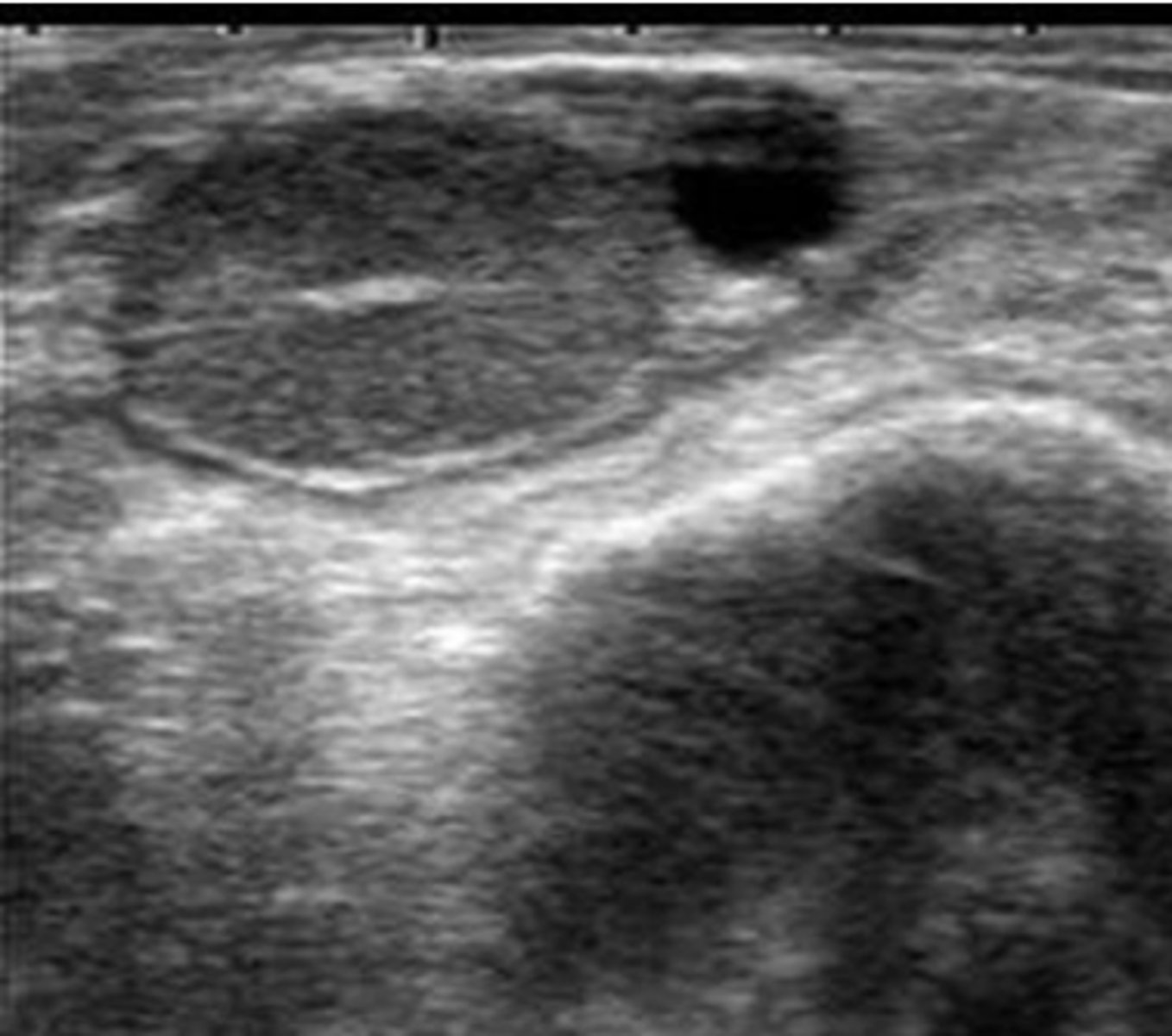
What structures are present in the ovary shown in the picture?
bovine ovary with CL and follicle
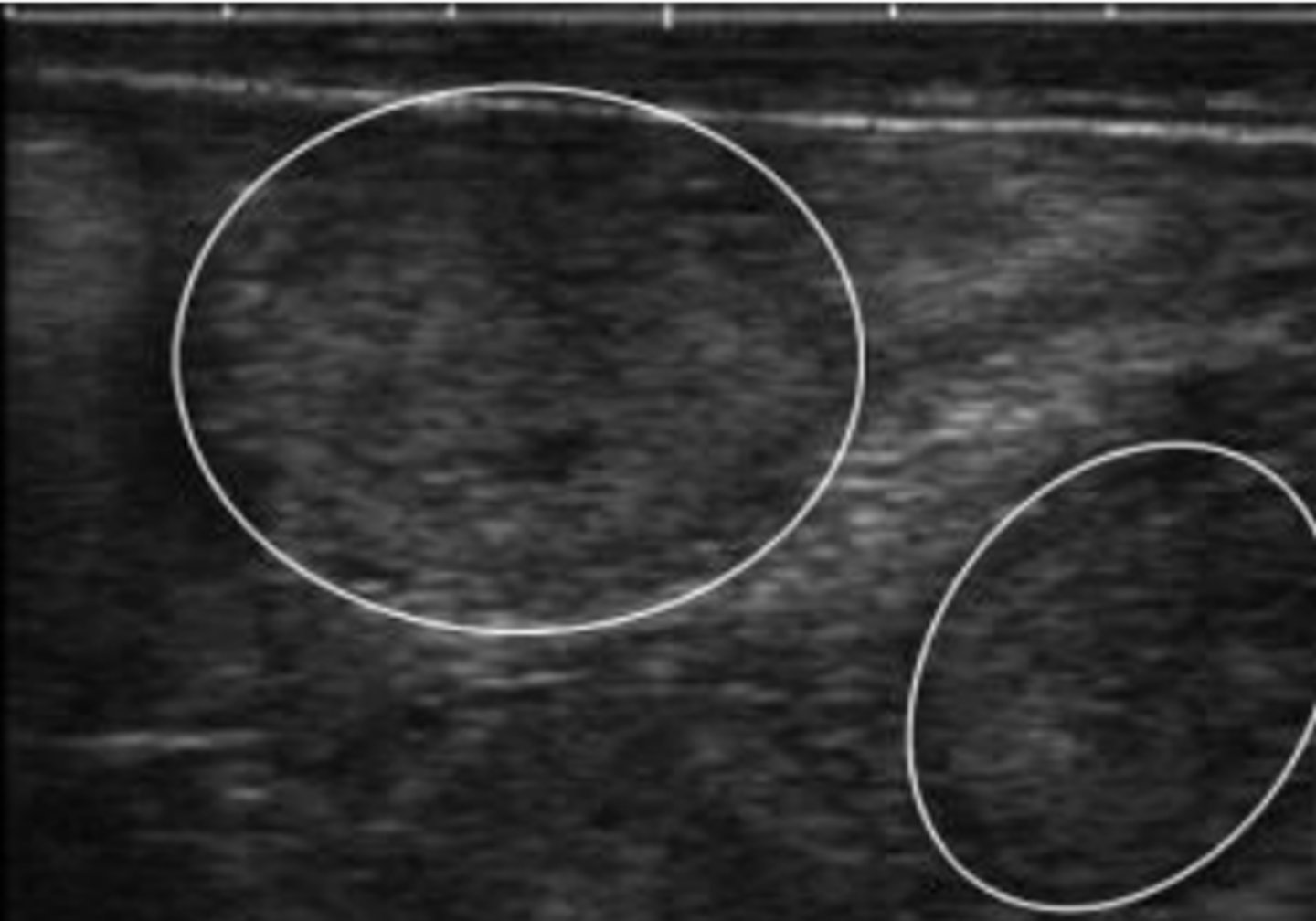
normal, non-pregnant bovine uterus during diestrus
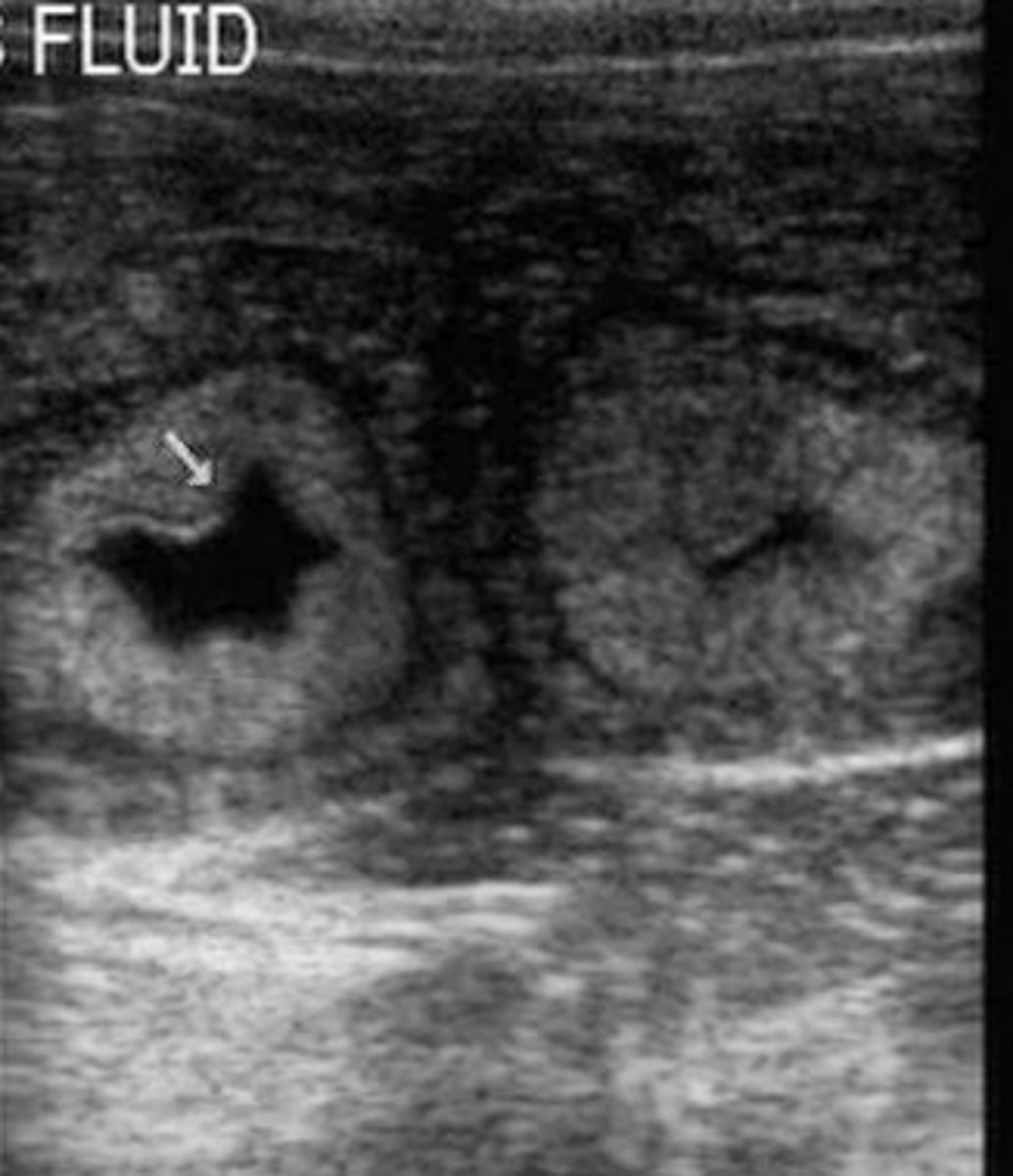
normal, non-pregnant bovine uterus during estrus
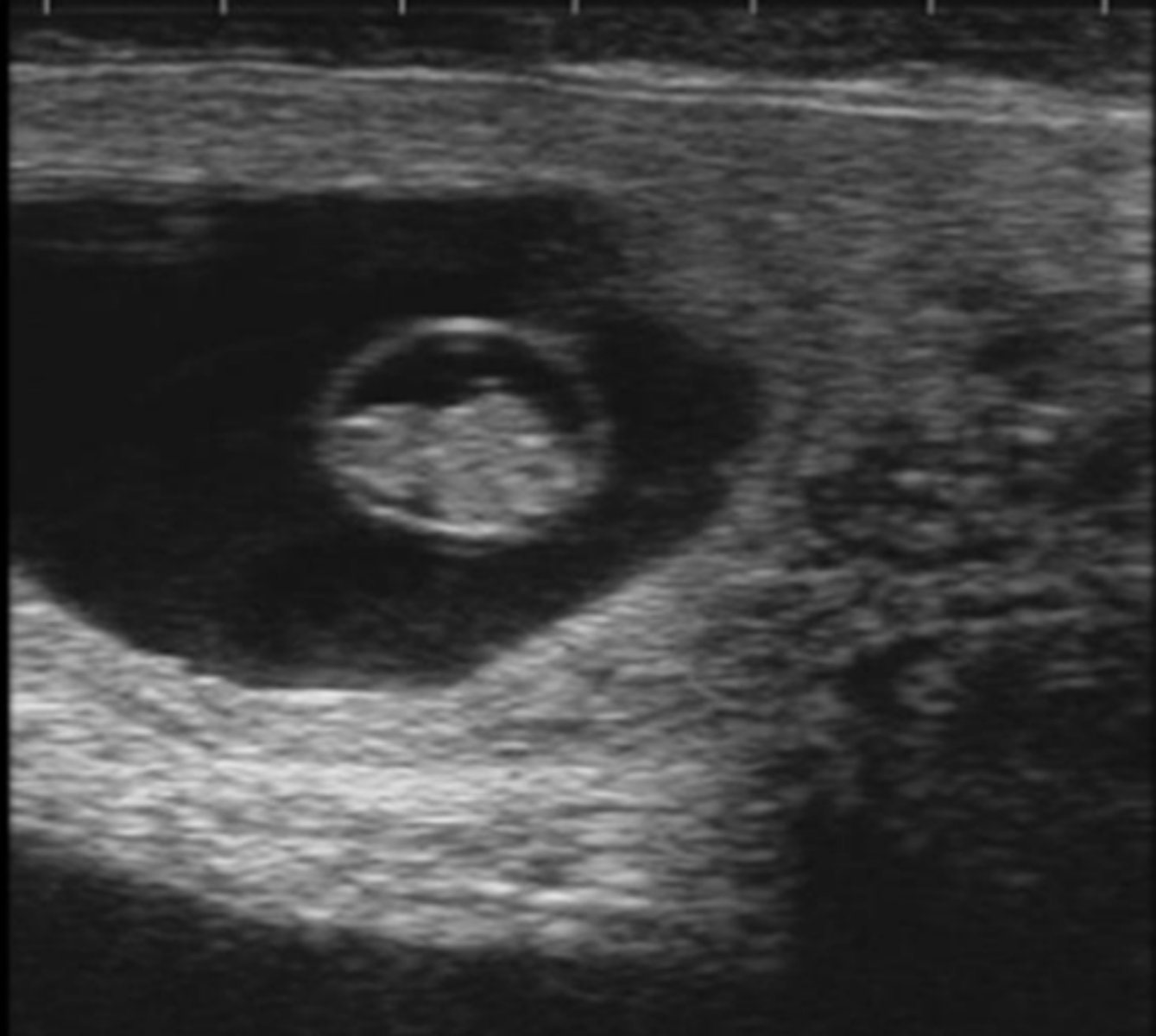
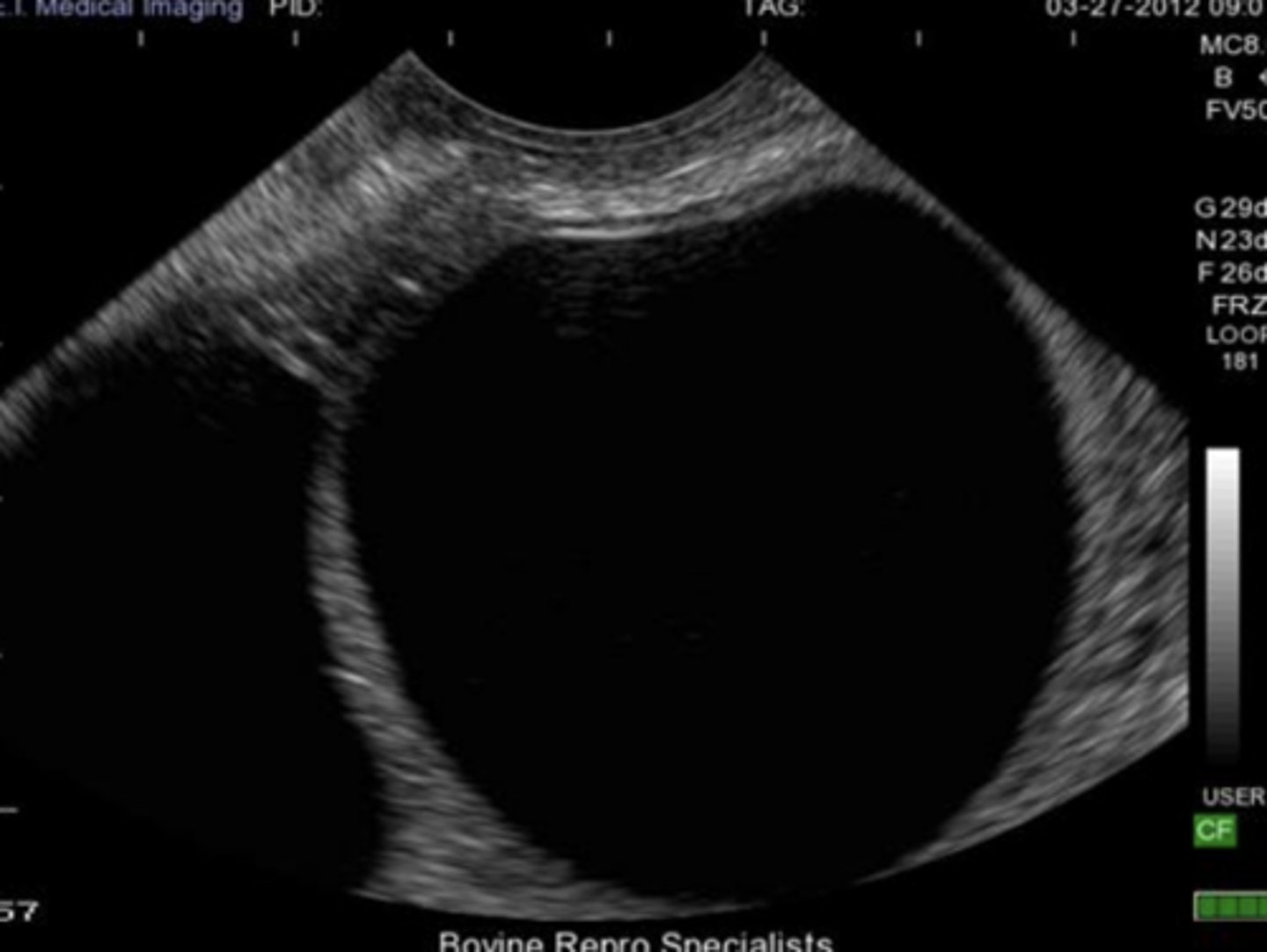
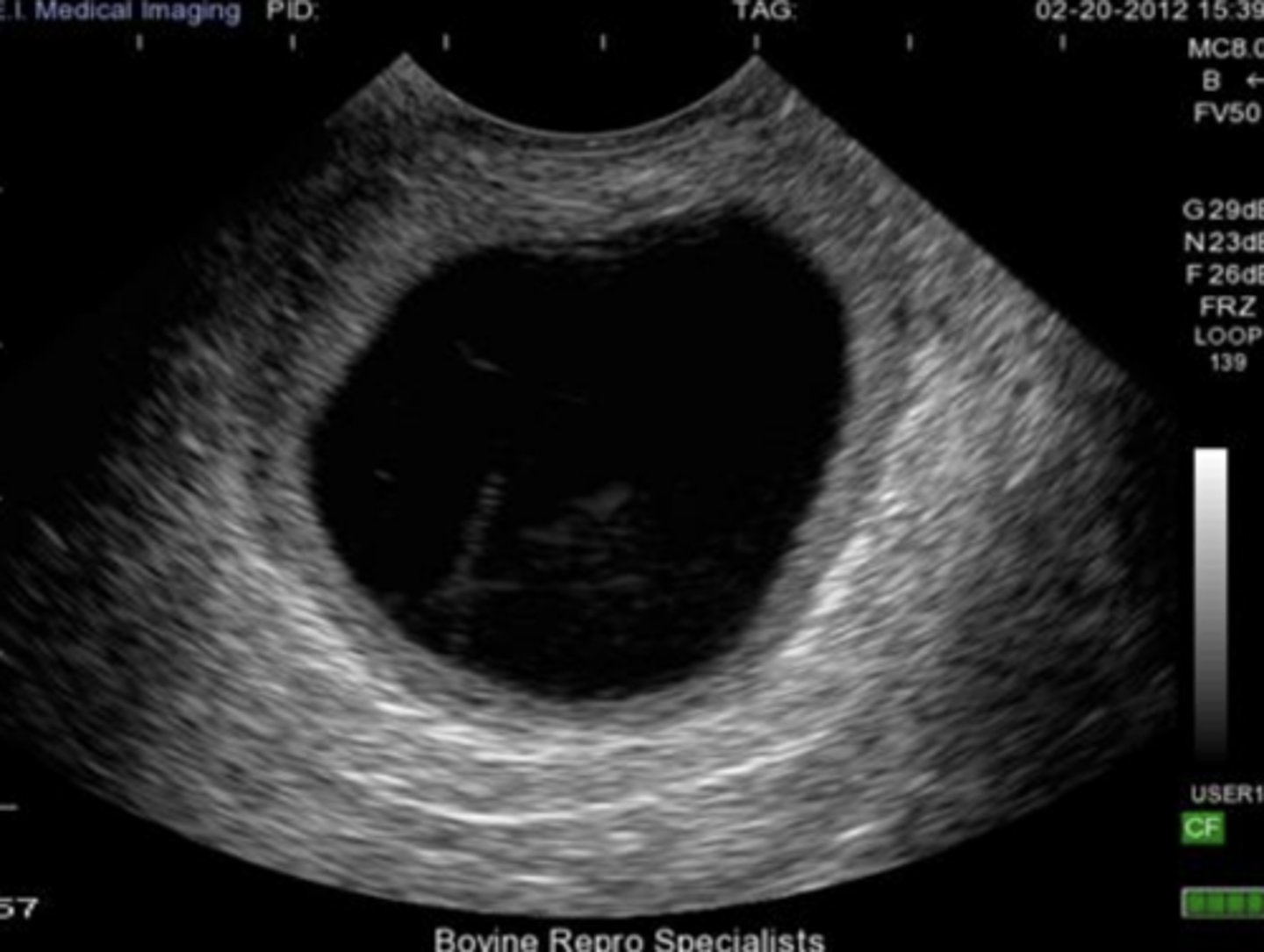
bovine pregnancy (about one month)
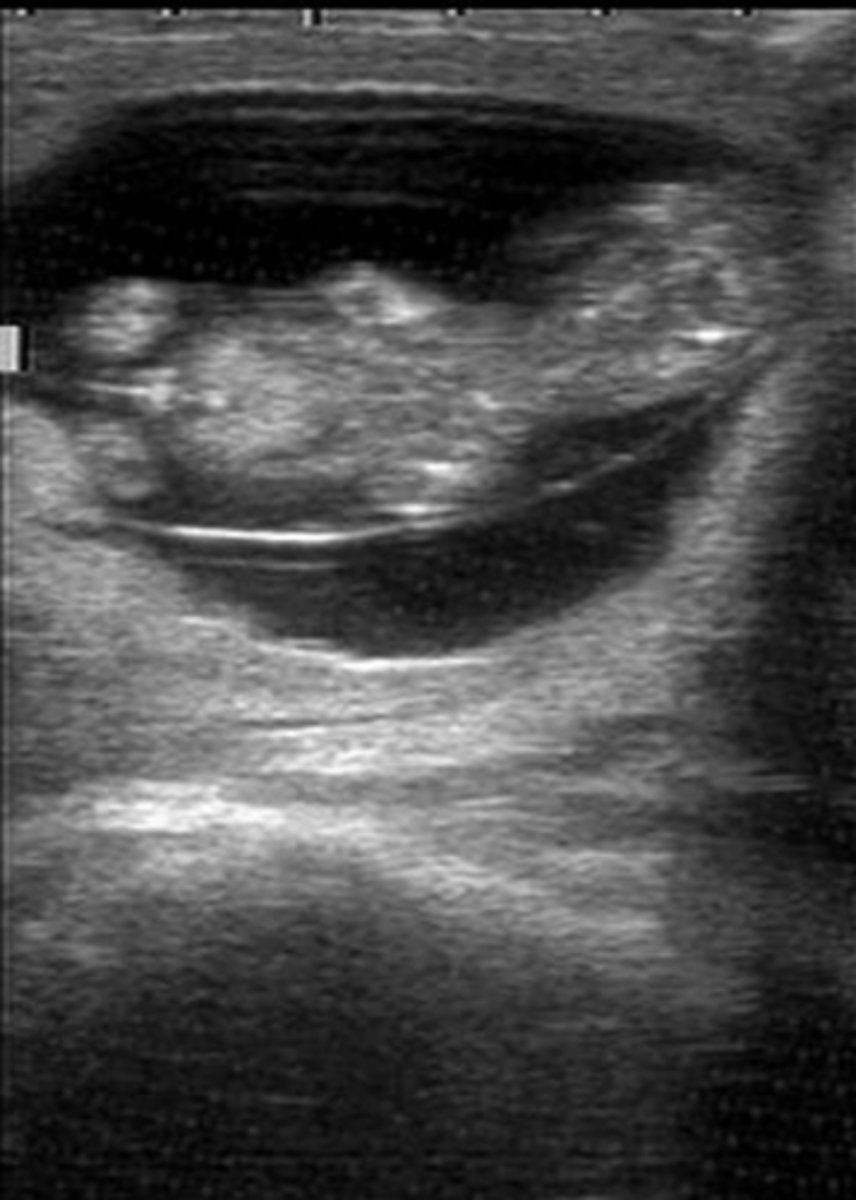
bovine pregnancy (about two months)
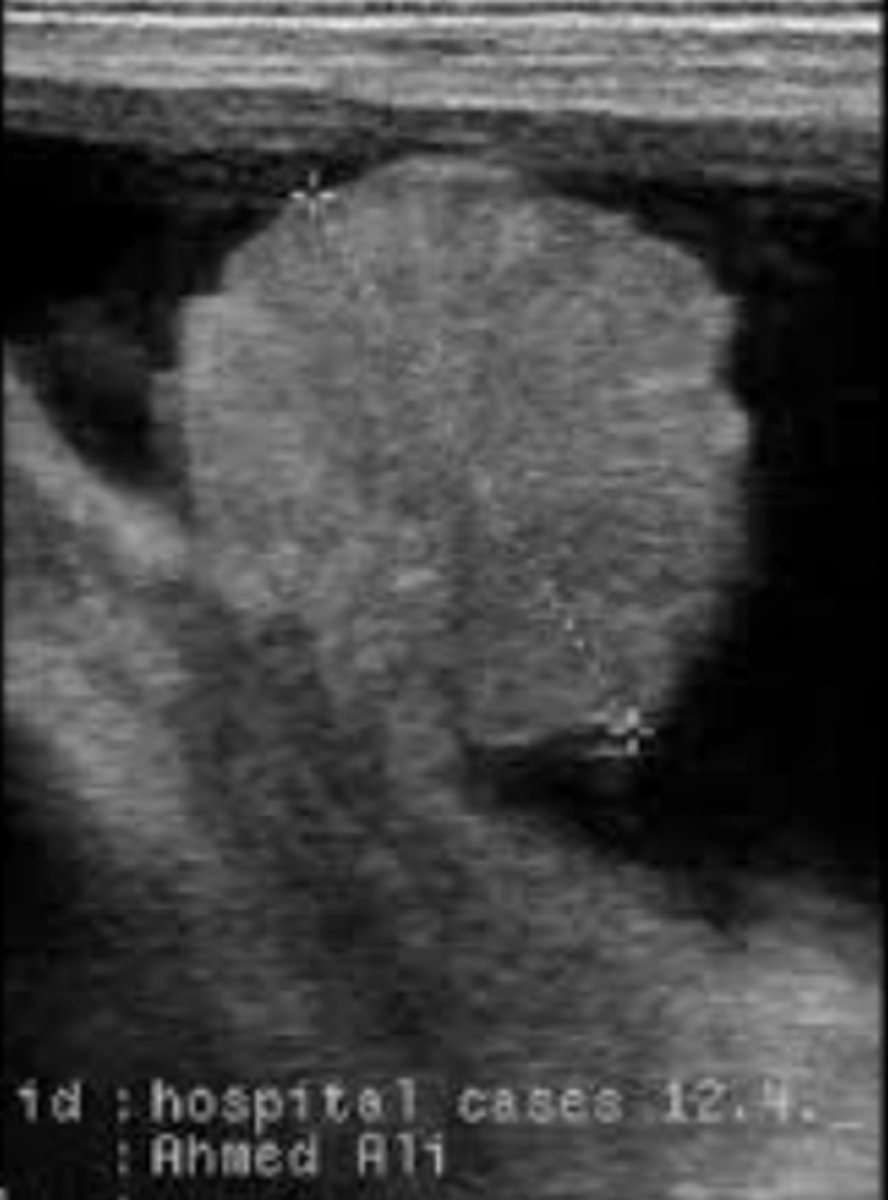
pregnant bovine placentome
How can fetal sex be evaluated using ultrasonography?
