Chap 6 Solute Transport 2025
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Chemical potential (µ)
The potential energy of a solute defined by concentration gradients and electrochemical conditions.
Electrochemical potential
The combined effects of chemical potential and electric charge on the distribution of charged solutes.
Membrane potential
The voltage across a membrane that affects the distribution of charged solutes.
Free energy (G)
The capacity to do work, quantified as energy (J*mol-1) in thermodynamics.
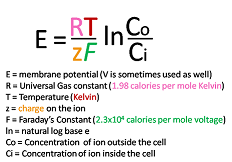
Nernst equation
A formula that relates the concentration gradient of an ion across a membrane to the voltage difference between two compartments.
Proton motive force (PMF)
The energy derived from the electrochemical gradient of protons (H+) across a membrane.
Semi-permeable membrane
A membrane that allows certain substances to pass while blocking others.
Passive transport
Movement of solutes across a membrane without the expenditure of energy.
Active transport
Movement of solutes against a concentration gradient that requires the input of energy.
Channel proteins
Membrane proteins that create pores through which ions and polar molecules can pass.
Carrier proteins
Proteins that facilitate the movement of specific substances across a cell membrane through conformational changes.
Symporters
Transport proteins that move two or more solutes in the same direction across a membrane.
Antiporters
Transport proteins that move one solute into a cell while moving another solute out.
Faraday’s constant (F)
A physical constant representing the amount of electric charge per mole of electrons (96,500 coulombs*mol-1).
Valence (z)
The charge of an ion; for example, K+ has valence +1, Cl- has valence -1, etc.
Cytosolic compartment
The fluid inside a cell where various concentrations of solutes can be measured.
Extracellular compartment
The fluid outside the cell, important for gradient comparisons.
Chemical potential difference (Δms)
The difference in chemical potential between the inside and outside of a cell.
Electrical potential difference (ΔE)
The difference in electrical potential, or voltage, between two spaces.
Membrane polarization
When there is a charge separation across a membrane, resulting in a voltage.
Logarithmic relationship
A mathematical relationship where a change in one quantity results in an exponential change in another, such as in the Nernst equation.
K+ ion
A potassium ion that commonly moves across cell membranes and contributes to membrane potential.
Hydrolysis of ATP
The chemical process that releases energy by breaking down ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Electrogenic pumps
Transporters that move charged ions and contribute to the membrane potential.
Conductance
The ability of a channel or carrier to allow ions or molecules to pass through a membrane.
Concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance across a space, driving passive transport.
Diffusion
The passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Gating mechanisms
The regulatory processes that control the opening and closing of channel proteins.
Equilibrium
The state where the concentrations of solutes are equal across a membrane, leading to no net movement.
Steady state
A condition where the concentration of ions remains constant due to the continuous active transport of additional ions.
Electrophysiology
The study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues.
Saturation point
The maximum concentration of a substance in a solution beyond which no more can dissolve.
Ion channel selectivity
The ability of an ion channel to preferentially allow certain ions to pass while excluding others.