Lecture #17: Lipid anabolism
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms

Core concept: Lipid synthesis is an energy-intensive process
Basic fatty acid building units
Addition of each unit to fatty acid
“Charging” glycerol
Energy storage (anabolism)
Lipid stored as triglycerides (3 fatty acids & glycerol
Glycerolipids are utilized for energy storage
Can also be structural (phosphatidylcholine)
Triglycerides stored in adipose tissue
Subcutaneous adipose (under the skin) not as bad bc it can overturn faster
Visceral adipose (associated with organs) bad bc it is associated with diseases & slower overturn rate
Involves fatty acids synthase enzyme
What are lipids stored as?
Triglycerides (3 fatty acids & glycerol)
Triglyceride and glycerol
Energy
Structural
Energy liberation (catabolism)
Break down glycerolipids into smaller components
Glycerol (glycolysis: make glucose & gluconeogenesis: derive energy from)
Fatty acids
Involves lipase enzyme
What components are made from energy liberation?
Glycerol (glycolysis: make glucose & gluconeogenesis: derive energy from)
Fatty acids
What are the two ways triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue?
Subcutaneous adipose (under the skin) not as bad bc it can overturn faster
Visceral adipose (associated with organs) bad bc it is associated with diseases & slower overturn rate
What type of lipid metabolism involves fatty acid synthase enzyme?
Energy storage (anabolism)
What type of lipid metabolism involves lipase enzyme?
Energy liberation (catabolism)
Subcutaneous adipose
Under the skin (not as bad bc it can overturn faster)
Visceral adipose
Associated with organs (bad bc it is associated with diseases & slower overturn rate)
Steps in lipid anabolism (organismal energy high)
Acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate in the mitochondria
2) Citrate is exported from mitochondria and re-converted to Acetyl-CoA (basic building block for fatty acids) in the cytosol
3) Fatty acid synthase complex (enzyme) synthesizes acetoacetyl-acyl (2-carbonds) carrier protein (ACP)
4) Fatty acid synthase complex synthesizes butyryl-ACP (4 carbons) from acetoacetyl-ACP
5) Two carbons at a time are added to butyryl-ACP until palmitate (most common FA)(16C: the stopping point) is formed
6) Palmitate reacts with glycerol to form triglycerides
Steps in lipid catabolism (organismal energy low)
1) Cells receive signal to initiate lipolysis (breaking lipids)
2) Triacylglycerol lipase cleaves fatty acids from glycerol in the cytosol
3) Fatty acids are activated in the cytosol
4) “Fatty acids” (not really the same molecule) are transported into the mitochondria
5) “Fatty acids” are oxidized in the mitochondria (beta oxidation) to capture
energy as reduced reducing equivalents (NADH & FADH2)
Why when doing beta-oxidation it is in the mitochondria?