locating the genital tubercle
What is the genital tubercle?
precursor to the penis and clitoris
Where can the genital tubercle be located?
close to the umbilicus in male fetus and the tail in the female fetus
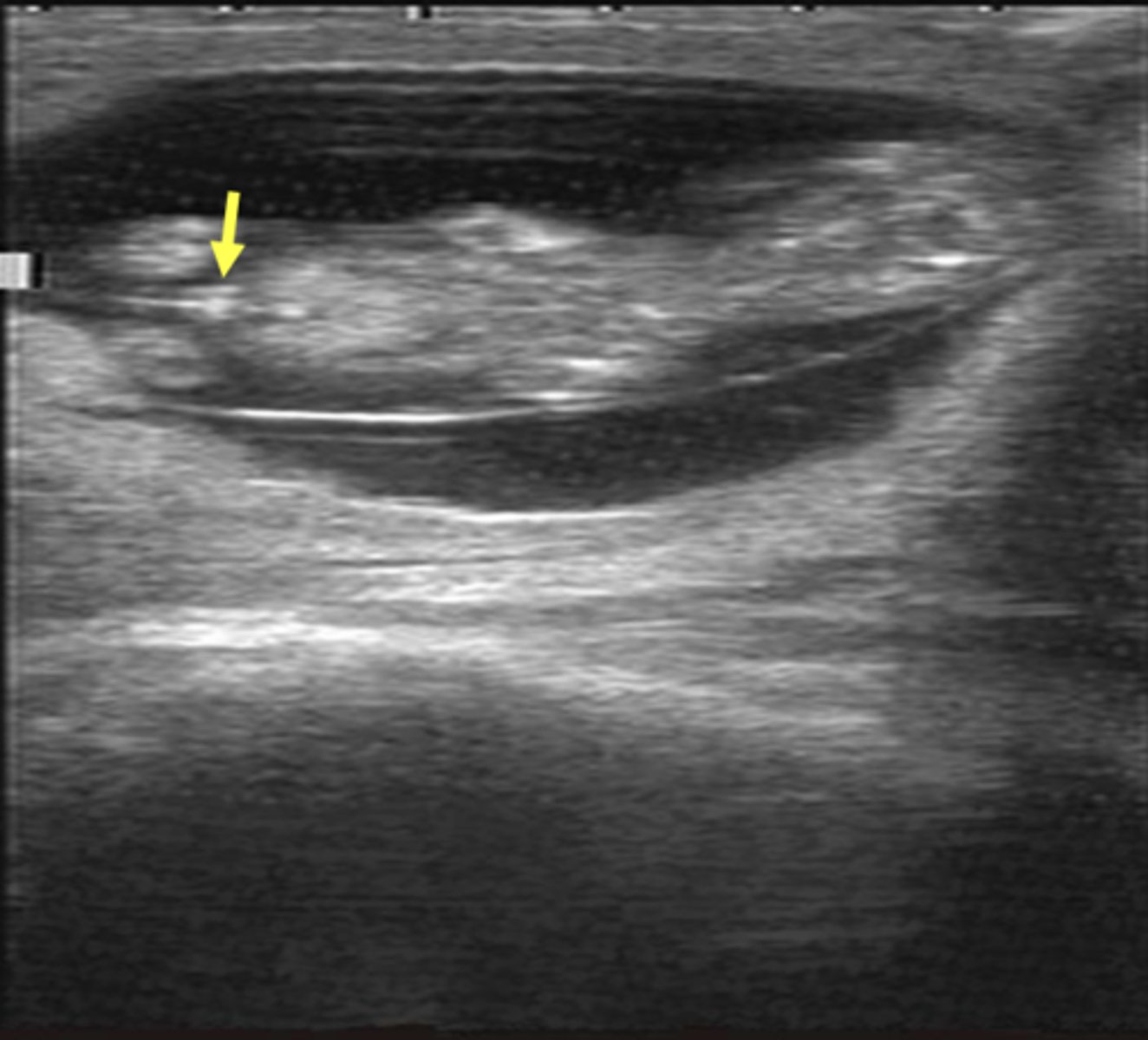
What sex is the fetus (bovine)?
male
What sex is the fetus (bovine)?
female
normal, non-pregnant equine uterus during diestrus
normal, non-pregnant equine uterus during estrus
What is important about day 14 in equine pregnancy?
good time to use US to diagnose pregnancy
What is important about day 25 in equine pregnancy?
should see blood flow and fetal heart beat on US
What can be used in addition to transrectal ultrasonography in advanced preganancy?
transabdominal ultrasonography
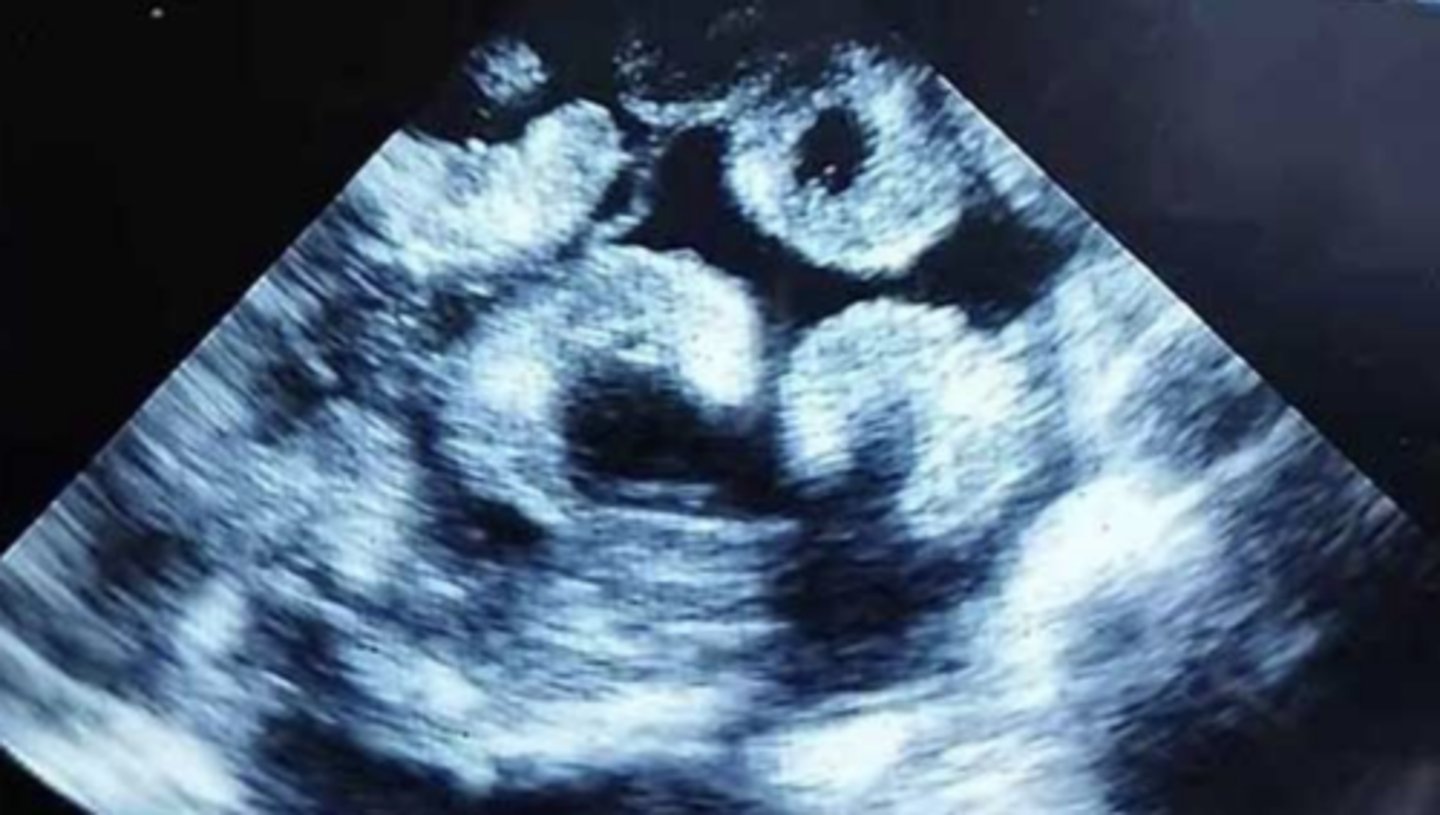
pregnant caprine placentomes visualized using transabdominal US
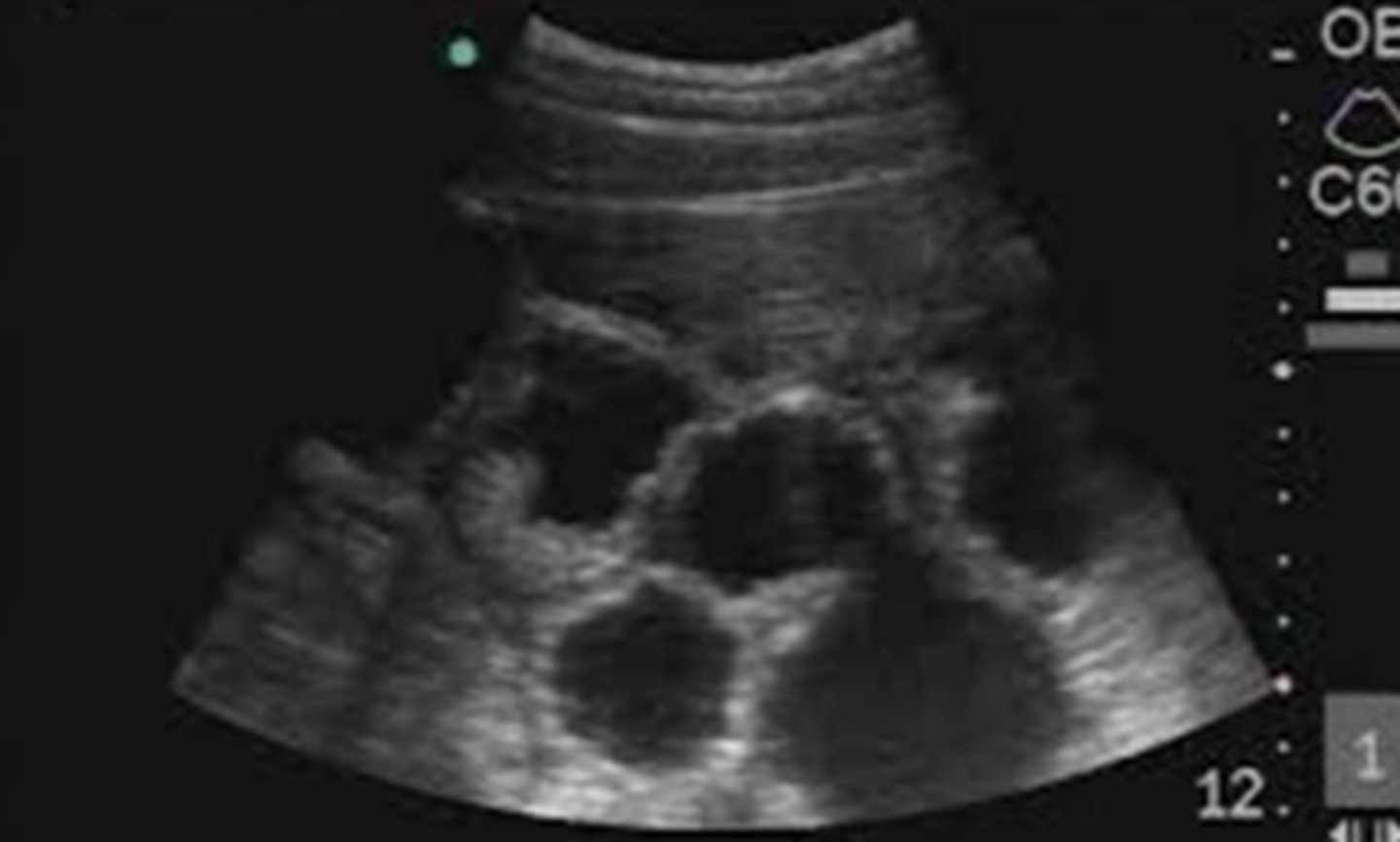
porcine pregnancy with multiple conceptuses visualized using transabdominal US
What structures we see on ultrasonography that we can use as definitive signs of pregnancy?
1. fetus
2. placentomes
3. gestational sacs
4. embryo
5. fetal membranes
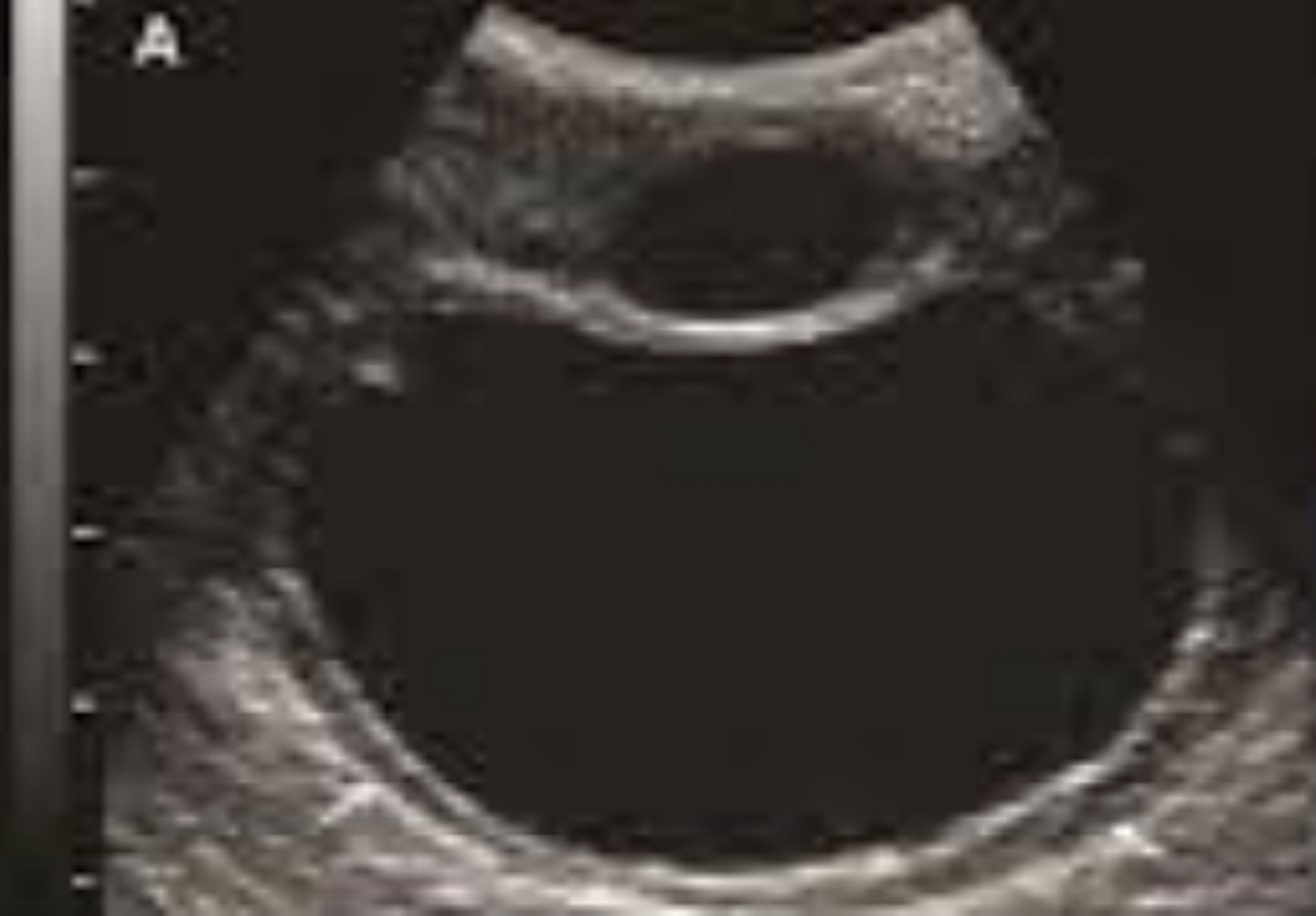
ovarian follicular cyst (thin wall; <3 mm thick)
ovarian luteal cyst (thicker wall; >3 mm thick)
hemorrhagic anovulatory follicle development in a mare
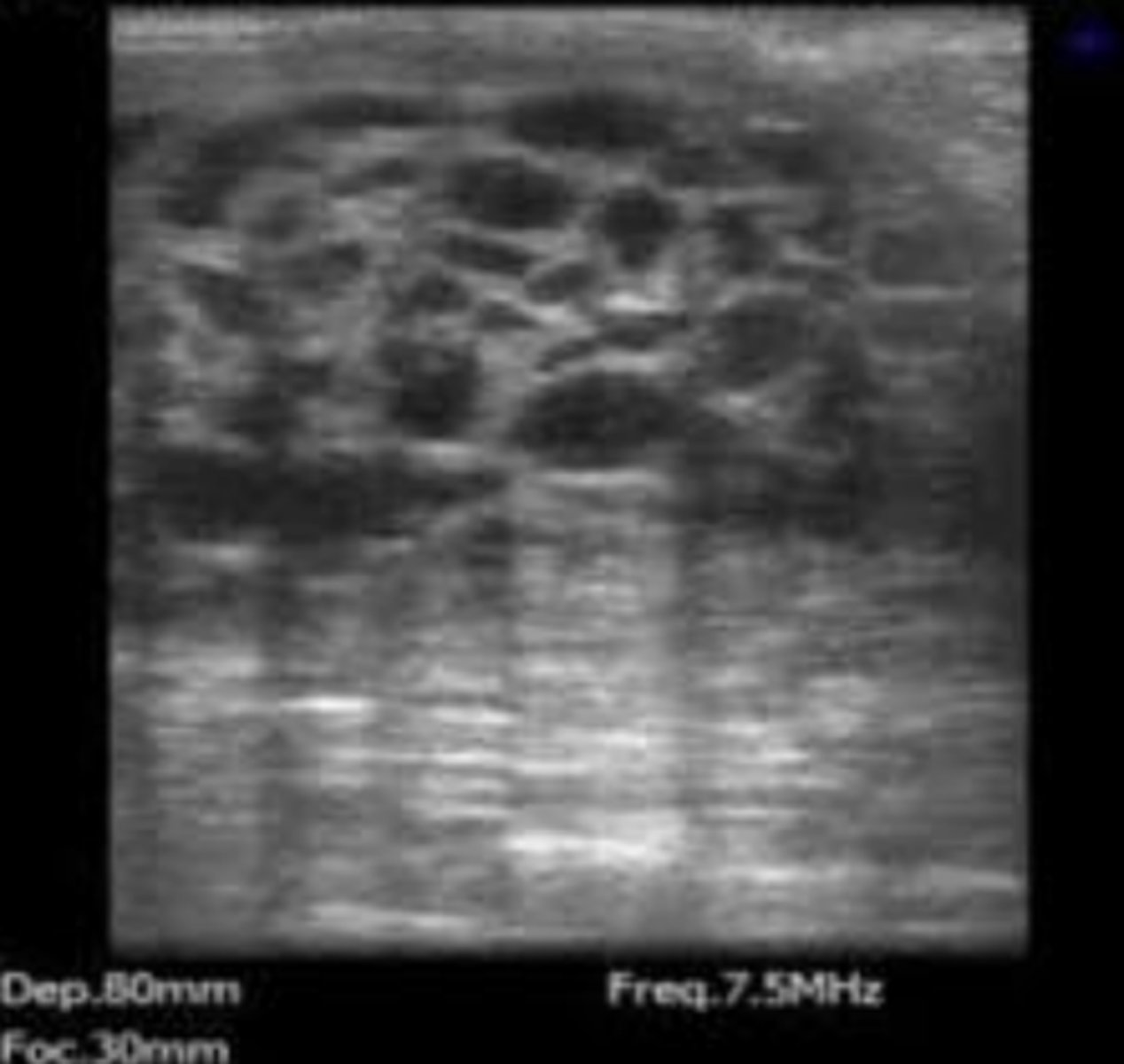
granulosa cell tumor in a mare
pyometra
mucometra
hydrometra in a goat
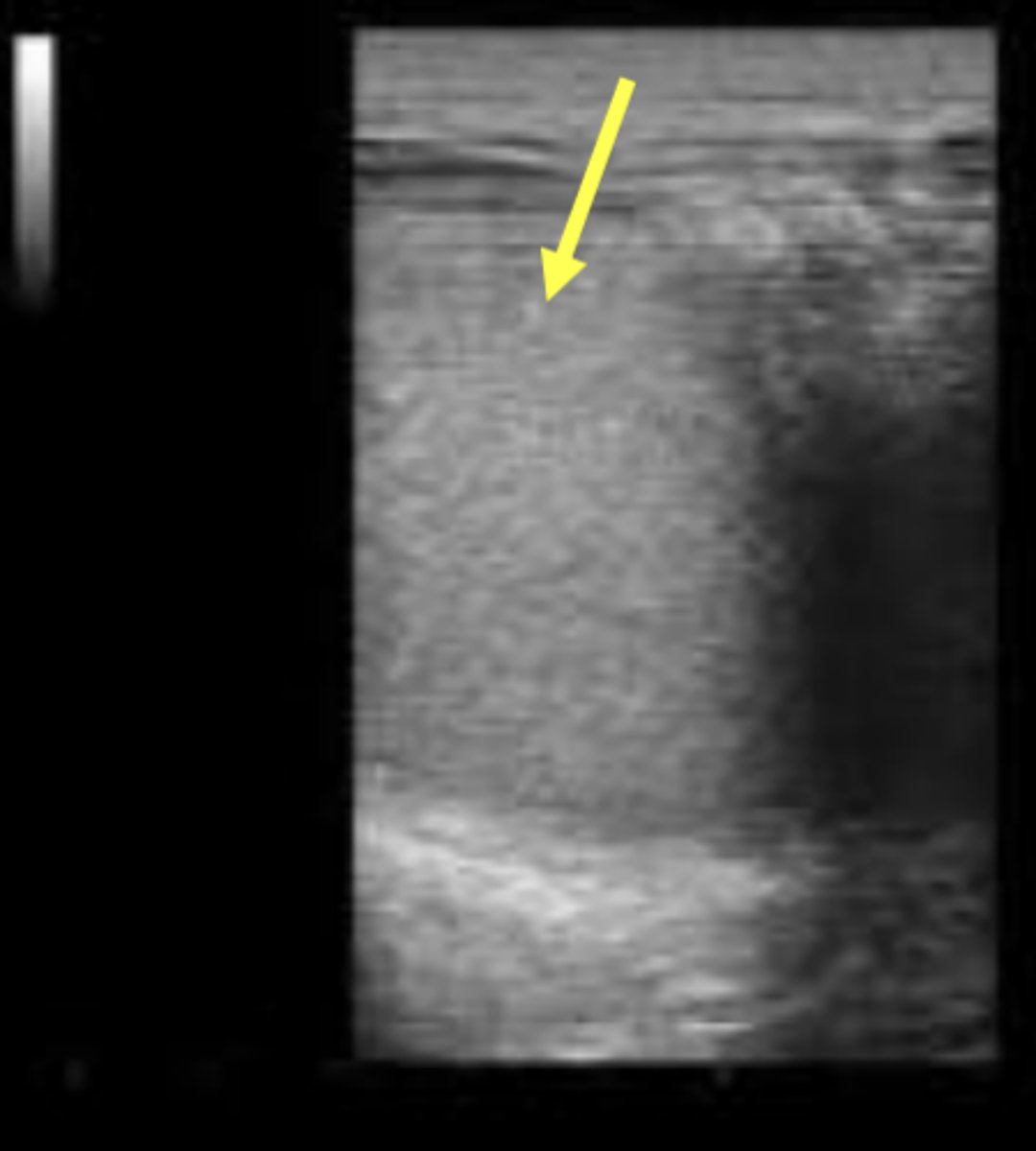
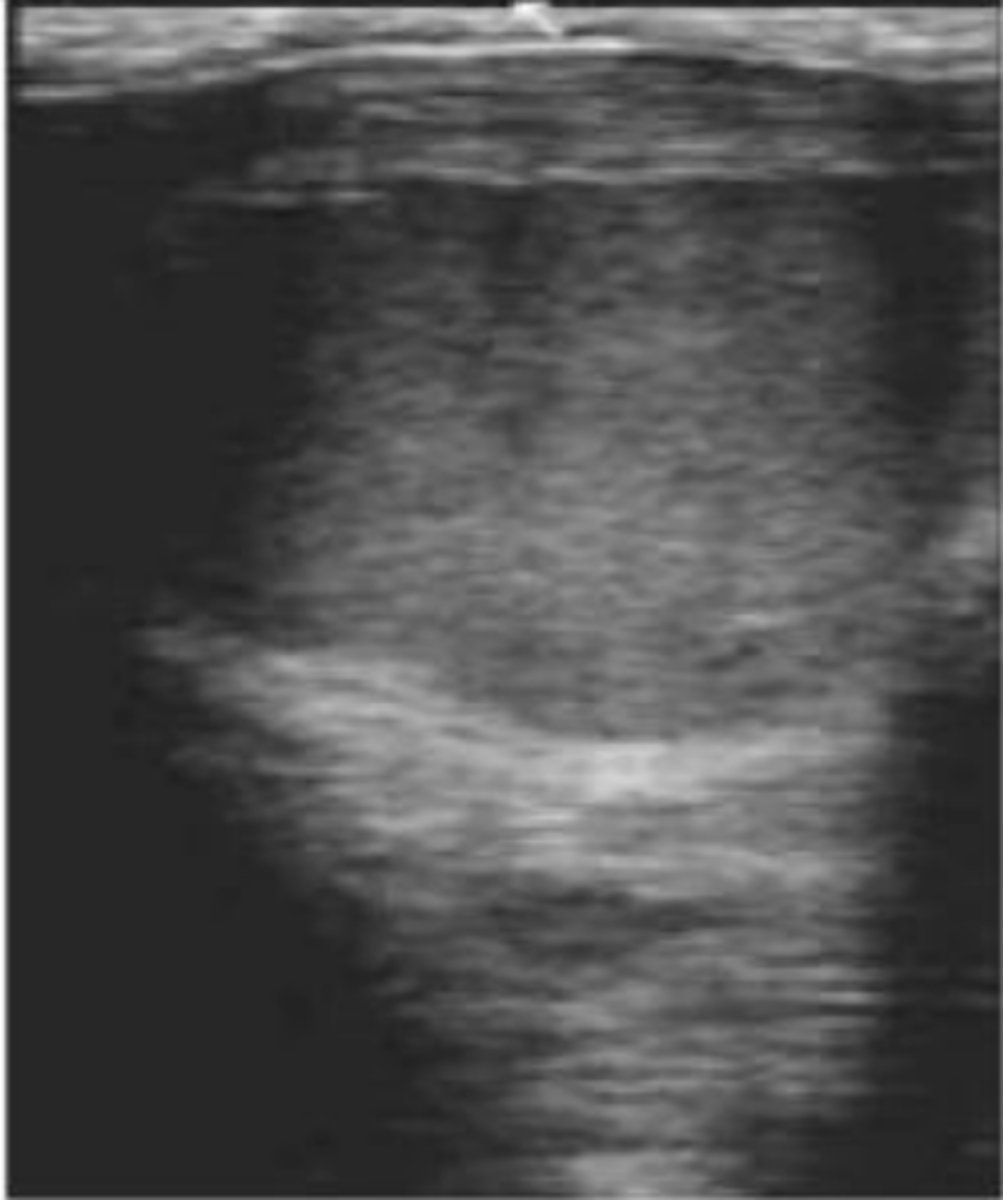
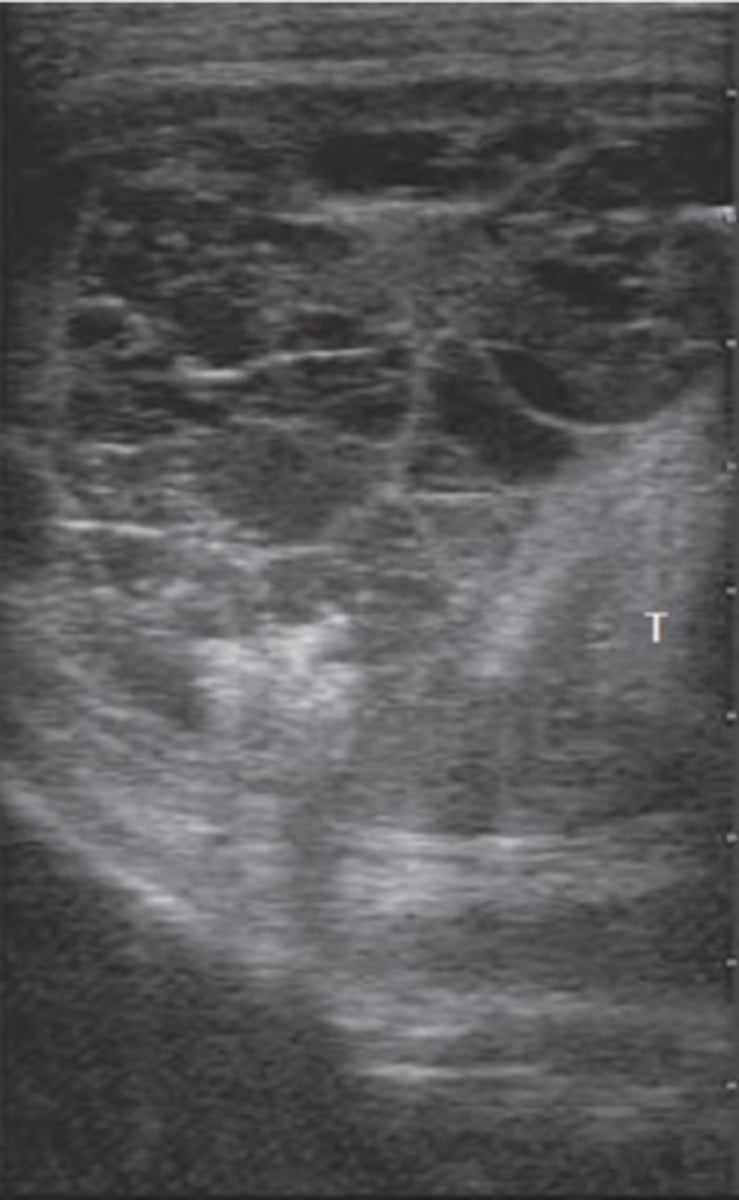
Transrectal ultrasonography of a cow with history of anestrus reveals presence of a corpus luteum on the right ovary, small follicles on the left ovary, and the uterus appears as shown in the picture. What clinical condition are we most likely dealing with?
