BIOL 3010 Exam 1 Vocab
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
denaturation
first step of PCR- double-stranded DNA broken into two separate strands
-hydrogen bonds are broken
annealment
second step of PCR- hydrogen bonds formed between complementary bases
-joining of the template strand and the primer
elongation
final step of PCR- polymerase extends the amplified strand of DNA based on complementary template strand
segregation
separation of alleles in gamete formation
-one allele of each gene goes to the gamete
-one of Mendel’s laws:within one gene
independent assortment
random distribution of different alleles of different genes in gamete formation
ex. the gene for smooth v wrinkled will be passed down separately from the gene for green v yellow
-between genes!
locus
designated location on a chromosome
-sometimes refers to a gene
allele
alternative forms of a single gene
selection
eliminates individuals whose fitness is low and chooses individuals of high fitness to be the parents of the next generation
fitness
based on fecundity and survivorship: the relative advantage or disadvantage a particular genotype gives to an individual
inheritance/heredity
way genes transmit physiological, physical, and behavioral traits from parents to offspring
preformationism
the pre-Mendelian idea that organisms develop from a miniature version of themselves
genetic model organism
Mendelian created the first one with his pea plants
an organism that is used to understand biological phenomena
dominance
an allele that if present, will result in a particular genotype
recessivity
an allele that if present in BOTH alleles, will show phenotype, but is hidden if paired with a dominant allele
additivity
genes that code fore the same trait and all contribute to the phenotype
continuous v discrete trait
a continuous trait appears in a range of different phenotypes while a discrete trait is one or the other
thermal cycler/ pcr machine
used to amplify DNA through PCR
nucleotide
subunit of DNA or RNA consisting of a phosphate group, nitrogenous base, and a sugar
nucleoside
only the ribose and the nitrogenous base of DNA/RNA
nitrogenous base
components of nucleotides
DNA: adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
RNA: adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
phosphate group
phosphate bound to four oxygen atoms
-part of a nucleotide
ribose
sugar in an RNA nucleotide - 5 carbons
deoxyribose
sugar in a DNA nucleotide
hydrogen bond
an intermolecular force that holds complementary nucleotides together in DNA
covalent bond
sharing of electrons that result in a sigma bond
antiparallel
the structure of DNA: strands run in opposite directions so that one is 3’ to 5’ (template) and one is 5’ to 3’ (coding strand)
minor v major groove
in a DNA molecule, the minor groove is the smaller gap resulting from the displacement of the backbone whereas the major groove is the larger gap
-each have different reactivites and interactions with other molecules
amino acid
the building blocks of proteins produced during translation
built from triplets of nucleotides
ribosome
cytoplasmic structures composed of ribosomal RNA and protein; the sites of protein synthesis
ribozyme
RNA molecules that can act as enzymes to catalyze specific chemical reactions
catalysis
the acceleration of a chemical reaction due to a catalyst
RNase
ribonuclease, are enzymes that catalyze RNA into smaller components
DNAse
Deoxyribonuclease are enzymes that catalyze DNA into smaller components
mutagenesis
the process by which an organism's deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) change, resulting in a gene mutation
haploid
contains one set of chromosome - often used in mutagenesis experiments to isolate certain alleles
ex. haploid yeast in determining transformation of virulence
diploid
two matching set of chromosomes
nonsense mutation
an amino acid codon is changed into stop codon, terminating translation
missense mutation
mutation in a gene that changes a codon for one amino acid to a codon that specifies a different amino acid
