chapter 15: psychedelics and dissociative anesthetics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
psychedelic definition
- A psychoactive substance that causes perceptual changes, visual hallucinations, altered awareness of the mind and body, and cognitive distortions without producing a state of toxic delirium.
- distinguishes psychedelics from drugs that, at high doses, can produce a delirious state with some of the features of the psychedelic drug experience
“The girl with kaleidoscope eyes” Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds
novel, stimulating, or even spiritually up-lifting
mescaline
- Found in several species of cactus
- Peyote cactus (Lophophor williamsii)
- native to the US southwest and northern Mexico
- used for thousands of years by Native Americans for religious and healing rituals
- it is possible to legally purchase the peyote cactus and harvest peyote buttons for consumption!
Aldous Huxley
- tried mescaline in 1953—from Humphry Osmond
- The Doors of Perception (1954)
psilocybin
”Magic mushrooms”
- several different species (Psilocybe cubensis—most common)
- produce alkaloids with
hallucinogenic properties
- dried mushrooms (1-5 g) eaten raw or cooked or made into tea
- “shrooming”
main compound is psilocybin (prodrug)
- converted to psilocin
- actual psychoactive agent
history of psilocybin
- Aztec and Mayans: religious rituals (veladas) around psilocybin mushrooms
- Largely ingored by the West until 1938
- “re-discovered” by Harvard botanist
Richard Schultes in the Mazatec people
- 1957 Life Magazine article by R. Gordon Wasson “Seeking the Magic Mushroom” about a Mazatec ritual
- 1960—Timothy Leary eats “magic mushrooms” in Mexico
- founds the Harvard Psilocybin Project
- Marsh Chapel Experiment
- Concord Prison Experiment— reduced recidivism to 20% from 60%
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25)
- Synthesized in 1938 by Albert Hoffman at Novartis (Sandoz)
- synthetic compound based on fungal alkaloids (from ergot)
- wanted to generate a new circulatory and respiratory stimulant (analeptic) >>>based on the structural similarity of LSD to nicotinic acid diethylamide, a known analeptic drug
- psychedelic properties were not recognized until 1943 (4/16)
- Sandoz first marketed LSD in 1947 as Delysid for the purpose of helping patients with neuroses to uncover repressed thoughts and feelings
- The company also suggested that psychiatrists self- administer the drug to better understand the perceptual distortions and hallucinations suffered by patients with schizophrenia (psychotomimetic)
- LSD arrived in the United States in 1949
World's first acid trip (4/16)
From the book My Problem Child (1979) written by Hofmann:
The following description of this incident is from the report that I sent to Professor Stoll:
"Last Friday, April 16,1943. I have been forced to interrupt my work in the laboratory right in the middle of the afternoon and proceed home, being affected by a remarkable restlessness, combined with a slight dizziness. At home I lay down and sank into a hallucinogenic-like condition, characterized by an extremely stimulated imagination. In a dreamlike state, with eyes closed (I found the daylight to be unpleasantly loud), I perceived an uninterrupted stream of fantastic pictures, extraordinary shapes with intense, kaleidoscopic play of colors. About two hours later this condition faded away"
experiences of ppl who did LSD
Kary Mullis, Noble Laureate for the Invention of PCR:
"Back in the 1960s and early '70s I took plenty of LSD. A lot of people were doing that in Berkeley back then. And I found it to be a mind-opening experience. It was certainly much more important than any courses I ever took."
"What if I had not taken LSD ever; would I have still invented PCR?" He replied, " I don't know. I doubt it. I seriously doubt it.”
•
Steve Jobs:
“Doing LSD was one of the two or three most important things I have done in my life.”
•
Francis Crick:
Told his Cambridge fellow, Dick Kemp, that he surprisingly had “perceived the double-helix shape while on
LSD.”
Michel Foucault
Foucault wrote Wade and Stoneman a few months later to tell them “it was the greatest experience of his life,
and that it profoundly changed his life and his work…. He wrote us that he had thrown volumes two and
three of his History of Sexuality into the fire and that he had to start over again.”
Phil Jackson:
“In his book Maverick: More Than a Game, Jackson says that an LSD-induced vision that he had in Malibu in
May of 1973 helped him to see basketball in a new way that boosted his coaching performance. He said that the experience— which he called one of the peak experiences of his life–gave him a new love for the sport and a deeper appreciation of team play.” (http://www.maps.org/news-letters/v21n1/v21n1-3to6.pdf)
Dock Ellis (June 12, 1970): Who?
