9 - Cell-Cell Communication: Neurons
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Central Nervous System
The brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Neurons and ganglia
Neurons
Specialized nerve cells in the nervous system responsible for transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals
Glia cells
non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that provide support and protection to neurons
Function of neurons
Integrate incoming signals - to determine whether or not the information should be passed along
Communicate signals to target cells - other neurons, muscles, or glands
Neuron anatomy
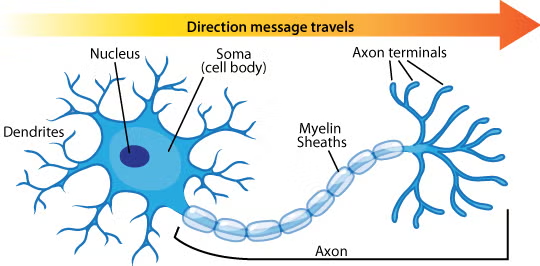
Dendrites
Receive signals from neighboring neurons
Axon
Transmits signals over a distance
Axon terminal
Transmits signals to other neuron dendrites of tissue
Concentration gradient
The difference in ion concentrations between the inside of the neuron and the outside of the neuron
Neuron charge…
Negative
Neuron resting membrane potential…
-70 mV
Concentration of Na/K during resting potential…
There are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside the neuron
Size of action potential along the axon…
The size of the action potential remains the same as it travels down the axon
Synapse
The place where neurons connect and communicate with each other
Depolarizing
The inside of the cell becomes more positive
Hyperpolarizing
The inside of the cell becomes more negative (less positive)
Excitatory neurotransmitters
The change makes the target cell more likely to fire its own action potential
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
The change makes the target cell less likely to fire an action potential
Modulatory neurotransmitters
The change makes the target cell adjust or “tweak” the action potential
Microglia
Immune cells/macrophages
Oligodendrocytes
Myelinating cells in central nervous system (CNS)
Schwann cells
Myelinating cells in peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Astrocytes
Blood-brain barrier (touch neurons and capillaries)
Ependymal cells
Produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Gated Channels
Can be either open (allowing ions to flow through) or closed depending on the protein conformation
Voltage-gated channel
Ion channels in the cell membrane that open or close in response to changes in the membrane potential or voltage difference across the membrane
Ligand-activated channels
Sensitive to binding of ligand/signal; they undergo a change in shape when a neurotransmitter binds, causing the channel to open (this may either be inhibitory or excitatory)
Mechanosensitive channel
Sensitive to mechanical stress on membrane
Ratio of Na/K in/out
3 Na+ ions out for every 2 K+ ions inW
When does action potential occur (threshold value) ?
-55 mV