lab manual exercise 6 & 7
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
epithelial tissues
sheet of cells that cover body surface or lines a body cavities
epithetial tissues occur in the body as
covering and lining epithelium / grandular epithelium
types of tissue
connective
epithelium
muscle
nerve
function of epithelium
protection
absorption
excretion
secretion (unique to glandular epithelium)
sensory receptor
polarity of epithelium
apical surface
basal surface
basement membrane
apical surface
once side of cell membrane is free and different, exposed to surface or lumen
basal surface
other sides of cell membrane, attached to the underlying basement membrane
basement membrane
acellular secretory material by epithelium cells (basal lamina) and connective tissue (reticular lamina) lie next to each other
specialized contact of epithelium
cells fit close together to form sheet bounded by specialized junction
epithelium supported by connective tissue
cells supported by adhesive basement membrane
epithelium: avascular but innervated
supplied by nerve but no blood supply of their own
depend on diffusion of nutrients from underlying connective tissue
regeneration: epithelium
divide easily; important for abrasion
types of epithelia
simple
stratified
pseudostratified
transitional
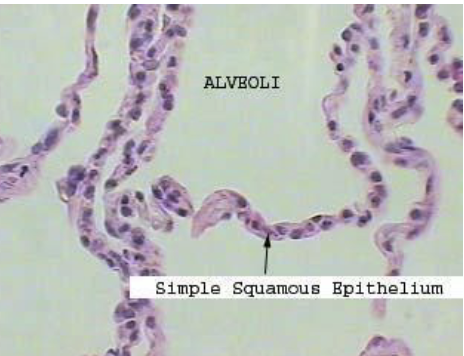