Sandoz first marketed the drug (LSD) in 1947 for...
neurosis: uncovering repressed feelings
- made it freely available for research in 1950s
- 1000’s of papers describing its therapeutic
potential in psychotherapy
- Sidney Cohen M.D.: psychiatrist>>>promoted its use in psychotherapy
Housewife on Acid
- Non-medical (illicit) use exploded with the
hippie culture in the 1960s
- backlash occurred amid growing anecdotal accounts and scientific reports of LSD- related problems
- recreational use was banned in 1967
characteristics of LSD
- very potent and orally active
- single dose in crystalline form is
barely visible
- Larger amounts are dissolved in water>>>droplets containing single- dose units are applied to a sheet of paper (a “blotter”) and dried
- paper is divided into individual
squares or “tabs”
❿War on Drugs: Mandatory
minimums
Ayahuasca (and DMT)
- orally active tryptamine-based hallucinogen
- prepared by boiling the bark or crushed stems of Banisteriopsis caapi and leaves of Psychotria viridis
- leaves of Psychotria viridis contain substantial concentrations of DMT (a structural analogue of 5HT and other tryptamine psychedelics)
- Banisteriopsis contains high concentrations of b-carboline alkaloids
- potent MAO-A inhibitors
- protect the DMT from degradation in
the liver and gut
- onset of drug effects is delayed for up to an hour after ingestion, but the effects persist for about 4 hours
Hallucinogens vary widely in potency...
LSD: most potent; mescaline: least
- Psychedelic effects begin ~30 to 90 minutes after ingestion
- LSD “trip”>>> 6 to 12 hours
- DMT (smoked): felt within seconds, peak over a few minutes, and are
gone within an hour
Most hallucinogenic drugs: have either a...
serotonin-like or a catecholamine-like structure
- Salvinorin A action may require activation of the κ-opiate receptor
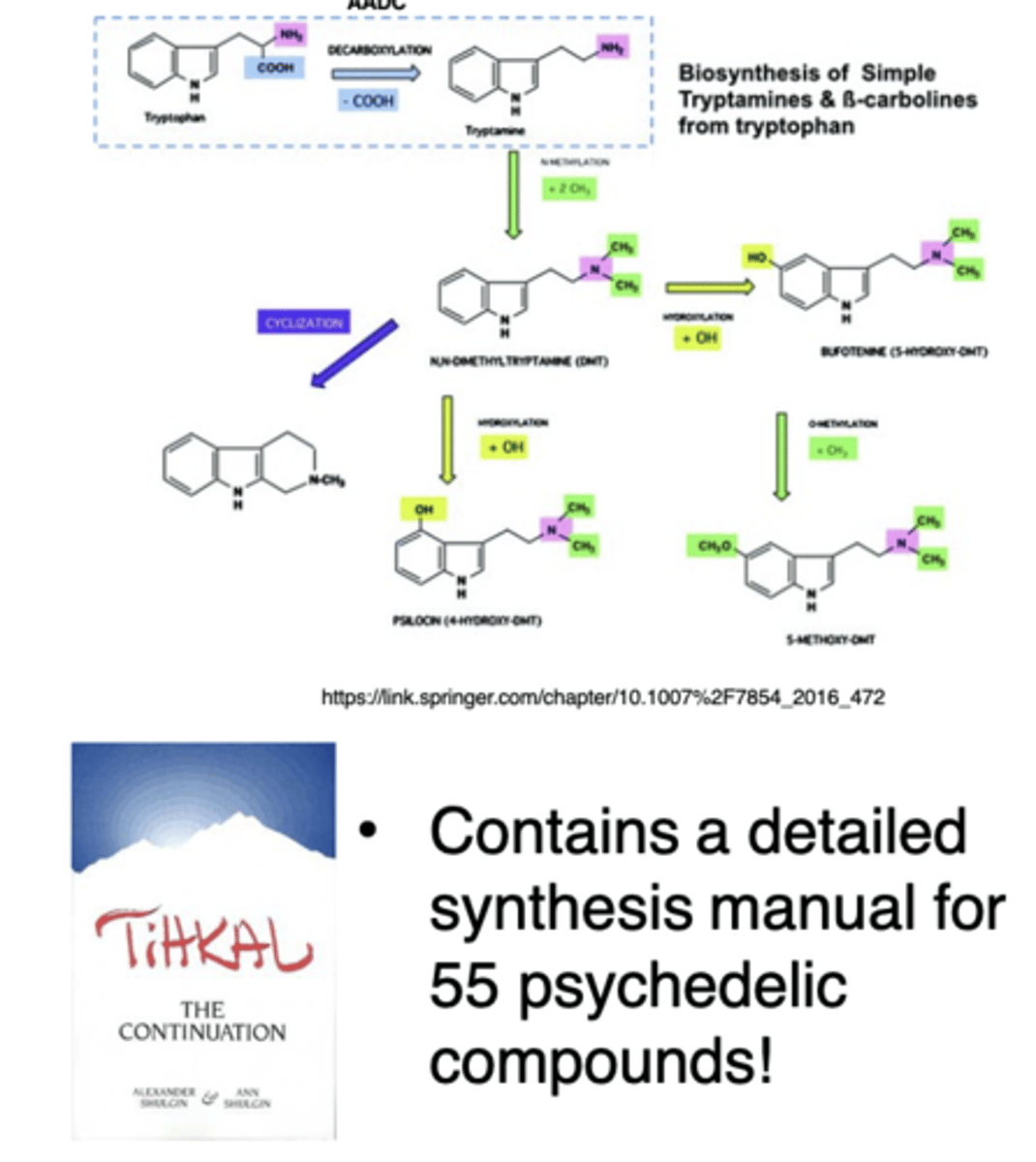
Serotonin-like (indoleamine)
hallucinogens:
- LSD, psilocybin, psilocin, DMT, and synthetic tryptamines
Phenethylamine hallucinogens
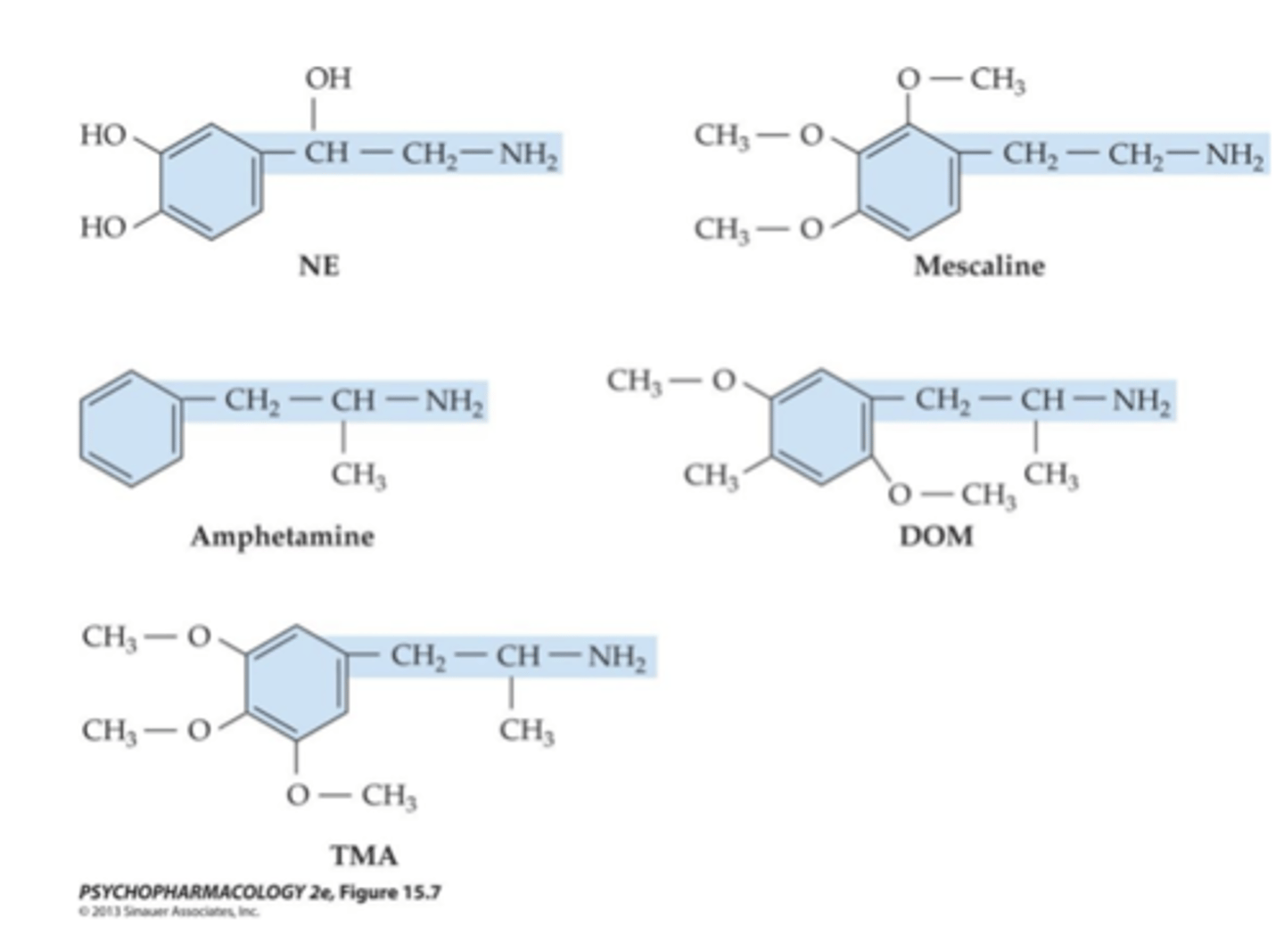
Mescaline:
structurally similar to NE and AMPH
LSD binds with...