Beta oxidation occurs in the mitochondria because the reduced reduced equivalents aren’t transported bc they will be used in the ETC in the inner mitochondrial membrane
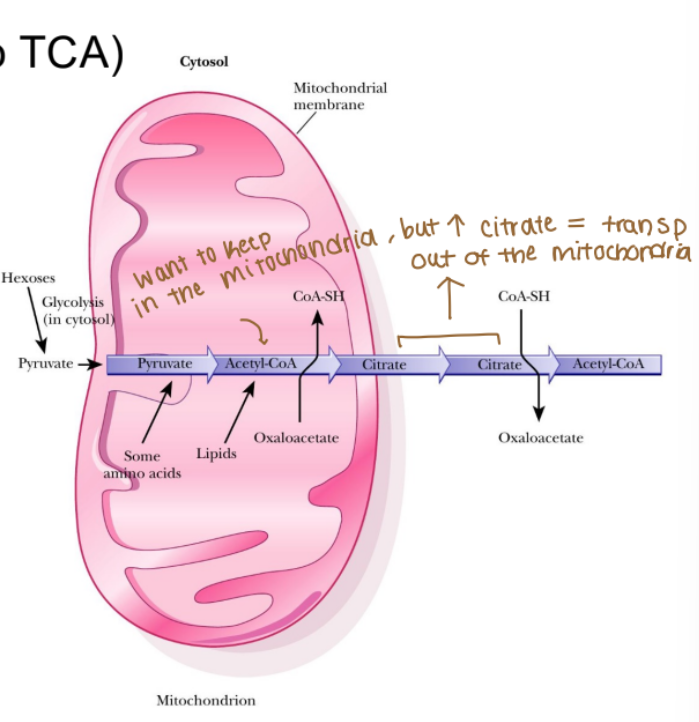
Fatty acid synthesis (anabolism)
Acetyl-CoA is the starting material, comes from:
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (bridge from glycolysis to TCA)
Ketogenic amino acids (protein catabolism)
First, acetyl-CoA is condensed with oxaloacetate to form citrate (first step of TCA), which can be transported out of the mitochondria
In the cytosol, citrate is converted back into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate
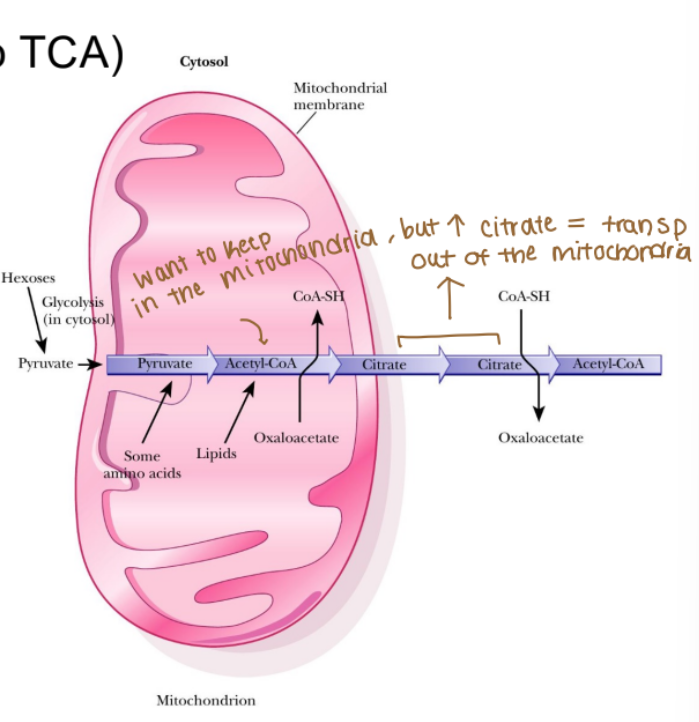
What is the starting material in fatty acid synthesis (anabolism)