simple epithelium
epithelia consist of 1 layer of cells attached to basement membrane
stratified epithelia
consist of 2 or more layer of cell
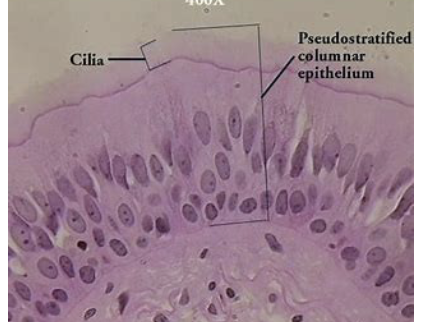
pseudostratified epithelium
simple columnar
often ciliated
nuclei lie at different levels above the basement membrane = give false appearance of being stratified
may contain mucus-secreting goblet cells and bear cilia
3 types of cell shape
squamous
cubodial
columnar
squamous
disc-shaped
cuboidal
cubelike with large central nuclei
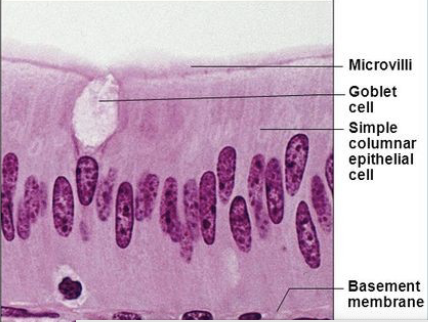
columnar
column-shaped with oval nuclei, some bear cilia or mucus-secreting unicellular gland
transitional epithelium
made of round stratified squamous epithelium
cell slides over one other to allow organs to be stretched
superficial cell ( transitional epithelium)
flat when organ is full & round when organ is empty
endocrine gland
ductless gland and secrete hormones into extracellular fluid
exocrine gland
retain duct and secretion empty through duct to body surface or body cavities
function of simple squamous epithelium
allows material to pass by diffusion and filtration
function of simple cuboidal epithelium
secretion and absorption
function of simple columnar epithelium
absorption; secretion of mucus, enzyme and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus by ciliary action
