Genes to Proteins (Chapter 17)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
transcription
-The synthesis of RNA using a DNA template.
translation
-The synthesis of a polypeptide using the genetic information encoded in an mRNA molecule. There is a change of "language" from nucleotides to amino acids.
messenger RNA (mRNA)
-A type of RNA, synthesized using a DNA template that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein.
transfer RNA (tRNA)
-An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA.
Ribosomes
-A complex of rRNA and protein molecules that functions as a site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm; consists of a large and a small subunit. In eukaryotic cells, each subunit is assembled in a nucleolus.
RNA Polymerase
-An enzyme that links ribonucleotides into a growing RNA chain during transcription.
Interfering RNA (RNAi)
-RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression or translation, by neutralizing targeted mRNA molecules.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is the RNA component of the ribosome, and is essential for protein synthesis in all living organisms.
Promoter
-A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase, positioning it to start transcribing RNA at the appropriate place.
TATA Box
-A DNA sequence in eukaryotic promoters crucial in forming the transcription initiation complex.
Exons
-A sequence within a primary transcript that remains in the RNA after RNA processing; also refers to the region of DNA from which this sequence was transcribed.
Introns
-A noncoding, intervening sequence within a primary transcript that is removed from the transcript during RNA processing; also refers to the region of DNA from which this sequence was transcribed.
Spliceosome
-A large complex made up of proteins and RNA molecules that splices RNA by interacting with the ends of an RNA intron, releasing the intron and joining the two adjacent exons.
5' cap
-A modified form of guanine nucleotide added onto the nucleotide at the 5' end of a pre-mRNA molecule.
Poly-A Tail
-A sequence of 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides added onto the 3' end of a pre-mRNA molecule.
Signal Sequence
-A short stretch of amino acids that is responisble for determining the location of a protein in the cell
Initiation
-RNA polymerase reaches a promoter, which initiates transcription.
Elongation
-RNA polymerase continues to transcribe the DNA into mRNA. It moves along the DNA template, from the 5' to the 3'.
Termination
-Pre-mRNA is released, and after a period of more transcription, RNA polymerase detaches as well.
Central Dogma
-DNA-->RNA-->Protein
(Exception: Retroviruses, which use their RNA to make DNA)
Genetic Code
-The genetic code is... (specific for certain groups or universal)
Universal, except for slight variations among certain unicellular eukaryotes and certain specie's organelles.
Codons
-A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code
Anticodons
-A nucleotide triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule.
Mutations
-Changes to genetic material.
Missense Mutation
-Altered codons make sense, but not the right sense.
(Type of mutation)
Deletion Mutation
-Removal of nucleotide pairs in a gene.
Substitution Mutation
-Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
(Type of mutation)
Frameshift Mutation
-Shift in the reading frame of a polypeptide chain.
(Type of mutation).
Insertion Mutation
-Addition of nucleotide pairs in a gene.
Nonsense Mutation
-Causes an early stop in the polypeptide chain.
(Type of mutation).
How did Beadle and Tatum's work on auxotroph's suggest that metabolism was controlled by protein enzymes?
-State the hypothesis formulated by George Beadle with studying eye color in Drosophilia
-each of the various mutations of affecting eye color blocks pigment synthesis at a specific step by preventing the production of the enzyme
-showed that genes control the production of enzymes and that the enzymes are related to traits
What strategy did Beadle and Tatum adopt to test this hypothesis?
bombarded bread mold Neurospora with X-Rays and then looks amoung survivors for mutants that differ in their nutritional needs form the wild type bread mold
How does RNA polymerase identify where to begin transcription of a gene?
-specific sequences of nucleotides along DNA mark where transcription of a gene begins and ends.
Explain the relationship between the promoter, enhancers, and transcription factors.
-promoter: the DNA sequence where RNA polymerase attaches initiates transcription
terminator: the sequence that signals the end of transcription (IN BACTERIA)
transcription unit: the stretch of DNA that is transcribed into RNA
Diagram each of the following phases of transcription.
initiation
elongation
termination
-Initiation: RNA polymerase pries the two strands of DNA apart at the promoter site and hooks together the RNA nucleotides as they base-pair along the DNA template
-Elongation: the polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript from the 5'( 5 prime) to 3' (3 prime) end. As transcription is occurring the DNA strands re-from a double helix.
-Termination: the RNA transcript is eventually released and the polymerase detaches from the DNA. Different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Explain what happens during each of the following post-transcriptional modifications of eukaryotic transcripts:
splicing
5' capping
poly adenylation.
-Splicing: portions of RNA are removed.
-5' capping: a 7-methylguanosine is attached to the 5' terminal end of mRNA through an unusual 5'-->5' triphosphate linkage (this is resistant to most nucleases)
-Polyadenylation: addition of a 3' poly A tail to RNA
How do eukaryotic cells utilize alternative splicing to maximize variety of gene products that they can produce?
-How do cells regulate gene expression using alternative RNA splicing?
Alternative RNA splicing determines which proteins are produced from each gene
-Why can alternative splicing of messenger RNAs be advantageous for eukaryotic organisms?