pyometra
What are the different US views of the male reproductive system?
sagittal and transverse
What parameters are evaluated with US of the male repro system?
size and quality of the parenchyma (echogenicity and structure of the tissue, identification of blood vessels)
How does normal testicular parenchyma appear on US?
homogeneous and moderately echogenic
How does normal mediastinum testis appear on US?
linear and slightly more echogenic structure in the center of the testicle
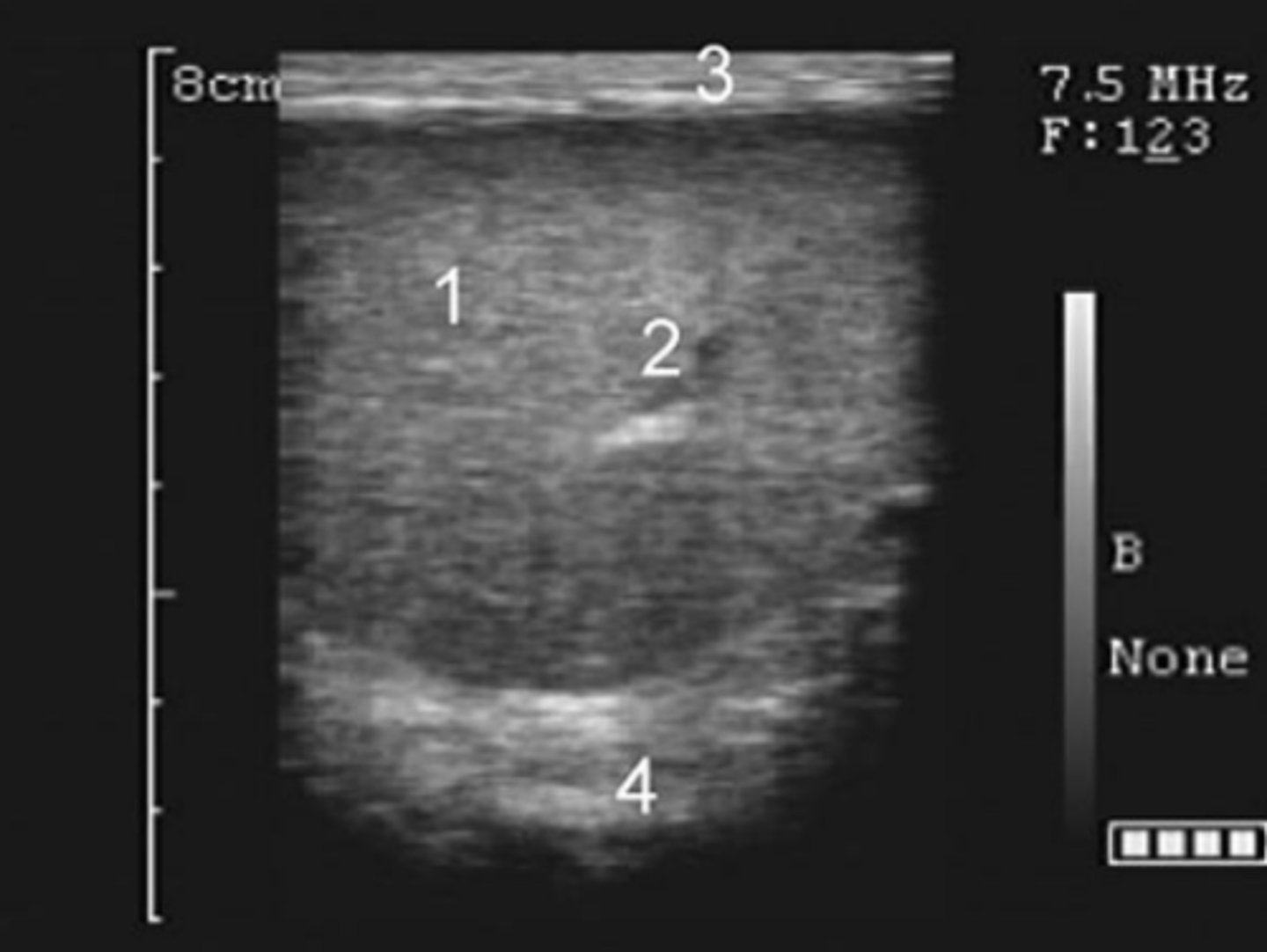
transversal view of bovine testis
sagittal view of bovine testis
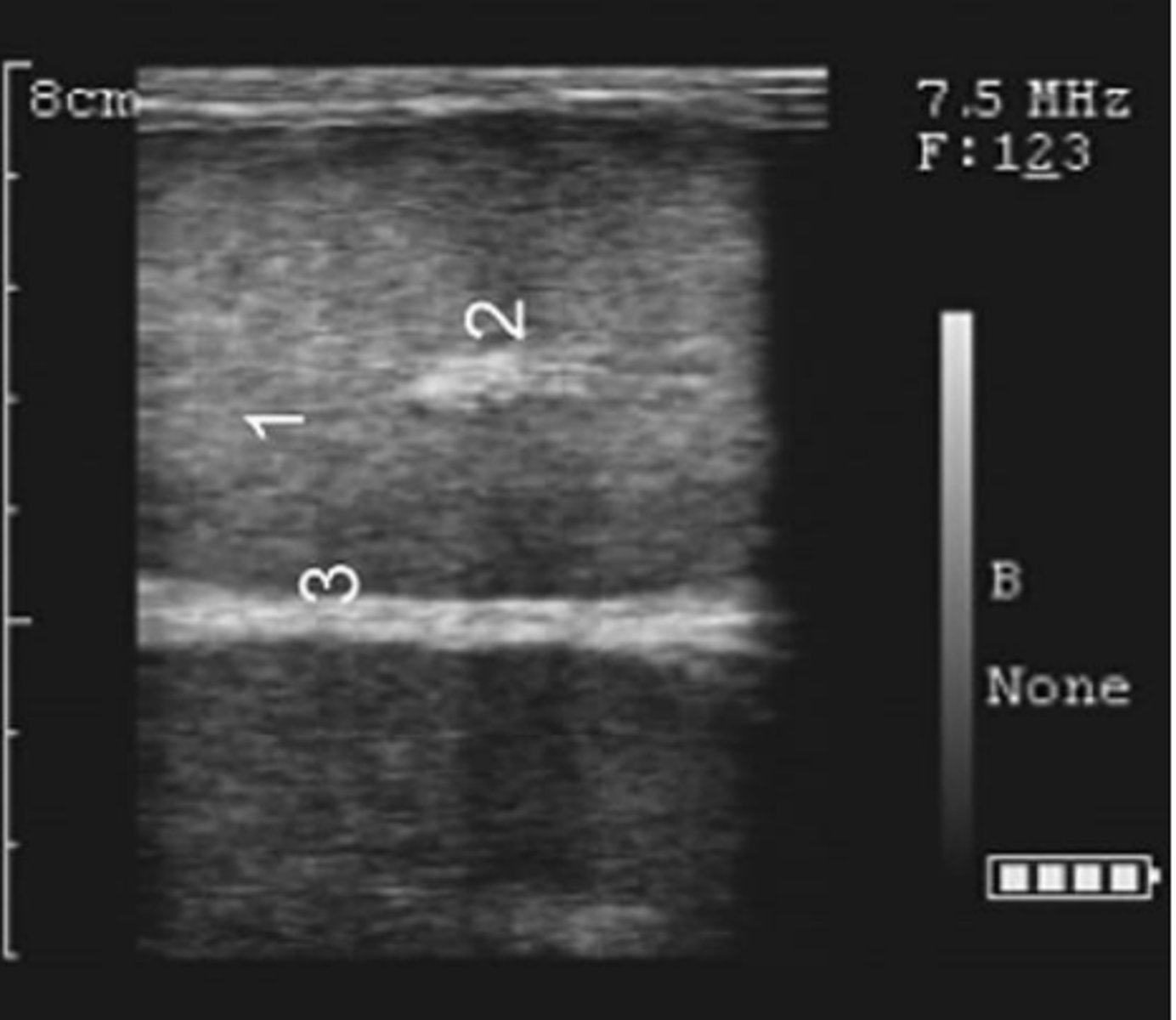
bovine caput epididymis (epididymal head)
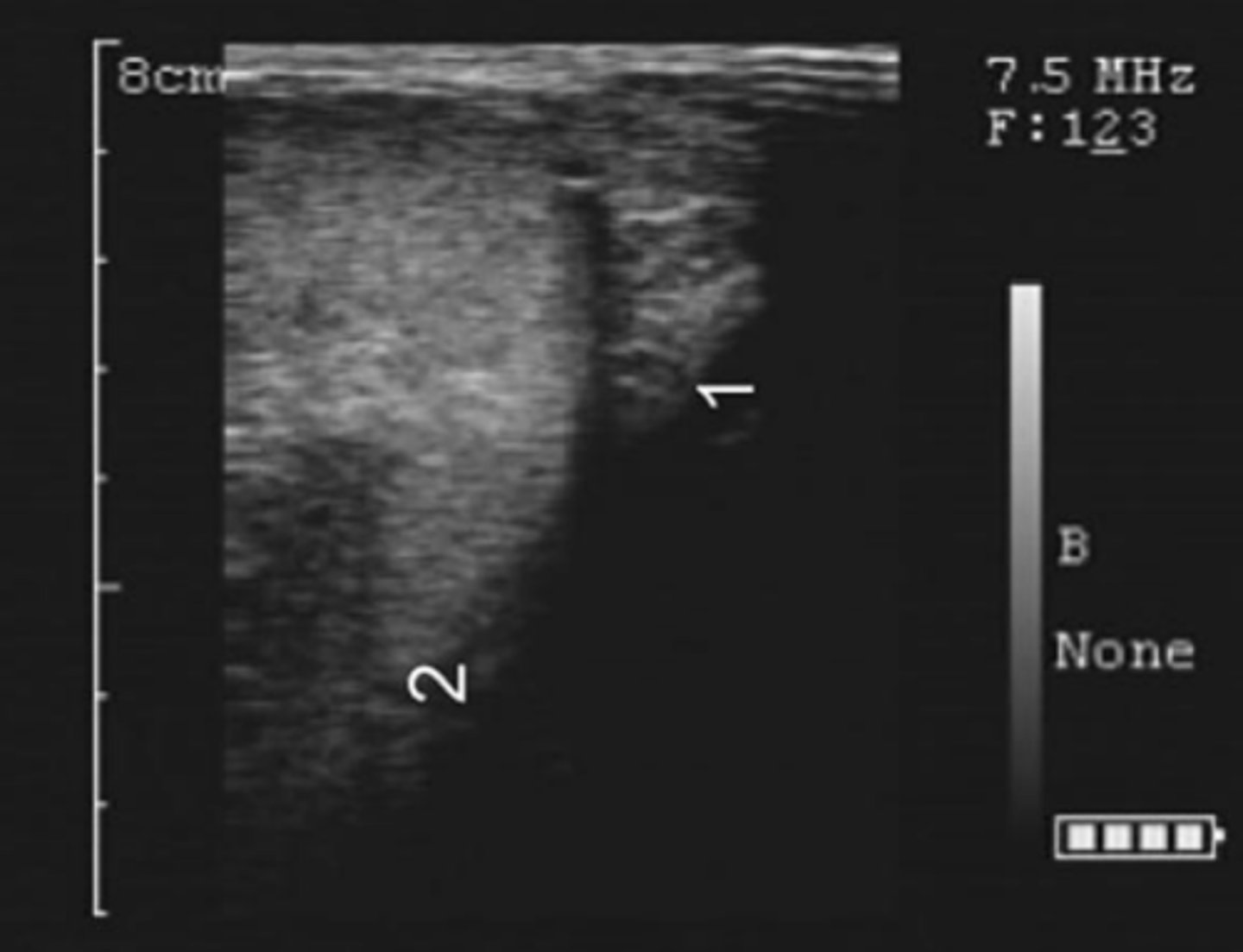
bovine cauda epididymis (epididymal tail)
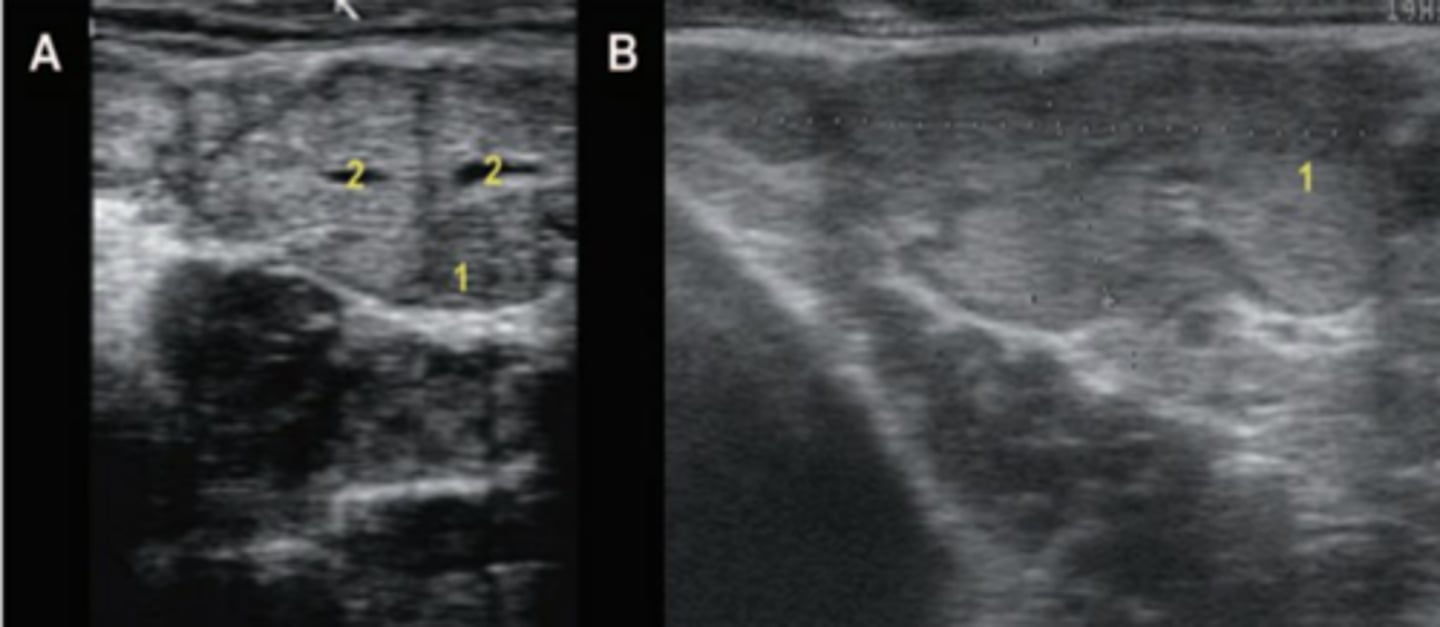
What is A?
seminal vesicles/vesicular glands in transverse view
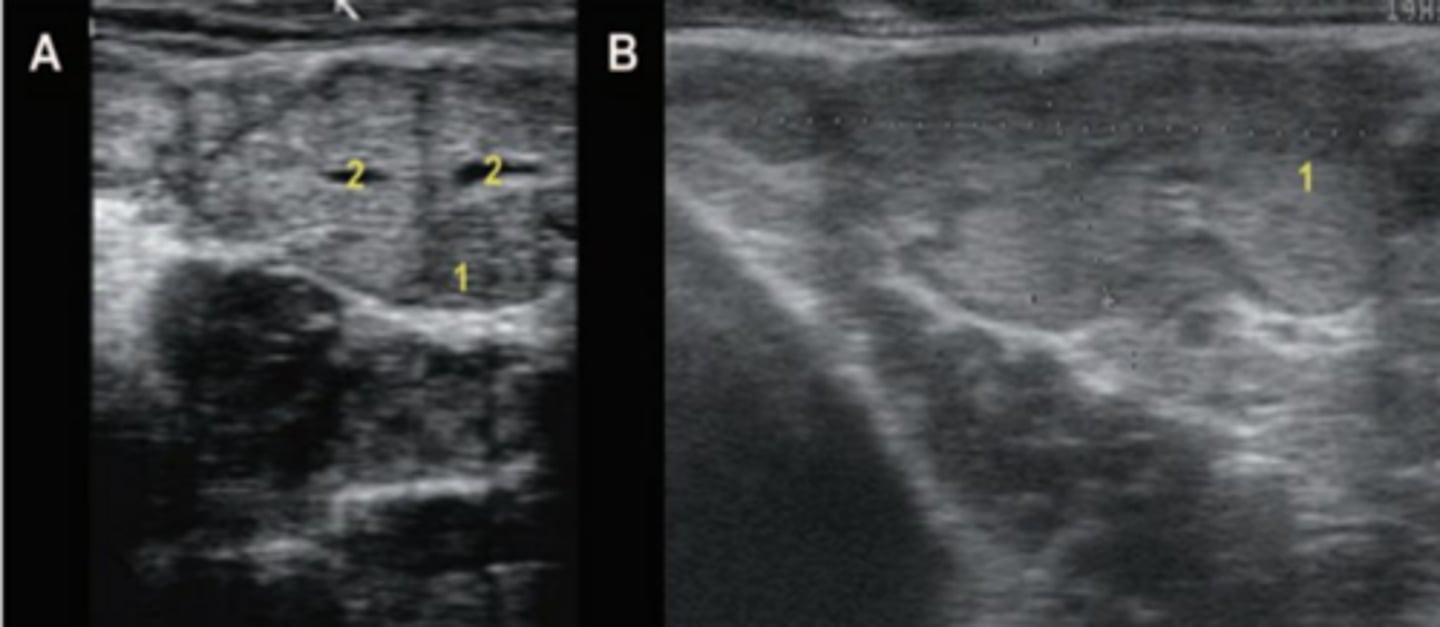
What is B?
seminal vesicles/vesicular glands in a longitudinal view
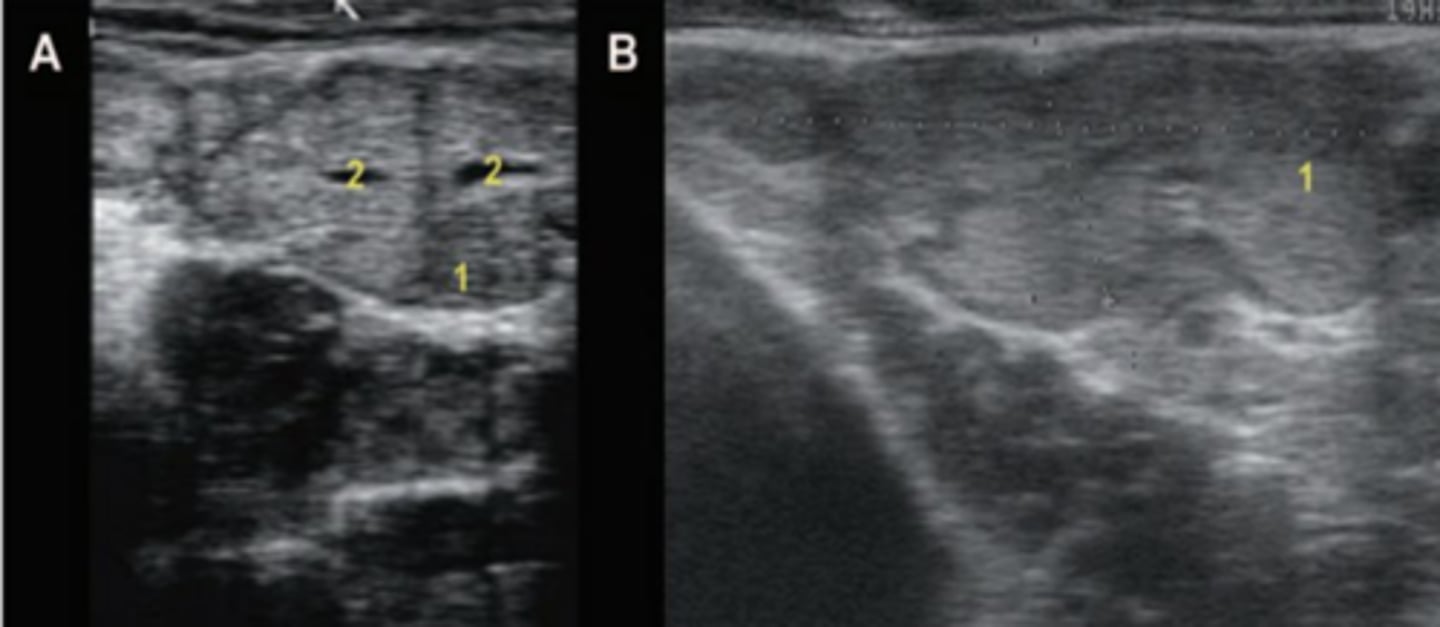
What is 1?
parenchyma
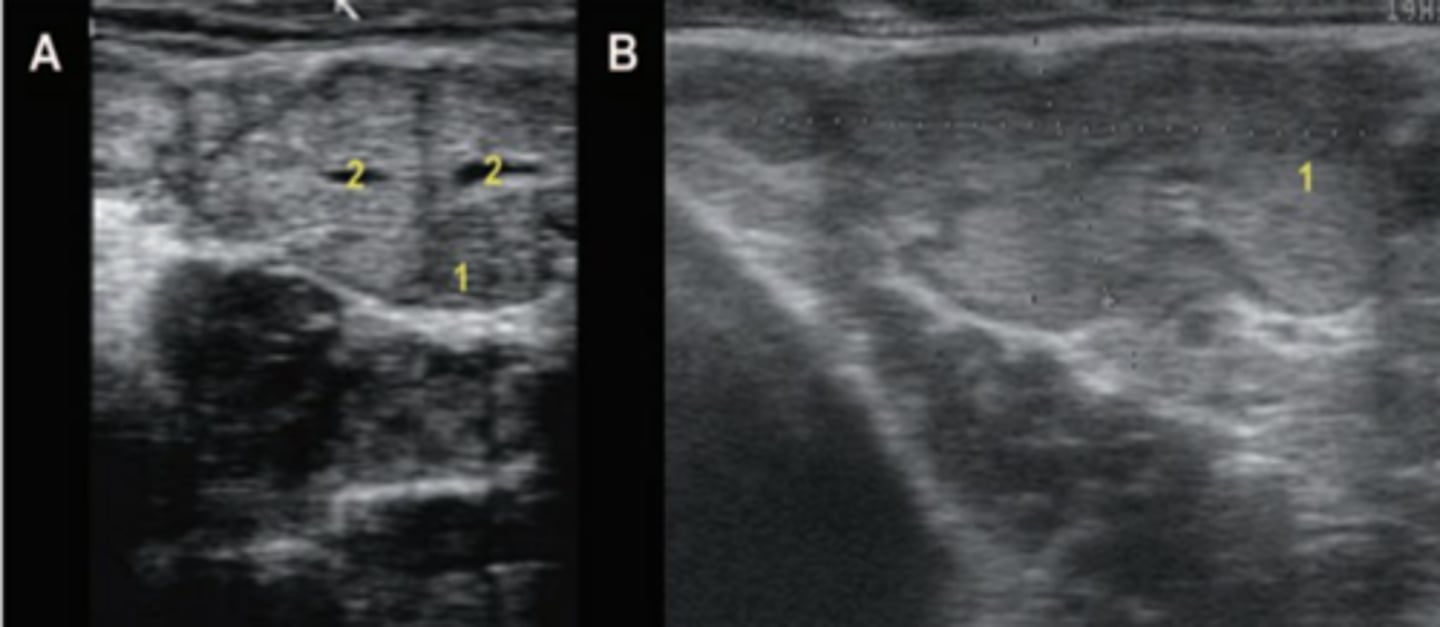
What is 2?
lumen of the vesicular gland.