function of pseudostratified ciliated columnar
secrete substances (mucus) ; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
stratified squamous epithelium
thick membrane composed of several cell layers
basal cells = cuboidal/ columnar (active in mitosis)
surface cell = squamous cells ( keratin and dead)
function of stratified squamous epithelium
protect underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
stratified cuboidal
two layers of cubical cells for protection
stratified columnar
basal cell= cubical
superficial cells elongated and columnar
protection/secretion
transitional epithelium
resembles Both stratified cubiodal and squamous cell
basal = cubiodal or columnar
connective tissue
present as discrete structure (most abundant )
4 main type of connective
connective tissue proper
a. loose connective tissue
b. dense connective tissue
cartilage
bone
blood
loose connective tissue
areolar
adipose
reticular
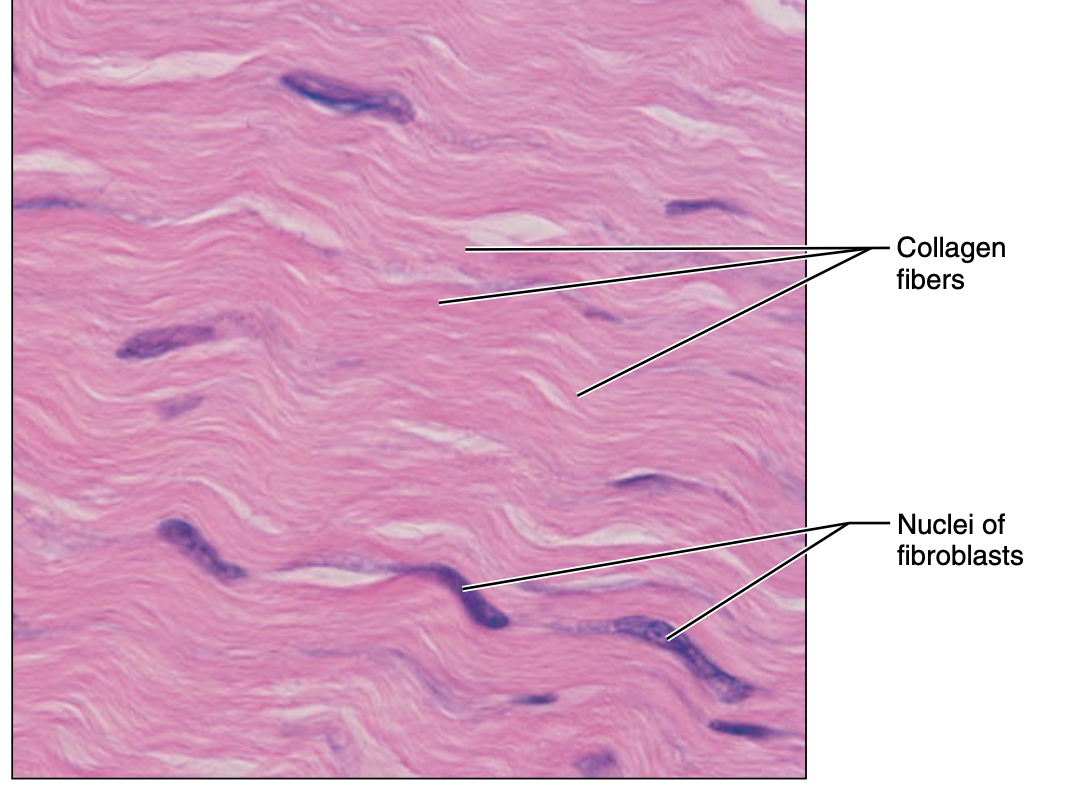
dense connective tissue
dense regular
dense irregular
elastic
function of connection tissue
protect
support
insulate
bind other tissue
areolar connective tissue
soft pack-aging material that cushions and protect body organs
adipose tissue
provides insulation for body tissue and a source stored energy
organ of connective tissue
