Topic 3 Genetics terms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
allelic series
a group of alleles of a gene that display a hierarchy of dominance relationship among them
biosynthetic pathway
a multistep biochemical pathway that synthesizes an end product or compound
codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive; both contribute to the phenotype
complementation analysis
allows the determination of whether two mutations yielding similar phenotypes are on the same gene or on separate genes
complementation group
a group of mutations that affect the same gene
Delayed age of onset
the appearance of an abnormal phenotype that is not present at birth but appears later in life and is caused by an inherited mutation
dominant negative mutation
Exerts a dominant effect. A heterozygote produces a nonfunctional altered protein that also prevents the normal gene product from functioning
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
gain of function mutation
causes the appearance of a new trait or function or causes the appearance of a trait in inappropriate tissue or at an inappropriate time
gene interaction
interaction between genes at different loci that affect the same characteristic
gene-environment interaction
situation in which the effects of genes depend on the environment in which they are expressed
genetic complementation
production of wild-type progeny when recessive mutations in two different genes are combined
genetic dissection
The use of recombination and mutation to piece together the various components of a given biological function.
genetic heterogeneity
a phenotype that can be caused by variants of any of several genes
Haploinsuffient
-a single copy (haplo) is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype in the heterozygous genotype
hypermorphic mutation
a mutant whose phenotype is similar to, but greater than, the wild-type phenotype
hypomorphic (leaky) mutation
reduced gene expression or activity of a product
(e.g. replacement impairs protein function but doesn't eliminate it, reduced transcription)
(effects on gene function)
incomplete/partial dominance
expressing a heterozygous phenotype that is distinct from the phenotype of either homozygous parent
lethal mutation
a gene or chromosomal mutation that influences the development of an organism in such a way that the organism cannot survive
loss of function mutation
Causes the complete or partial absence of normal function.
neomorphic mutation
generate gene product with new function or that is expressed at inappropriate time or place
null mutation
a mutation that results in complete absence of function for the gene
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that actually displays the phenotype associated with the genotype.
incomplete penetrance
Not all individuals with a mutant genotype show the mutant phenotype
Pleiotropy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype
sex-influenced trait
an autosomal trait that is influenced by the presence of male or female sex hormones
sex-limited traits
a characteristic controlled by autosomal genes that is phenotypically exhibited in only one of the two sexes.
temperature-sensitive mutation/allele
a mutation evident only at or above a certain temperature due to an abnormality of the protein product that affects its stability
variable expressivity