collinearity
the length of a DNA sequence in a gene is proportional to the length of the polypeptide encoded by the gene
the same part of the gene correlated with the location of an amino acid in the polypeptide
transformation
transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane
ex. R form taking up dead S form debris to become virulent
codon
three consecutive nucleotides of DNA/RNA that code for an amino acid
initiation codon
AUG
stop codon
UAG, UGA, UAA
degeneracy
several different codons can code for the same amino acid
sense strand
aka coding or + strand: 5’ to 3’ strand of DNA that is the exact copy of a mRNA to be translated
antisense strand
aka noncoding, template or - strand : 3’ to 5’ strand of DNA that is complementary to the mRNA transcribed
frameshift mutation
insertions or deletions that alter the grouping of nucleotides by the reading frame- results in different amino acids
TSS
transcriptional start site
-The first base of a gene to be transcribed by an RNA polymerase, corresponding to the 5′-most base of the resulting transcript
untranslated region
or UTR, a part of the gene body that is not transcribed occurring before the promoter and after the transcriptional termination site
exon
short regions of DNA that are transcribed to become a part of the mRNA and later translated into protein
intron
part of the gene body that is in pre-mRNA, but is spliced out by spliceosomes before transcription
-important for genetic variation, only in eukaryotes
core promoter
where transcription is initiated
cis-regulatory element
a DNA motif located ON the gene being described that impacts gene expression by interacting with other transcription factors like trans-regulatory proteins
enhancer
cis-acting DNA sequences that promote the transcription of genes
Sanger sequencing
uses DNA sequencing machinery to make a copy of desired template- “first generation”
-extended with oligonucleotide primer and separated by size with electrophoresis
-involves the use of ddNTPs which randomly terminates extension at corresponding nucleotide-varying sizes then separated and read off of a gel
-only feasible with small portions of DNA
dNTP
Deoxynucleotide triphosphates that are building blocks of amino acids
ddNTP
dideoxynucleotide triphosphates used in sanger sequencing
-randomly terminates sequence at the corresponding base by inhibiting DNA polymerase enzyme
bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)
an engineered DNA molecule used to clone DNA sequences in bacterial cells
flow cell
glass slide coated with oligonucleotides complementary with nucleotides
-single-stranded, adapter-ligated DNA fragments can attach through hybridization
capillary sequencer
a part of improved first gen sequencing
-reactions with ddNTP sent through capillary and the laser separates them by size
dye terminator
eliminated the need to run 4 separate runs of Sanger sequencing by attaching fluorescent dyes to ddNTPs
Moore’s law
based on computer chips, the idea that technological advances doubles every two years
-gave hope to those attempting to sequence the genome that we would have the advances necessary to make it possible
-advances in sequences surpass this
illumina sequencing
“Second generation” sequencing
sequences tethered to a flow cell, adding one nucleotide at a time
-Terminator could be reverse- turned into regular nucleotide and the original dye quenched
contig
stretches of contiguous DNA sequence obtained by computer alignment of sequence reads; each chromosome is a contig
coverage
describes the number of sequencing reads that are uniquely mapped to a reference and “cover” a known part of the genome
-need high coverage to ensure no genes are missing from the sequence
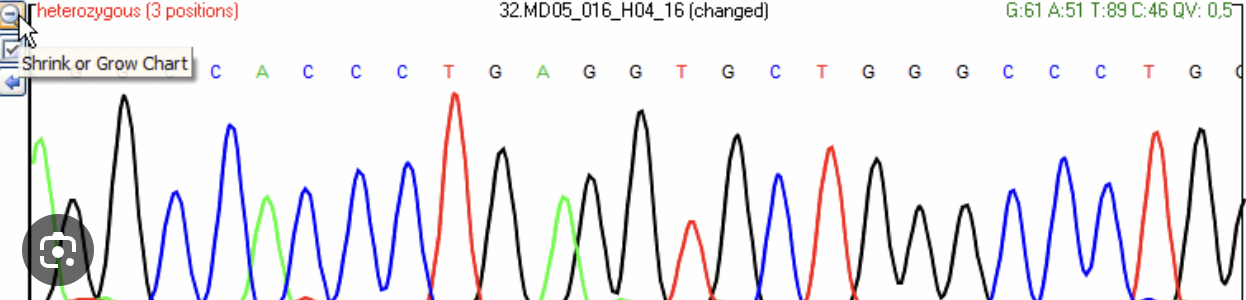
electropherogram
a plot of DNA fragment sizes, typically used for genotyping such as DNA sequencing
pseudogenes
a nonfunctioning gene - originally functioning gene has undergone mutations such that it no longer functions.
