Medieval - Romanesque and Gothic
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms

Merovingian Looped Fibulae: (Early Medieval)
Merovingian Dynasty = France + Germany
silver gilt, semi precious stones
A clamp-like pin used to fasten cloth together (used on togas)
Cloisonne technique: thin bands of medal with colored areas between
zoomorphic (animal) elements (fish, birds)
Significance: Rome has fallen → a new style emerging
showing influence of Visigoths

Lindisfarne Gospels: (Early Medieval)
Lindisfarne, England (island that created bibles, constantly raided)
Hiberno Saxon (Ireland and England)
ink, pigments, and gold on vellum (animal skin) parchment
most likely written and decorated by Eadfrith (Bishop of Lindisfarne)
blends both Latin and English script (oldest known Bible with English
contains four gospels, each with an incipit, portrait, and cross page
Cross Page:
Book of Matthew
horror vacui
dog headed snakes and birds
Cloisonne designs throughout
mixes local Celtic imagery and Christian imagery
Saint Luke Portrait Page:
Calf = symbol for luke
he sits writing on a school (symbolic of his gospel)
in Greek: “Hagios Lucas”
Cloisonné designs at each corner
Saint Luke Incipit Page:
opening words of St. Luke’s gospel
Large letter Q leading into Quoniam Quidem
celtic patterns in q
teeming with animal life (cat eating birds)
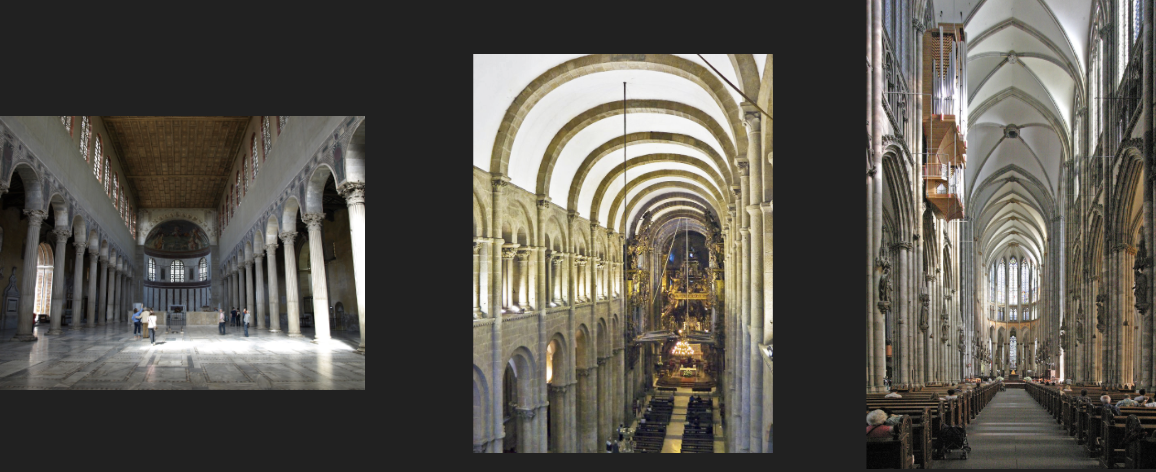