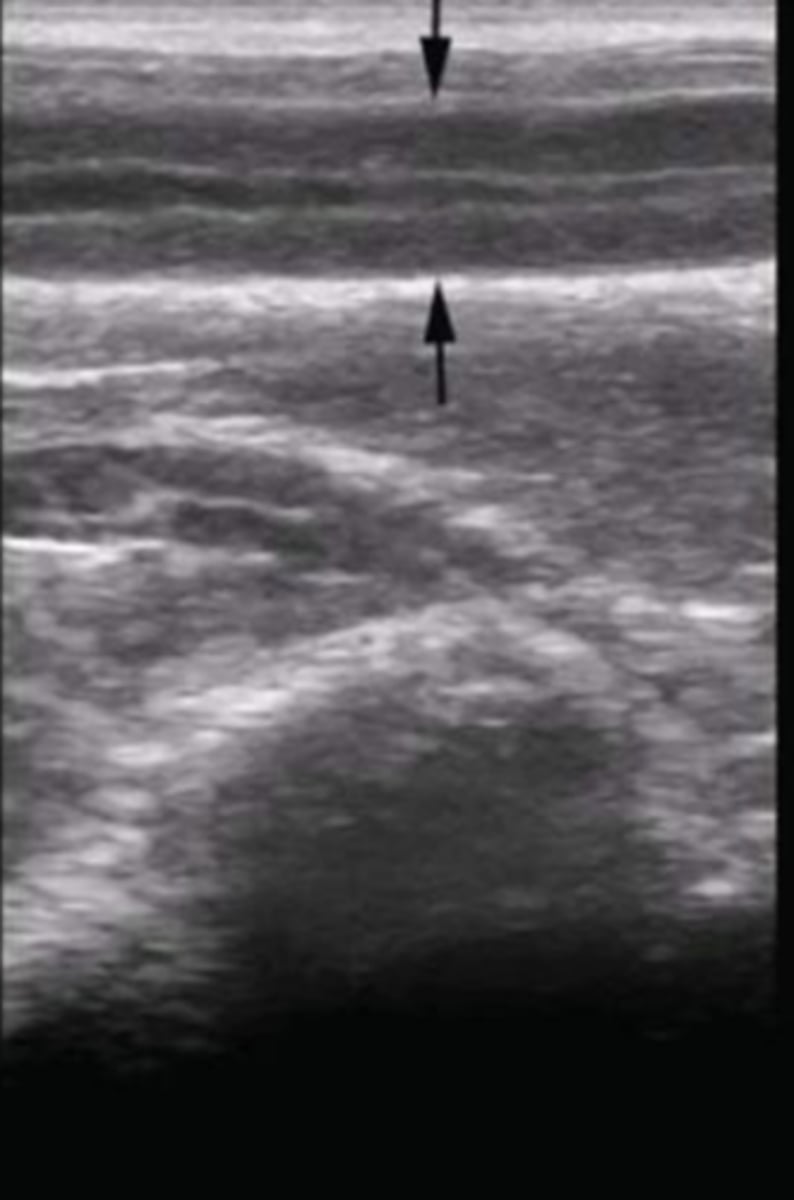
equine ampulla (sagittal/longitudinal view)
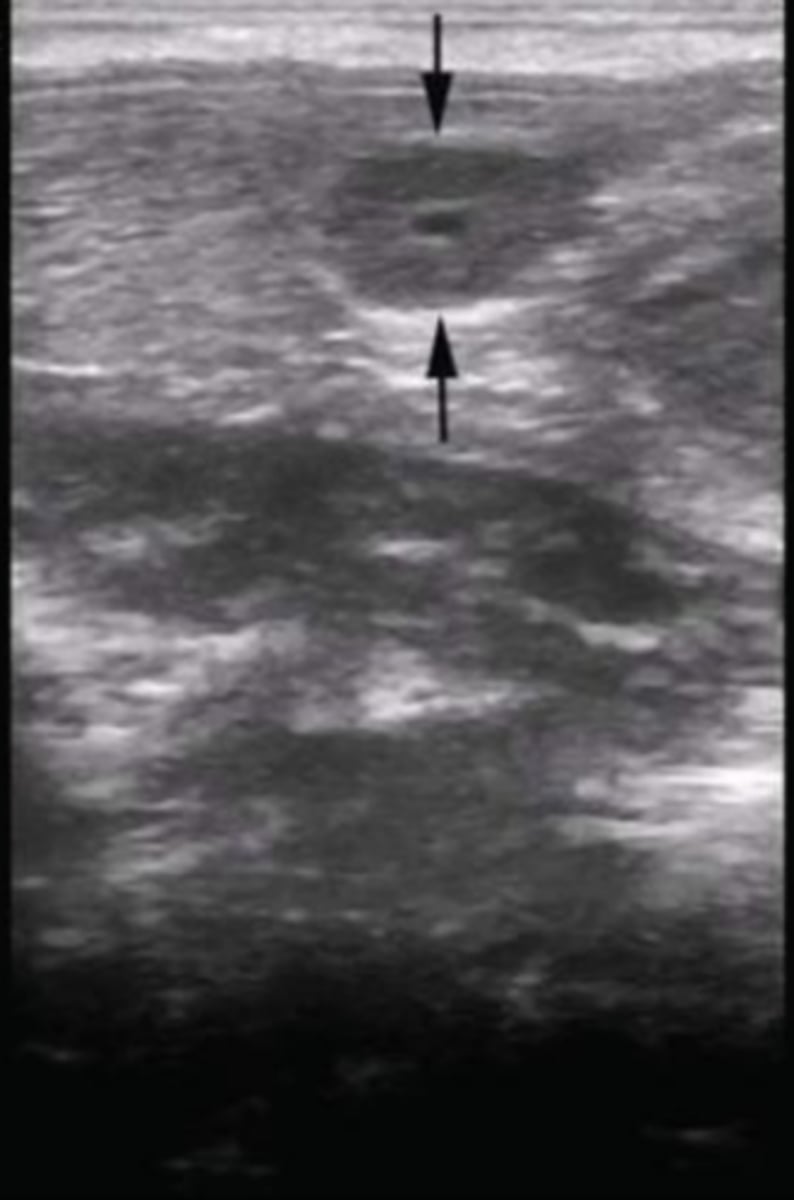
equine ampulla (transverse view)
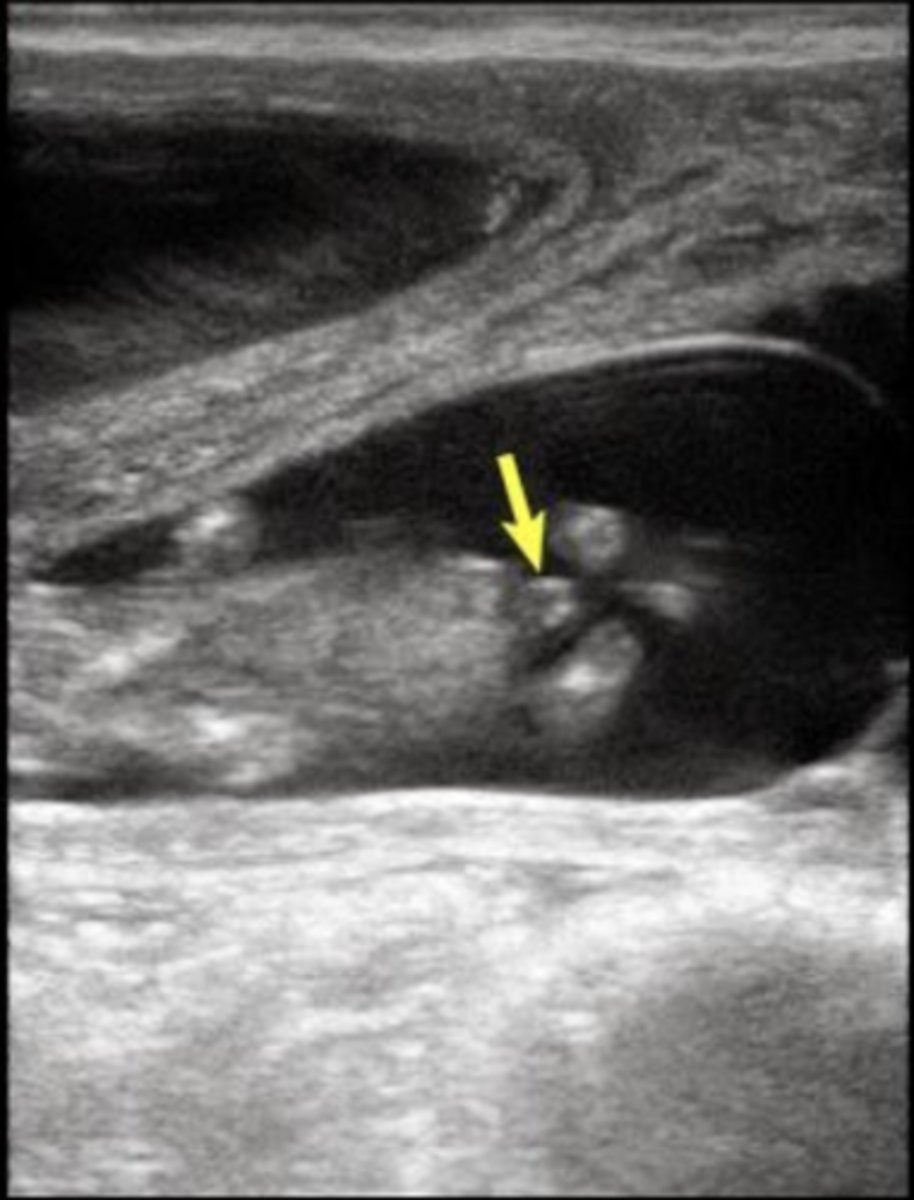
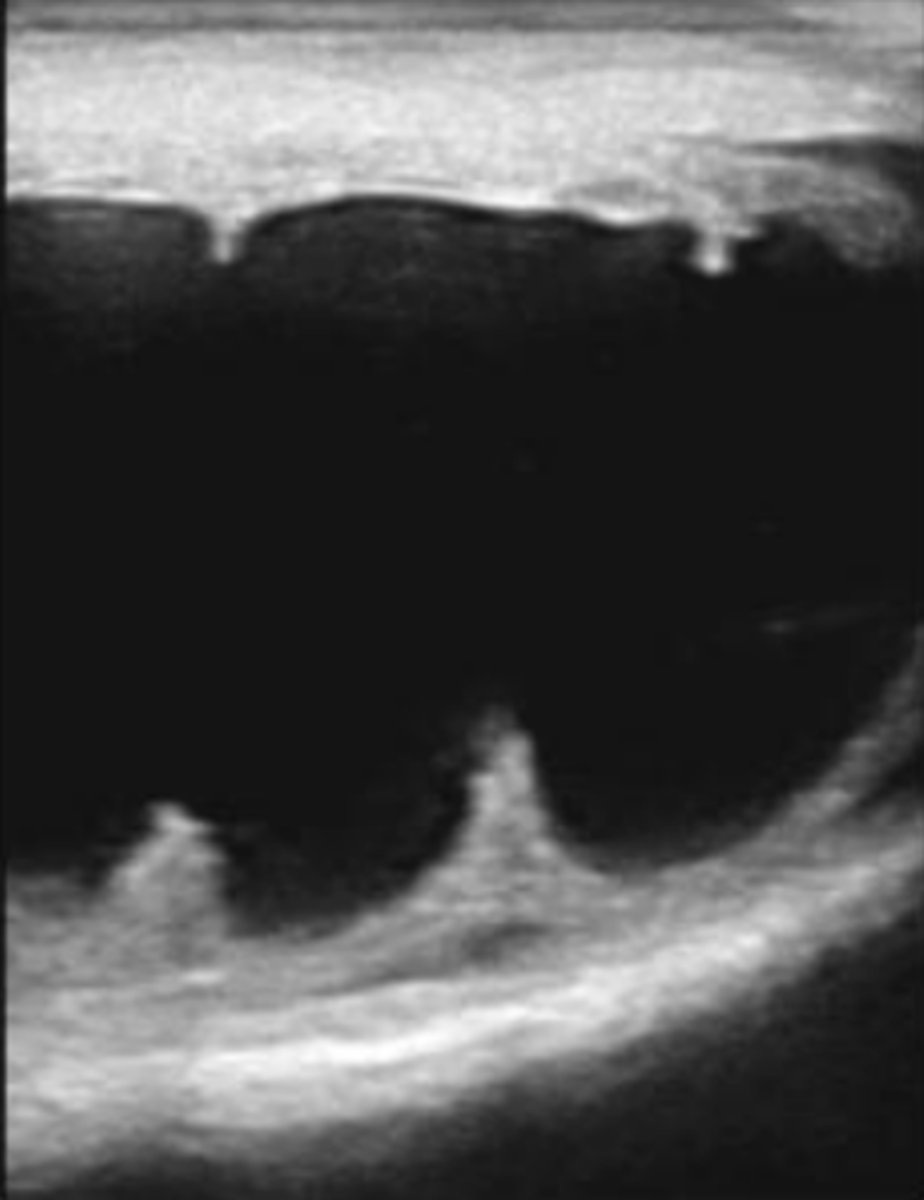
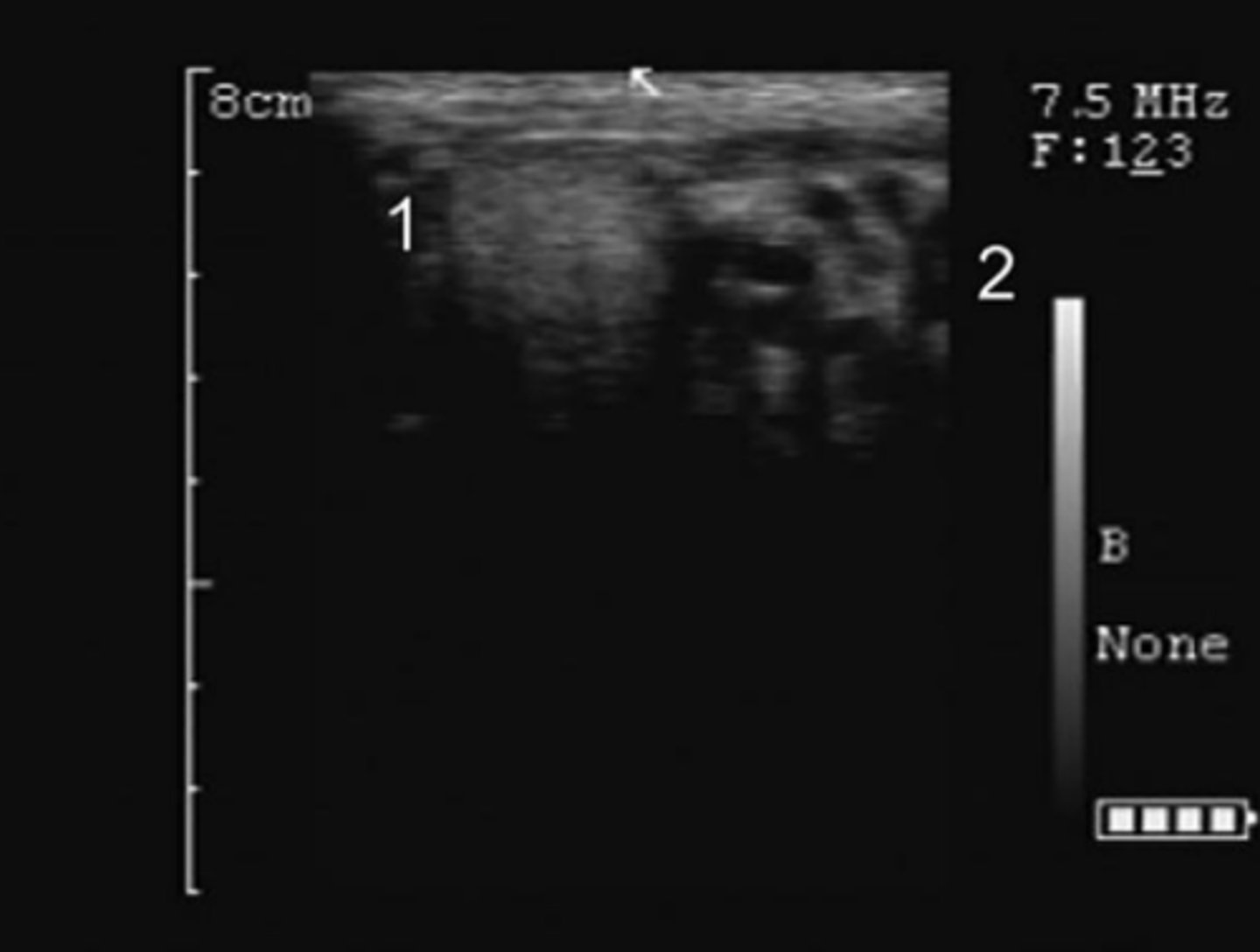
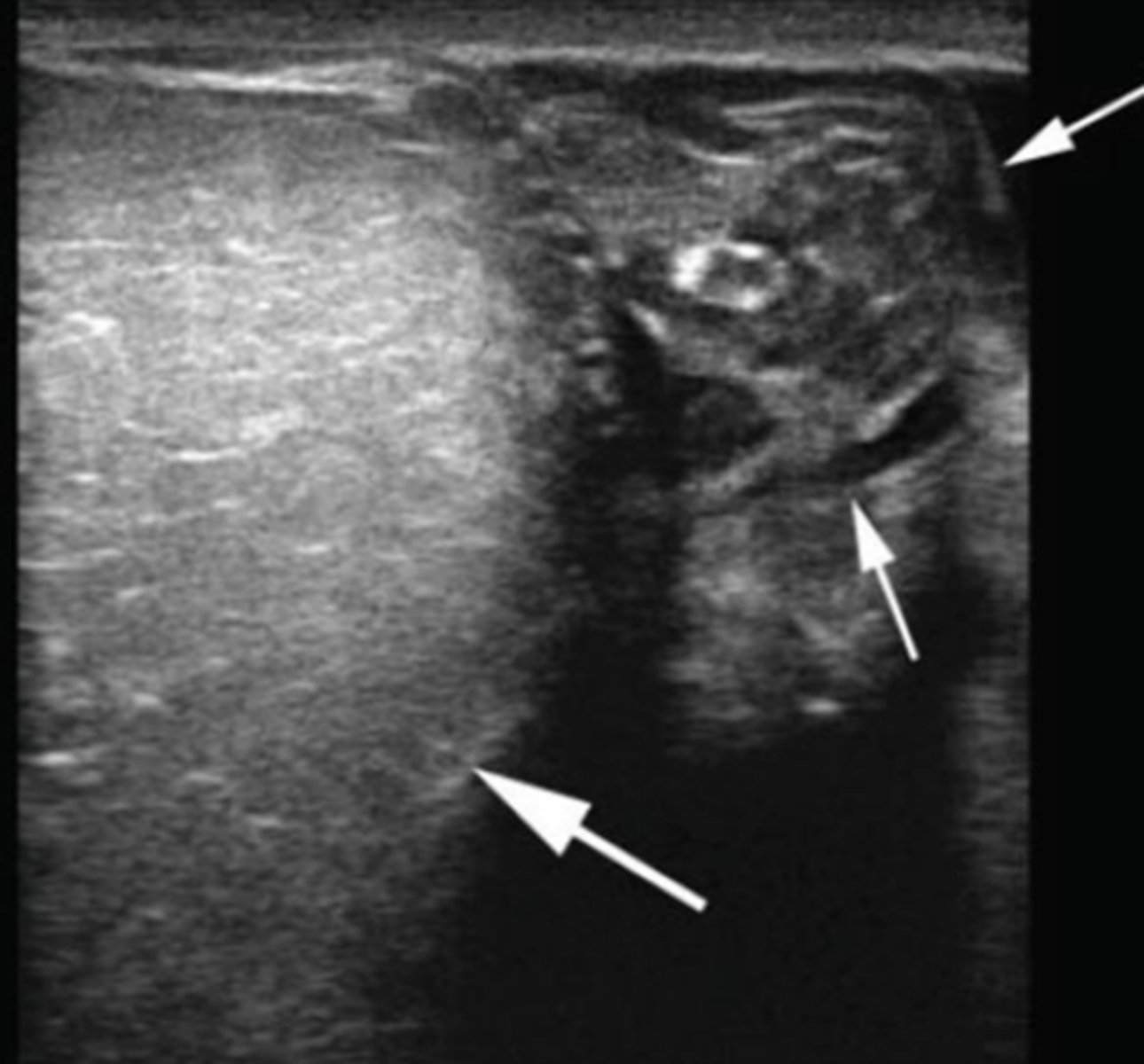
What is the white arrow pointing to?