all derived from mesenchyme in embryo
vascularity of connective tissue
rich in blood supply except cartilage (avascular) and dense connective tissue (poor vascularize)
extracellular matrix (connective tissue)
cellular non-living material btw cells
amt of matrix varied in different connective tissue
two component of extracellular matrix
ground substance and fibers
ground substance
made of extracellular fluid, cell adhesion protein and proteoglycans
lacunae
when matrix is firm and hard as bone, forms cavity in matrix
fibers
collagen fibers (white)
elastic fibers (yellow)
reticular fibers (fine collagen) provide support
fibroblast cells
secrete its matrix ; other white blood cell types are presented
bones, cartilage and other dense connective tissue
compose of firm matrix and more fibers
All CT are variation of areolar CT
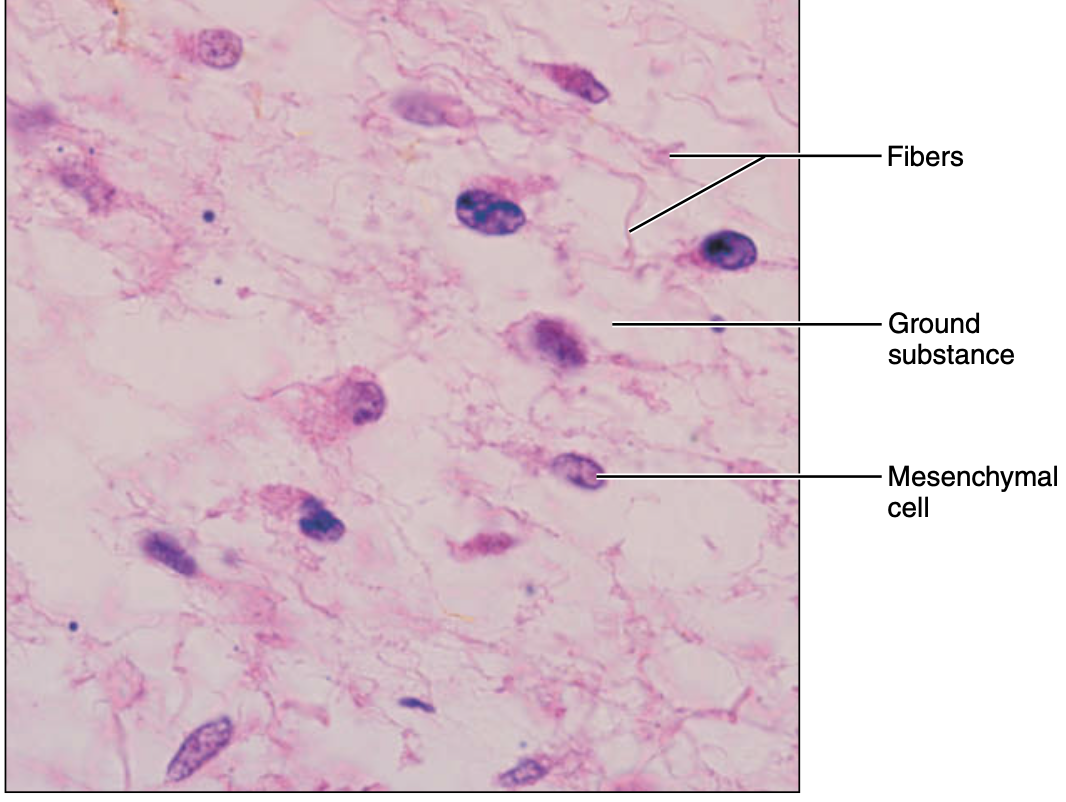
embryonic connective tissue: mesenchyme
gel-like ground substance containing fibers; star-shaped mesenchyme cells
function of embryonic connective tissue: mesenchyme
give rise to all other Connective tissue type
loose connective tissue areolar
gel-like matrix with three fibers type, mast cell and some white blood cell
function of loose connective tissue areolar
wrap and cushion organs; plays important role in inflammation; holds and convey tissue fluid
loose connective tissue, adipose