Difference between basilica, romanesque, and gothic interior
Basilica:
wooden roof over nave
shallow ceiling
transverse arches
apse
Romanesque:
nave is a barrel vault
very dark due to small windows, lots of candles
Gothic:
nave is a series of groin vaults, stronger vaults
lots of windows, lots of natural light
stained glass
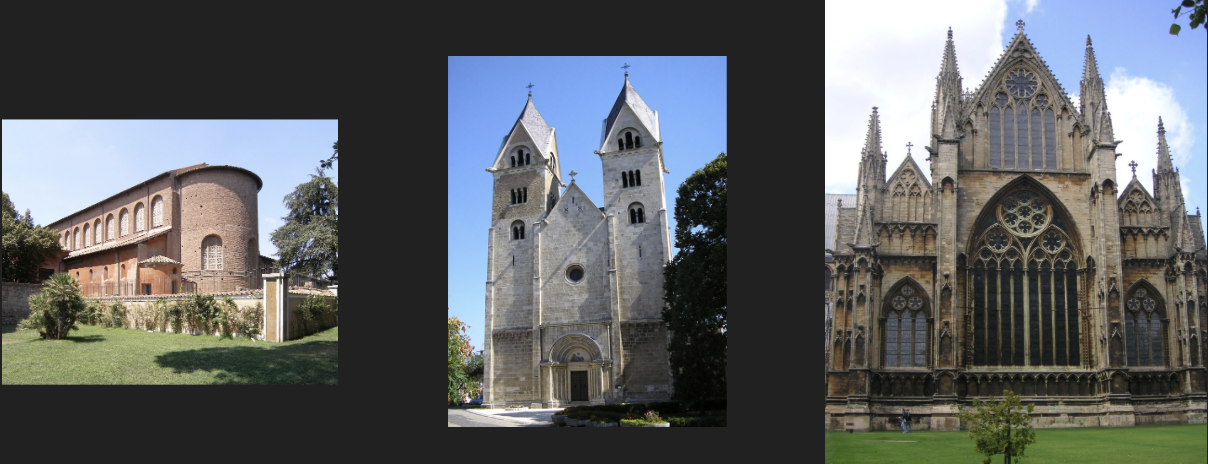

Difference between Basilica, Romanesque, and Gothic models
Basilica:
Smaller
Shorter
Apse
Based on Roman arch
Romanesque:
Taller
Based on Basilica
Small windows
Based on Roman arch
Gothic:
Tallest
Based on Basilica
Massive windows
Based on pointed Goth arch

Church of Sainte-Foy: (Romanesque)
Conques, France
Stone
Pilgrimages to Santiago de Compostela
a church on the way that held relics
very large church (built to handle lots of pilgrims)
basilica w/ transept (cross section)
Apse has ambulatory built/added to it with radiating chapels, hold relics
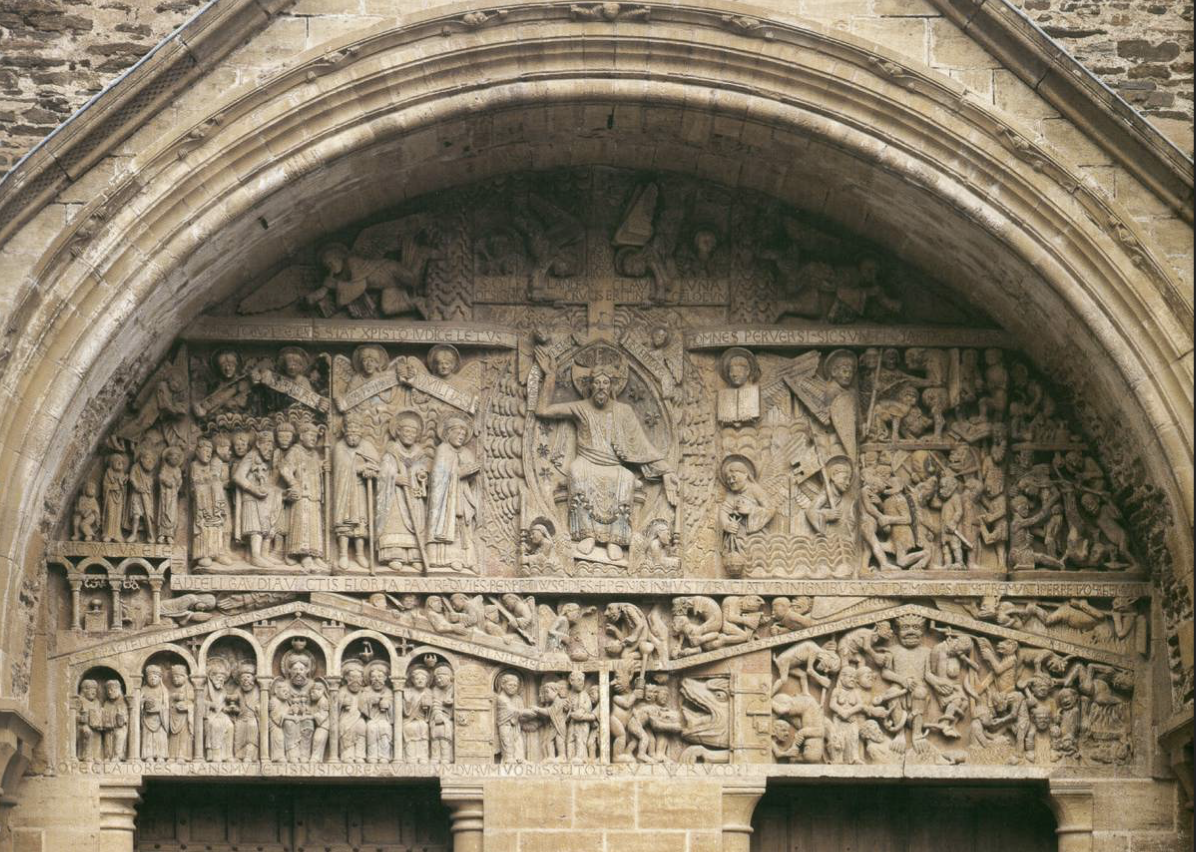