high affinity to at least eight different 5-HT receptor subtypes
- Phenylethylamines: also bind to some 5-HT receptors
- common receptor subtypes
are 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C
❿Suggests that these receptors may play a central role in producing hallucinations
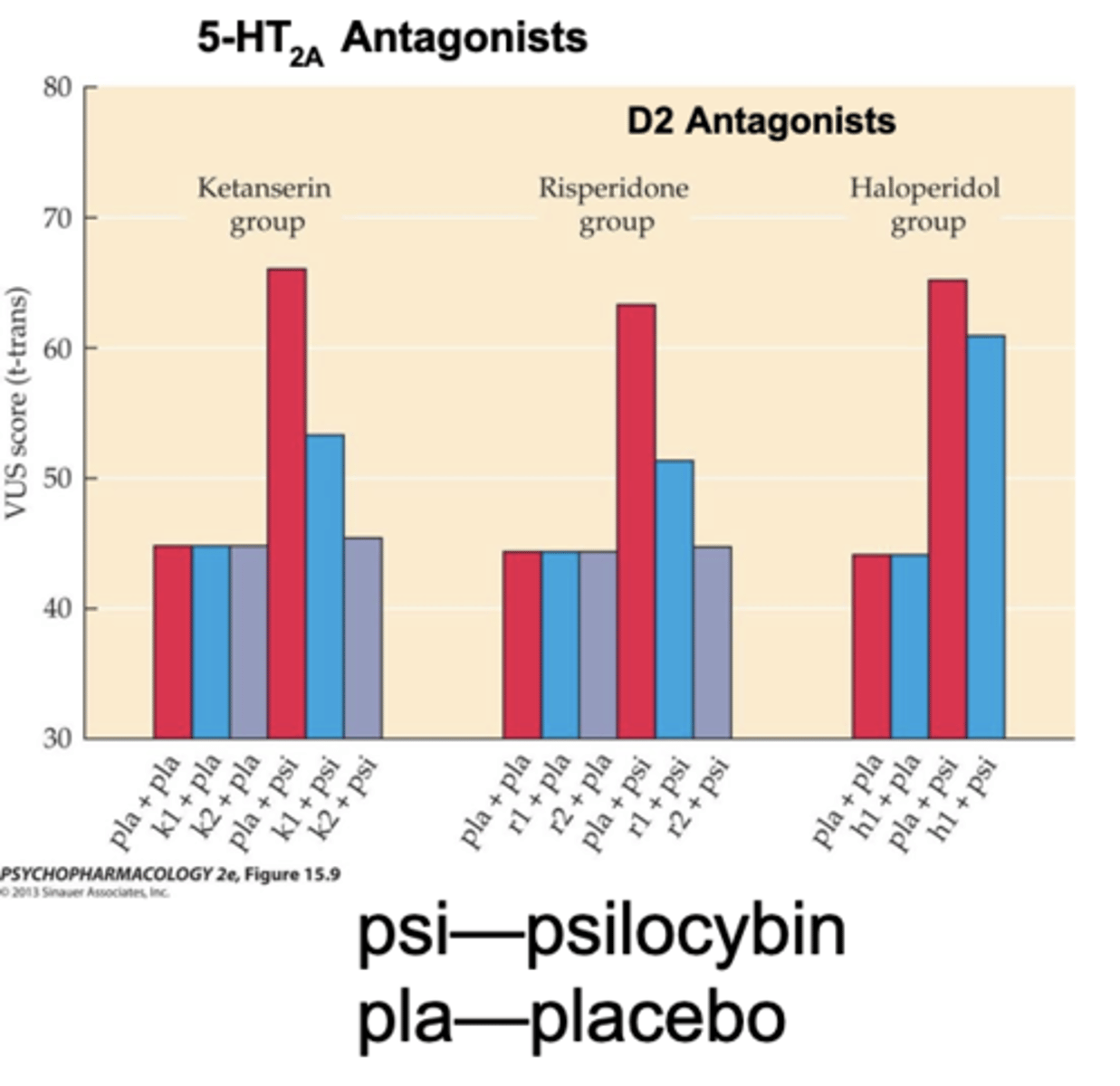
what generates hallucinations?
