Shoulder Girdle Projections
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merrill's Atlas - CH 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Which projection best shows the greater tubercle?
AP shoulder, external rotation
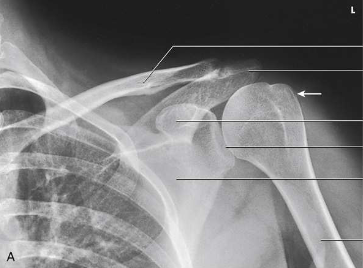
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP shoulder, external rotation
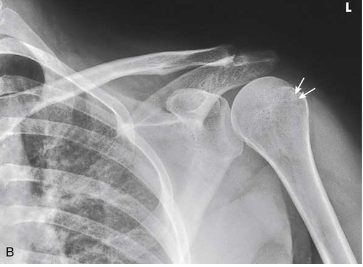
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP shoulder, neutral rotation
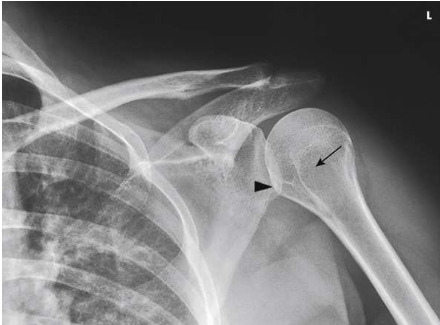
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP shoulder, internal rotation
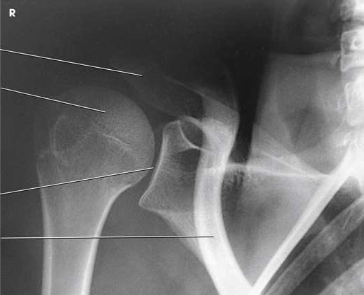
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP oblique, Grashey
Which projection best shows the glenoid cavity?
AP oblique, Grashey
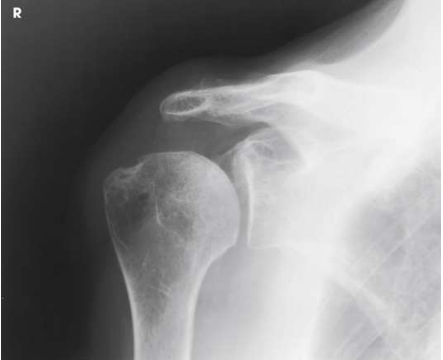
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP oblique, Grashey!
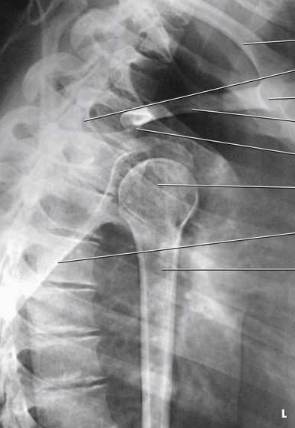
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
transthoracic projection, lateral shoulder position, Lawrence
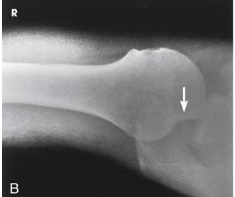
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
inferosuperior axial projection of the shoulder joint
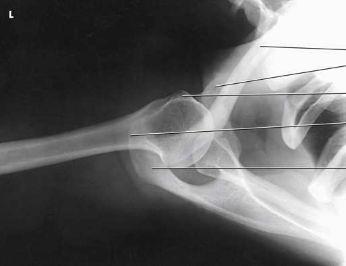
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
superoinferior axial projection of the shoulder joint
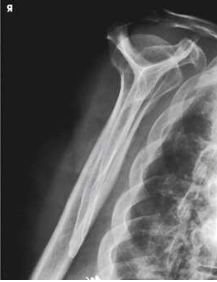
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
PA oblique shoulder, Y-view
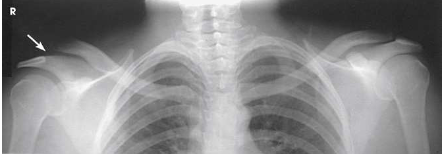
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP bilateral AC joints s
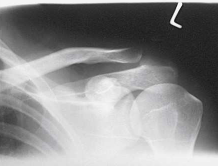
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP unilateral AC joint
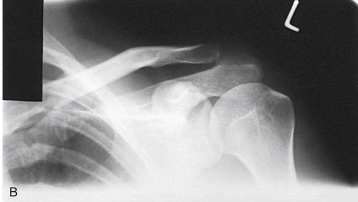
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP unilateral AC projection
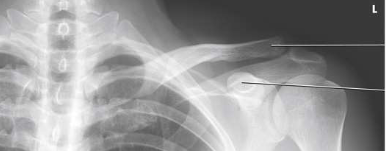
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP clavicle
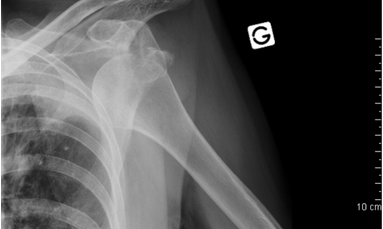
What type of pathology is shown here?
