bio 38 unit 3
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
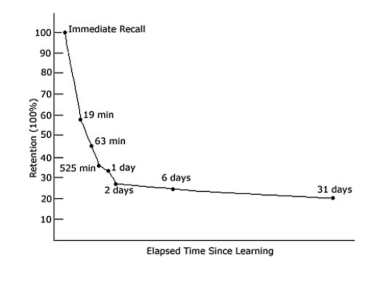
ebbinghaus’ forgetting curve
ebbinghaus taught himself nonsense words, then checked his retention for them
he found that after a very steep slope of forgetting, there is a flattening of retention
main findings
if you remember something after 2 days, you’re likely to also remember it after 30
most forgetting occurs immediately after learning
do memories become inaccessible or just lost?
they likely become inaccessible, and just need the right cue to get them back
evidence
people were able to match names to pictures of people from their high school from decades ago, and they were able to do it because they got the right cue
optogenetically activating neurons in the dentate gyrus (hippocampus) makes remote memories come back in mice
stimulating regions of epileptic brains made patients vaguely remember things
decay
cause of forgetting where memories gradually deteriorate with time
evidence = synaptic pruning makes inactive synapses smaller and less prone to activation
interference
cause of forgetting where memories interfere with each other
the more similar they are, the more likely they are to compete
a memory cue leads to several memories
ex: losing your car in a parking lot because there is too much interference in memories
change in context
cause of forgetting where memories are less accessible when you switch contexts
being in the same context during retrieval as you were during encoding improves retention
directed forgetting
the DLPFC works to inhibit memory systems to help us not remember something
evidence = participants are cued to either remember or forget something, and instruction to forget led to worse memory
memory suppression
in the think/no think method, participants are instructed to avoid thinking of a word/to push it out of mind
after multiple repetitions, the no-think instructions lead to a weakening of memory
retrieval-induced forgetting
retrieval of one memory can harm retrieval for another memory
AKA being tested for one item vs the other improves the recall for the item that was tested
compromises testimony because being asked one question repeatedly harms the retention for other important details
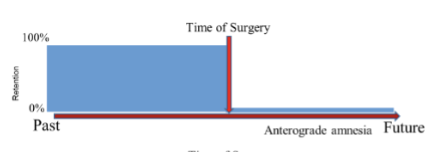
anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories due to hippocampal damage
memories can’t be formed without the hippocampus
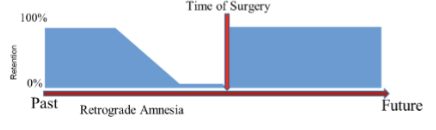
retrograde amnesia
inability to remember recent remote memories due to hippocampal damage
younger memories rely on the hippocampus
graded in time with the most remote memories remaining intact
tested by asking about past events before the accident while gradually moving further and further back in time
amnesia primarily impacts what type of memory?
episodic
what types of memory are intact in amnesia?
remote declarative
working/short term memory
HM could retain a 3 digit number for 15 min without interference
nondeclarative memory (priming and conditioning)
lesions
selective brain damage resulting in behavioral changes based on the site of damage
pros
causal manipulation with animals AND humans
tests necessity
aided us in history
cons
not super well controlled/exact damage
small sample sizes
not generalizable
brain adapts once damage occurs (compensatory mechanisms)
we do not always know what the person was like before the lesion
patient HM
had bilateral hippocampal lesion during surgery for epilepsy
intact working/short term memory and general cognition (could copy an image and improve on the mirror drawing task)
could not draw an image later on or remember doing the mirror drawing task
patient EP
contracted a herpes infection that caused encephalitis of the MTL
anterograde amnesia (could not remember that he had already told a story or remember lists of words he just learned)
childhood/infantile amnesia
inability of adults to retrieve episodic memories from before 2-4 years old and even afterwards up until about 10
occurs in humans and animals
caused by an immature hippocampus and cortex, and lots of hippocampal neurogensis
human hippocampus reaches full maturity at 3-5 years old