Competitive Markets and Monopoly: Market Structures, Pricing, and Industry Dynamics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is the primary goal of Chapter 9?
To explain how competitive markets are formulated.
What are the learning objectives of this chapter?
Understand market characteristics of perfect competition, how prices are established, why economic profits approach zero, and how society benefits from market competition.
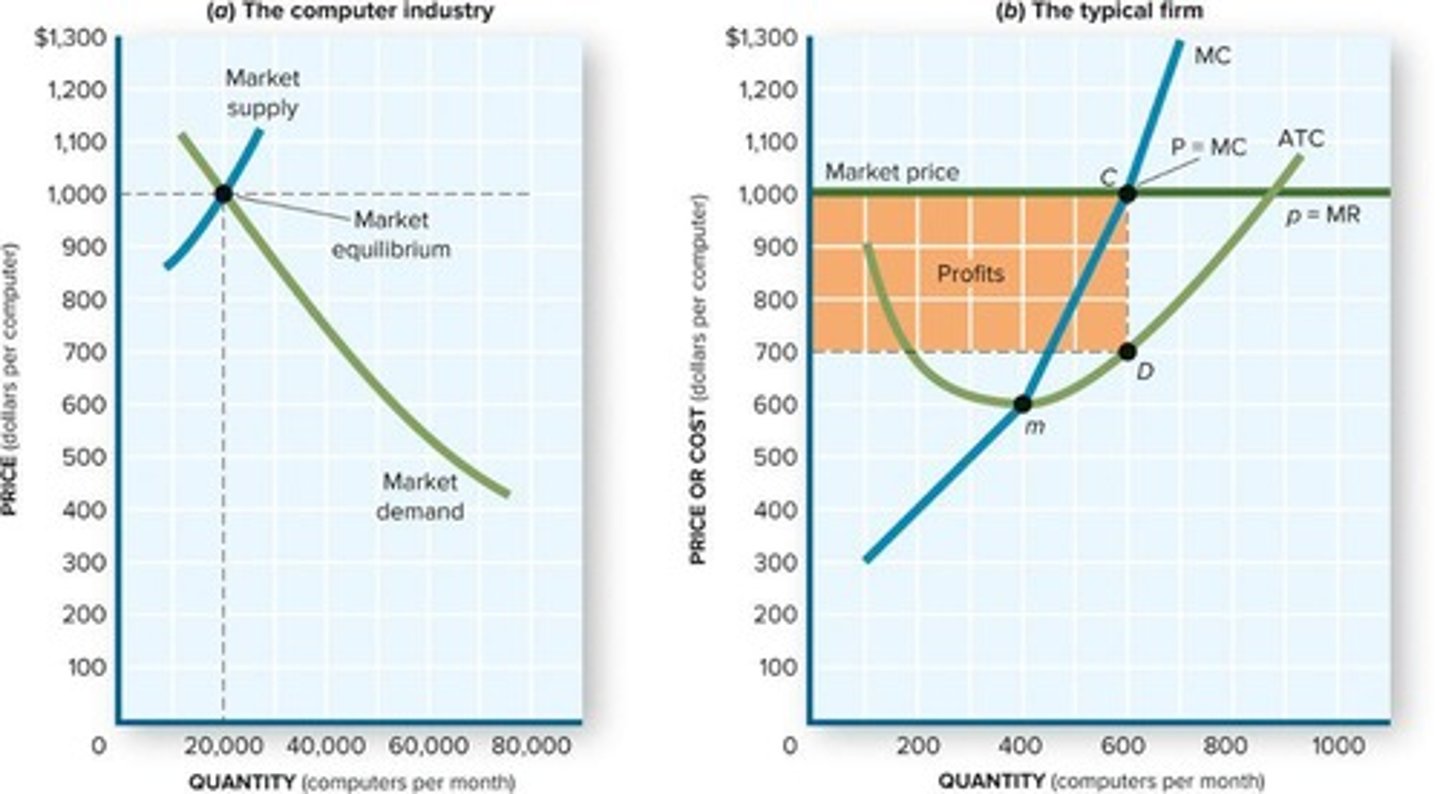
What does each firm's supply curve represent in a competitive market?
Each firm's supply curve is its marginal cost (MC) curve.
What determines the market supply curve?
The market supply curve is determined by the price of factor inputs, technology, expectations, taxes and subsidies, and the number of firms in the industry.
What happens to the market supply curve when an industry is profitable?
New firms enter the market or existing firms expand, causing the supply curve to shift right.
What is the effect of new firms entering a profitable market?