hydrocele
hematocele
spermatic cord torsion
longitudinal and transverse views of a left testis with seminoma (testicular neoplasia)
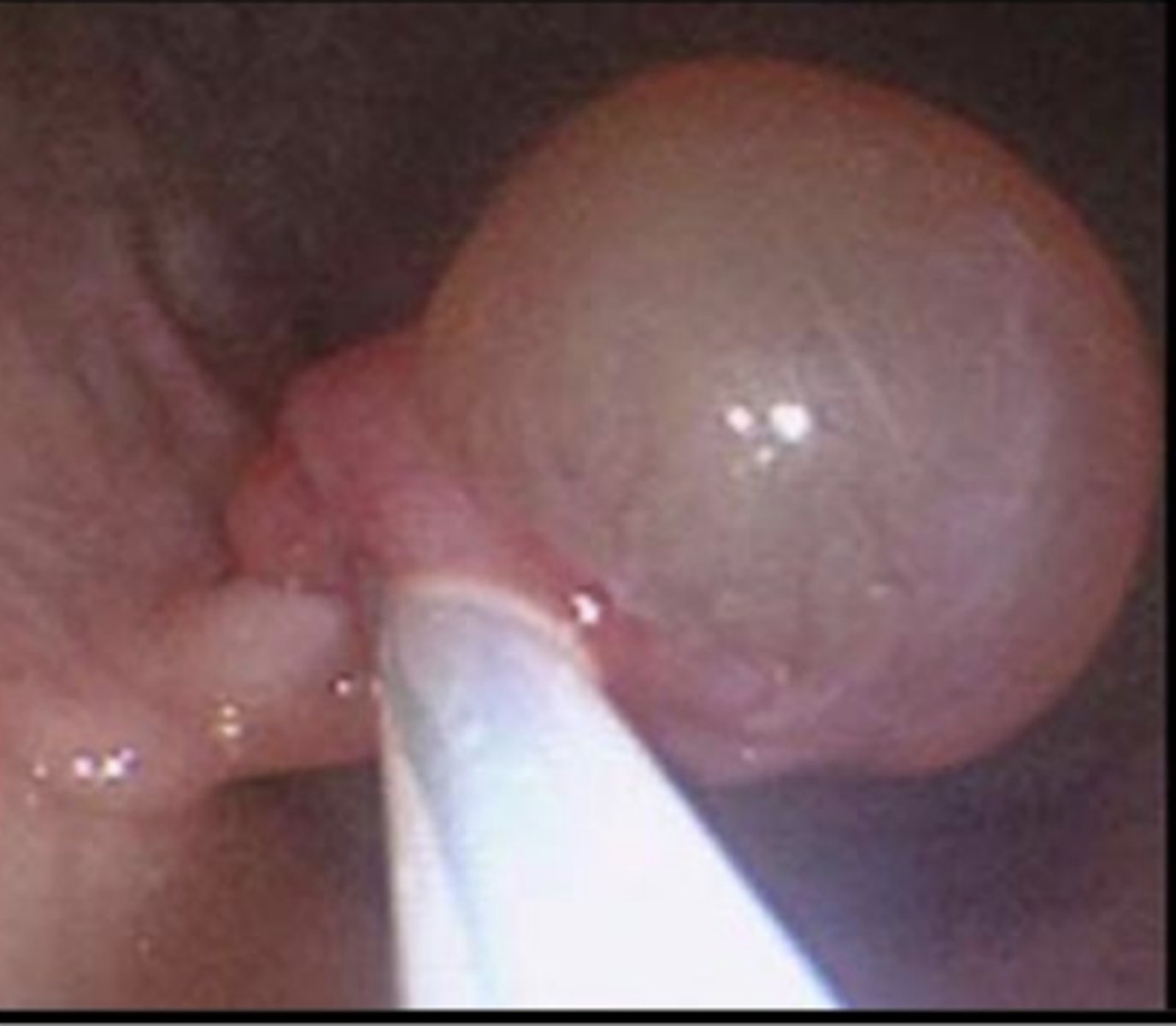
endometrial cyst visualized using endoscopy
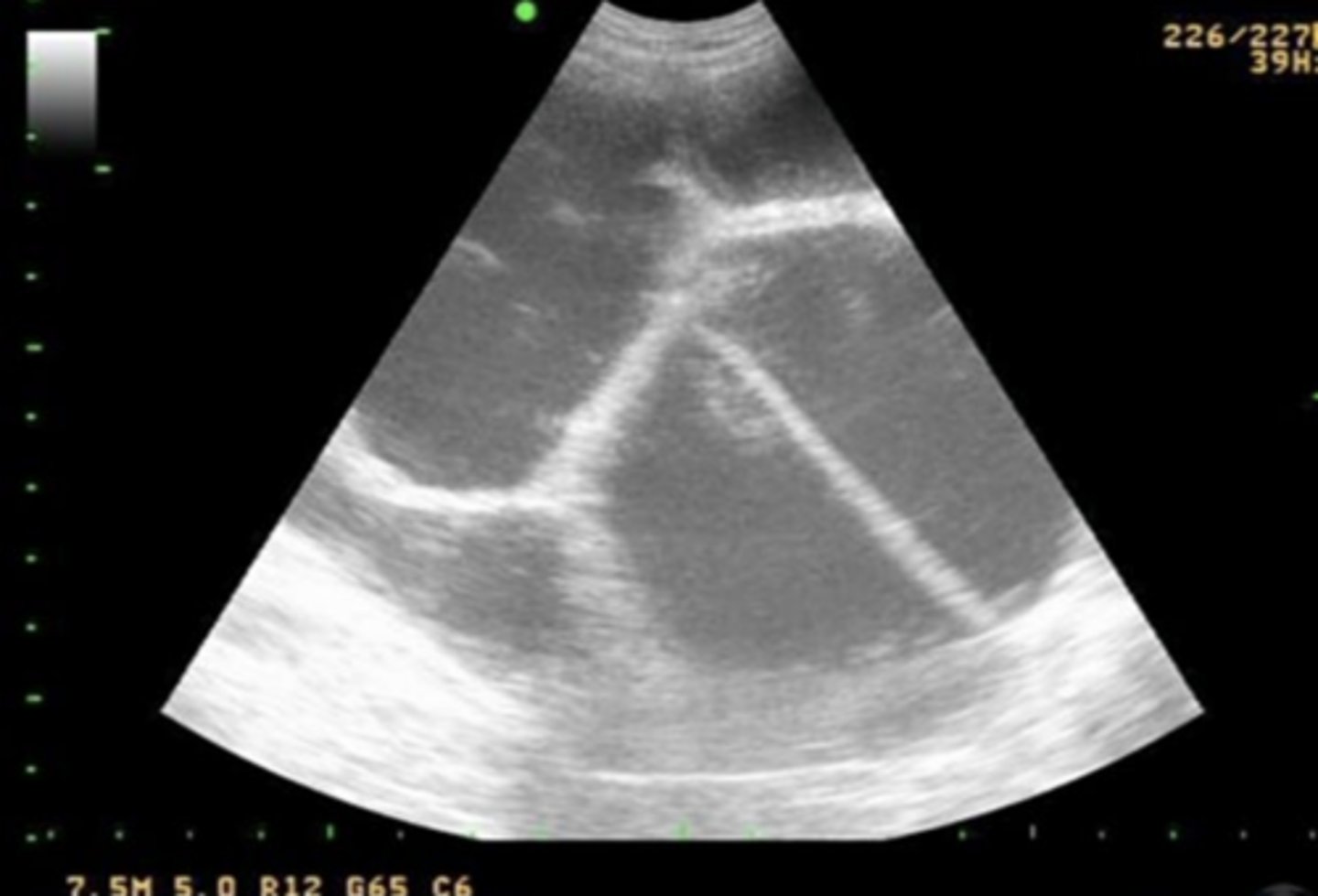
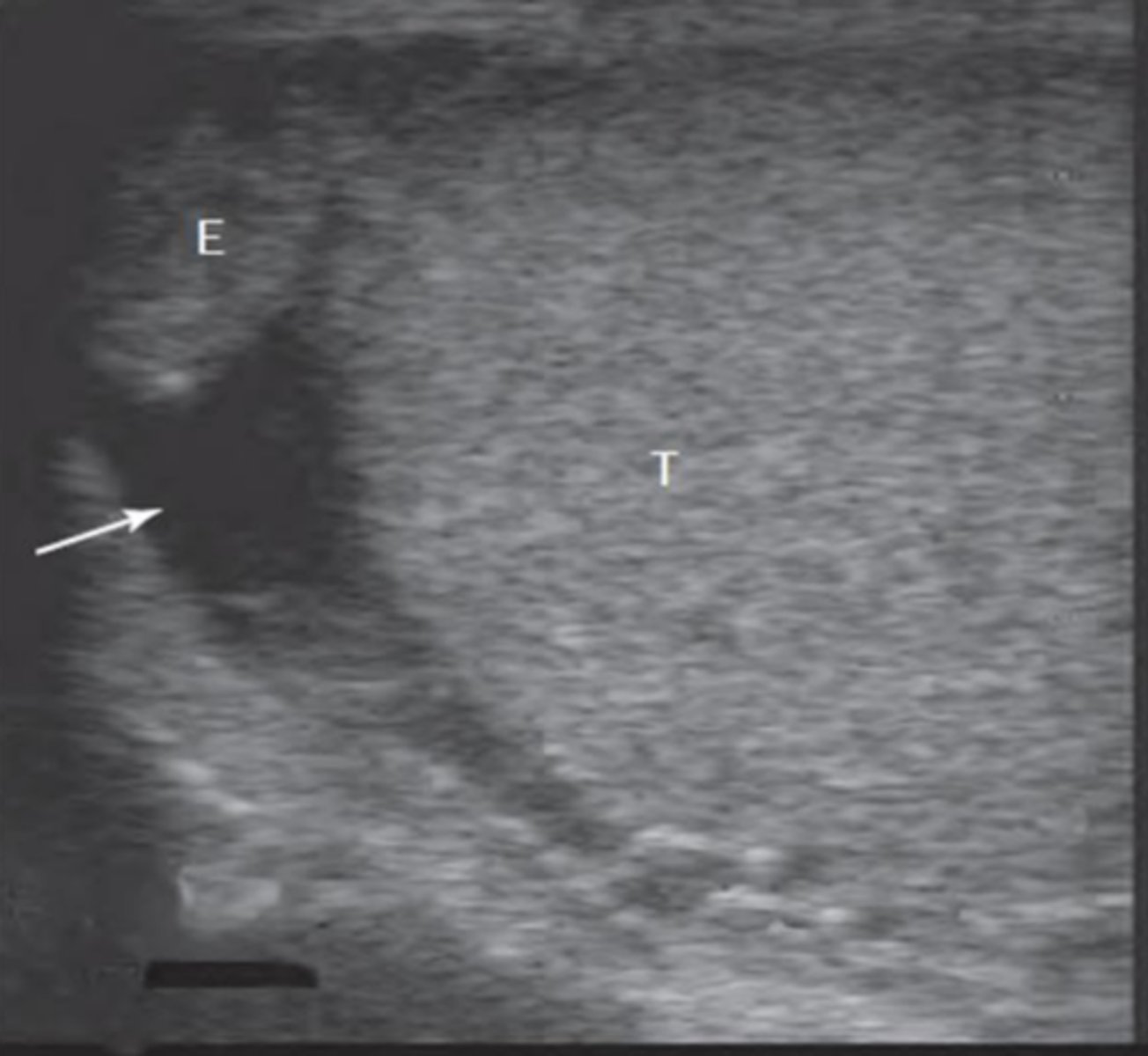
A veterinarian is examining a stallion that presents with an enlarged scrotum. Ultrasonography of the scrotum reveals the findings shown in the picture. What is the most likely diagnosis?
hydrocele
What probe is used for small animal repro system US?
7.5-12 MHz linear or microconvex transducer
What positioning and approach is used for small animal repro system US?
dorsal or lateral recumbency with a transabdominal approach
What preparation is used for small animal repro system US?
clip hair (if feasible), apply coupling medium, use alcohol if too much hair and not allowed to clip
How do normal small animal ovarian structures appear on US?
1. isoechoic to hypoechoic to surrounding tissues
2. often obscured by intestines
3. oval, heterogeneous with follicles (anechoic) or corpora lutea (hypoechoic)
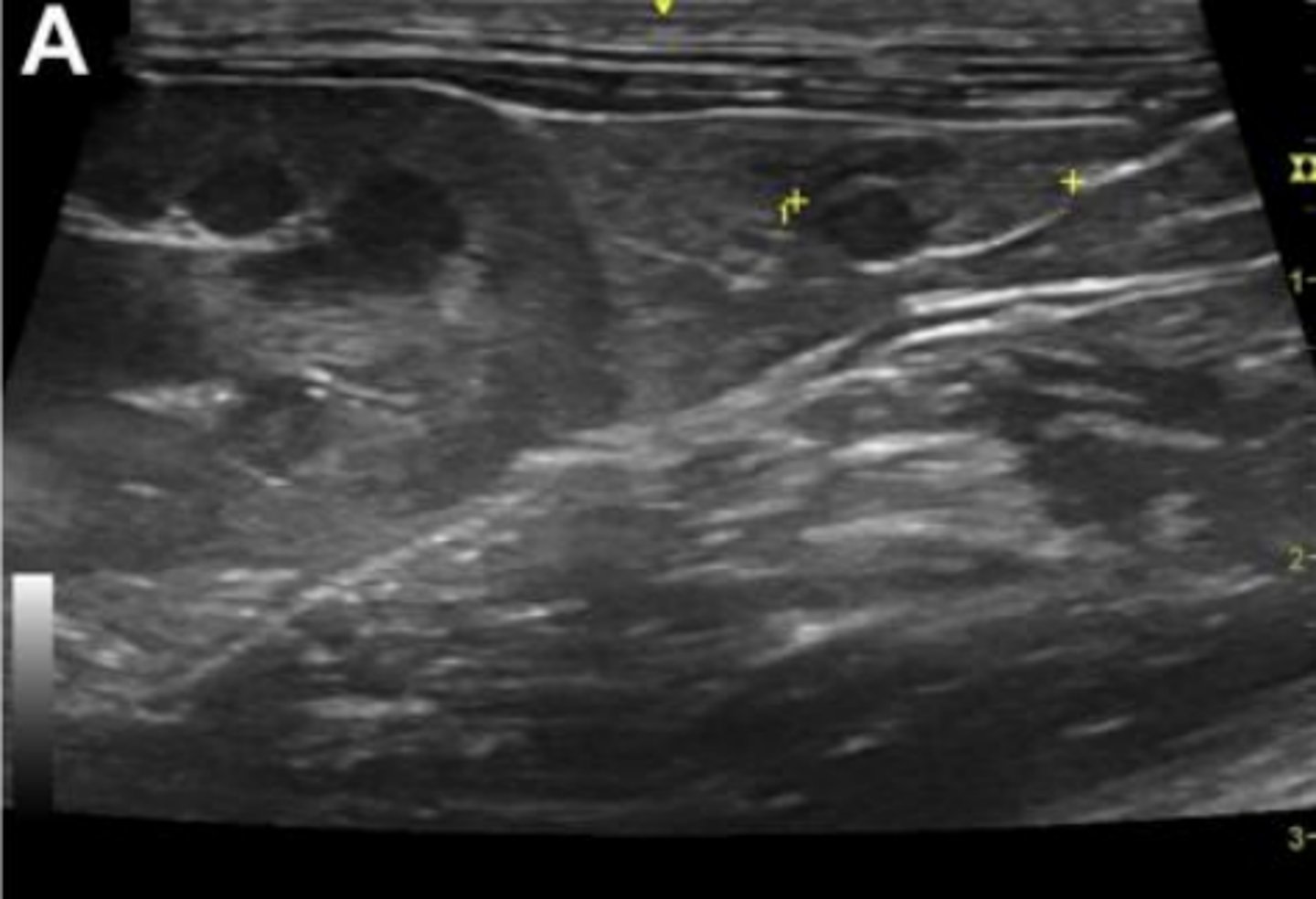
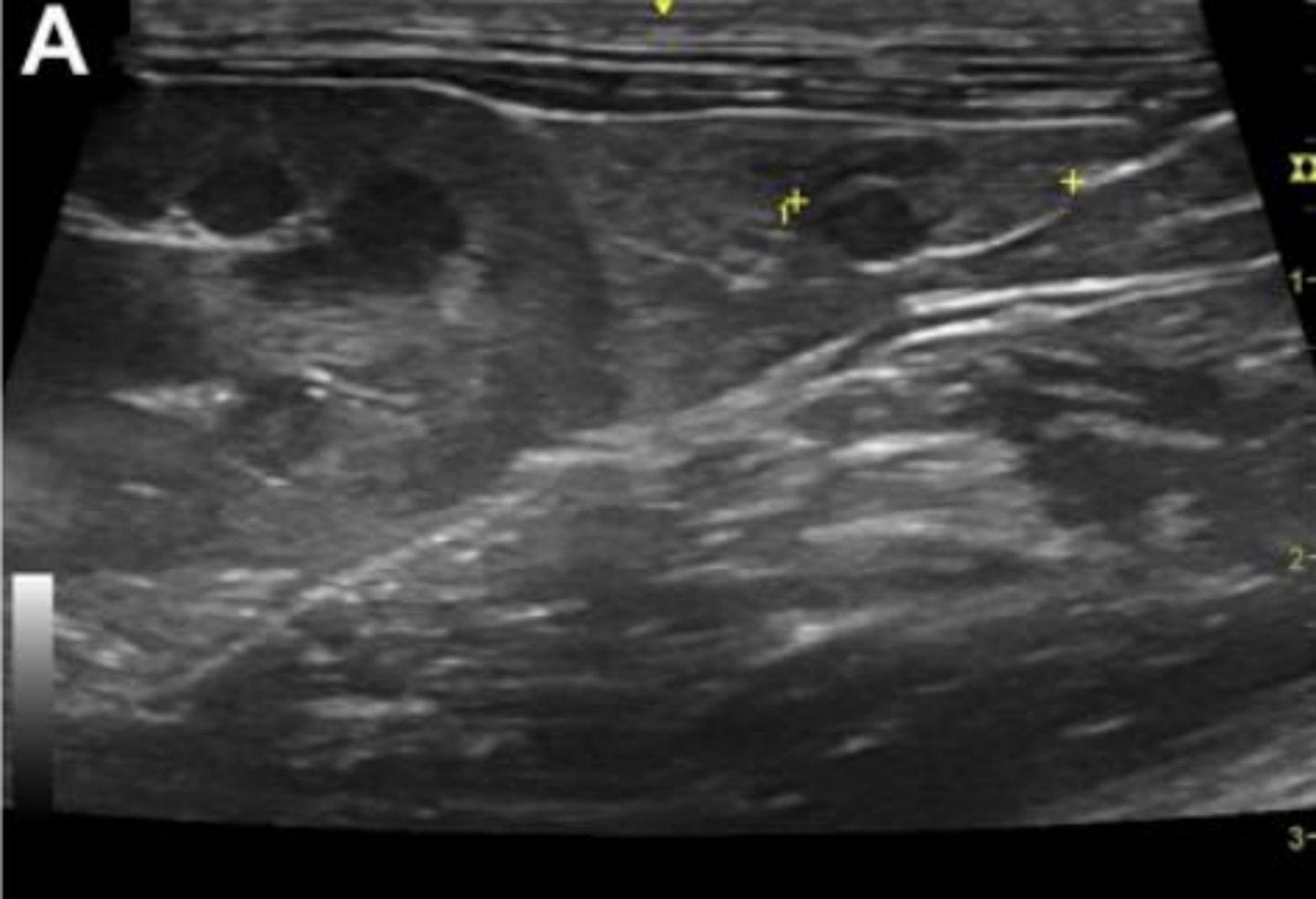
normal ovary (marked by caliper points) in longitudinal plane with a normal follicle
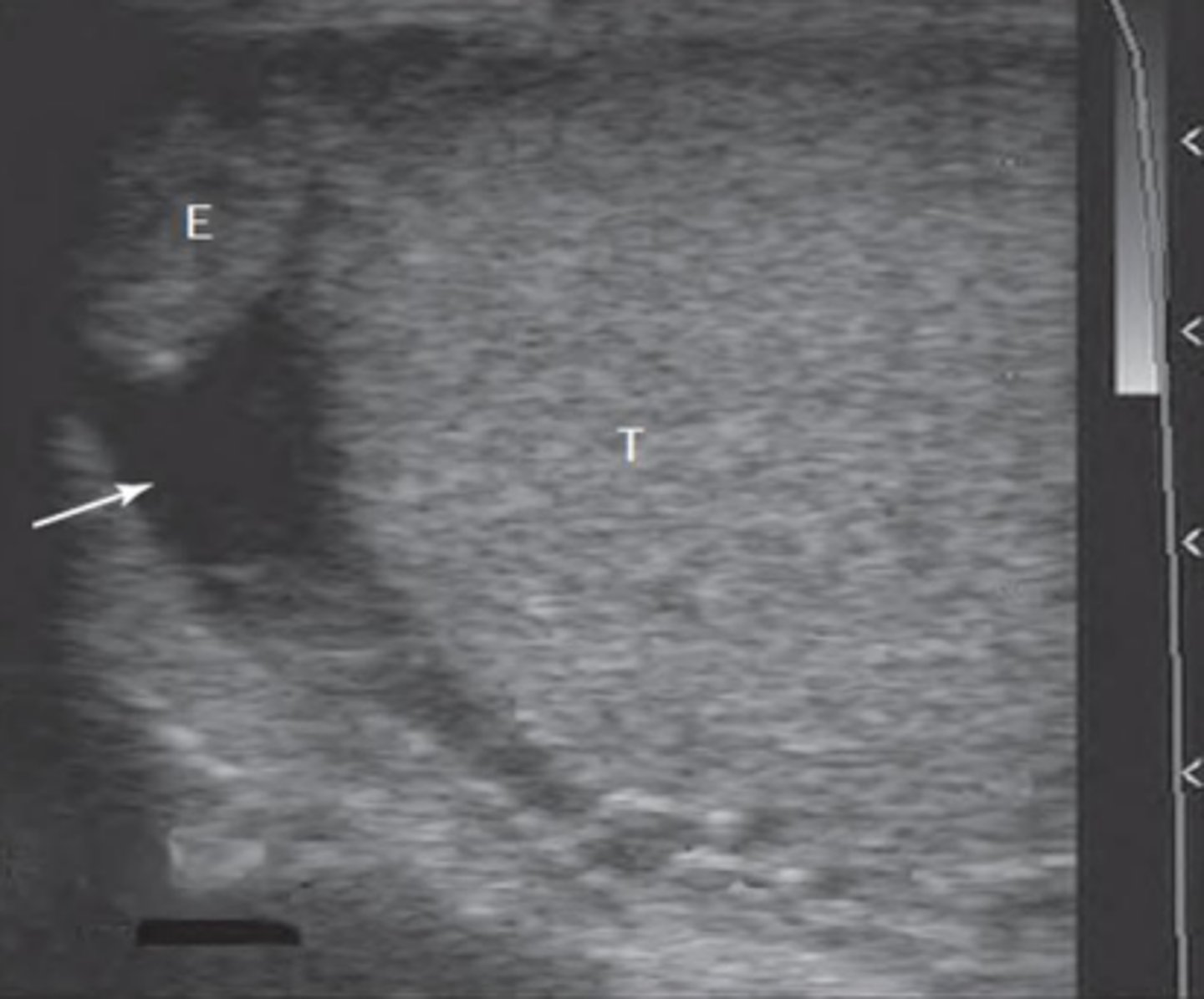
What is seen in the left portion of the image that serves as the most consistent landmark for locating the ovary?
caudal pole of the ipsilateral kidney