matrix as in areolar but closely packed fat cells with nucleus pushed onto the side
function of loose connective tissue, adipose
provided reserve fuel; insulate against heat loss; support and protect organs
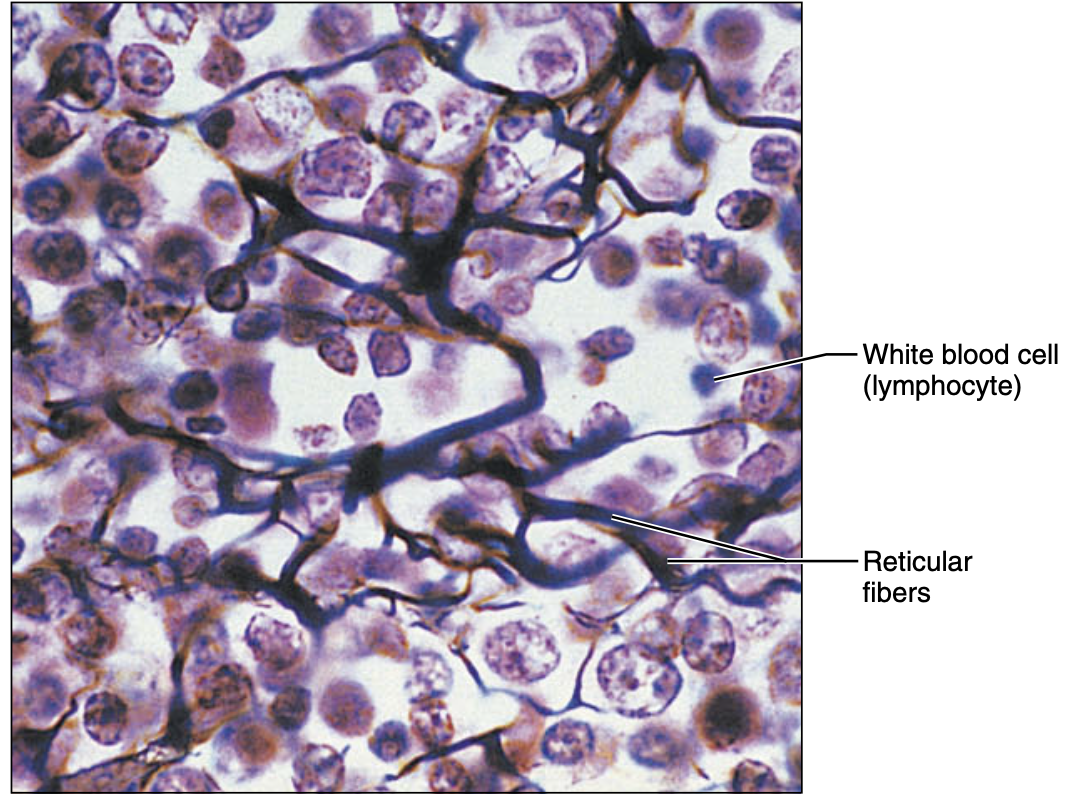
loose connective tissue ,reticular
network of reticular fibers in a loose ground substance, reticular cells lie on network
function of loose connective tissue ,reticular
fiver form a soft internal skeletal that support other cell types including white blood cell, mast cell and macrophages
mast cell
a type of immune cell
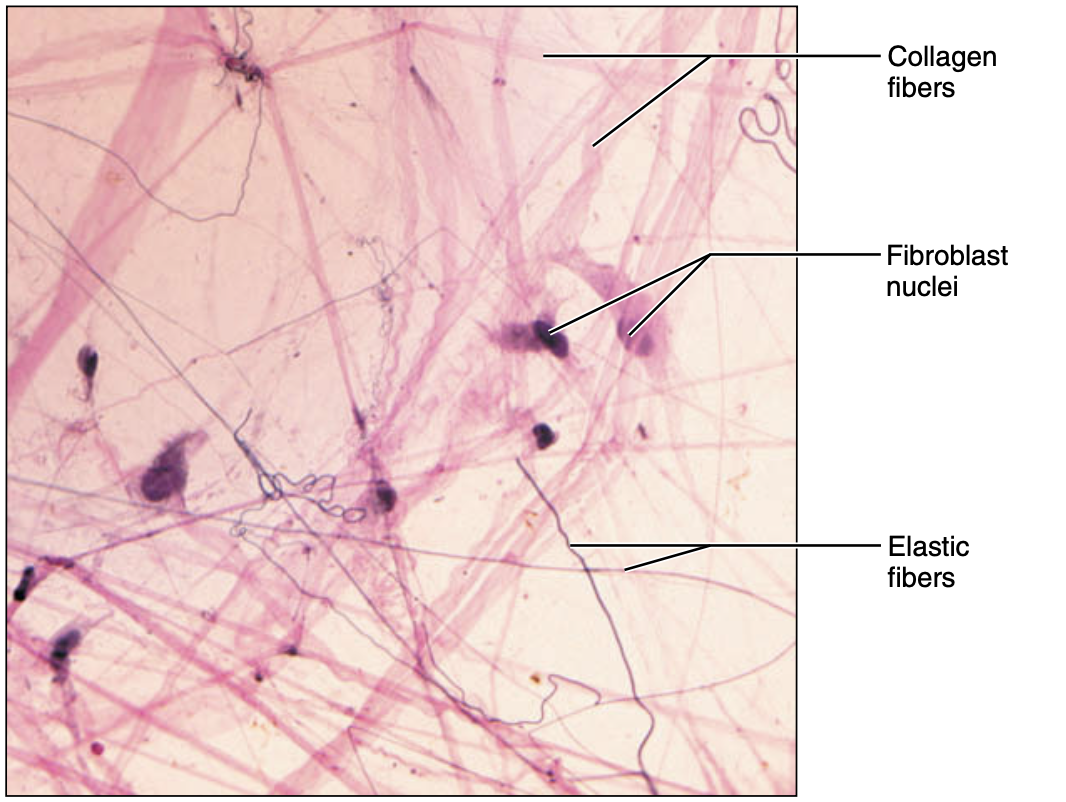
dense regular connective tissue
parallel collagen fires; few elastic fiber; major fibroblast
function of dense regular connective tissue
attach muscle to bone withstand great tensile stress when pulling force applied el
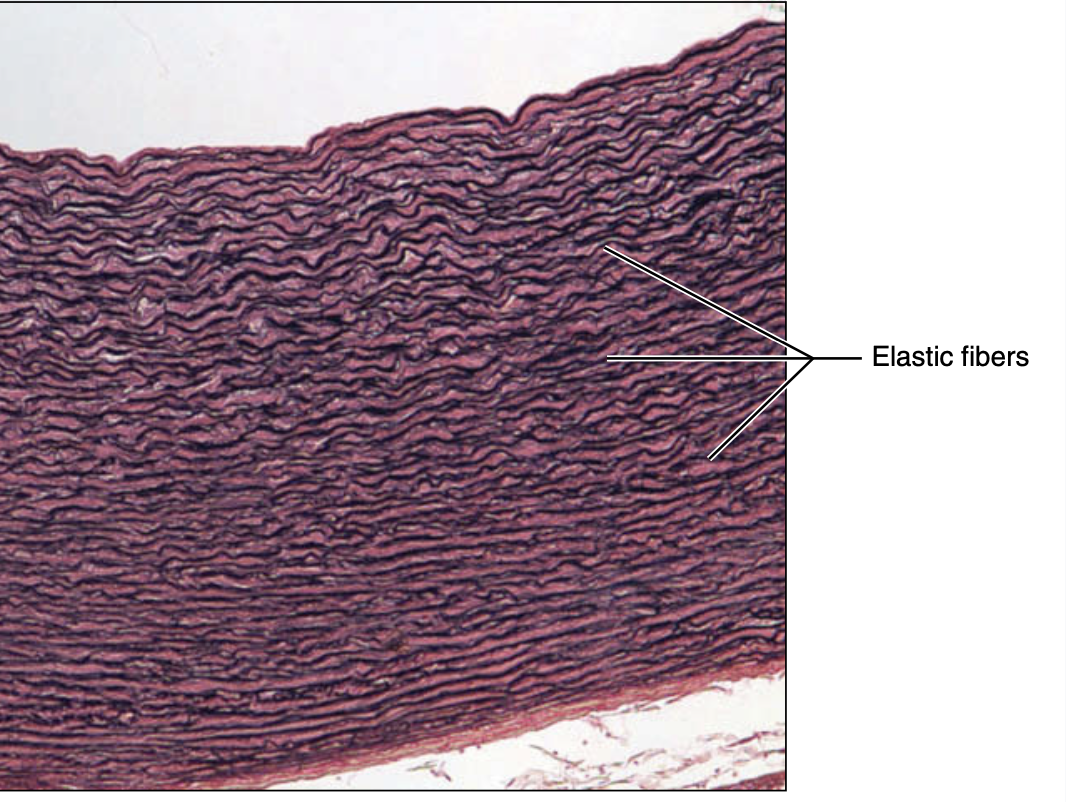
elastic connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue contain a high proportion of elastic fiber
function of elastic connective tissue
allow recoil of tissue following stretching; maintain pulsatile flow of blood; aid passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
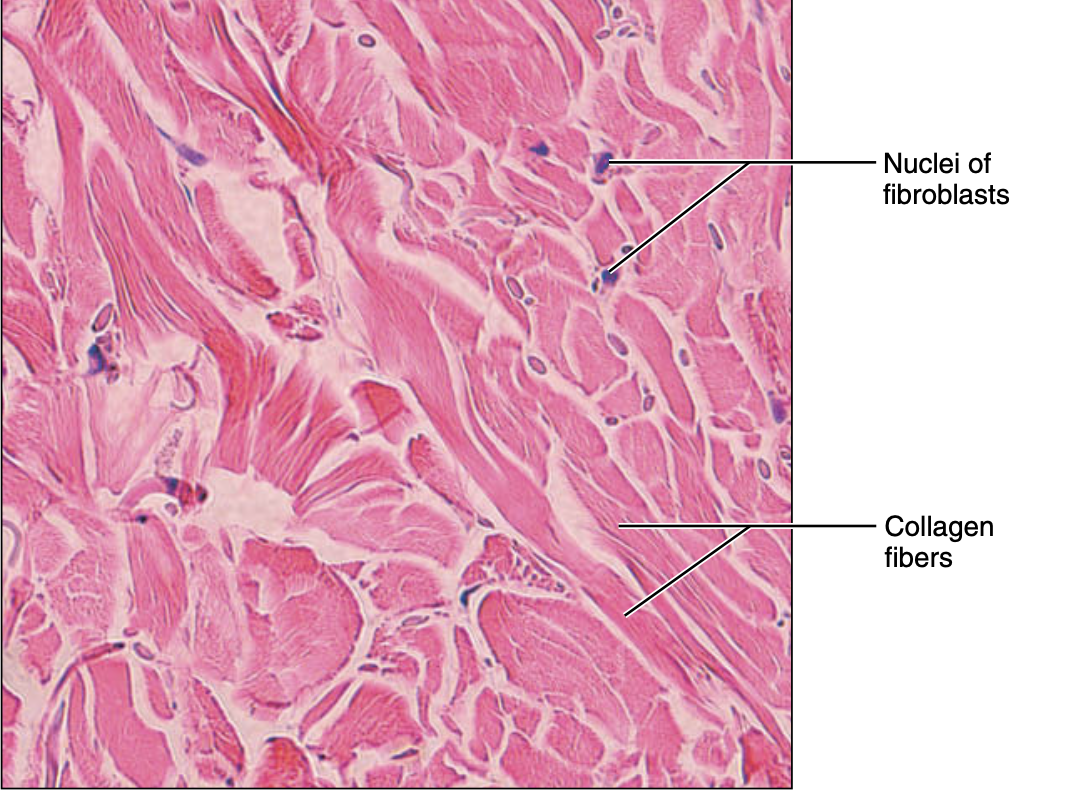
dense irregular connective tissue
irregular arranged collagen fibers, elastic fiber and fibroblast
function of dense irregular connective tissue