Acetyl-CoA, comes from:
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (bridge from glycolysis to TCA)
Ketogenic amino acids (protein catabolism)
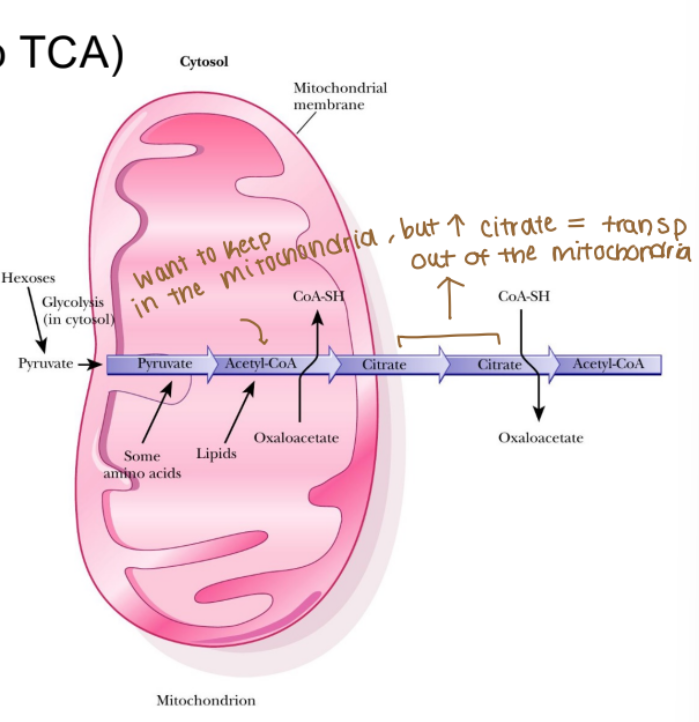
Where does the acetyl-CoA (starting material in the TCA) come from?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (bridge from glycolysis to TCA)
Ketogenic amino acids (protein catabolism)
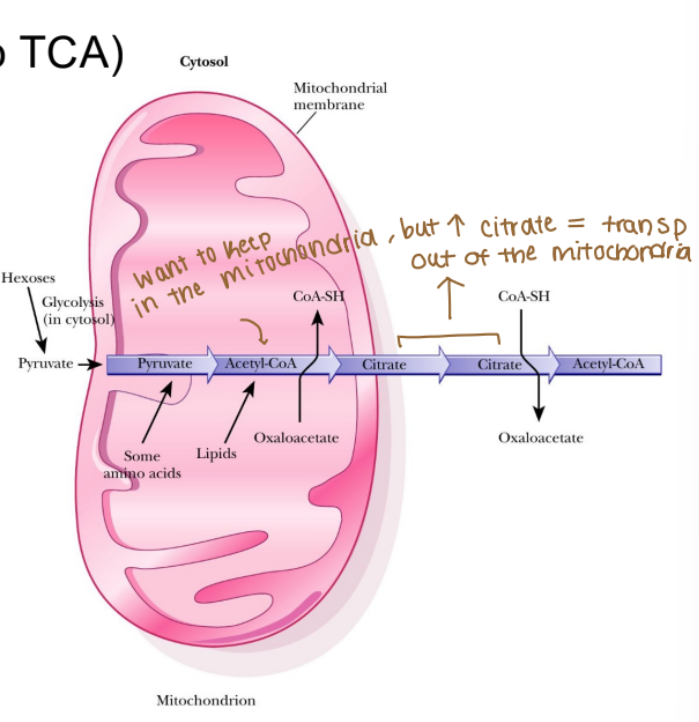
What is the first step in fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl-CoA is condensed with oxaloacetate to form citrate (first step of TCA), which can be transported out of the mitochondria
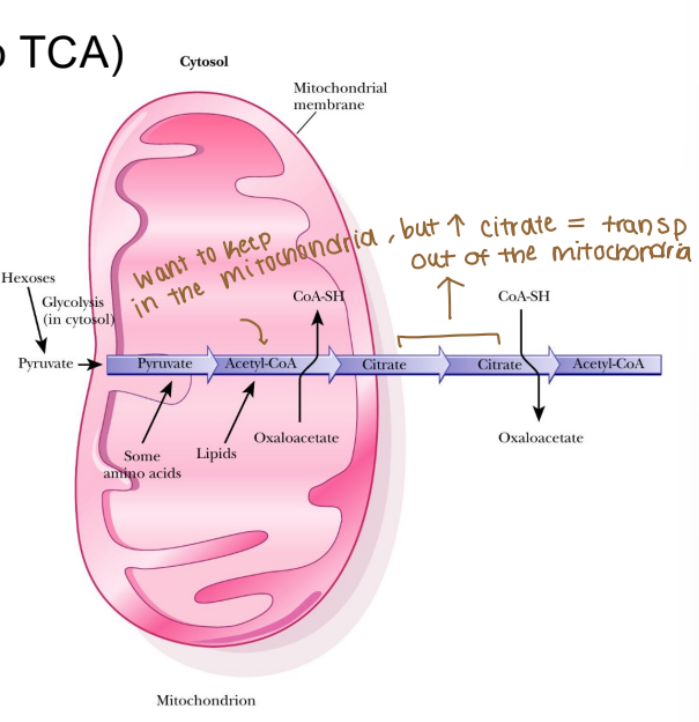
Where does the citrate first produced in fatty acid synthesis (anabolism) first start and ends up?