transposable elements
DNA segments that move about in the genome
-a barrier to DNA sequencing
transcription factors
cis: on the gene, trans: produced by sites on a different gene (mostly proteins that interact with cis sites to either inhibit or promote transcription)
-protein whose DNA sequence-specific binding to a cis-control element regulates the timing, location, or level of a particular gene’s transcription
chromatin
-DNA must be organized into chromatin in the nucleus- with 1/3 being DNA, histone proteins, and non-histone proteins
-helps condense naked DNA
nucleosome
DNA coiled around histone proteins, refers to particular part of chromatin
euchromatin
“open chromatin” that is more accessible to RNA polymerase and transcription factors
heterochromatin
“closed chromatin” that is more condensed and less accessible to RNA polymerase and transcription factors
acetylation
addition of an acetyl group to histones during histone modification
-takes + charge and neutralizes it so it is no longer as attracted to - charge in DNA → results in more accessible chromatin
histone acetyltransferase
enzymes that acetylate histone tail and opens up chromatin
histone deacetyletransferase
enzymes that removes acetyl group from histone tail and condenses chromatin
methylation
addition of a methyl group on the histone tail that usually closes up chromatin but can have both effects
Protein arginine methyltransferase (PMRT)
enzyme that methylates arginine
histone methyltransferases (HMTs)
enzyme that methylates histone tails, impacting chromatin structure
histone mark
places where histones are modified
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
chip sequencing used to locate histone marks
-antibodies of the protein are incubated with the protein, unattached DNA is washed out, and you are left with the fragments that contain the modification of interest
pioneer transcription factor
can weasel in to relatively condensed chromatin that other transcription factors cannot
-bind DNA sequence to permit binding of other transcription factors, histone variants, and chromatin remodelers
pre-initiation complex
aka PIC, a complex of proteins that is formed before the transcription
-includes RNA polymerase 2 and other transcription factors
-important for RNA pol 2 recruitment, also opens DNA helix, through DNA translocase XPB so transcription can be initiated
mediator
promotes PIC assembly and helps pol 2 to be localized in the correct spot
acts as a bridge between the promoter DNA sequence bound to an enhancer or silencer, and RNA polymerase II at the initiation site
TATA-box
-a sequence of DNA found in the core promoter region of genes
a part of the PIC and determines the side where transcription begins
initiator
A site, upstream from a structural gene, for attachment of a protein that stimulates initiation of transcription
general transcription factor
proteins that help to position Pol II correctly on the promoter, a part of the PIC
pre-mRNA
the initial form of mRNA that still includes introns
mRNA
messenger RNA, the product of transcription that is then sent out into the cell to be translated
eRNA
enhancer RNAs result from RNA pol2 attaching to an enhancer instead of a promoter due to their similarities
uaRNA
antisense RNA, transcribed upstream instead of downstream
DNA binding domain
independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA
transactivation domain
contains binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators.
cofactor (coactivators and repressors)
-lack DNA binding domains
bound to a protein (usually an enzyme) and is required for the protein's biological activity
Bridge activators to basal transcriptional apparatus
ex. mediator complex
coactivator promotes transcription while corepressors inhibit it
DNA methyltransferase
methylates CpG islands (not to be confused with histone methyltransferase!!)
removes transcription factor off of the promoter to inhibit transcription
leads to histone methylation
Methylated cytosines recognized by methyl-CpG binding proteins (meCPs) - leads to chromatin condensation
CpG island
large number of CpG nucleotide repeats often near the promoter - can be methylated, leading to the inhibition of transcription
epigenetic silencing
non mutational gene inactivation that can be passed down to daughter cells
ex. methylation of CpG islands
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler
alters chromatin structure by sliding, displacement, modification
-share affinity for nucleosome, domains to recognize histone modifications/other proteins, and similar ATPase domains for overcoming nucleosome-DNA interactions
-exposes DNA for DNA binding protein to access, allows accessibility for transcription factors to interact with cis-regulatory elements
phosphorylation
-A process in which a phosphate group is added to a molecule, such as a sugar or a protein.
-changes chromatin state
cancer driver mutation
changes in the DNA sequence of genes that cause cells to become cancer cells and grow and spread in the body
-dysregulation of gene expression