withstand tension exerted in many direction; provides structural strength
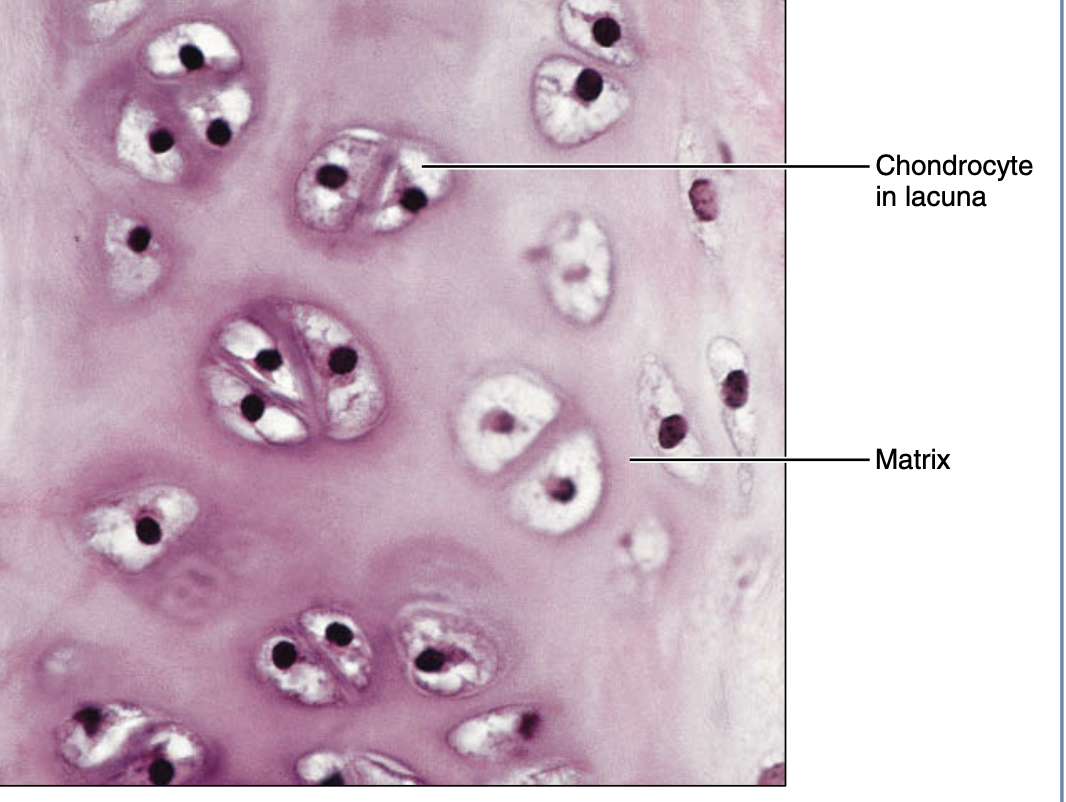
hyaline (cartilage)
Amorphous but firm matrix produced by
chondroblasts /chondrocytes
• Most of embryonic skeleton
• Covers the end of long bones in cavities
• Costal cartilage of ribs, nose, trachea and larynx
• Resist compression
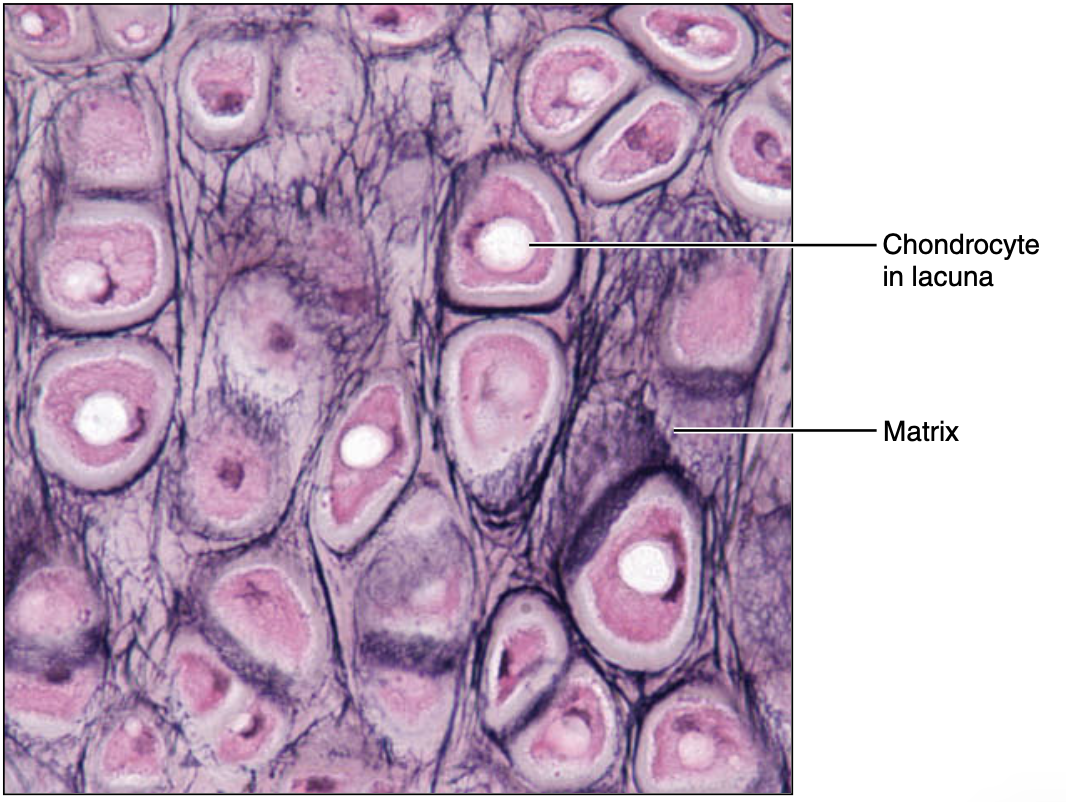
elastic cartilage
Similar to Hyaline cartilage but more elastic fibers in
matrix
• Maintains shape with flexibility-Ex. auricle, epiglottis
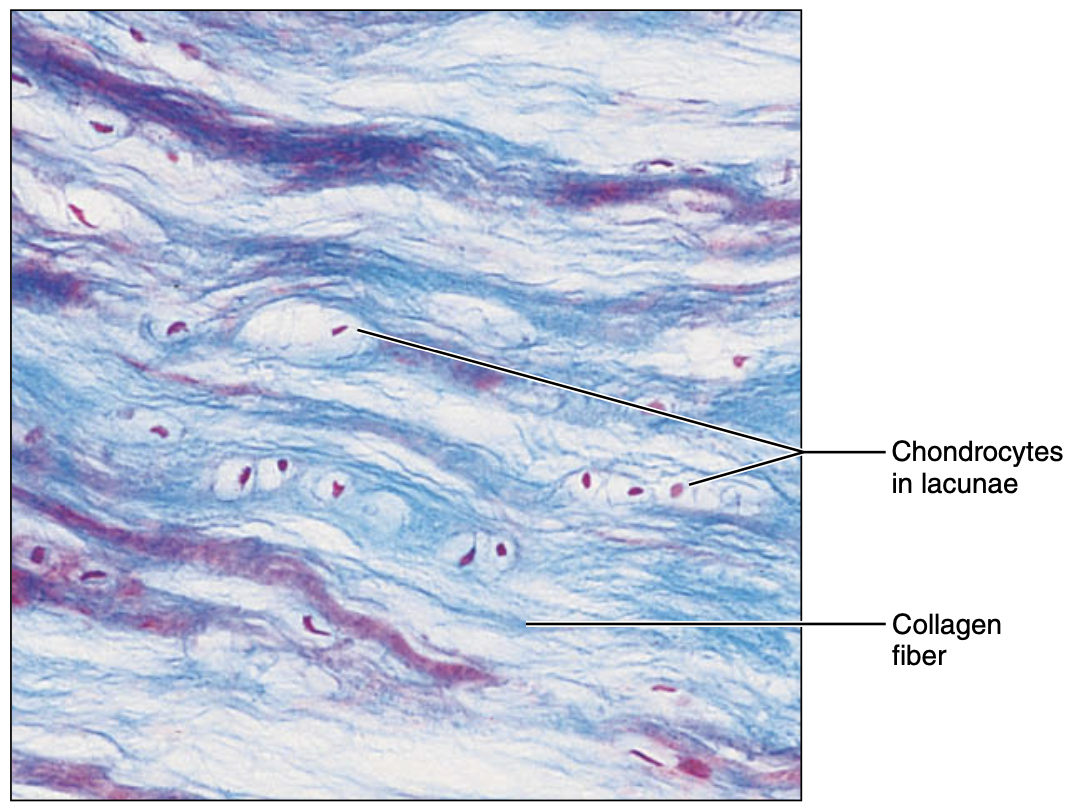
fibrocartilage
Matrix is similar to Hyaline but less firm
• Thick Collagen fibers predominate
• Intervertebral disks Pubic symphysis, knee joint discs
bone (osseous tissue)
hard, calcified matrix contain many collagen fivers
osteoblast/osteocytes lie in the lacunae
well vascularized
function of bone (osseous tissue)
bone support and protect
provides lever for muscle to act on
store calcium and other minerals and fats
marrow is the site of hematopoiesis (blood cell formation)
types of white blood cell
granulocytes and agranulocytes
granulocytes
neutrophil
eosinophil
basophil
neutrophil
helps in phagocyotosis
eosinophil
fight against parasitic infection
basophil
product inflammatory and allergic reaction
agranuloctyes
lymphocyte and monocyte