First: mitochondria
End: Cytosol
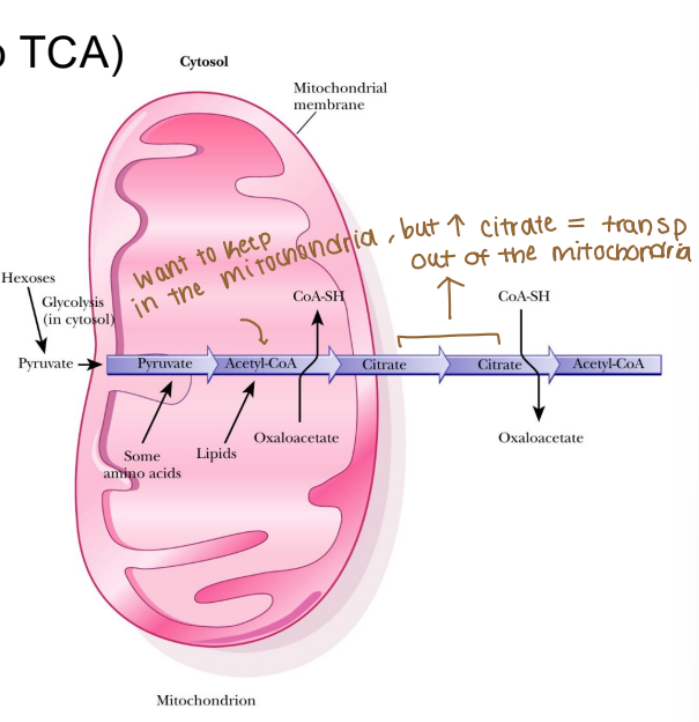
When citrate is transported out of the mitochondria, into the cytosol what does it become?
It is converted back into acetyl-CoA and ozaloacetate
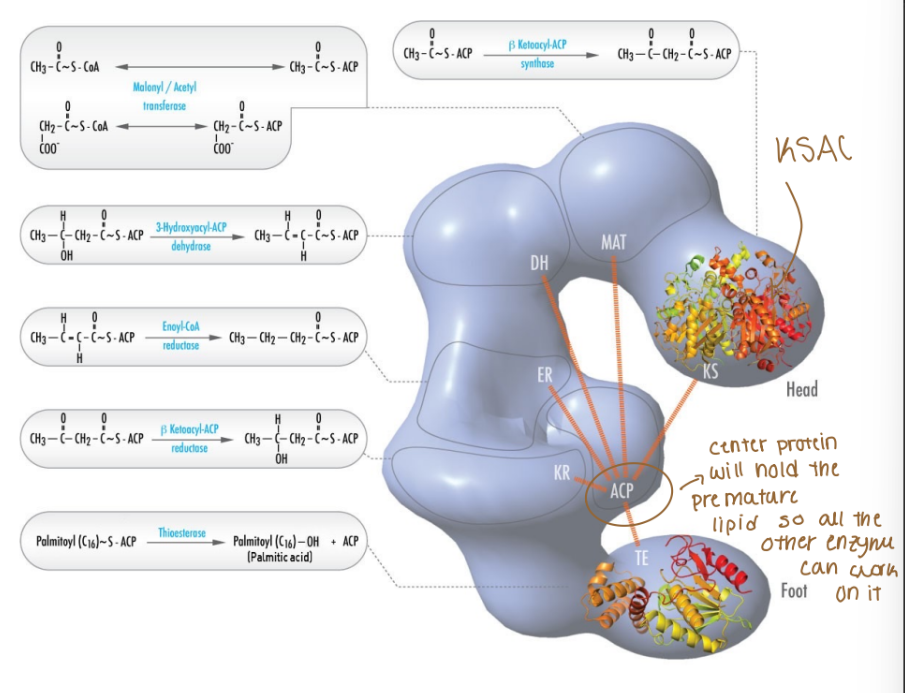
Acyl- carrier protein (ACP)
Center protein will hold the premature lipid so all the other enzymes can work on it
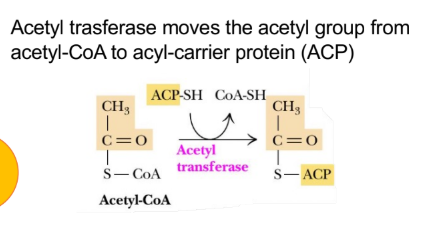
Transferase (fatty acid anabolism)
Enzyme names: X transferase
Reaction type: moves entire functional groups from one compound to another
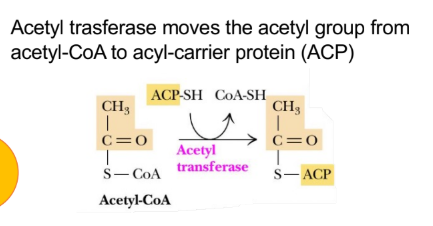
What is the reaction type for transferase (fatty acid anabolism)?