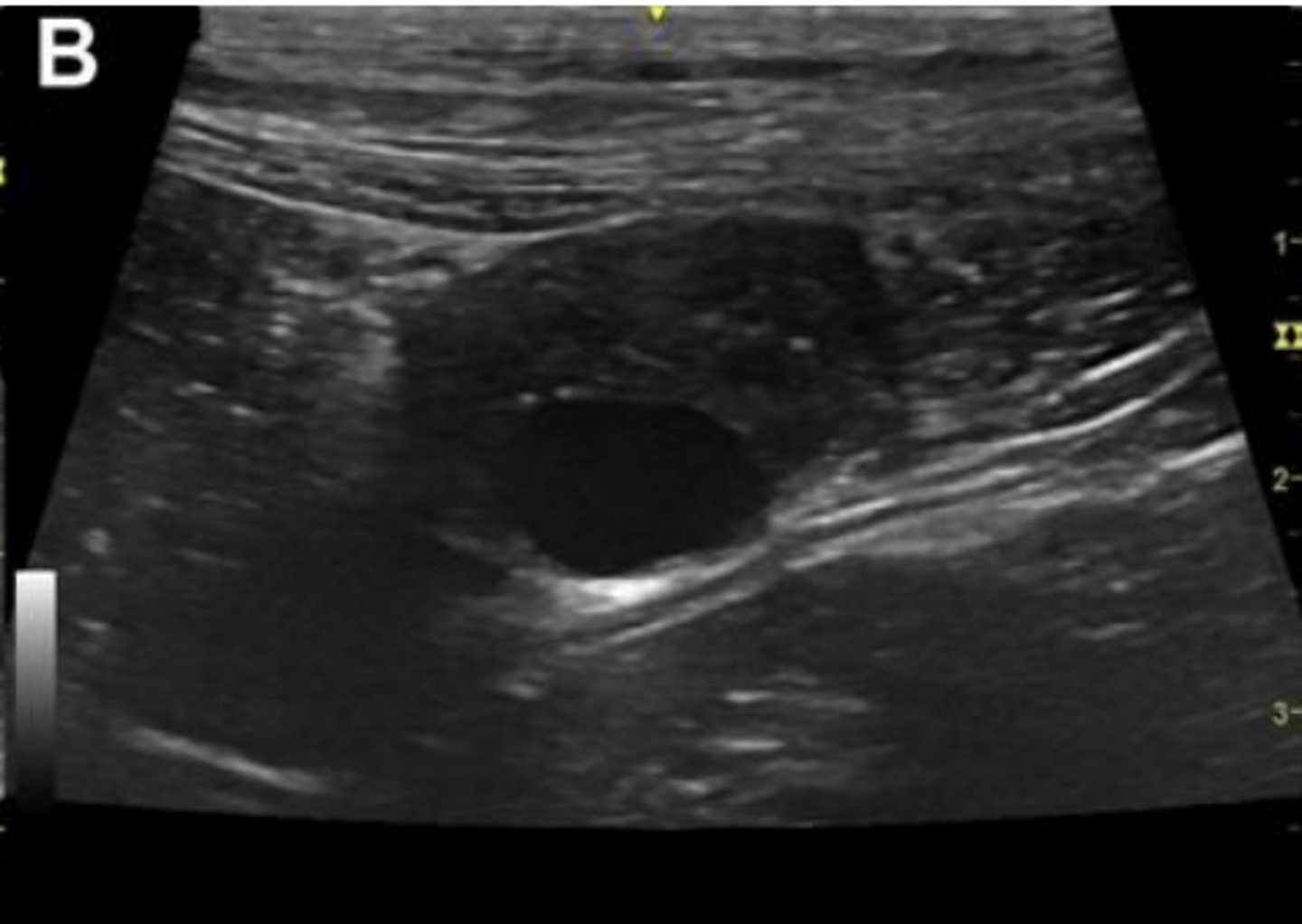
normal ovary with an estrus follicle
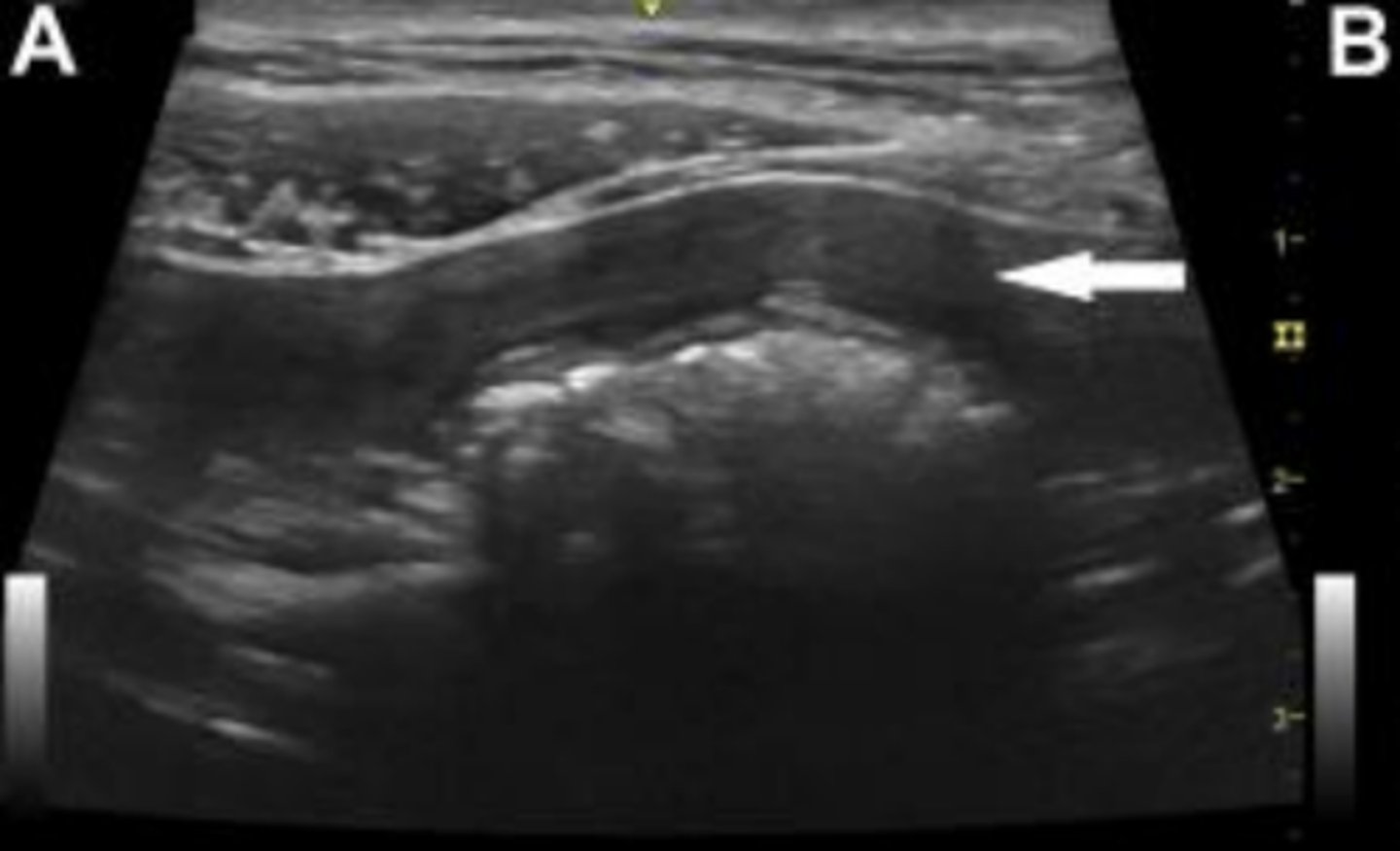
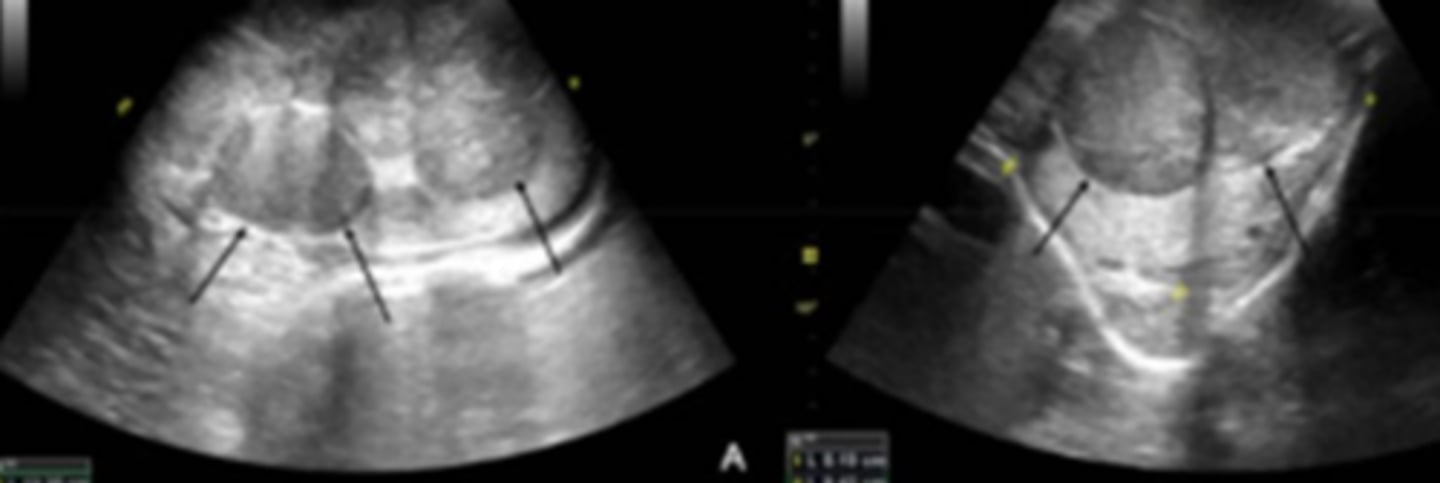
uterus in the longitudinal plane
uterus in the transverse plane
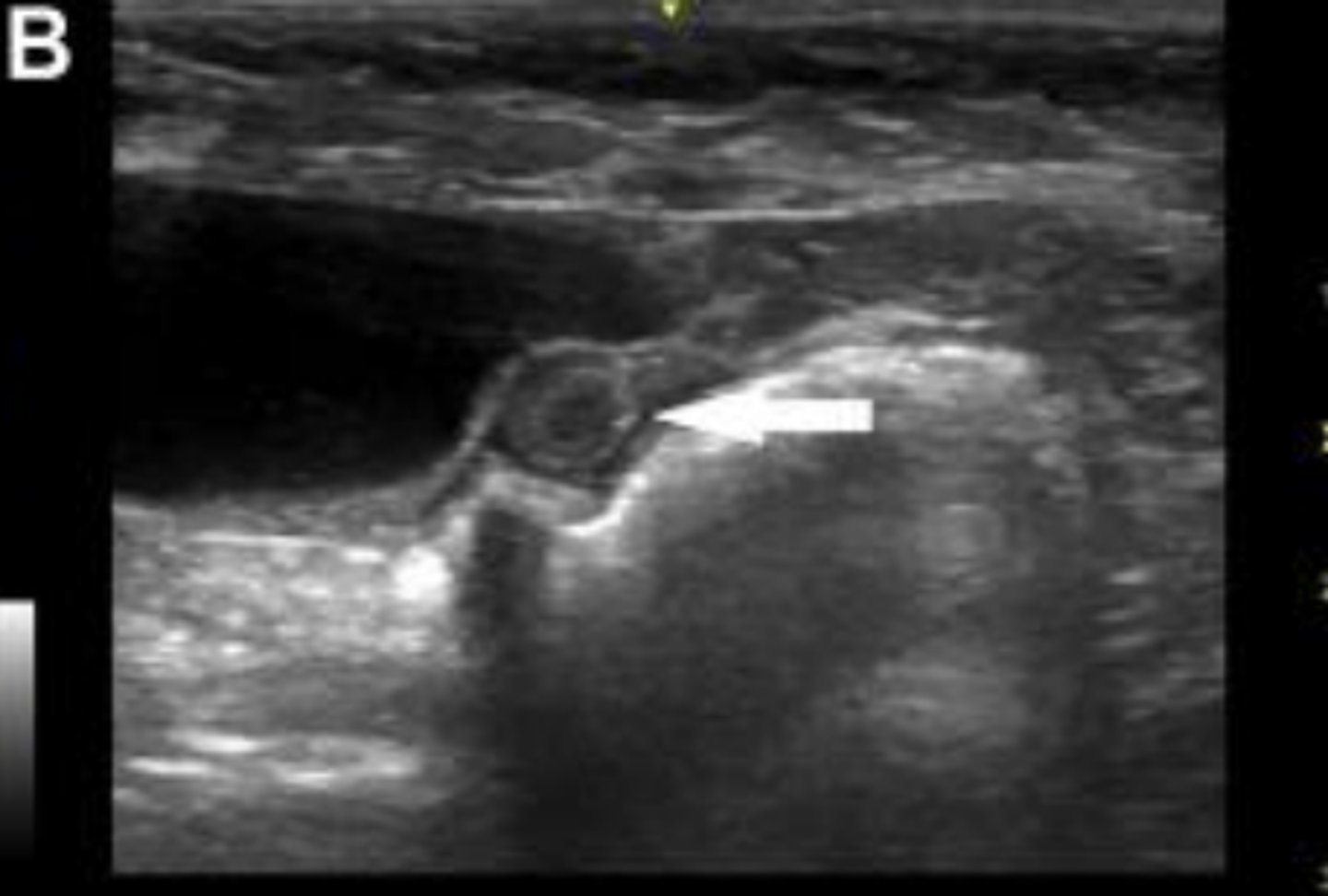
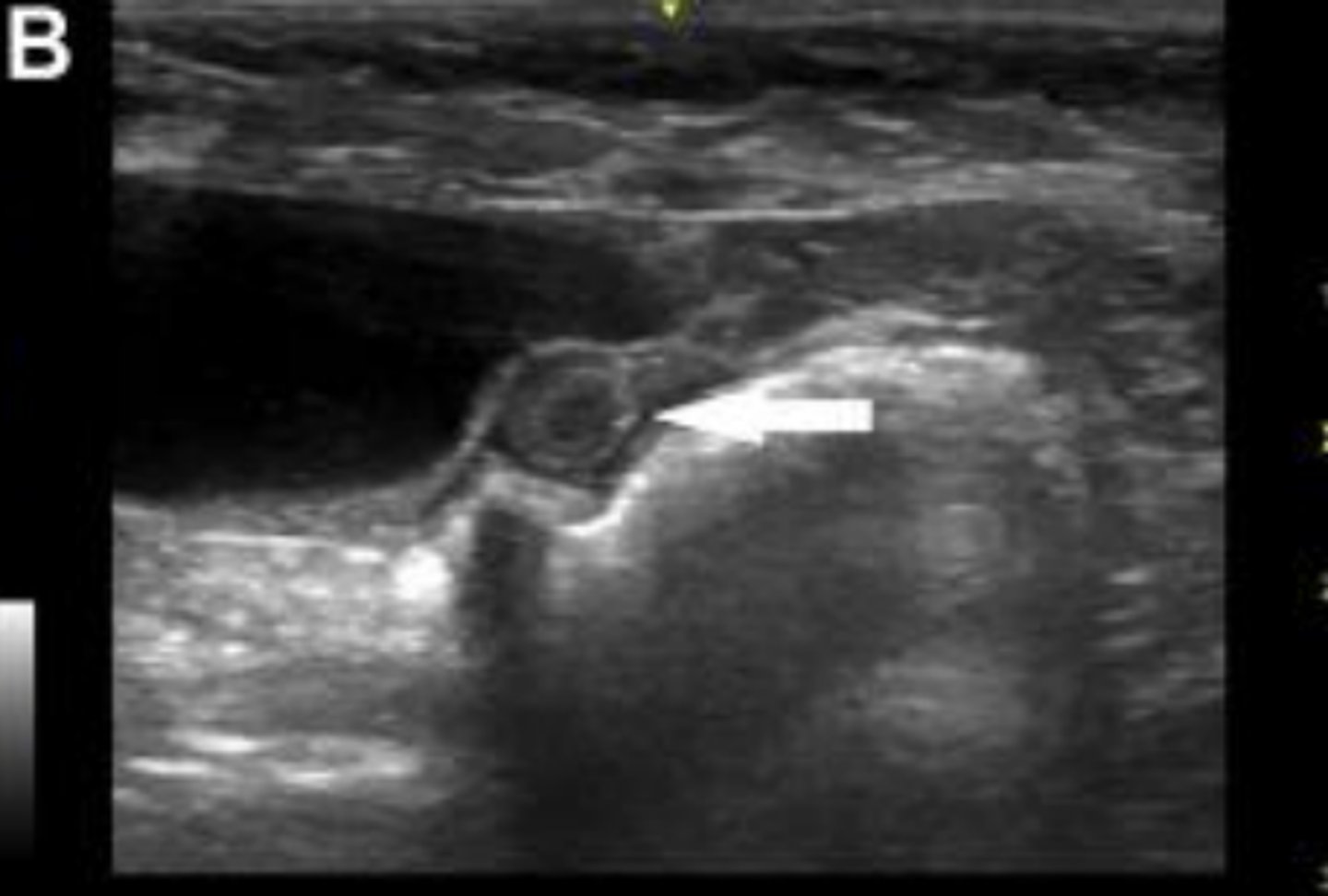
What is the white arrow pointing to?
uterine body located between the urinary bladder (filled with anechoic urine) and the colon (with characteristic hyperechogenicity and gas shadowing)
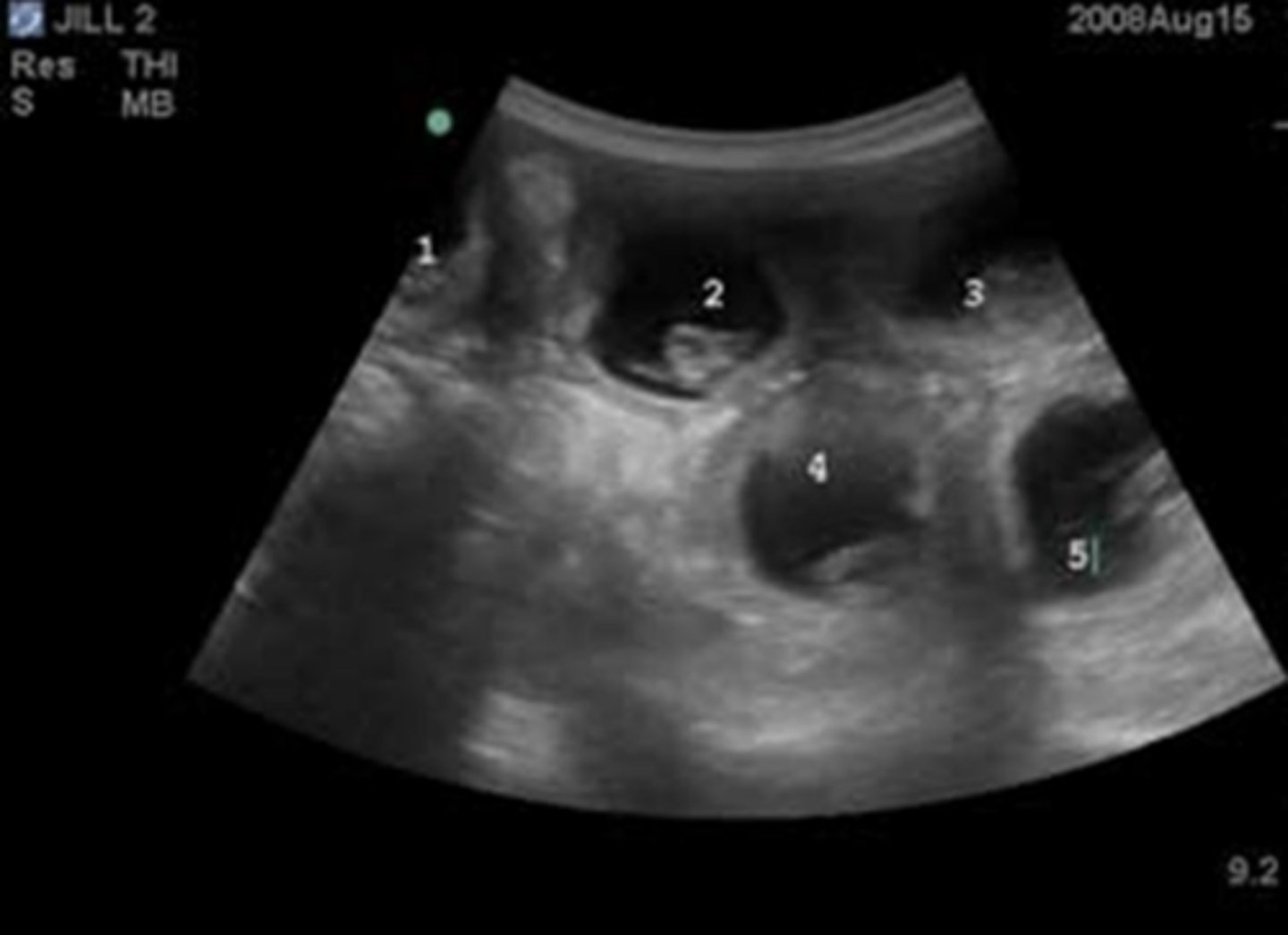
multiple gestational sacs in a bitch
What can be measured to estimate gestational age or days before parturition when ovulation date is unknown?
fetal biparietal diameter
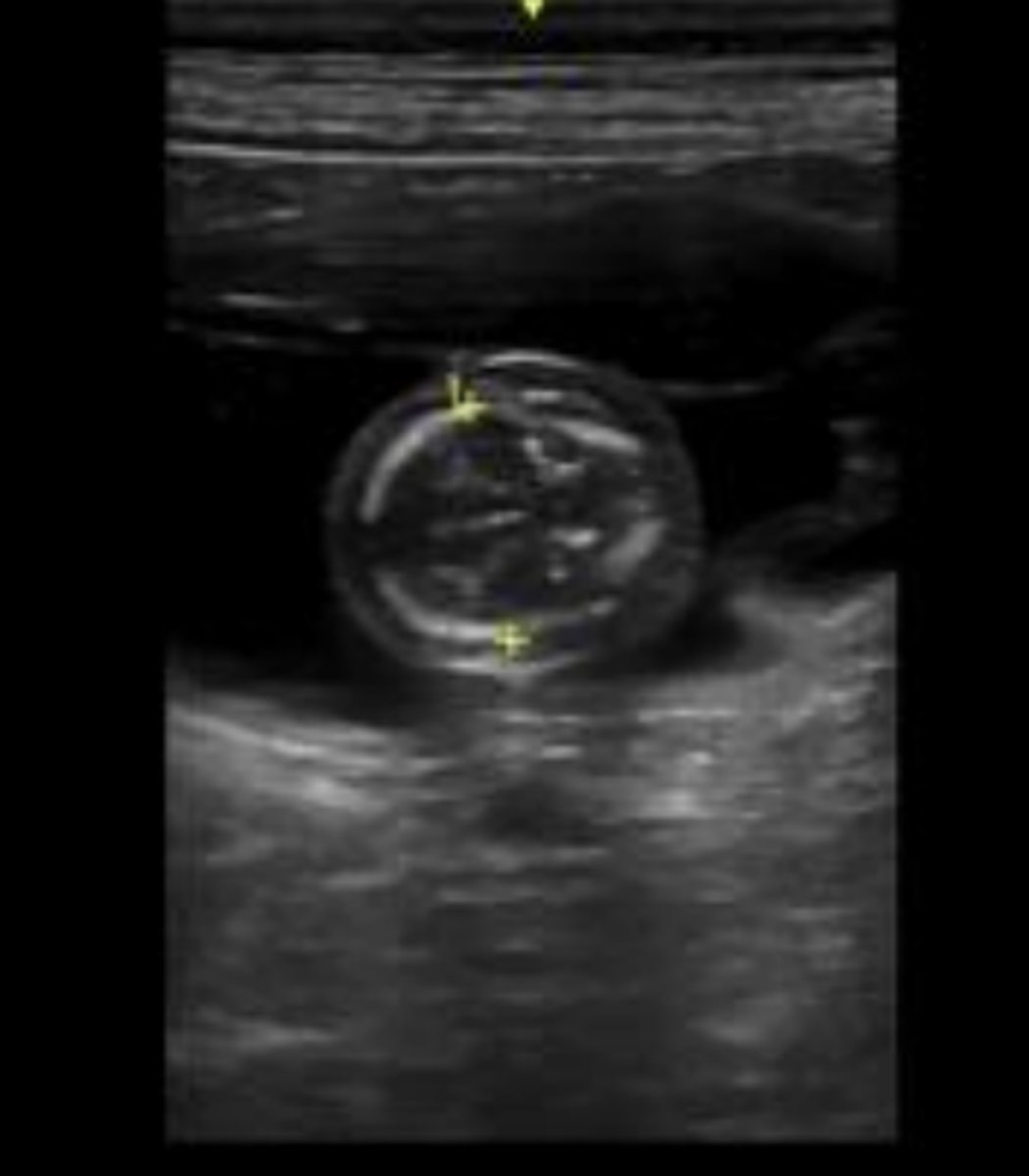
fetus estimated to be about 40 days
What is the final organ in a fetus to develop their sonographic identity with layering evident between day 57 and day 63 from the LH peak?
intestines
What marks the final maturation of the intestines?
constant peristalsis
What other organ development marks fetal maturity?
kidneys
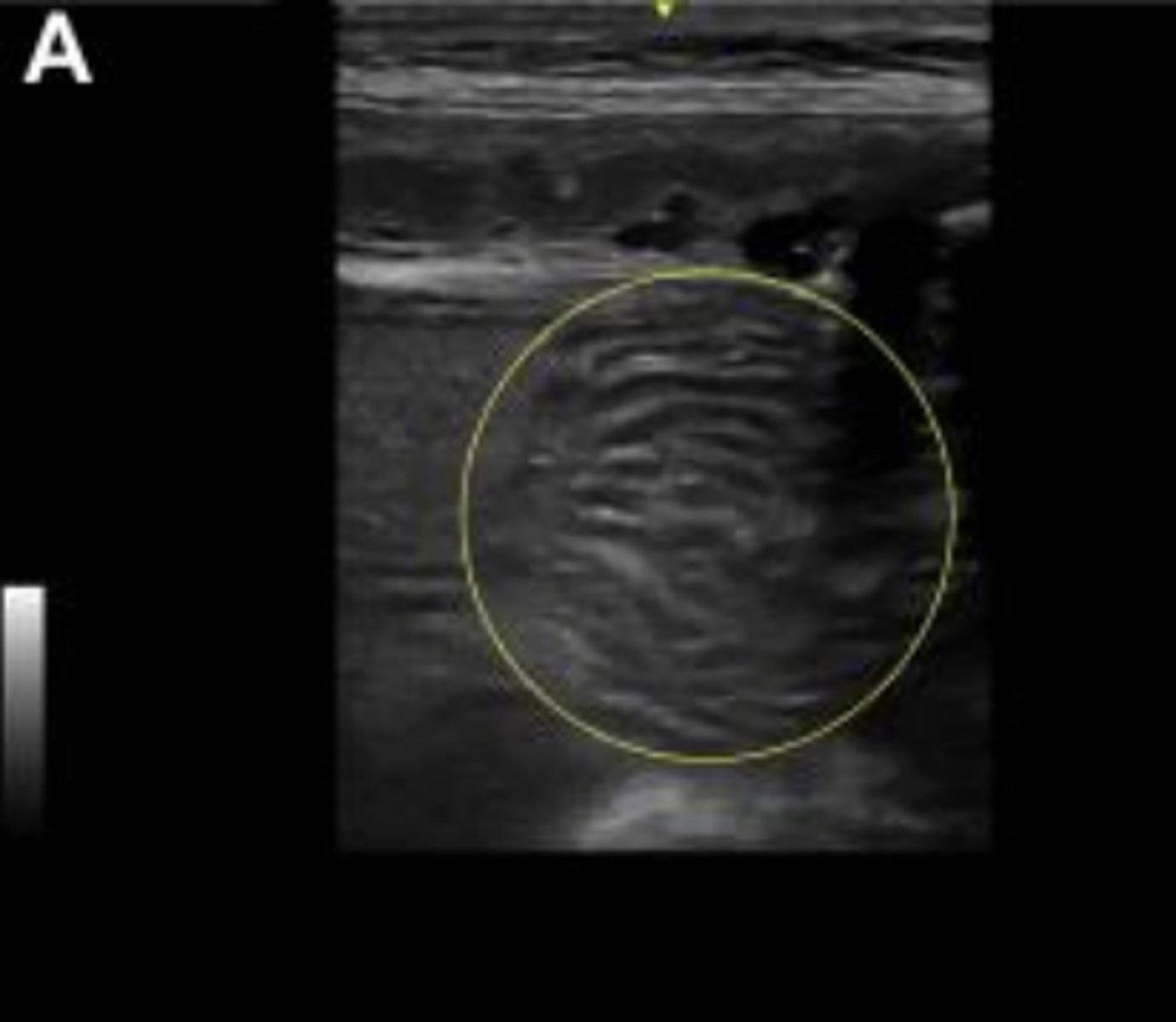
developed intestines in a fetus 3 days prior to parturition
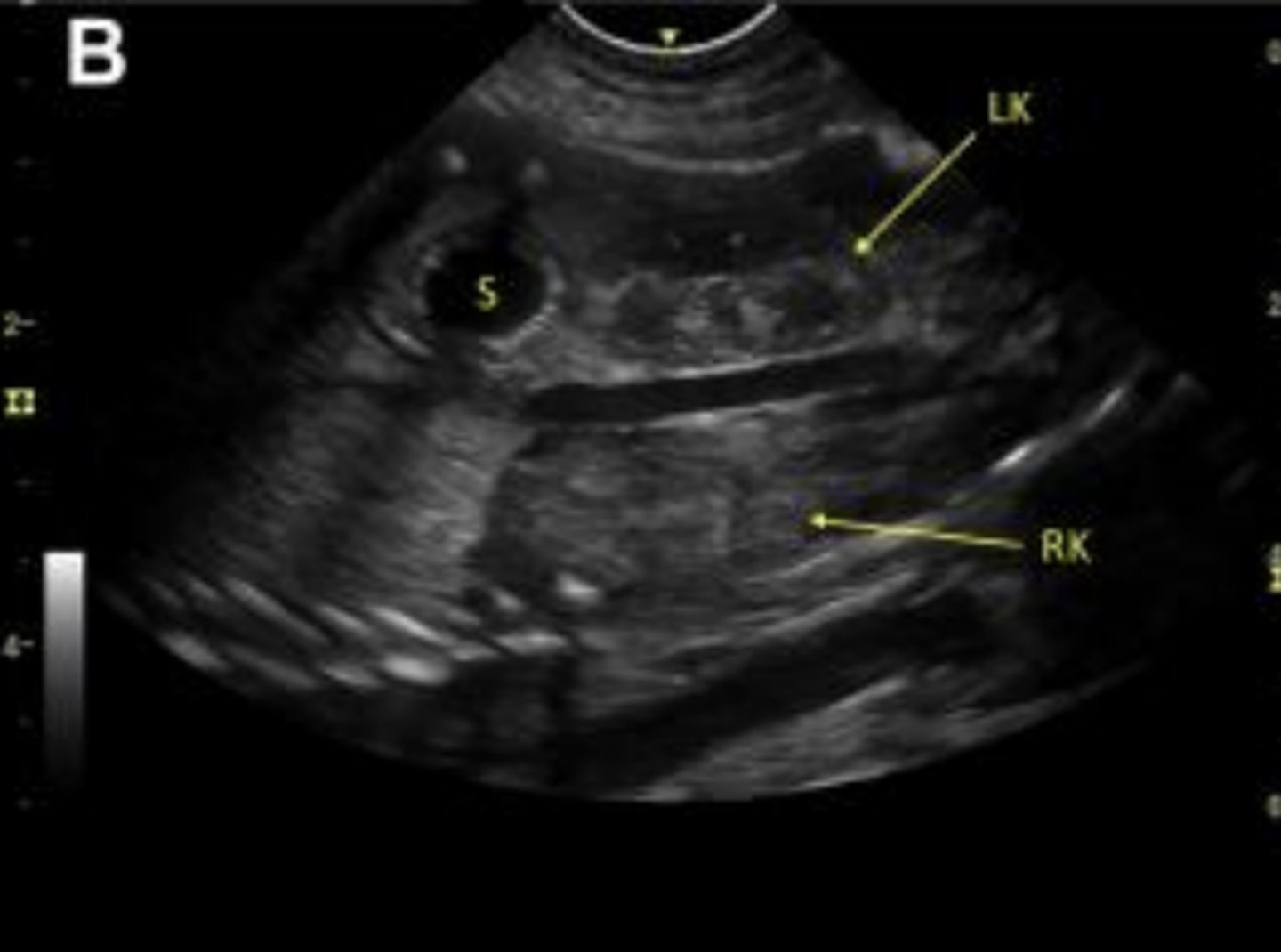
developed stomach (S) and left and right kidneys in a fetus 3 days prior to parturition
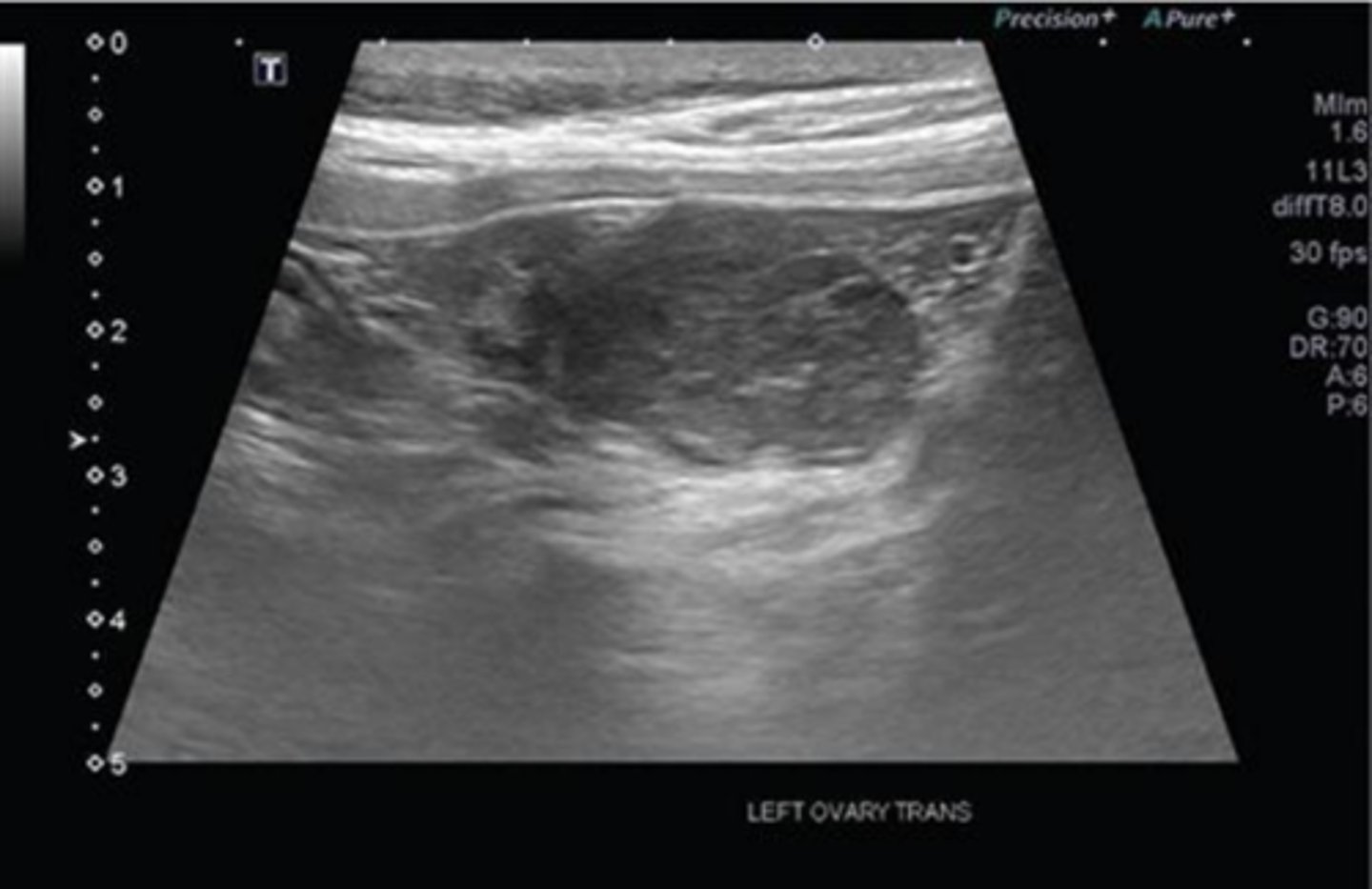
granulosa cell tumor in a bitch
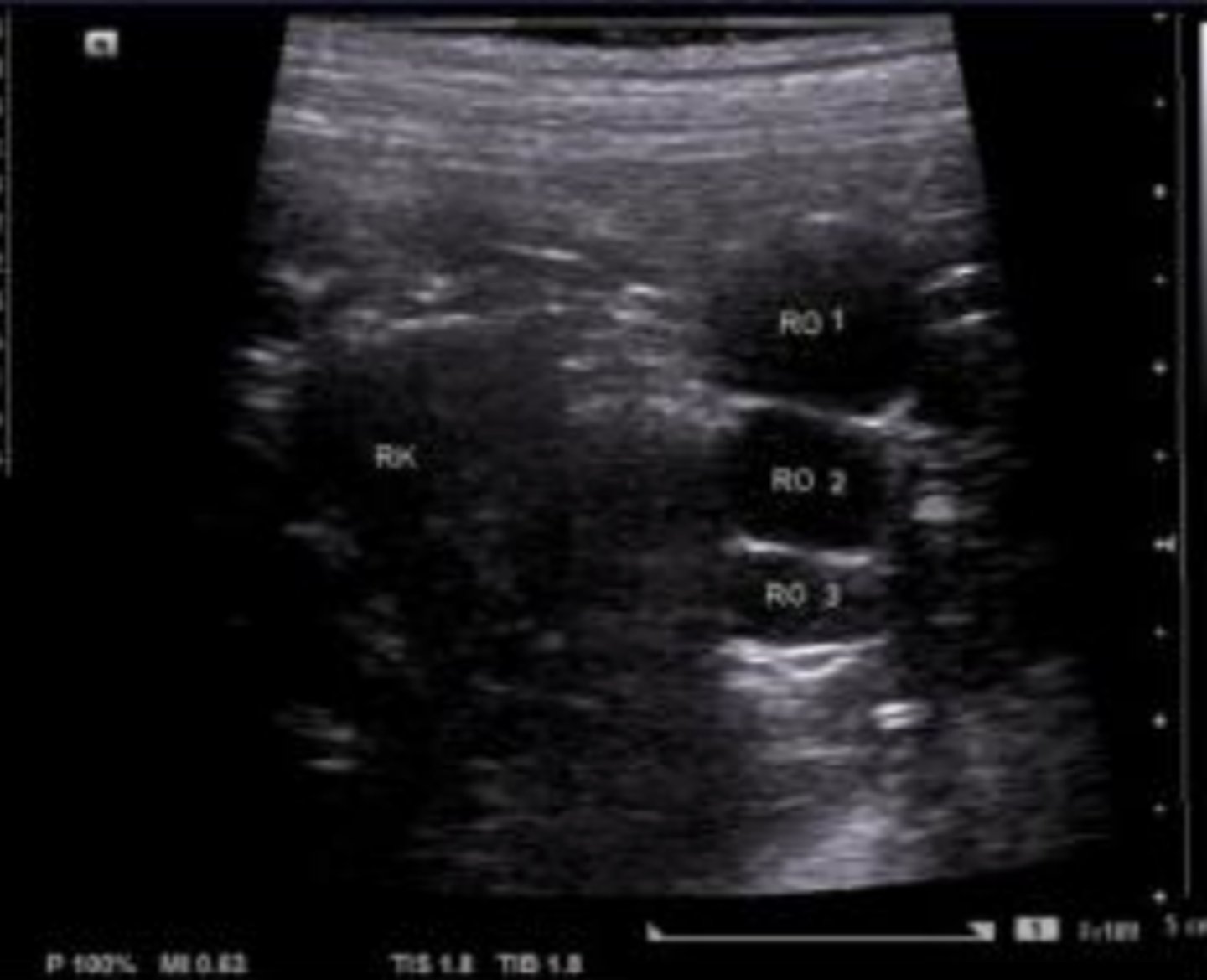
ovarian cysts in a bitch
What uterine pathologies have the same sonographic appearance?