lymphoctye
produce specific immune response
monocytes
fight bacteria, virus and fungi
neurons
Receives stimuli, generates
electrical signals and
transmits to other parts of
body.
• Cell structure composed of
cell body containing nucleus
and elongated cytoplasmic
process , as long as 1 meter
neuroglia cell
surround the neuron and support, protect and insulate the neuron
muscle tissue type
skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
attach to skeleton
voluntary control
long cylindraical cell, multinucleate
non branching and has striation
cardiac muscle
found in heart only
involuntary control
uninucleate cell
stratified but interdigitate at cell junction called intercalated disc
smooth muscle
Found in the walls of hollow organs such as digestive tracts, urinary tracts, uterus, blood vessels
• Smooth muscles in these organs are of two layers run at right angles .
• Thus, smooth muscle contraction constricts and dilates the lumen of these organs facilitating expulsion of lumen
content.
• Contain uninucleated cells, spindle shaped, no striations (hence smooth muscle).
• Involuntary control
integrument system
consist of multiple organs, skin, accessory organs
skin has two distinct region
superficial epidermis and undying connective tissue (dermis)
what’s below dermis
subcutaneous layer or hypodermic (adipose tissue not part of skin)
avascular epidermis
a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
keratinocytes
manly product keratin ( a fibrous protein that give epidermis its durability and protective capability)
what connect keratinocytes tightly together
desmosomes
melanoctyes
spidery black cell that produce black pigment called melanin which increase when skin is exposed to UV light
purpose of melanin
provides protective pigment over nuclei of the cells from damage of UV radiation
Dendritic cell (langerhans cell)
arise from bone marrow and migrate to epidermis
ingest foreign substances and plays a role in activating immune response
tactile epithelial cells
spiky hemisphere that form sensitive touch receptor located at the epidermal -dermal junction
layers of epidermis
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basle
stratum corneum
the outermost layer consist of dead keratinocytes and constantly being replaced by division of deeper cell
stratum lucidum (clear layer)
presented only in thick skin
stratum granulosum
thin layer that ocntain lamellar granules which contain water proof glycolipid and keratohyaline which form keratin
stratum spinosum
several layers of cell that contain thick bundle of intermediate filament
stratum basale
single row of cell above dermis constant undergoing mitosis to form new cell