Moves an entire functional group from one compound to another

What is the enzyme name for transferase (fatty acid anabolism)?
X transferase
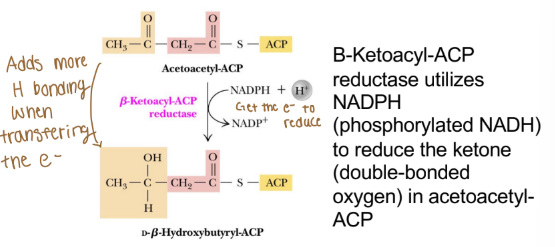
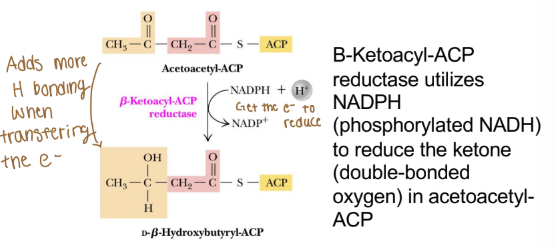
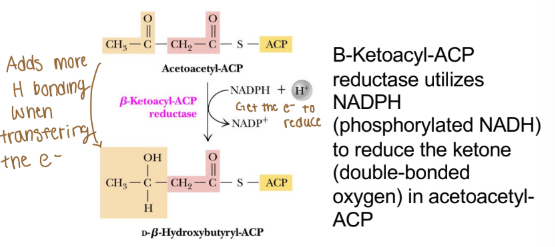
Reductase (fatty acid anabolism)
Enzyme name: X reductase
Reaction type: catalyzes reduction of the substrate, often consuming a reduced, reducing equivalent (adding electrons-reduction)
***never uses ATP***
Does reductase fatty acid anabolism) use ATP?
No ATP used
What is the enzyme name of reductase (fatty acid anabolism)
X reductase
Ex. Β-Ketoacyl-ACP
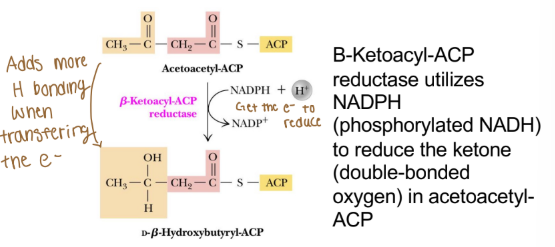
What is the reaction type for reductase (fatty acid anabolism)?