Increases the variety of proteins that can be produced
-What are the possible outcomes of the alternative splicing shown?
1. Isoform-A mRNA is degraded faster than isoform-B mRNA is
2. The protein translated from isoform-A mRNA possesses an additional functional domain
3. The protein translated from isoform B is stable but lacks a functional domain
Explain the meaning of this statement: "The genetic code is punctuated, unambiguous, and redundant."
-It is punctuated because it is always made of 3 letter codons. It is unambiguous because it i not open for interpretation
It is redundant because different codons can code for same amino acid.
How does the structure of a tRNA molecules enable its function?
-The tRNA is responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosome.
The tRNA contains an anti-codon that matches up with a codon, when it does this it will release an amino acid.
How does the structure of a ribosome enable its function?
-The ribosomes are made of three sites where it holds the mRNA and allows the tRNA to come and match up with the mRNA and drop off the amino acid as it moves through the three sites.
Diagram what happens during each of the following phases of translation. Include the location (A, P, or E site) of incoming tRNA molecules, incoming amino acids, the growing polypeptide chain, uncharged tRNA molecules and release factors as appropriate:
initiation
elongation
termination
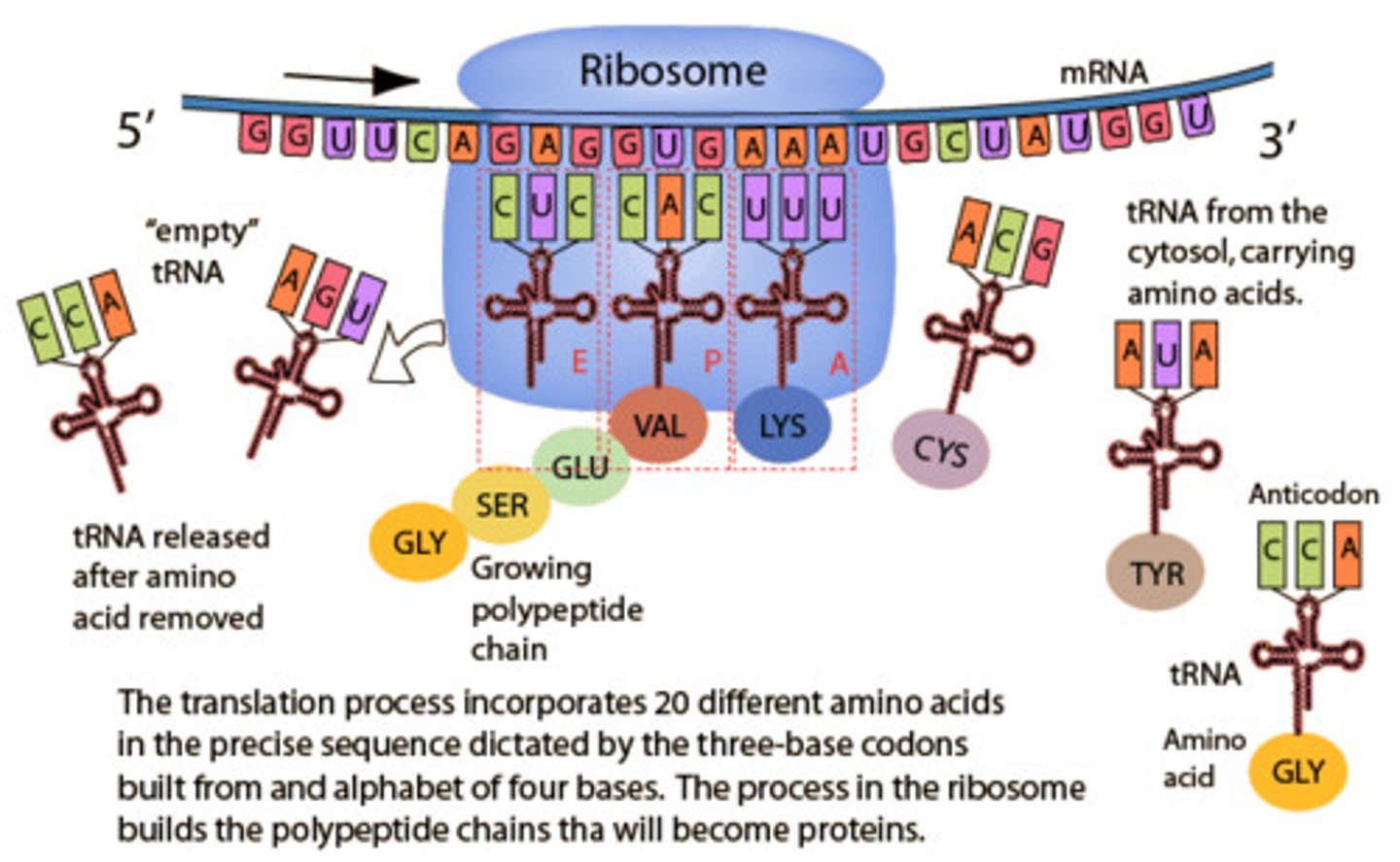
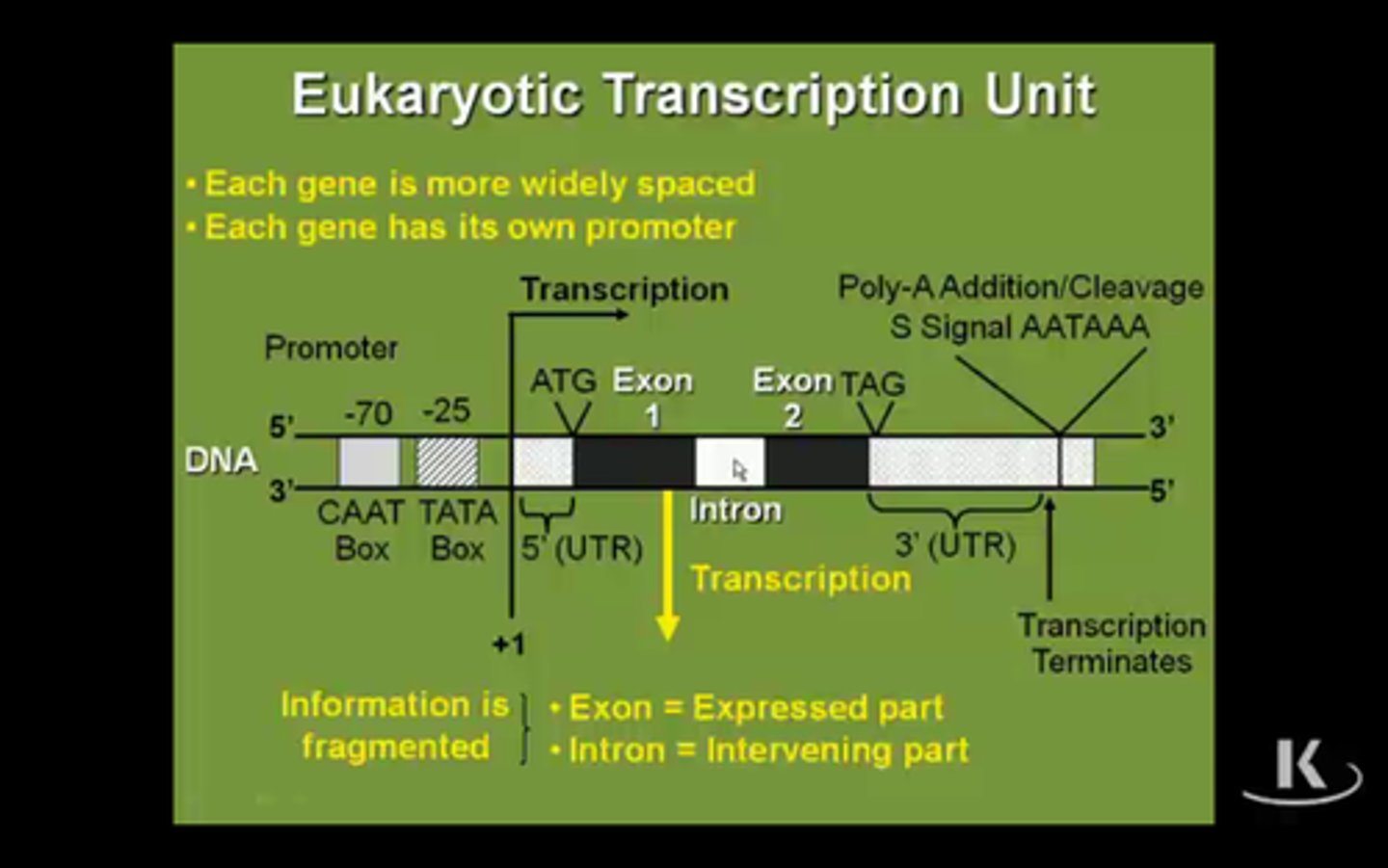
Diagram a complete eukaryotic transcription unit. Define each part.
Explain the effect that point mutations and frameshift mutations can have on gene products. Make sure to differentiate between:
neutral (silent) mutations
missense mutations
nonsense mutations
-For neutral mutations the gene product is not effected.
For missense mutations the gene product is effected. It effects one amino acid.
For nonsense mutations the gene product is effected. It causes an early stop codon.
.
Why insertion/deletion of three bases is less deleterious than insertion/deletion of one or two bases.
Insertion/deletion counts off by three so if three pairings are deleted it will still be the same. However, if only one is deleted then all the codons will shift causing them to be in different groups
Things to Make Sure You Understand
The relationship between DNA, RNA, Protein, Cells and the Organism.
Why transcription is necessary for cells, where it happens, its inputs and its outputs.
The major structural differences between RNA and DNA.
The specific details of the process of transcription.
The major differences in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
How mRNA sequence dictates protein sequence.
Why translation is necessary for cells, where it happens, its inputs and its outputs.
How amino acids are associated and disassociated from tRNA molecules.
The major differences in translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
How and why the meaning of the term "gene" has changed over the past 100 years.