In humans, activation of 5- HT2A receptors is the critical mechanism
- hallucinations are blocked by 5-HT2A antagonists
Persistent reduction of hippocampal-default mode network connectivity may represent a...
neuroanatomical and mechanistic correlate of the proplasticity and therapeutic effects of psychedelics
a 5-HT2A receptor-stimulating psychedelics produce...
rapid increases in dendritic complexity, density of dendritic spines (number of spines per unit length of dendrite), and synapse number
- These changes are hypothesized to contribute to the rapid antidepressant effects of this class of psychedelic agents
animal models to study hallucinogens:
- Can not assess if an animal is experiencing a change of
consciousness
- Head-twitch response
Can be trained in drug discrimination tasks to recognize the
subjective effects of hallucinogens vs. saline
- Selective antagonists of 5-HT2A receptors blocks drug discrimination
LSDs do not...
have high abuse potential
✦no withdrawal symptoms and not an effective reinforcer
- Dependence does occur in a very small number of users
- Most hallucinogens produce rapid tolerance with repeated use
- down-regulation of 5-HT2A receptors seen in rats
Negative effects (some users)
“bad trip”
- acute anxiety or panic
- impossible to predict whether a user will have a “good trip” or a “bad trip” b/c drug effects depend on the user’s expectations and past experiences with psychedelics
- Flashbacks—re-experiencing the psychedelic after
drug use has stopped
- If they occur for a long time, the individual is suffering from hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD)>>>rare
- most severe reaction is a psychotic reaction
- With a few exceptions, prolonged psychotic episodes typically involve individuals who had already been diagnosed with a psychotic disorder or who had pre-psychotic symptoms before taking the drug
- May occur for weeks or months after
pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction
- 12 of 15 participants (80%) showed seven-day point
prevalence abstinence at 6-month follow-up.
- The researchers strongly caution that their study results are not an endorsement of do-it-yourself psychedelic drug use for smoking cessation, but instead are specific to the controlled administration of the drug in the context of a treatment program involving cognitive behavioral therapy.
therapeutic benefits of hallucinogen
- "It is unclear whether these benefits exist beyond the placebo effect. One source of uncertainty is that people who microdose psychedelic substances usually have a specific hope for what it will achieve. As a result, some of the findings might be explained by the placebo effect."
- One way to tackle the question is with the help of placebo-based trials, in which some participants are given a microdose of a psychedelic, and others are given an inactive substance. The evidence that is beginning to emerge from such studies, however, doesn't look promising.
Phencyclidine (PCP)
- developed as an anesthetic
- did not cause respiratory depression
- Patients had atypical response:
- catatonic-like state (vacant stares, no facial expression)
- Motor rigidity
- Some patients experienced blurred vision and dizziness, hallucinations and severe agitation
✦ Clinical use stopped in 1965
✦ in 1967, became an illicit street drug (“angel dust”, “hog”)
- powdered or pill
- taken orally, intranasally (snorted), injected, or applied to cigarettes and smoked
Ketamine
developed as a safer alternative to PCP less potent and shorter-acting
- anesthetic for certain procedures:
- Adults given an anesthetic dose lose all contact with their environment, but eyes are open and muscle tone remains
- children do not!