anterior dislocation of the humerus
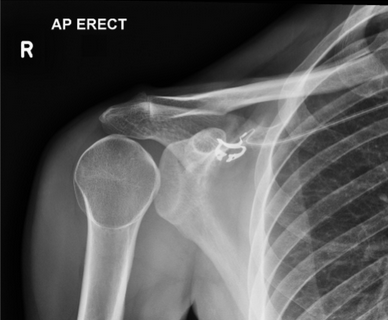
What type of pathology is shown here?
posterior dislocation of the humerus
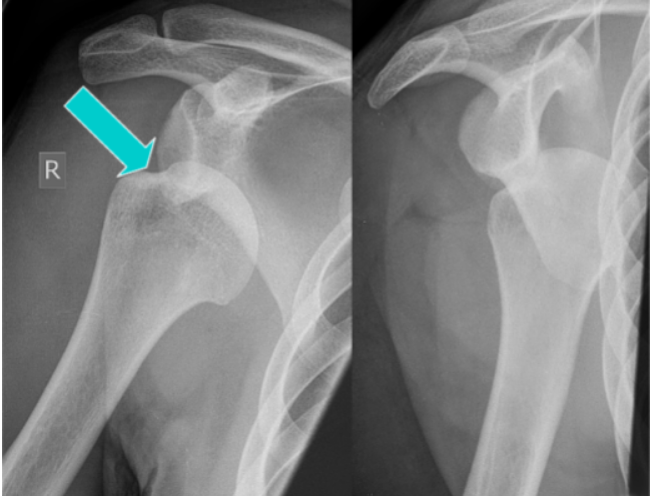
What type of pathology is shown here?
Hill Sachs Defect
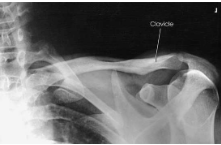
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
PA axial clavicle
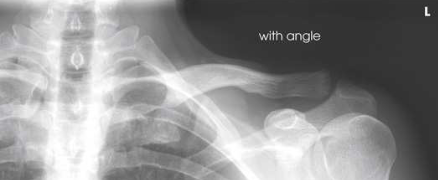
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP axial clavicle
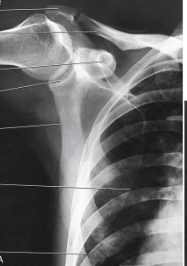
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
AP scapula
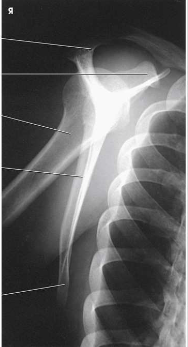
What type of projection, position and anatomy is this?
lateral scapula
What projection is used for those who cannot rotate or abduct their shoulder?
transthoracic lateral
What landmark should be seen on an AP shoulder projection with external rotation?
greater tubercle
What landmark should be seen on an AP shoulder projection with internal rotation?
lesser tubercle
Where is the CR directed for an AP shoulder projection?
1 in (2.5 cm) inferior to coracoid process
Where is the CR directed for an AP oblique shoulder projection?
2 in medial + 2 inferior to superolateral border (5 cm medial + 5 cm inferior)
Where is the CR directed in a transthoracic lateral shoulder projection?
surgical neck through mid - coronal plane
How much should the tube be angle if both shoulders are in the same plane (patient cannot move either arm)?
15 - 20 degrees cephalad
Which projection helps rule out a Hill Sachs defect?
infero - superior axial projection
How much should the arm (already in a right angle) be abducted in an infero - superior axial shoulder projection?
20 degrees
Where is the CR directed for an infero - superior axial shoulder projection?
axilla, passing through AC articulation
How much is the tube angled for an infero - superior axial shoulder projection?
15 - 30 degrees medially
What does the tangential humerus (proximal) projection show?
intertubercular groove
Where is the CR directed for a tangential humerus (proximal) projection?
intertubercular groove
How much is the tube angle for a tangential humerus (proximal) projection?
10 - 15 degrees cephalad
How much is the tube angled for an AP axial clavicle in lordotic position?
10 - 15 degrees cephalic
How much is the tube angled for an AP axial clavicle in supine position?
15 - 30 degrees cephalic
How much is the tube angled for a PA axial clavicle?
15 - 30 degrees caudal to supraclavicular fossa
Where should the top of the light of the IR be for an AP scapula projection?
2 in above shoulder
Where is the CR directed for an AP scapula projection?
2 in (5 cm) inferior to coracoid process
How much is the patient turned in a lateral scapula projection?
45 - 60 degrees