materials processing: ore refining
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
For blast iron furnace making, name the three material inputs
iron ore, limestone, coke
For a blast furnace, name the two material outputs
liquid pig iron, slag
what is the reducing agent in chemical reactions for a blast furnace
carbon monoxide
why is coke used instead of coal?
it has a higher % of carbon, more porous (more surface area)
how is a blast furnace heated
preheated pressurized air blown at bottom
____ is used to capture impurities to help purify and generate liquid pig iron, like ____ and _____
slag, silicon dioxide and sulfur
which is put in a blast iron furnace first, scrap or pig iron?
scrap
What is the main difference between steel and pig iron that necessitates BOF processing?
pig iron has 4%C, steel has 2%C
Which process is most commonly used to make intermediate solid forms from the molten steel produced by the basic oxygen furnace (BOF)?
continuous casting
The main products of the continuous caster are
• _____ (square or round sections up to 150 mm)
• _____ (square or round sections >150 mm)
• _____ (>600 mm by >40 mm)
billets, blooms, slabs
when refining aluminum metal, what is reduced at the cathode and what is oxidized at the anode?
aluminum gains e- (reduced) and oxygen loses e- (oxidized)
The microstructure of a plain carbon steel consists of ___________ and _____
proeutectoid ferrite and pearlite
it is a two-phase lamellar (parallel layers) mixture of ferrite and iron carbide (Fe3C).
pearlite
a blast furnace makes ______, not ______
pig iron, steel
what furnaces can steel be made in?
BOF and EAF
does EAF turn pig iron into steel?
no, only uses scraps
The steps in the Bayer process include _____ → _____ → _____ → _____
digestion, clarification, precipitation, calcination
what is the starting ore used in the bayer process?
bauxite
what is aluminum metal refined from?
aluminum oxide
what is the voltage needed for aluminum refining?
3-5V
low carbon steels use less that ___ %C
0.2%C
medium carbon steels use between ___ %C and ____ %C
0.2%C and 0.5%C
high carbon steels use between ___ %C and ____ %C
0.5%C and 2%C
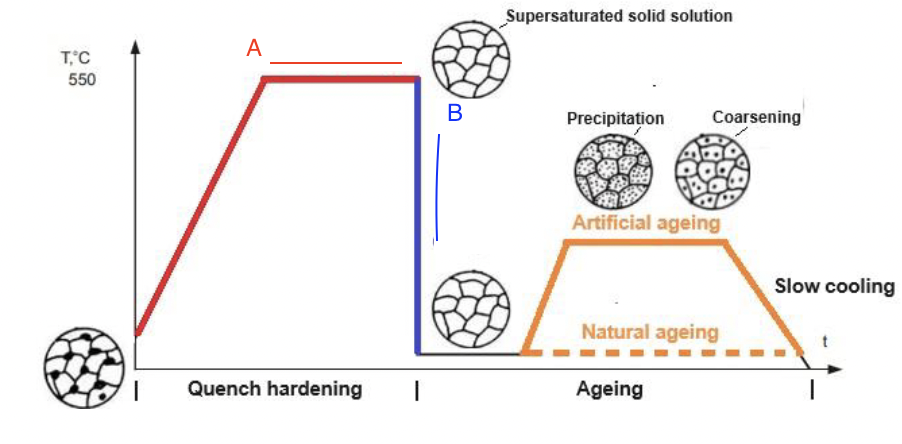
Precipitation hardening in aluminum alloys
A=solutionising, B=quenching
Overaging occurs due to ________
precipitate growth
what does the clarification of bauxite produce?
red mud
what are the primary components of slag? and from which materials are they from?
SiO2 from iron ore and CaO from limestone
Aluminum oxide needs to be dissolved in ______ to reduce the melting temperature during refinement
cryolite
for a basic oxygen furnace (BOF), what are the primary material inputs?
pig iron, scrap steel
for a BOF, what are the primary material outputs?
liquid steel, slag
alloying elements are added into the BOF after the ___ stage, why?
blow, more reactive than iron and will be lost in slag
molds for steel ingots are made of _______ iron
high carbon
introduces atom-size obstacles to molecular motion
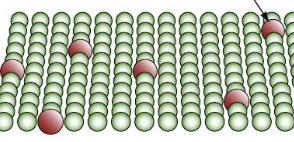
solution hardening
Cr content in stainless steels is normally above ___%
12
yield losses in fabrication depend on required change in _____ from stock to finished product
geometry
_____ is added to flux the removal of impurities such as SiO2, sulfur, and Al2O
limestone (CaCO3)
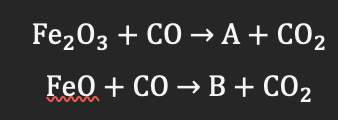
A=2FeO, B=Fe
what are the seven end of life alternatives for manufactured goods?