pyometra, mucometra, and hydrometra
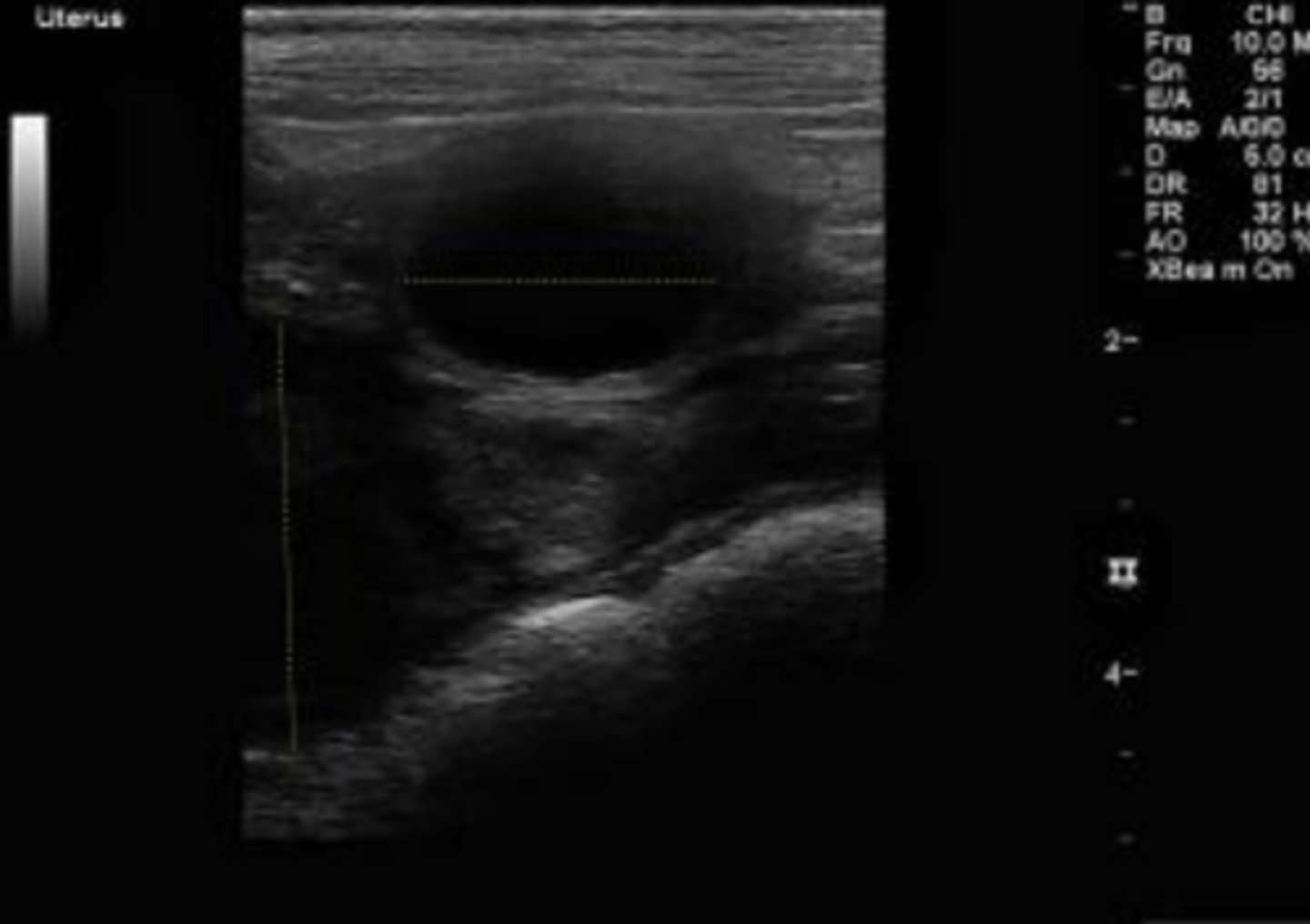
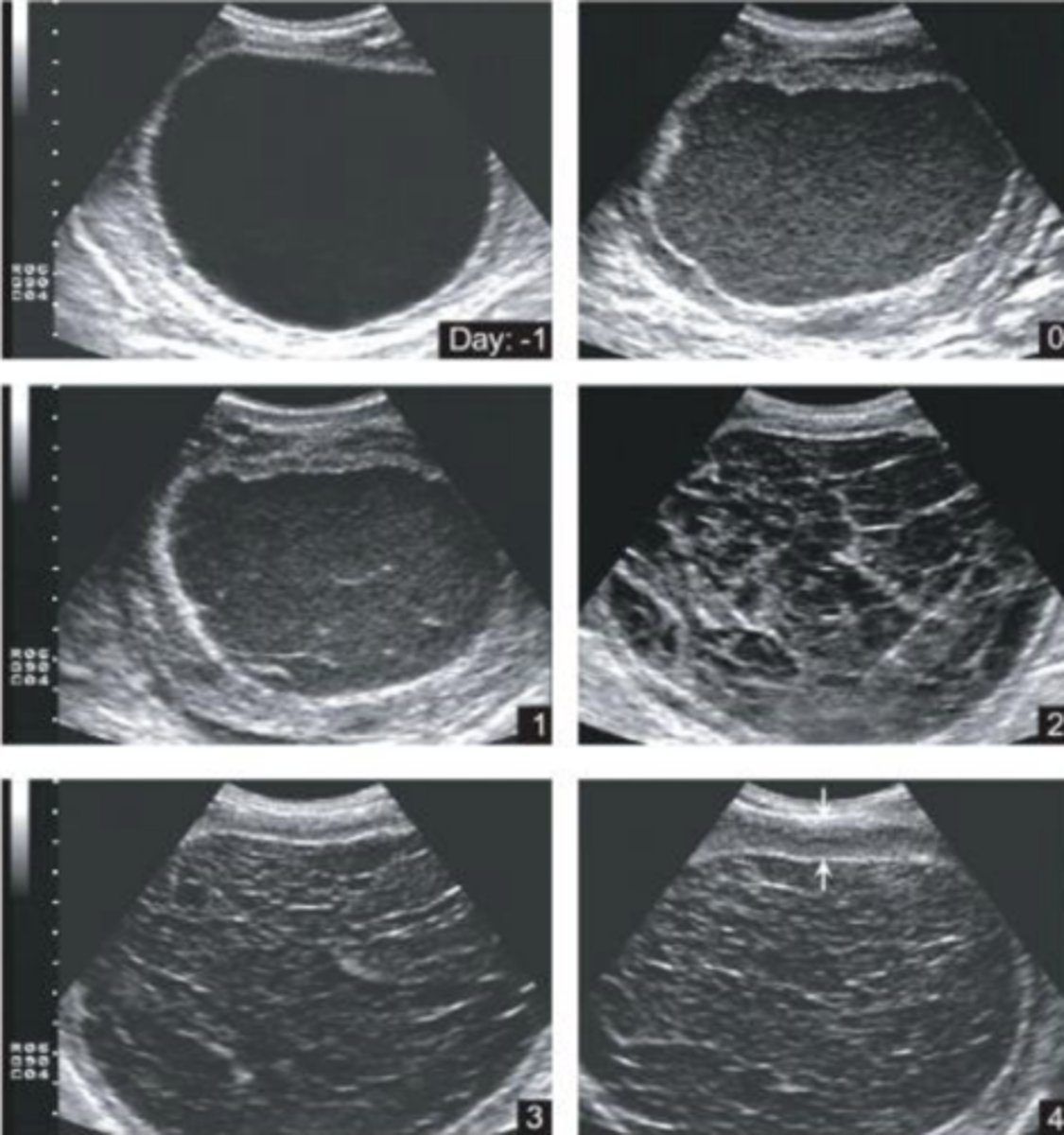
What are the hallmark sonographic findings for pyometra, mucometra, and hydrometra?
diffuse or segmental fluid distention of the uterine lumen (yellow dashed lines)
Since there is a lot of similarity in how pyometra and other conditions (hydrometra and mucometra) appear on ultrasonography, what would help differentiate between the clinical conditions?
CBC
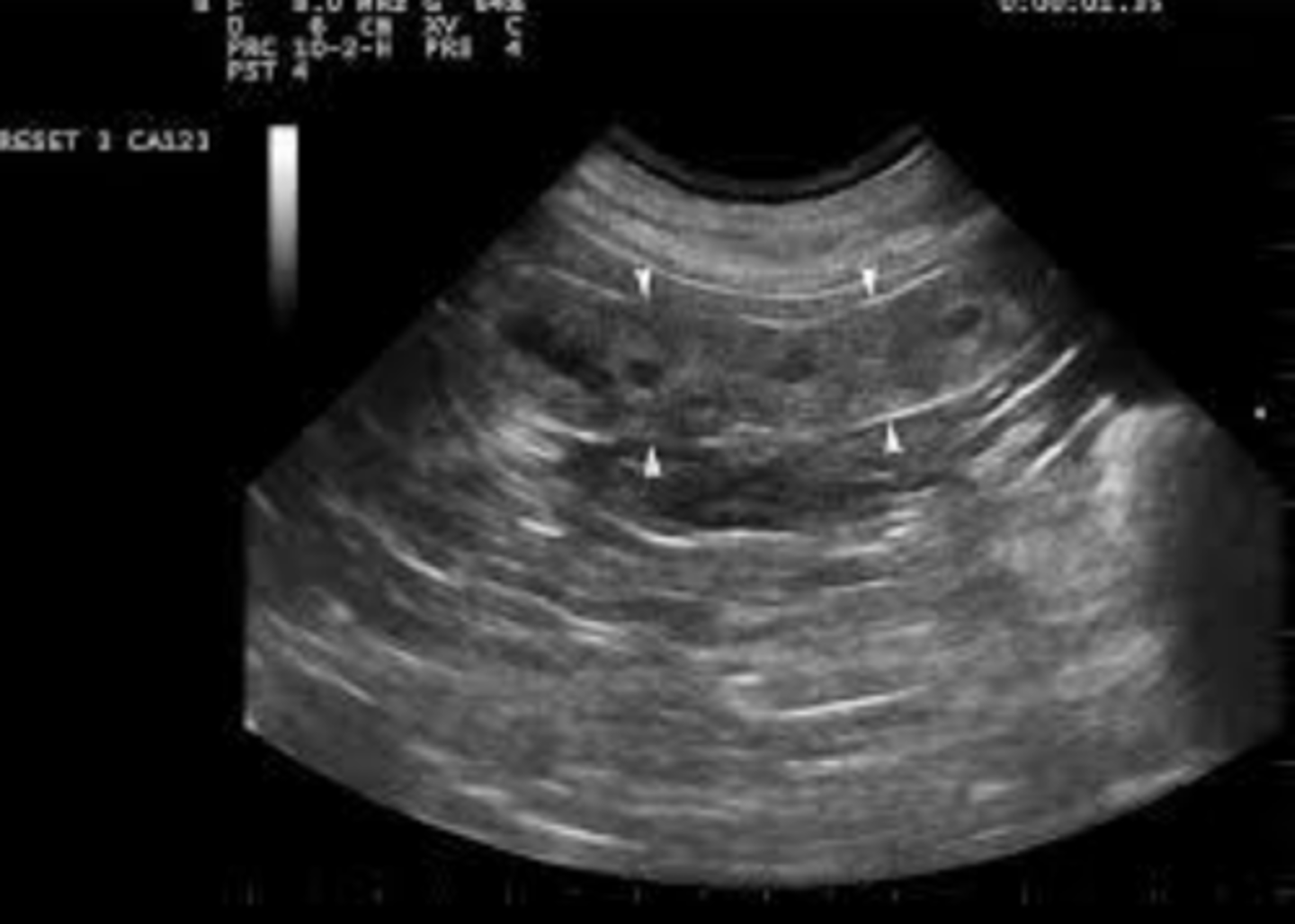
cystic endometrial hyperplasia in a bitch
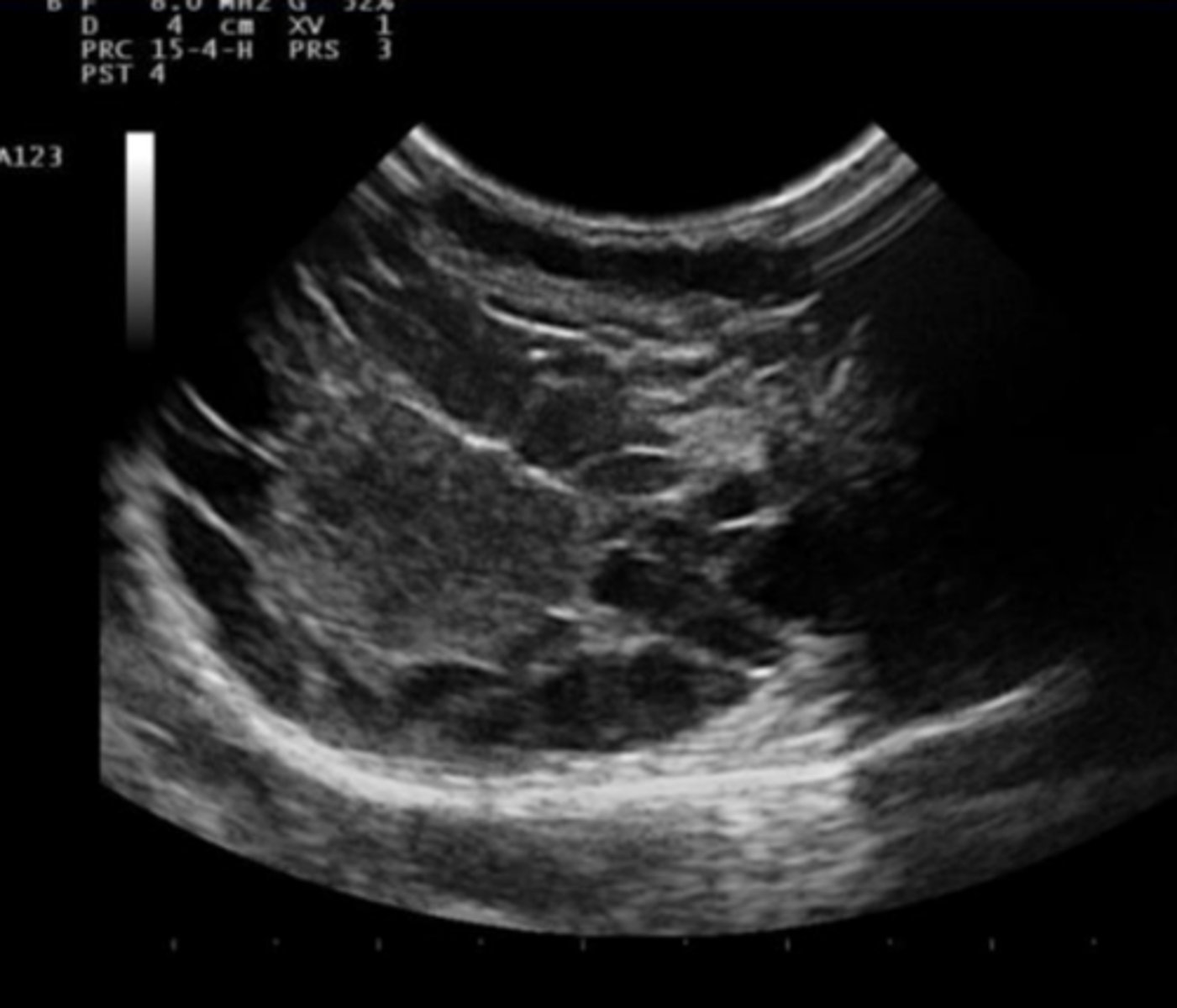
cystic endometrial hyperplasia with echoic contents in the uterine lumen
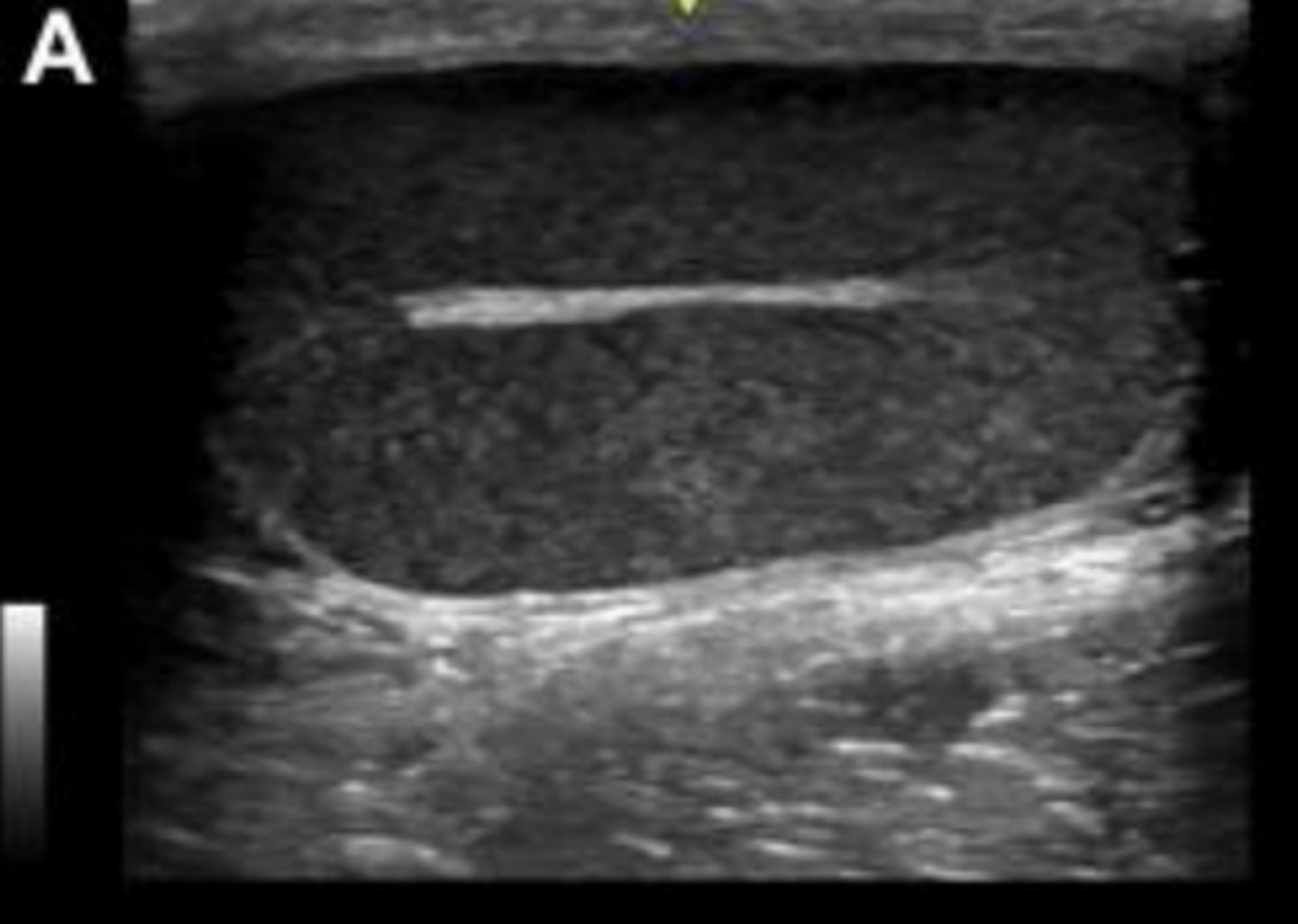
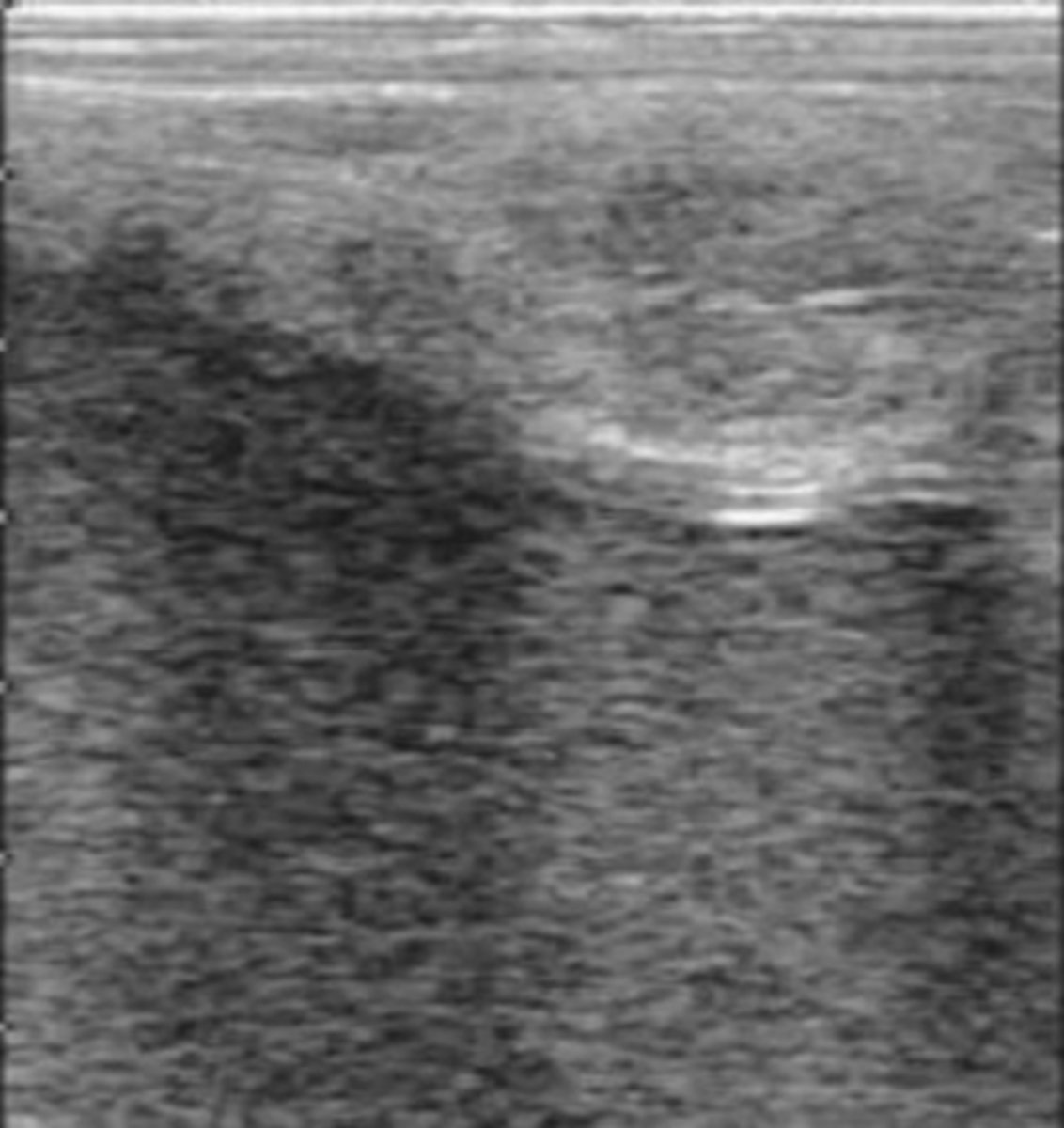
normal testis in the longitudinal plane
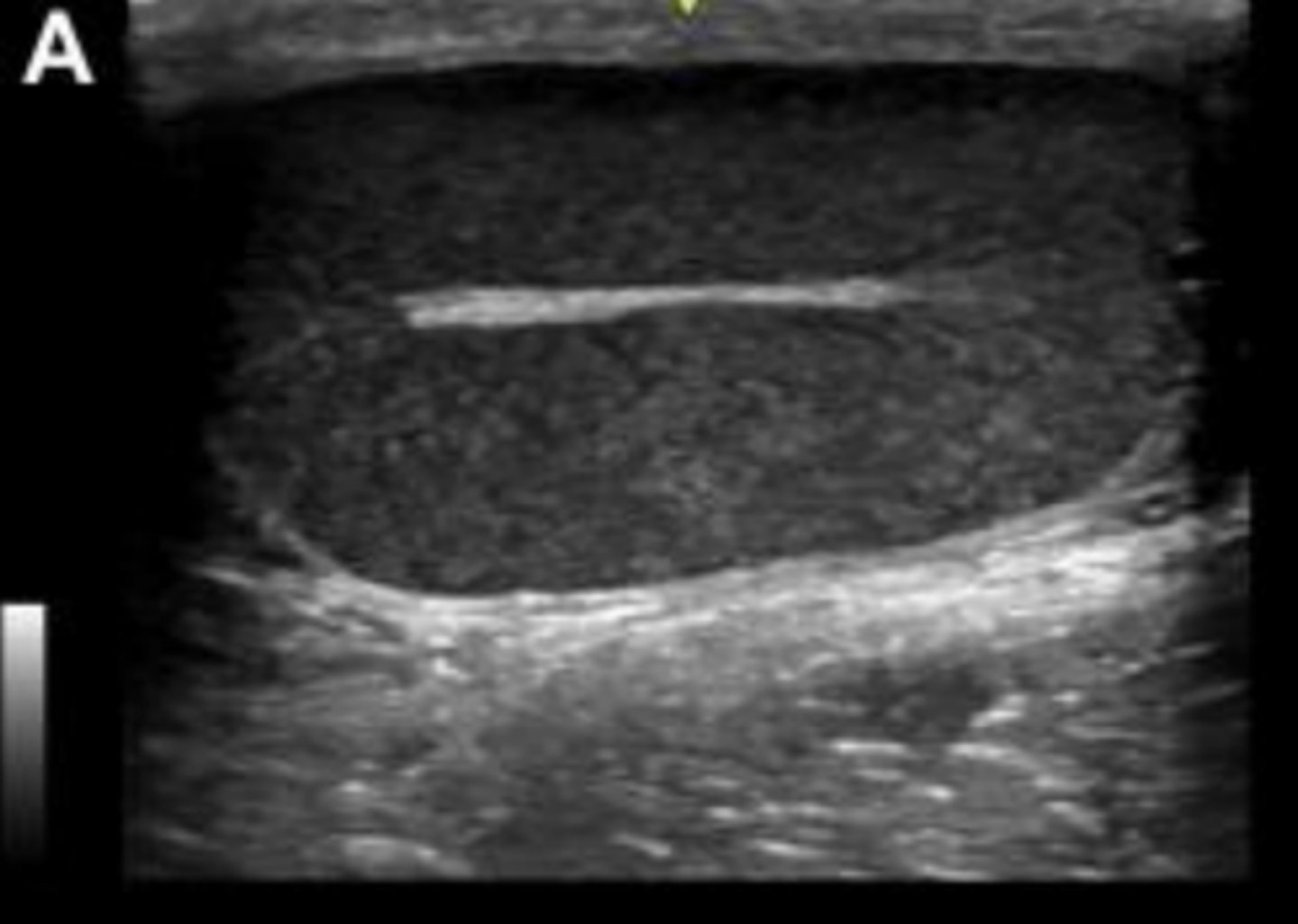
What is the hyperechoic linear structure in the center?