individuals with the same genotype have related phenotypes that vary in intensity

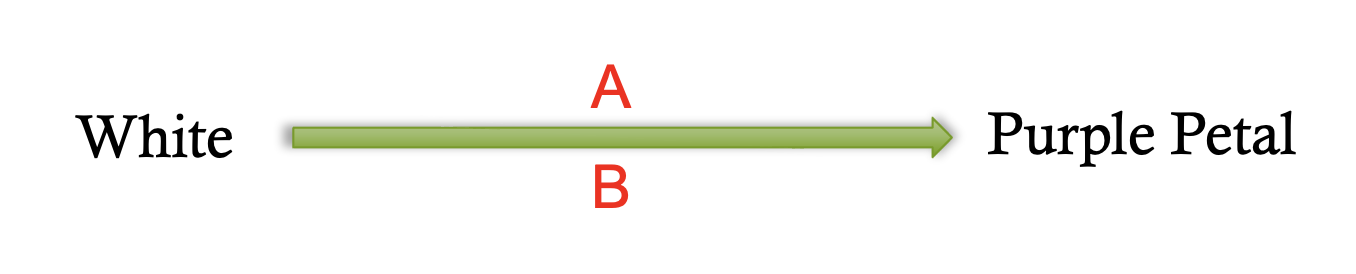
complementary gene interaction pathway
9:7
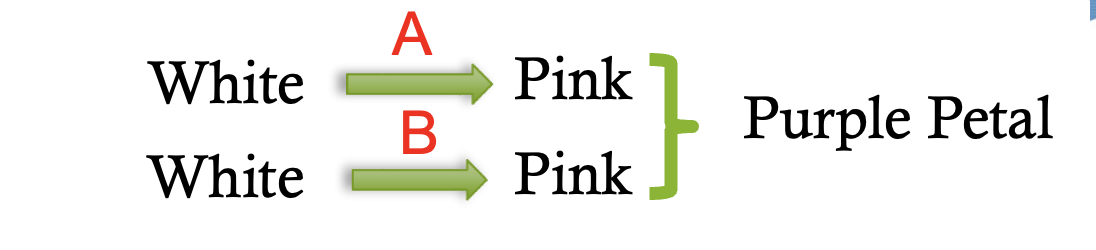
duplicate gene interaction pathway
15:1
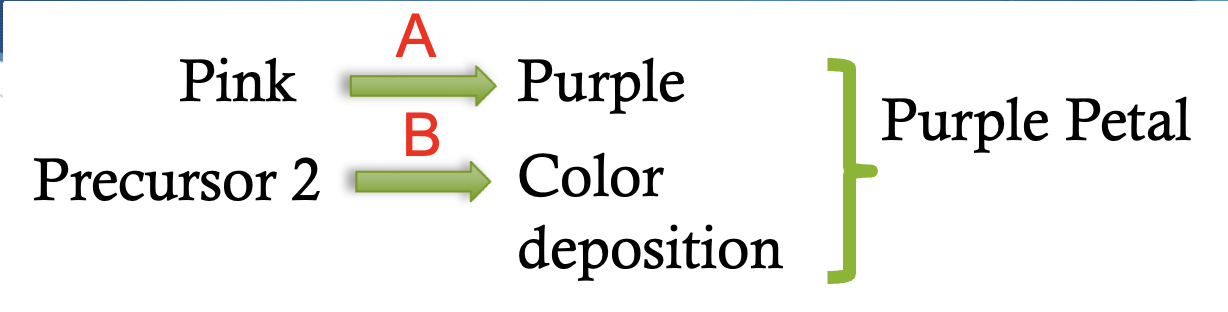
dominant gene interaction pathway
9:6:1
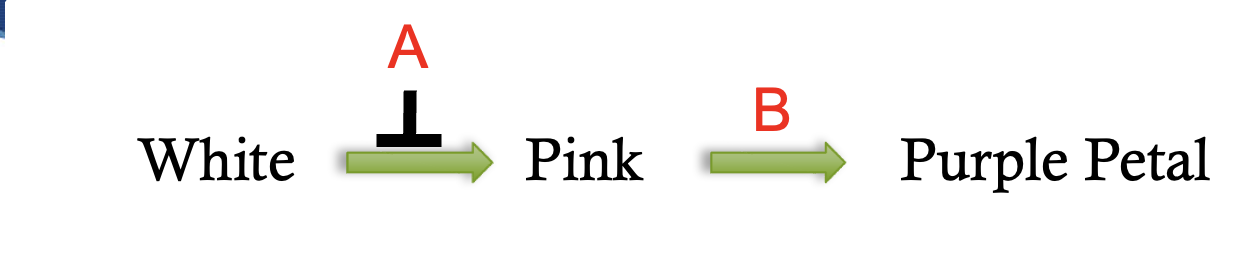
recessive epistasis gene interaction pathway
9:3:4
dominant epistasis gene interaction pathway
12:3:1
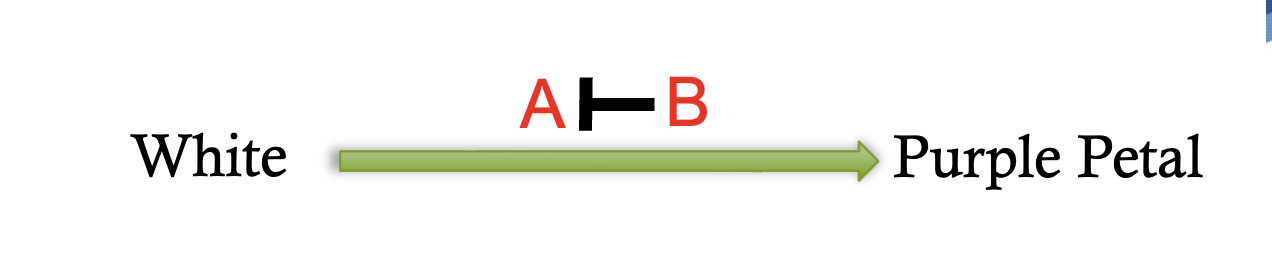
dominant suppression gene interaction pathway
13:3
allelic phase
the arrangements of alleles of linked genes on homologous copies of a chromosome pair
coefficient of coincidence
ratio of observed double crossovers to expected double crossovers
double recombinant (double crossover)
The occurrence of two crossovers between homologous chromosomes in a particular region. May involve two, three, or all four chromatids.
first division segregation
when the two alleles of a gene are segregated into different cells at the first meiotic division
genetic linkage
tendency for genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together
Haplotype
A group of alleles of different genes on a single chromosome that are closely enough linked to be inherited usually as a unit
genetic interference
The phenomenon where one cross over event may prevent subsequent events in nearby regions.
intragenic recombination
Recombination within a gene.
linkage disequilibrium
When a pair of alleles from two loci are inherited together in the same gamete more/less often than random chance would expect
linkage group
Alleles of different genes that are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together
LOD score
statistical value representing the probability of genetic linkage between the genes
mapping function
Relates recombination frequencies to actual physical distances between genes
map unit (m.u.)
Unit of measure for distances on a genetic map; 1 map unit equals 1% recombination.
Centimorgan (cM)
(also, map unit) relative distance that corresponds to a recombination frequency of 0.01
parental chromosomes (nonrecombinant chromosomes)
Chromosomes in gametes produced when crossing over does not take place between linked genes. Alleles marking each gene are retained in their initial (parental) configurations.
recombinant chromosome
Chromosomes that combine genes from both parents due to crossing-over
recombination frequency
With respect to two given genes, the number of recombinant progeny from a mating divided by the total number of progeny. Recombinant progeny carry combinations of alleles different from those in either of the parents as a result of independent assortment of chromosomes or crossing over.
second-division segregation
Different alleles go into different nuclei at the second meiotic division producing an MII division pattern of ascospores
syntenic genes
genes located on the same chromosome
Tetrad
structure containing four chromatids that forms during meiosis
tetrad analysis
The analysis of genetic linkage by analysis of different tetrad segregation types.
theta value
A variable indicating a recombination distance between genes. Used in lod score analysis.
three-point test-cross analysis
A test cross designed to identify genetic linkage between three genes and to provide data for determination of recombination frequency between linked genes.