Reuse, refurbish, upgrade, recycle, downcycle, combust, landfill
In _____, a new purpose for contaminated material is found instead of reusing for its original purpose, only delaying the end of life. On the other hand, _____ doesn’t degrade the properties of the product after repeated life cycles
downcycling, recycling
liquid pig iron is more/less dense than slag?
more
what is the function of the double bell system in a blast furnace?
minimize escape of gases and dust
pig iron contains over ___%C
4
A cupola furnace converts _____ to ____
pig iron, gray cast iron
horizontal line connecting the intersections of the solidus and solvus lines from both sides
eutectic line
cycle time of a basic oxygen furnace is approximately ___ minutes
45
Out of CO, CO2, and CO3, which of the two are removed as gases during the BOF process?
CO and CO2
cycle time of an electric arc furnace (EAF) ranges from ___-___ hours
1-4
Compared to a BOF, EAF produces _____ but is ____
better quality steel, more expensive per ton
During continuous casting, molten metal is poured into a _____ and then into a water-cooled mold → solidifies as it travels down in the mold
tundish
Austenite has ___ crystal structure
Ferrite has ____ crystal structure
Cementite (or iron carbide) has an _____ crystal structure
FCC, BCC, orthorhombic
Low-carbon steel has high ____ while high-carbon steel has high _____
ductility, strength
Low alloy steels are not easily welded at ____ and _____ carbon contents because of martensite formation
medium and high
Why do we alloy iron instead of using just pure iron?
pure iron has very low strength
slip plane becomes stepped and threaded with ‘forest’ dislocations
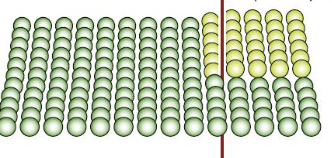
work hardening
presents larger dislocation obstacles