Last Judgement Tympanum: (In Church of St. Foy - Romanesque) (sacred image)
story being told for the illiterate as they walk through the entrance
Christ as the judge between Hell and Heaven
right hand welcomes into heaven
left hand banishes downward
reminds people entering the church to stay faithful
originally painted, horror vacui
translation: “oh sinners, change your morals before you might face a cruel judgement”

Sainte-Foy Reliquary: (In Church of St. Foy - Romanesque)
Wood sculpture covers in gold, silver, gemstones, and enamel
major draw of the pilgrims to St. Foy (would sit in the main radiating chapel - ambulatory)
martyred girl who refused to sacrifice to Roman gods
contains relics of her body (Child’s skull)
jewels, gems, and crown added over the years by wealthy donors
head may be spoil (reusing elements from older art) from an earlier roman sculpture

Bayeux Tapestry: (Romanesque - secular)
Bayeux, France
Embroidery on linen (made by women like tapa cloth)
patron: Odo, bishop of Bayeux (half-brother to William)
narrative
story of William the Conqueror’s conquest of England at the Battle of Hastings
three registers/sections:
bottom and top contain animals
middle is the main narrative
not really a tapestry
similar to column of Trajan

Pisa Cathedral Complex / Piazza Dei Miracoli (God’s Miracle Square): (Late Romanesque)
Tuscany, Italy
Pisa: wealthiest area in Europe at the time, coastal, merchants, with a large navy and military. Traded by sea with Byzantine Empire
Church: testament to the wealth of Pisa
Cathedral Complex: appropriation from Hagia Sophia, specially the dome
even though there are 3 structures, they are one complex
Cathedral and Duomo:
much larger and more decorated than other Romanesque churches in France, a sign of wealth