- used by veterinarians as a general sedative and immobilizing agent
- Ketalar, Ketaset, and Vetalar
- Street supply usually comes from of
medical or veterinary sources
- sold on the street as “K,” “special K,” or “cat Valium”
- Injectable liquid that is converted to a powder
>>>smoked or snorted
- half-life of ~2.5 hr
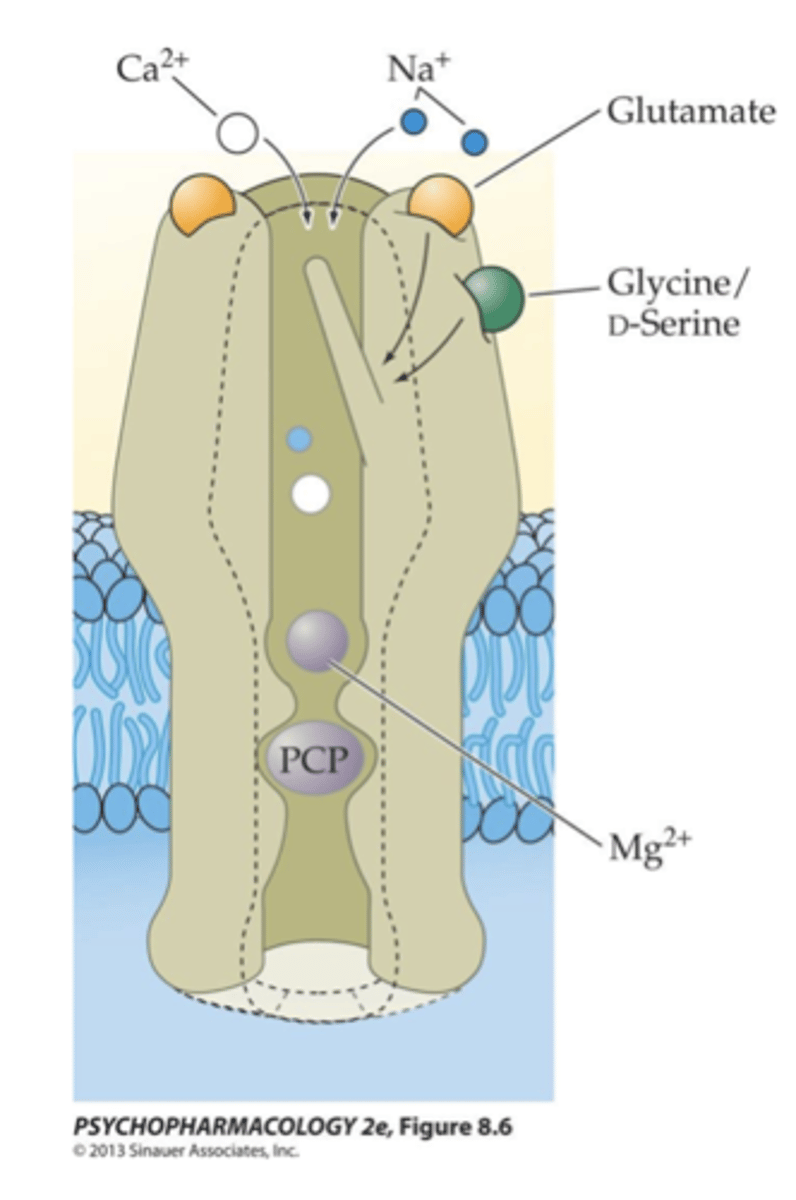
Noncompetitive antagonists of
NMDA receptors
- binding site is inside the
receptor’s ion channel
- Blockade in cortex and hippocampus likely contributes to cognitive deficits seen in users
Subjective effects of PCP
feeling detached from the body, floating sensation, numbness, a
dreamlike state (dissociative anesthetic)
Affective reactions of PCP
drowsiness and apathy, loneliness (social withdrawal), negativism or hostility,
- Possible euphoria and inebriation
Cognitive disorganization (most subjects) of PCP
difficulty concentrating, disruption in abstract thinking, and halting
speech
Effects of PCP>>>similar to symptoms of...