mediastinum testes
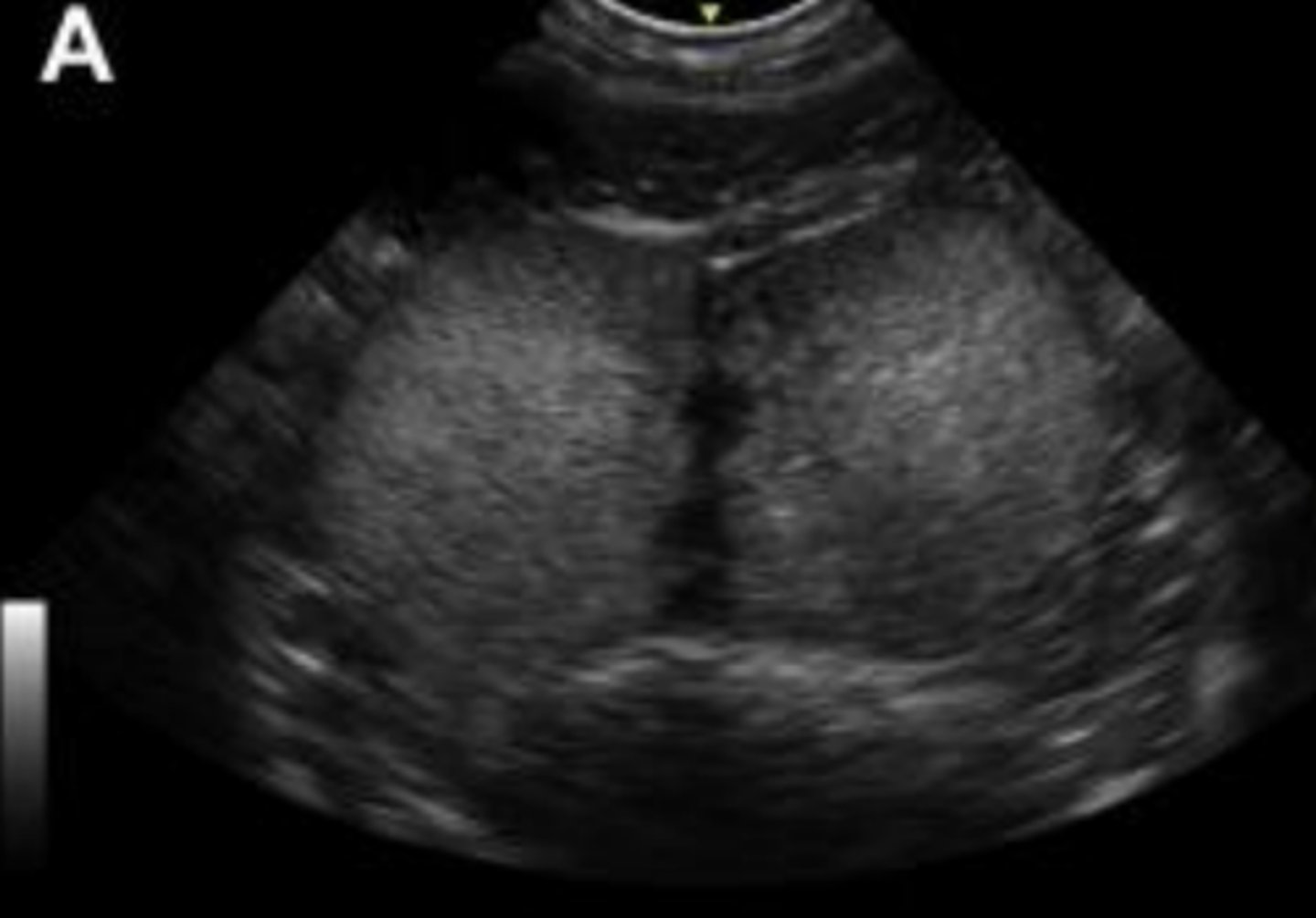
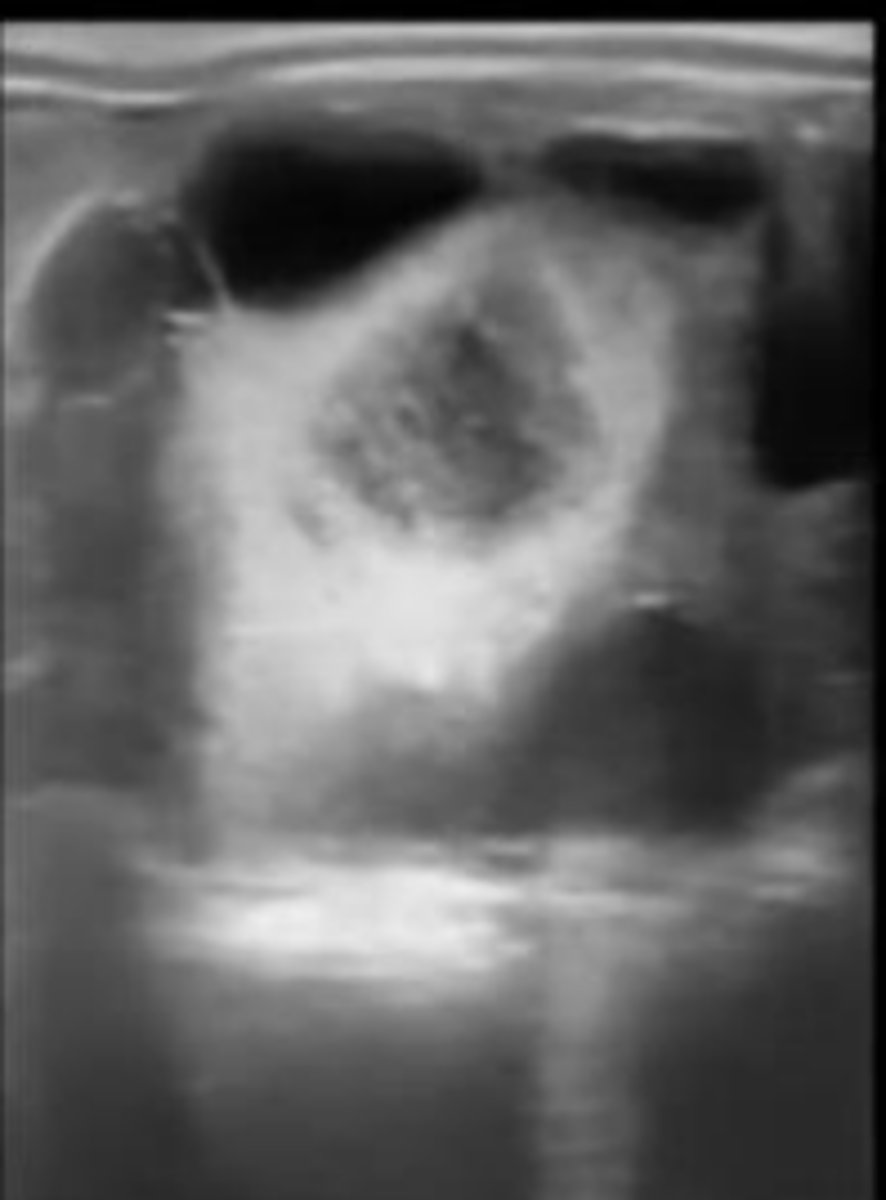
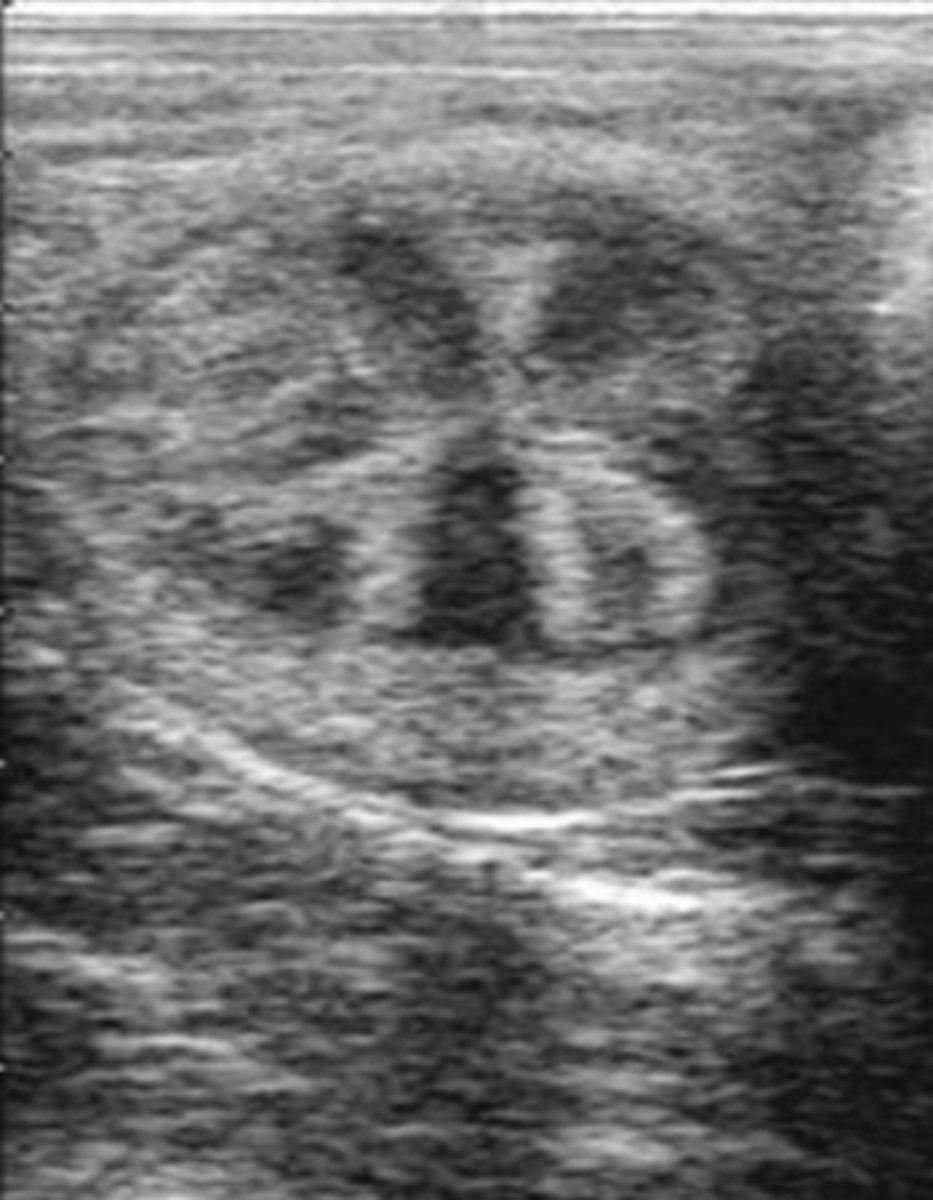
normal prostate in transverse plane
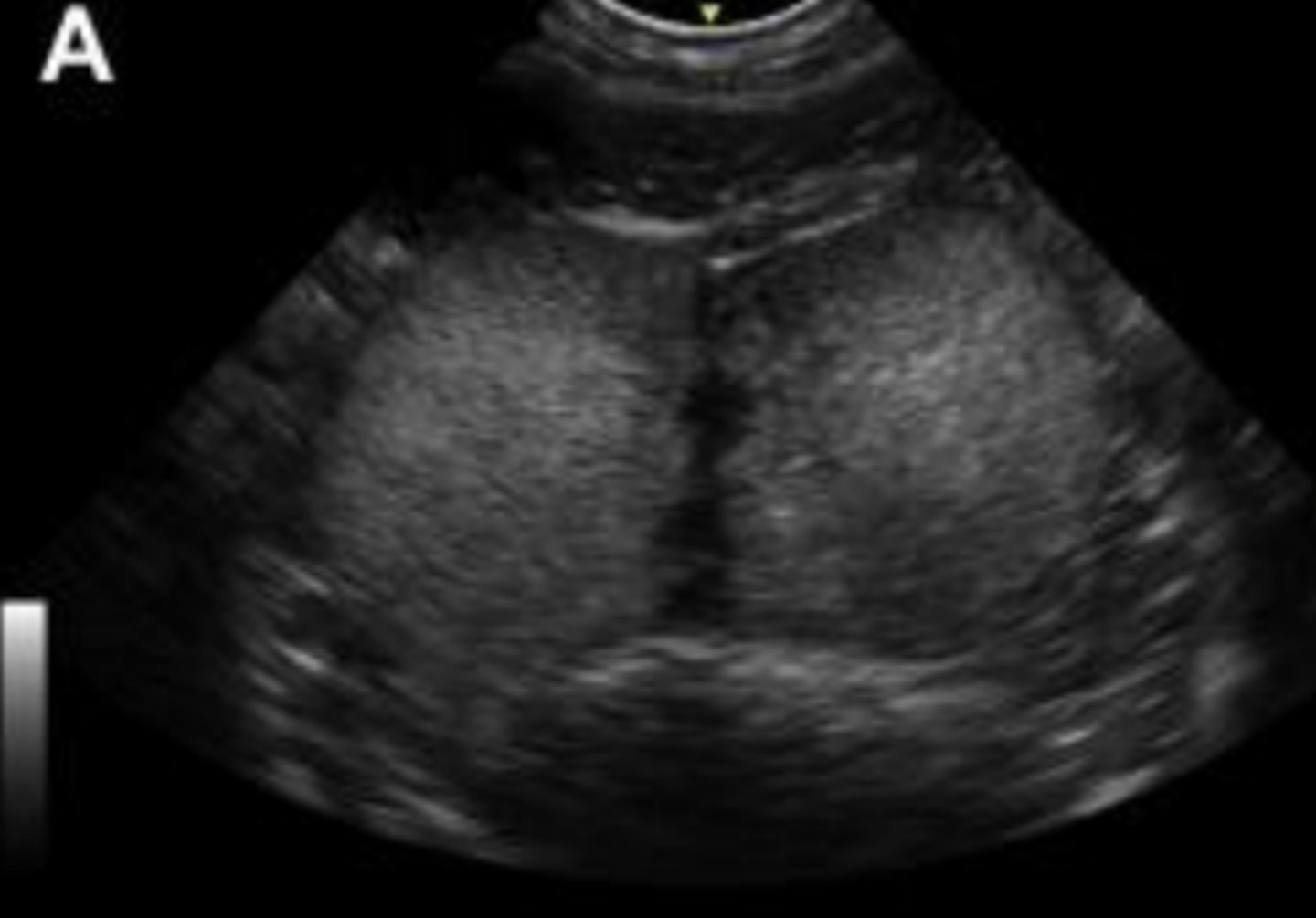
What is the round central anechoic structure?
prostatic urethra
What is seen sonographically in a healthy prostate?
homogenous echogenic parenchyma and centrally hypoechoic pattern resembling butterfly wings
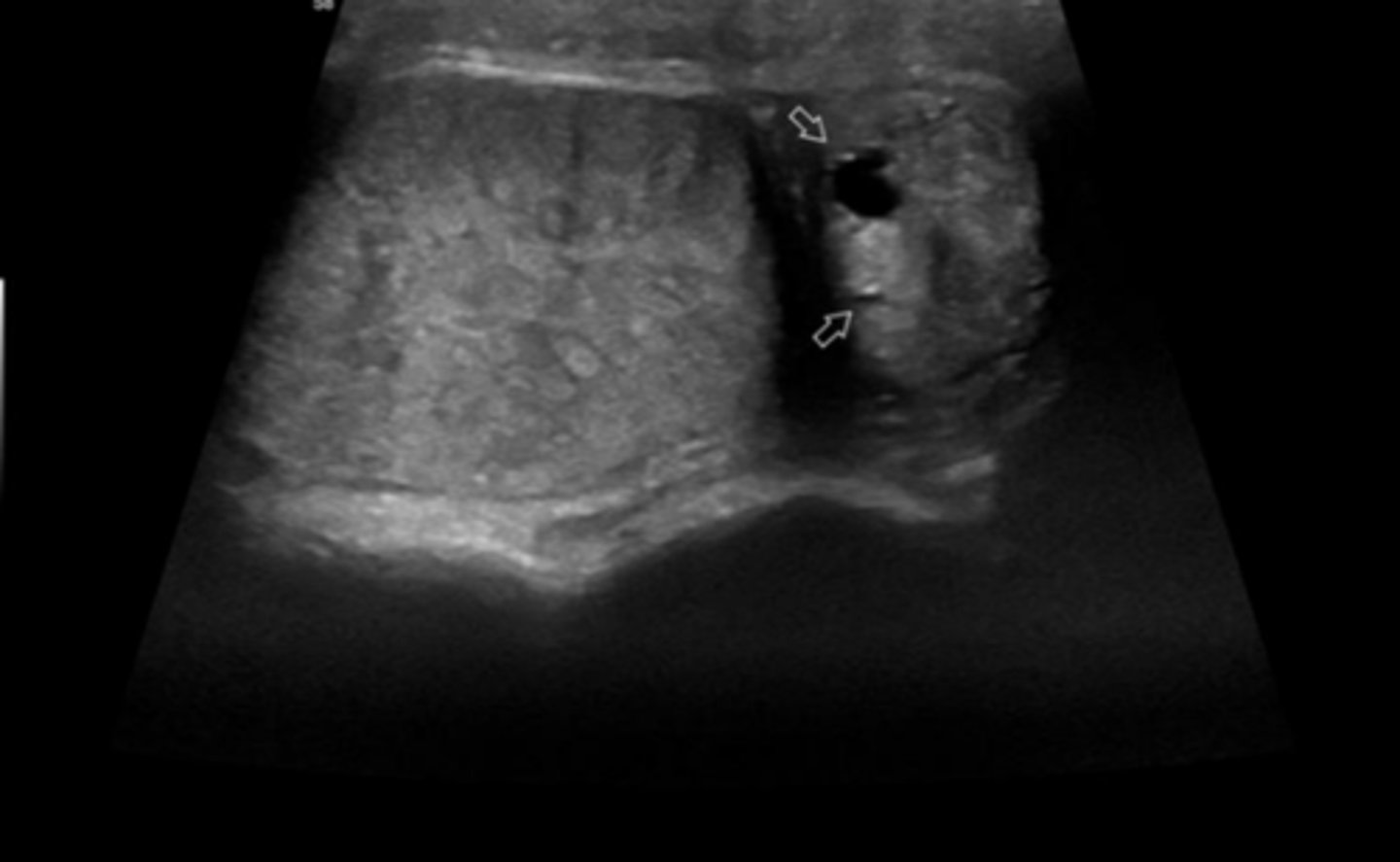
orchitis and epididymitis in a dog
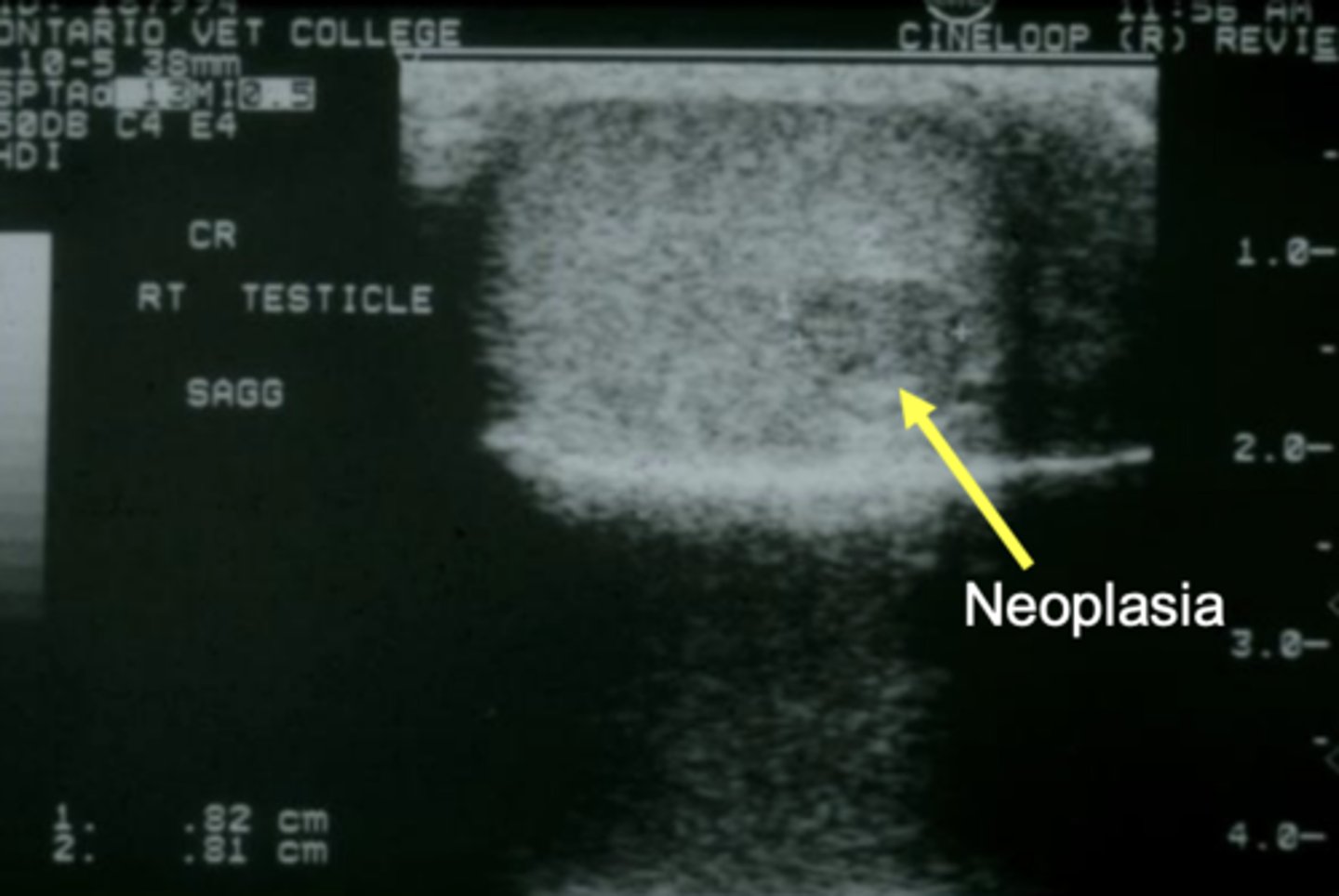
testicular neoplasia in a dog