transition from Roman to Gothic
has duomo at the transept
coffered ceiling (wood) like a basilica (Santa Sabina)
Baptistry and Campanile (bell tower)
Italian churches traditionally have the baptistry as a separate structure near the cathedral
Pisa baptistery is stylistically alike with the cathedral
a grand building to welcome converts and infants to Christianity
Campanile are also a separate structure in Italian churches
Tower is leaning due to a settling soil under the foundation
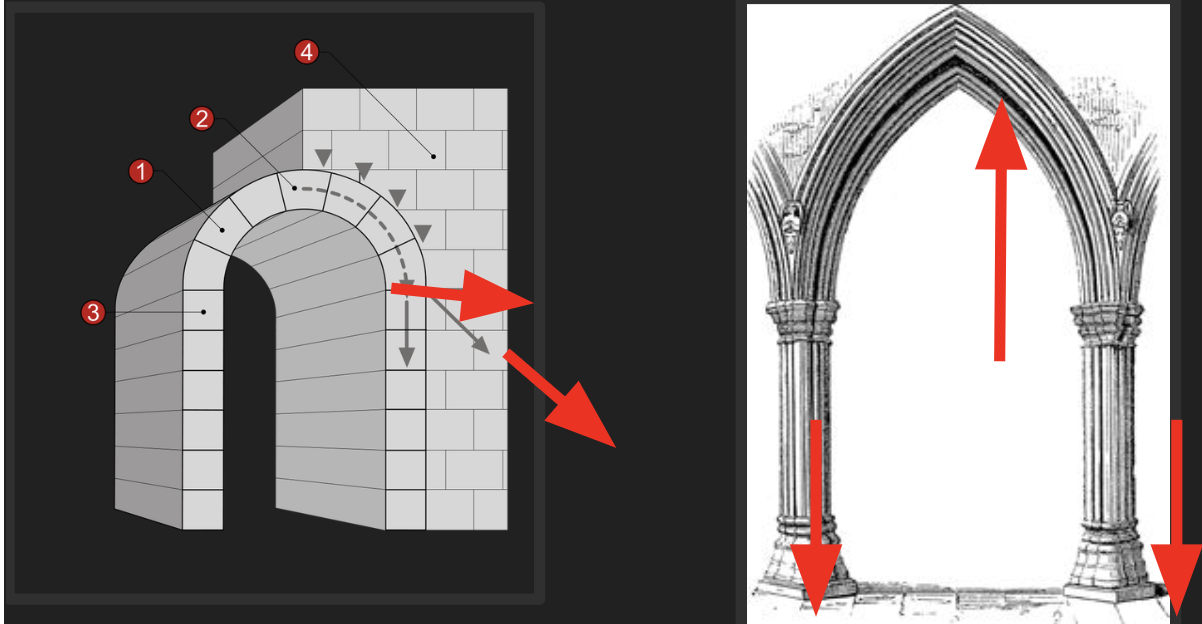
Transition from Romanesque to Gothic
Pilgrimages will continue through France and Spain for centuries to come
towns that innovated their churches could count on pilgrims to come through their towns
One French Parisian priest and architect named Abbot Sugar will architecturally innovate a smaller Romanesque church in northern Paris, St. Denis, in a manner to let in more light and bring in stained glass windows
changes made to St. Denis will spark the move from Romanesque to Gothic architecture
he removed the radiating chapels of ambulatory and open up the room will wall of stained glass
pointed arch forced the weight of the walls down to have thinner walls and more windows
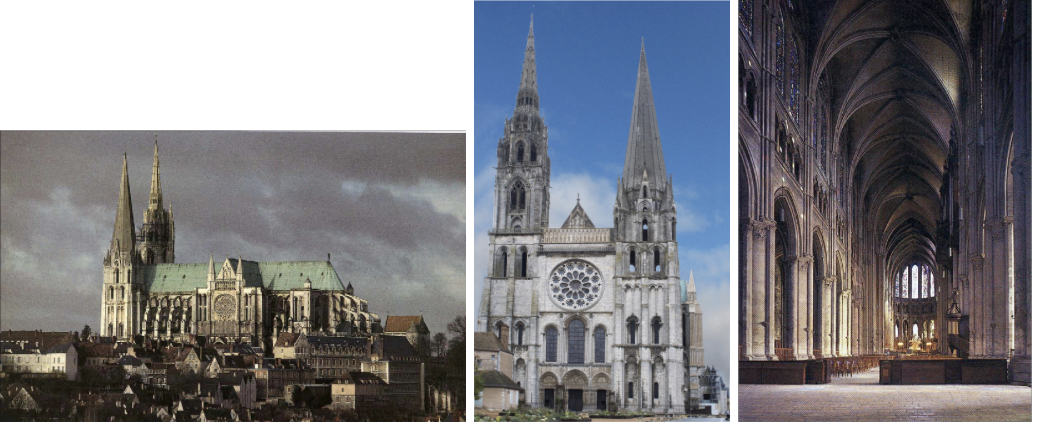

Chartres Cathedral:
Begun in Romanesque, rebuilt after fire and turned into Gothic
Chartres, France
Stone
Appropriates from St. Denis
Fire destroyed Romanesque church leaving only the west facade (front) and masonry of the crypt standing
Architects rebuilt the church using High Gothic model, first of the High Gothic Churches
Tall thing walls supported by flying buttresses allowed for stained glass clerestory
Meant to be symbolic of heaven, entering the portal viewers eyes are drawn upwards
Relic was the tunic of Mary