schizophrenia:
A psychotomimetic
Subjective Experiences Reported by Ketamine Users:
- Sensations of light coming through the body and/or of colorful visions
- Complete loss of time sense
- Bizarre distortions of body shape or size
- Altered perception of body consistency (e.g., feeling as though one is made of a strange material such as rubber, plastic, or wood)
- Sensations of floating or hovering weightlessly in space
- Feelings of leaving one's body
- Sudden insights into the mysteries of existence or of the self
- Experiences of being "at one" with the universe
- Visions of spiritual or supernatural beings
PCP and ketamine>>
highly reinforcing in primates and high abuse potential
- Both activate midbrain DA cell firing and stimulate DA release
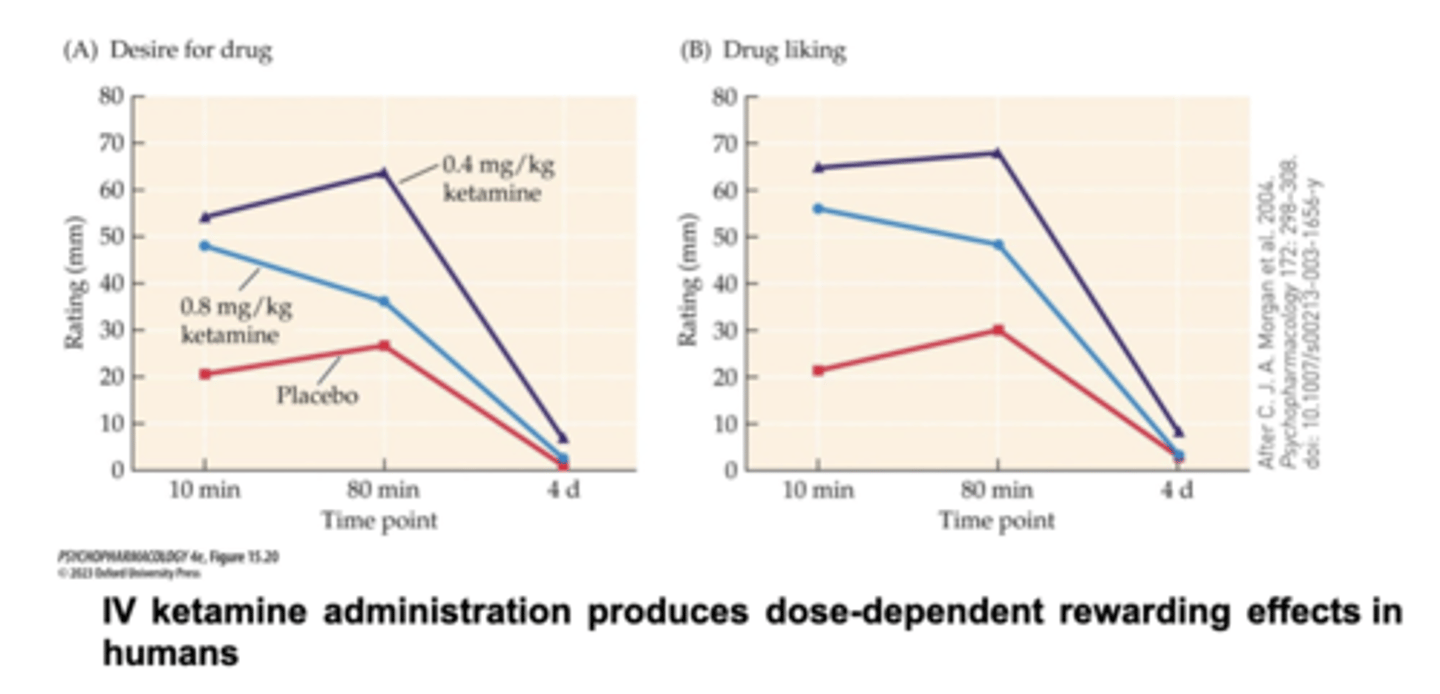
Chronic use of ketamine or PCP
- Urological problems (e.g., bladder pain and incontinence)
- Deficits in memory
- Gray- and white-matter abnormalities in chronic ketamine users
- bilateral frontal and left temporoparietal reductions in fractional anisotropy in patients with ketamine dependence in relation to control subjects
repeated administration of high doses of ketamine causes...
apoptotic cell death in developing brains of rats and monkeys
ketamine is...
a recommended anesthetic agent for pediatric procedures
ketamine and mood disorders
- "rapid and potent antidepressant effects of ketamine in
treatment-resistant (TR) depression"
- 5 million people in the US with TR MDD

Ketamine (A miracle ADM?)