Catalyzes reduction of the substrate, often consuming a reduced, reducing equivalent (adding electrons-reduction)
FAS
Fatty acid synthesis
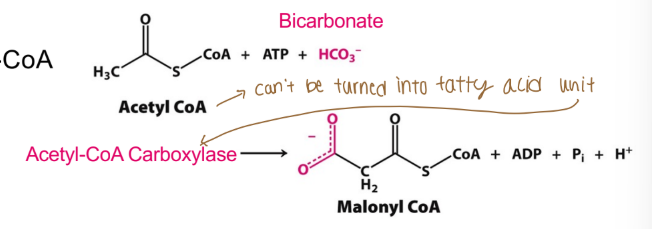
Acetyl-CoA is converted to what for fatty acid synthesis (FAS)
It is converted to malonyl-CoA
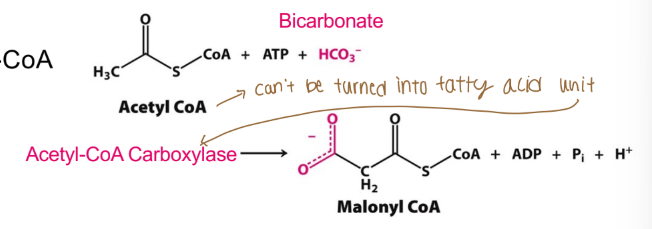
What is the primary building block when building fatty acids?
Malonyl-CoA
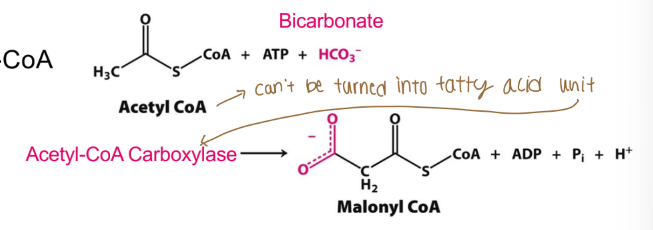
The activity of what determines if fatty acids are synthesized (or if acetyl-CoA enter TCA instead)?
The activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
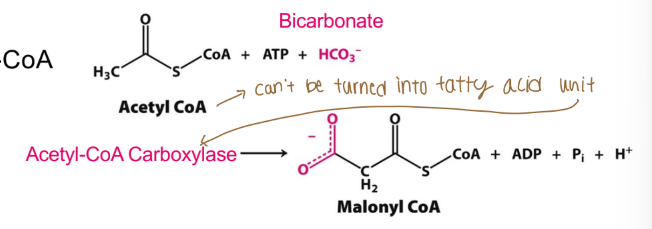
How many ATP is invested per malonyl-CoA?
One ATPe per malonyl-CoA (will need 7 total)
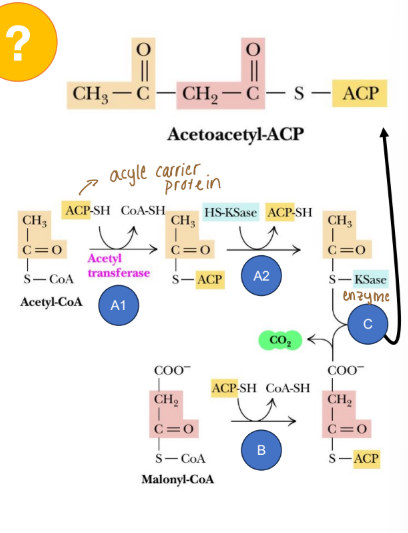
What is the overall idea of fatty acid synthesis (works in conjunction with ACP)?