The market supply curve shifts right, leading to a decrease in price and economic profits.
What occurs when firms exit an industry due to economic losses?
The market supply curve shifts left, causing prices to rise and economic losses to decrease.
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
Many small firms, identical products, perfect information, profit maximization at MC = P (= MR), low barriers to entry and exit, and zero economic profit.
How do firms maximize profits in the short run?
By setting output where marginal cost (MC) equals price (P) and marginal revenue (MR).
What happens to economic profits in a competitive market over time?
Economic profits are squeezed to zero as new firms enter the market and competition increases.
What is the significance of zero economic profit in a competitive market?
It indicates that firms earn normal profit, covering the opportunity cost of resources.
What drives the competitive process in markets?
Competitive forces drive prices down, improve product quality, and encourage lower costs.
What is allocative efficiency in the context of competitive markets?
It occurs when the industry produces the right output mix based on consumer demand.
What happens when economic profits are negative?
It signals that consumers are unwilling to pay the opportunity cost, leading producers to reduce output.
What role does technology play in competitive markets?
Firms must innovate technologically to remain competitive and improve their products.
What is the relationship between economic profits and market entry?
High economic profits attract new firms, shifting the supply curve right and lowering prices.
What can cause a firm to shut down in a competitive market?
If competition drives the price below average variable cost (AVC).
What happens to inventory when a firm exits the industry?
The exiting firm may dump its inventory at reduced prices, further lowering industry prices.
What is the impact of continuous new product introductions in competitive markets?
They captivate consumer interest and can lead to high economic profits, attracting competitors.
How does the competitive process affect consumer prices?
It drives prices down, making products more affordable and expanding the market.
What is the effect of lowering production costs on a firm's output?
It encourages increases in output as the cost curves fall and marginal cost shifts right.
What is the market mechanism?
The use of market prices and sales to signal desired outputs or resource allocations.
What happens to the market when economic profits stabilize at zero?
The market stabilizes at a higher output, lower price, and minimum average total cost (ATC).
What is the relationship between price, marginal cost, and marginal revenue in a competitive market?
In equilibrium, price equals marginal cost, which equals marginal revenue (P = MC = MR).
What defines a monopoly?
An industry with only one producer and no competition.
What is market power?
The ability to alter the market price of a good or service.
How does a monopolist determine price and output?
By producing where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC).

What is the relationship between price and marginal revenue in a monopoly?
In a monopoly, marginal revenue is less than price (MR < P).
What happens to profits if a monopolist charges a higher or lower price?
Charging a higher price decreases profits; charging a lower price also decreases profits.
What is the profit-maximizing output for a monopolist?
The output where MR equals MC.
What are the characteristics of a monopoly?
Total barriers to entry, no close substitutes, and no competitive pressure.
What are significant barriers to entry for monopolies?
Patents, exclusive franchises, control of key inputs, and economies of scale.
What is price discrimination?
Selling the same good at different prices to different consumers based on their willingness to pay.
What are the pros of monopolies?
Greater ability for research and development, incentives for invention, and efficient production.
What are the cons of monopolies?
Little incentive to improve products, suppression of potential competition, and lack of innovation.
What is a natural monopoly?
An industry where one firm can achieve economies of scale over the entire market.
How does the government regulate natural monopolies?
By setting service quality, area of service, and the rate charged to customers.
What is a contestable market?
An imperfectly competitive industry subject to potential entry if prices or profits increase.
What issues have been raised against Microsoft regarding monopoly?
Allegations of erecting entry barriers to suppress competition and product improvement.
What similar concerns have been raised about Google?
Monopolizing search services through unique keywords and suppressing rivals.
What is the impact of monopolies on consumer choice?
Consumers receive fewer products and pay higher prices.
How does a monopolist respond to increased consumer demand?
A monopolist need not increase quantity even if demand rises.
What does the profit-maximizing output look like on a graph?
The point where the MR curve intersects the MC curve.
What is the effect of competition on a competitive industry?
High profits attract more suppliers, shifting supply right and lowering prices.
What happens to economic profits in a competitive market?
Economic profits tend to zero due to competition.
What is the difference in pricing between competitive and monopoly markets?
In monopolies, price exceeds marginal cost (P > MC), while in competitive markets, price equals marginal cost (P = MC).
What is the monopolist's approach to maximizing profits?
Adjust output based on the relationship between MR and MC.
What is the significance of barriers to entry in monopolies?
They prevent new competitors from entering the market, allowing the monopolist to maintain market power.
How do monopolies affect research and development?
Monopolies may lack incentive to innovate due to the absence of competition.