- A serendipity>>>trying to model schizophrenia
- Therapeutic dose produces transient cognitive dysfunction similar to cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia
- Too high of a dose (into anesthetic range) loses its antidepressant effects
- Alleviates depression but is not euphoric
- Patients with high levels of co- morbid anxiety are poor responders to SSRI but respond well to ketamine
more information about ketamine
- rapid (within hours) reduction in depression symptoms for 65 to 70 percent of treatment- resistant (TR) patients
- Subanesthetic doses
Effects last weeks
- Plasma half-life is 2.5 hours
- antidepressant effects typically emerge ~4 hr after IV admin
- Patients are maintained on regimens of 1x every two weeks to two months
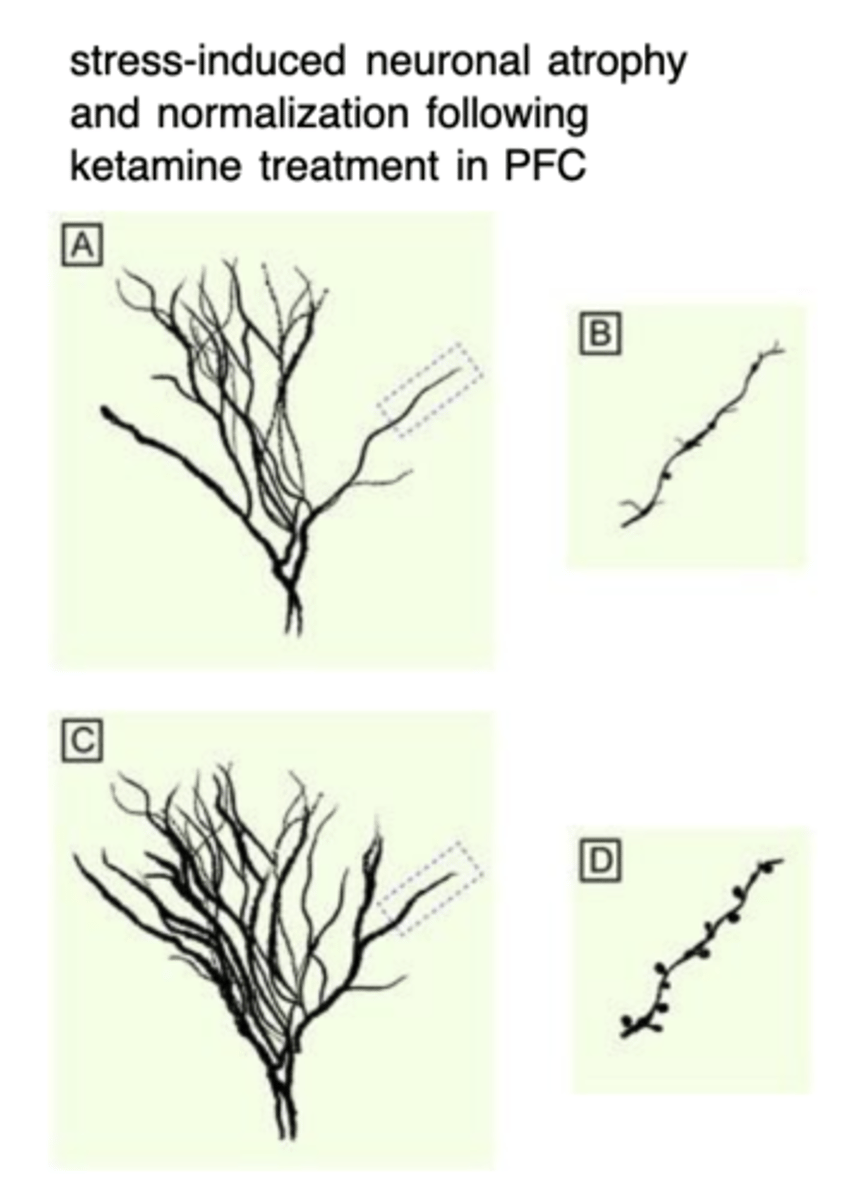
Chronic stress causes...
excess extracellular glutamate
- dendritic retraction, reduced dendritic arborization and spine density (A and B)
24 hours posttreatment (C and D):
- Sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine reverses the chronic stress-induced structural deficits
- Rapid induction of BDNF
- increased synaptogenesis and spine density
- Similar effects to traditional antidepressants (ADMs)
- Neuroadaptive state occurs much faster with ketamine
The Disinhibition Hypothesis
- depends on the antagonism of NMDARs on GABAergic interneurons preventing GABA release
- The inhibition of GABA release prevents the inhibition of pyramidal glutamatergic neurons
- allows for the release of glutamate and downstream effects of subsequent glutamate surge
- Glutamate binds to post-synaptic AMPARs, allowing for calcium influx
- Calcium influx leads to the calcium- dependent release of BDNF from the post-synaptic membrane
Dextromethorphan (the "DM" in Robitussin DM)
- metabolized to dextrorphan
- Antitussive agent: low doses>>>suppresses the cough reflex
- High doses>>>noncompetitive antagonist of NMDA receptor
- High doses of dextromethorphan: subjective effects similar to those observed with classical hallucinogens
- can be extracted from cough syrup and repackaged in pills