Fatty acid synthase complex needs one acetyl-CoA and one malonyl-CoA bound to acyl-carrier protein to begin fatty acid synthesis
A1) Acetyl group from acetyl-CoA (just came from mitochondria) is transferred to acyl carrier protein (ACP) via acetyl-transferase
A2) Acetyl group is transferred from ACP to β-ketoacyl-S- ACP-synthase (KSase)
B) Malonyl group from malonyl-CoA is transferred to ACP
C) Acetyl group from acetyl-KSase is transferred to malonyl-ACP to form acetoacetyl-ACP
Acetoacetyl-ACP is converted to butyryl-ACP
Overall Idea: Fatty acid synthase complex converts acetoacyl-ACP to butyryl-ACP (the substrate needed for progressive malonyl-CoA additions)
Progressively reduces acetoacyl-ACP to butyryl- ACP (adds electrons and removes oxygen)
Each reductase steps requires one NADPH
Loss of oxygen produces water (dehydration)
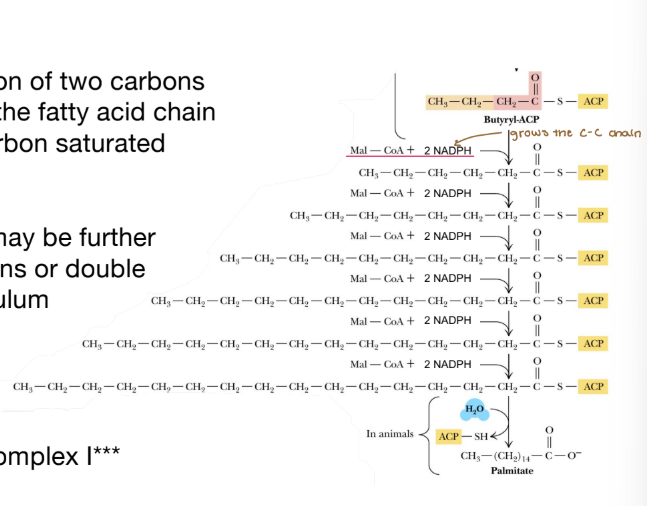
Fatty acids are elongated by 2C and requires energy
Overall Idea: Progressive addition of two carbons from each malonyl-CoA grows the fatty acid chain until palmitate is formed (16-carbon saturated fatty acid)
After hydrolysis, the fatty acid may be further modified to contain more carbons or double bonds in the endoplasmic reticulum
Uses 2 NADPH to add each 2C
***NADPH also enters ETC at complex I***
For each molecule of palmitate formed:
8 molecules of acetyl-CoA (comes from 4 glucose molecules)
7 acetyl-CoA converted to malonyl-CoA (= 7 ATP)
7 additions of malonyl-CoA to the growing fatty acids (=14 NADPH)
If NADPH enters ETC at complex I, each NADPH pumps 10 protons
Total ATP equivalents INVESTED: 42 ATP
8 Molecules of acetyl-CoA = 80 ATP (after TCA and ETC)
Oxidation of palmitate = ??? ATP ??? Next lecture!
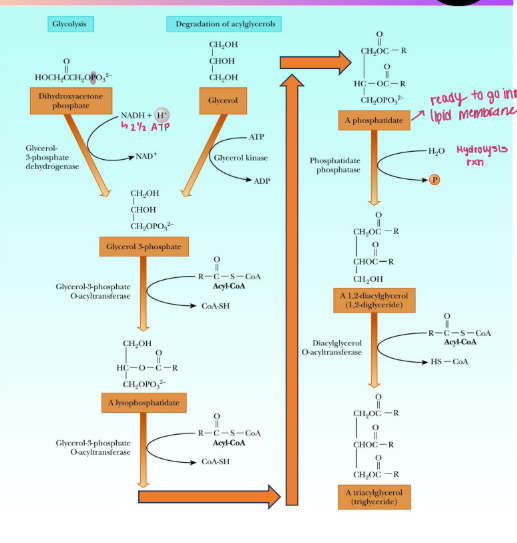
Triacylglycerol Synthesis
Glycerol backbone may come from lipolysis or glycolysis
Initial phosphorylation requires energy (ATP or NADH, depending on the source
of glycerol)
Progressive addition of fatty acyl-CoAs to the other hydroxyl groups (not
phosphorylated group) occurs first to form a new triacylglycerol
Which type of tissue stores lipids under the skin?
Subcutaneous adipose
Which product of pyruvate dehydrogenase is utilized in fatty acid synthesis?
Acety-CoA
Where in the cell does fatty acid synthesis occur?
Cytosol
Which enzyme regulates fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl-CoA regulates
Where does NADPH enter the electron transport chain?
Complex I