Protein structure & function I
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
X-ray crystallography
Myoglobin is the first protein to have its 3-dimensional structure revealed by x-ray crystallography
myoglobin binds oxygen in muscles
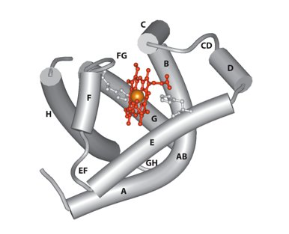
Structure of Myoglobin
Made up of 153 amino acids
8 helices (A-H)
The ability of myoglobin to bind oxygen depends on the presence of a haem group
It is a globular protein
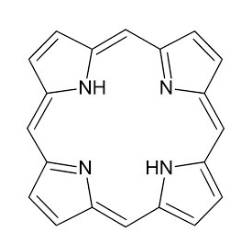
Porphyrins
The porphyrin ring system is flat
Iron in the ferrous form (Fe2+) lies in the middle of the porphyrin molecule bound to 4 nitrogen atoms
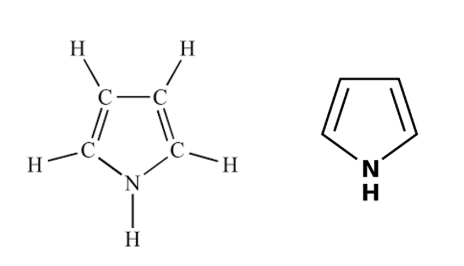
pyrrol
Binding of oxygen to Myoglobin
Types of haem proteins and their functions
Myoglobin (stores oxygen in muscles)
Haemoglobin (Transports oxygen)
Cytochromes (generates energy within the mitochondria)
Function of Haemoglobin
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues (high demand). Haemaglobin is the protein which gives blood its red colour and has the role for transporting oxygen around the body
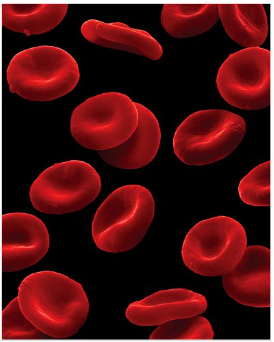
What does haemoglobin consist of
4 chains, 2 identical alpha chains and 2 identical beta chains α2β2
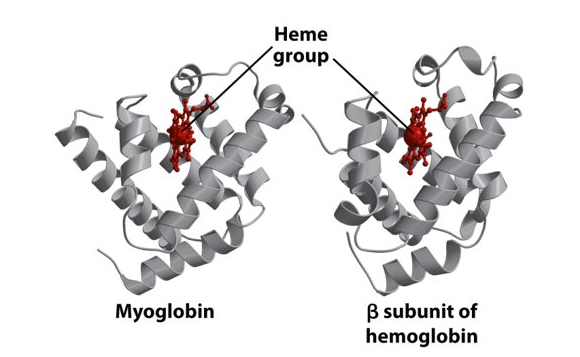
Quaternary structure of haemoglobin
Haemoglobin always has a quaternary structure
The bottom part of the protein structure remains the same but the top part of the protein structure changes with a 15 degree turn
Oxygen binding by myoglobin and haemoglobin
Myoglobin can bind 1 oxygen molecule
Haemoglobin can bind to 4 oxygen molecules
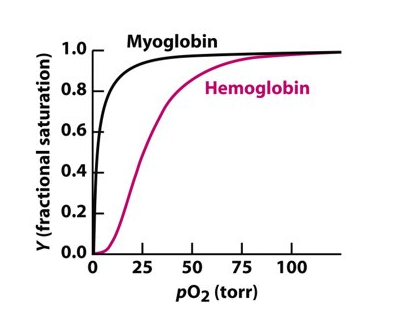
Oxygen binding changes the position of the iron ion
Conformational changes in haemoglobin
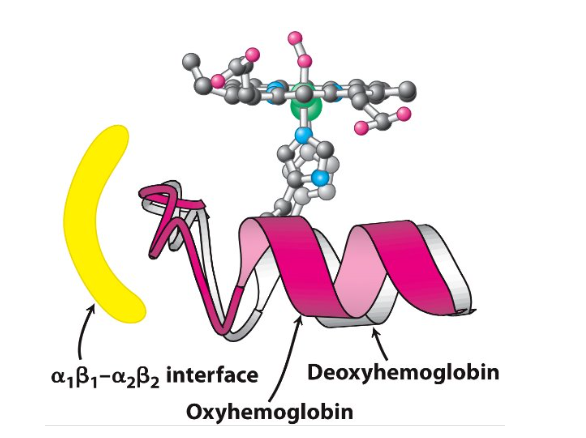
Changes of haemoglobin quaternary structure
Deoxyhaemoglobin changes to oxyhaemoglobin