Royal Portal at Chartres: (Early Gothic)
Stone
Survived the fire
Early Gothic, not High Gothic like the rest of the cathedral
Called the Royal Portal because the statues of Old testament kings and queens on the sides of the portal
Right portal tympanum: Baby Christ in the lap of the Virgin, appropriates from Theotokos and countless other images of Mary and baby Jesus
Left Portal tympanum: Christ’s ascension into heaven.
Center portal: Second coming of Christ, Christ as judge, symbols of Matthew, Mark, Luke and John appear around Christ
Last Judgement theme like at St. Foy
Gothic last judgement was more of a theme of salvation than the Romanesque damnation
Lintels below the three tympanums shows scenes from the life of Christ
romanesque sculptures (Kings and queens of Old Testament)
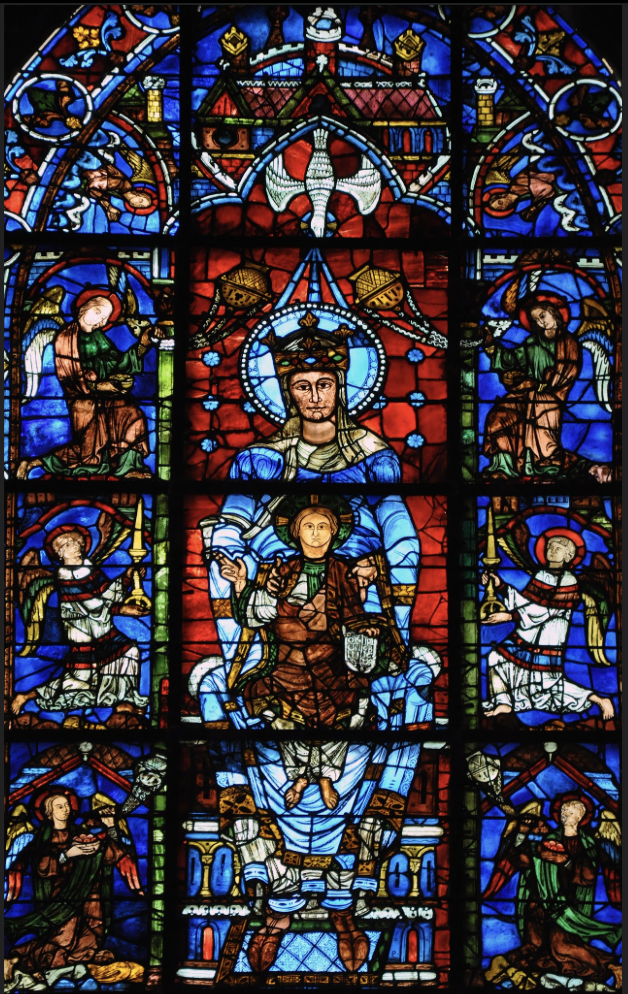

Notre Dame de La Belle Verrière: (Chartres, High Gothic)
Stained glass
No stained glass in the Romanesque
Thinner walls and buttressing allowed for much more glass in the walls, much more light
Light was considered divine, gave color to the grey stone throughout
Appropriates Cloisonne technique
Mary is young, haloed, crowned, Christ Child on lap, dove the Holy Spirit above
compared to Byzantine mosaics at Ravenna, and Theotokos
Mary is more important in the Gothic period
Mary is a pillar of faith
Our Lady of the Beautiful Window
roundels = circles
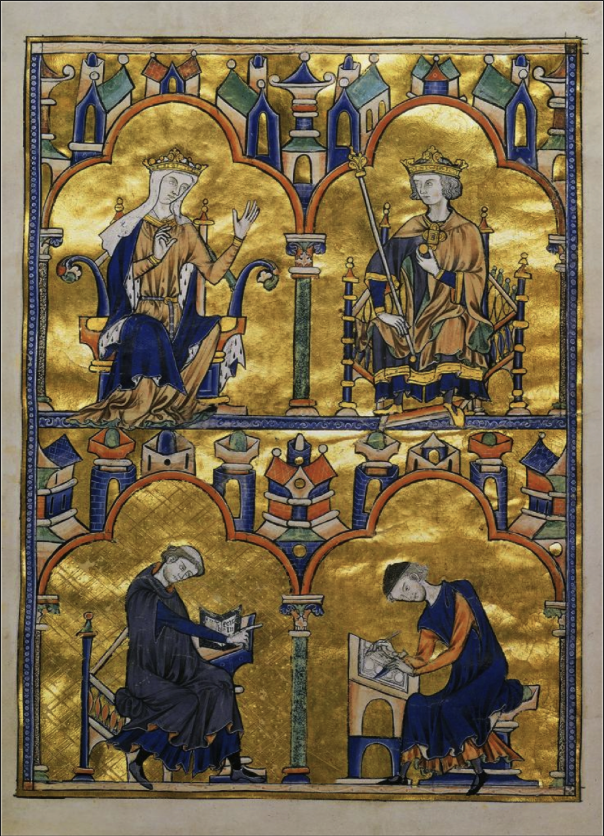