precipitation hardening
only resistance is the intrinsic strength of the crystal
perfect
low alloy steels often require ____ for their properties to be realized
heat treatment
tool steels are ____ carbon and ____ alloy, usually containing what 4 alloys?
high, high, chromium, vanadium, tungsten, and molybdenum
Austenitic Stainless steels: Usually ___% Cr and ___%Ni . Nickel stabilizes austenite at room temperature. Low carbon, very ductile. Used in chemical and food industries, etc
18,8
Ferritic stainless steels: ___ to ___% Cr, no nickel, low carbon. Used for many applications, from kitchen utensils to jet engines
15 to 20
austenitic SS is ___ corrosion resistant than ferritic SS
more
The ____ process refines aluminum oxide from bauxite and then aluminum oxide is smelted to aluminum using the _______ process
bayer, hall-heroult
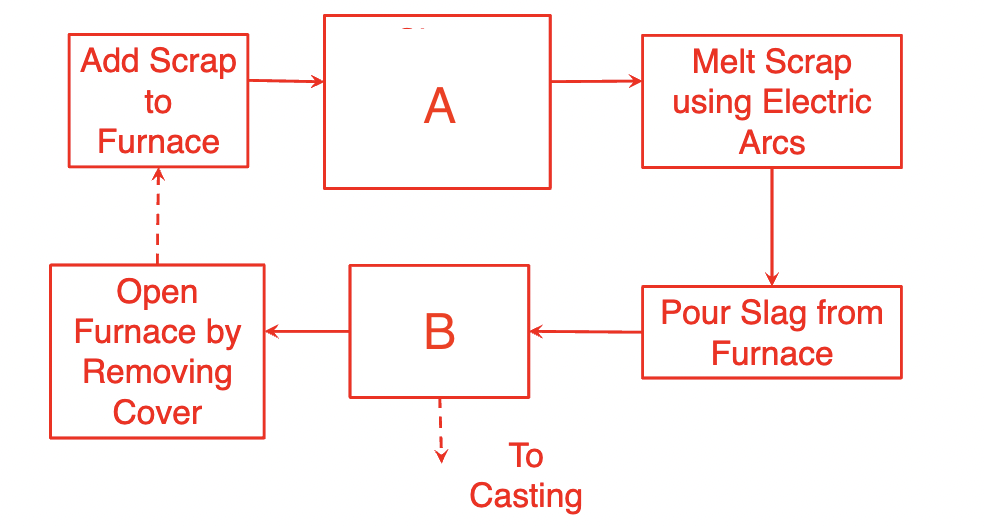
Fill in the blank for EAF flow diagram
A=close furnace by replacing cover
B=tap liquid steel into ladle
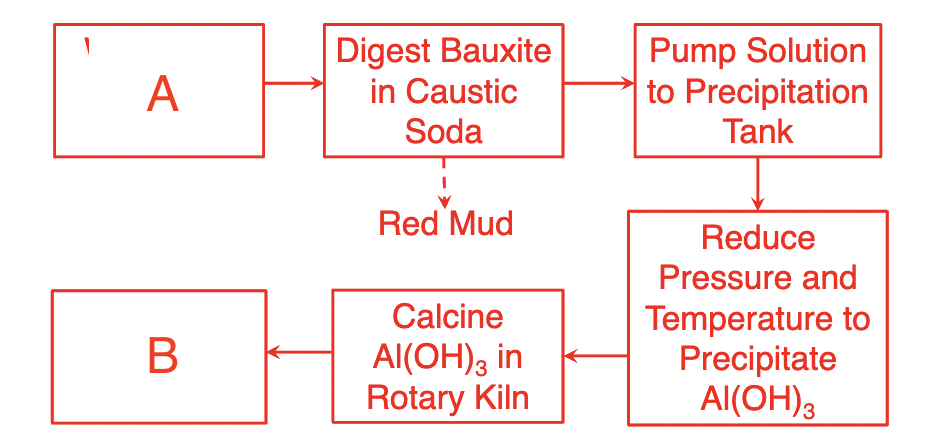
fill in the blanks for the bayer process
A=wash and crush bauxite
B=purified Al2O3 product
Low alloy steel is a carbon steel containing additional alloying elements with a total less than __ wt%.
5
What is the process that produces titanium metal?
Kroll
What is the byproduct of the Kroll process that needs to be removed after titanium metal is produced?
magnesium chloride
Which process is more sensitive to the composition of scrap steel added, EAF or BOF?
EAF
Which is more commonly used to convert pig iron into steel, BOF or EAF?
BOF
What is the reducing agent is used in the Kroll process to produce titanium metal?
magnesium
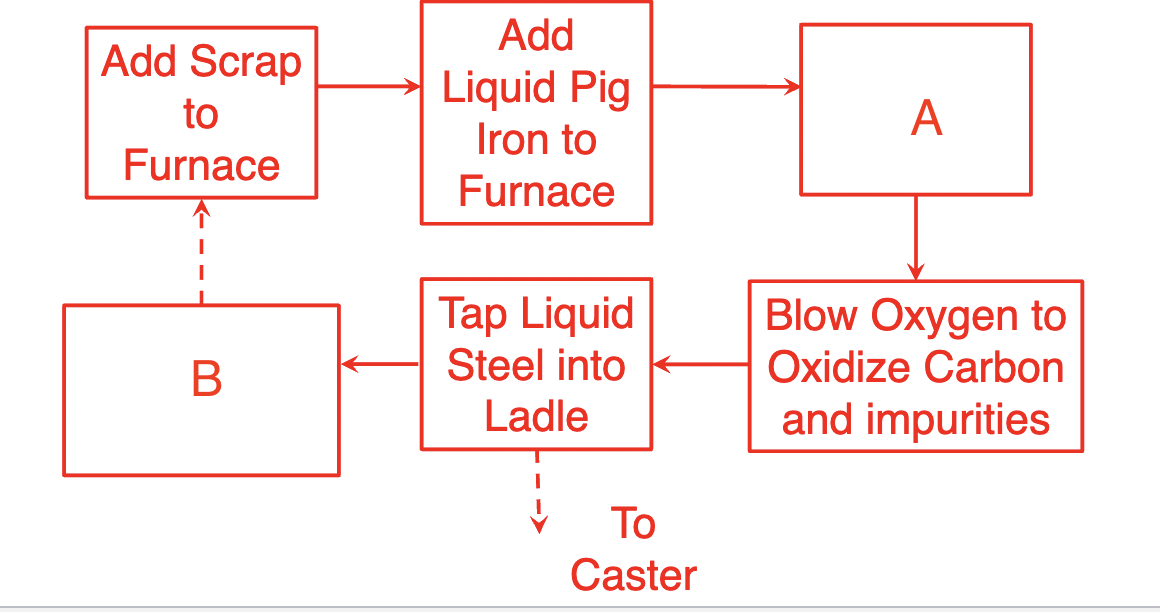
fill in the blank for the BOF process
A=add fluxes to furnace
B=tap slag from furnace