Dedication Page with Blanche of Castile and King Louis IX of France: (Gothic)
Ink, Tempera, Gold Leaf (very expensive), on Vellum
A moralized Bible: Bible with expensively decorated art to explain scripture (decorated with images to teach morals)
France known for illuminated manuscript (showing an image/story)
top left: Blanche of Castile (mother to king and regent) (Patron)
top right: Louis IX as teenager (Patron)
bottom: older monk dictates to a younger monk (artists)
Commissioned during Blanche’s regency after her husband’s death
had a lot of political strife at the time
shows status of women at the time; Queen Blanche has high power in ruling until her son is old enough to (put at the same level as the king)
has architecture similar to Paris in the background

Scenes from the Apocalypse:
ink, tempera, gold leaf on Vellum
illuminated manuscript
eight roundels, similar to stained glass
each scenes has text with a summary of what is depicted (biblical and commentary text)
tells story in Book of Revelations
temptation of clergy, clergy engaging in sin
devils on the backs of clergy

Rottgen Pieta: (Gothic)
Rottgen, Germany
painted wood sculpture
Madonna (mom): Mary holding a baby Jesus VS Pieta (pity): Mary holding a deceased Jesus
Gothic is ending, Renaissance is beginning (renaissance = emotion)
Used for private devotion, not in a church, focal point for private prayer
Expressed the sadness and horror of the crucifixion of Christ
Humanizing effect to religion, you see the suffering in both Mary and Jesus
Earlier depictions of Jesus show him painlessly on the cross, not human
Blood, agony, and sadness are felt
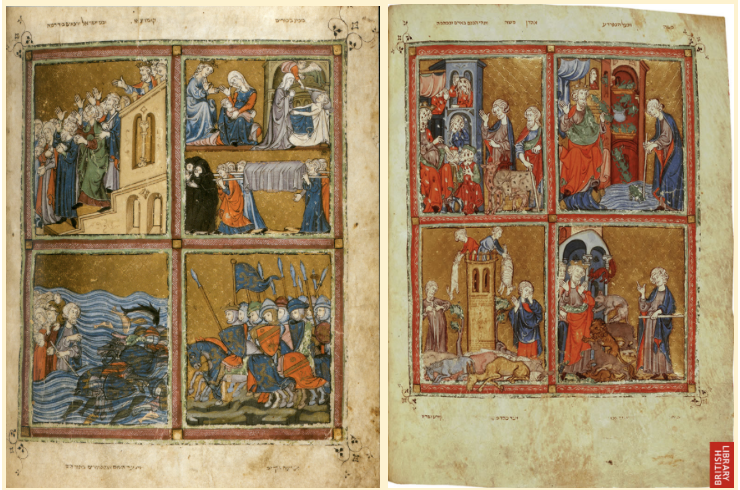

Golden Haggadah (Story): (Gothic)
Barcelona, Spain
pigment on Vellum, gold leaf backgrounds
Story of Passover in a very Gothic medium and style
European style of art: (but a Hebrew story)
gold leaf background
medieval characteristics
Ramses depicted as a French/European King
read right to left, Hebrew
very expensive, cross cultural borrowing styles
points to large and diverse Jewish community in Spain that could afford and produce this art
medieval Spain was an intercultural mix of Christians, Jews, and Muslims
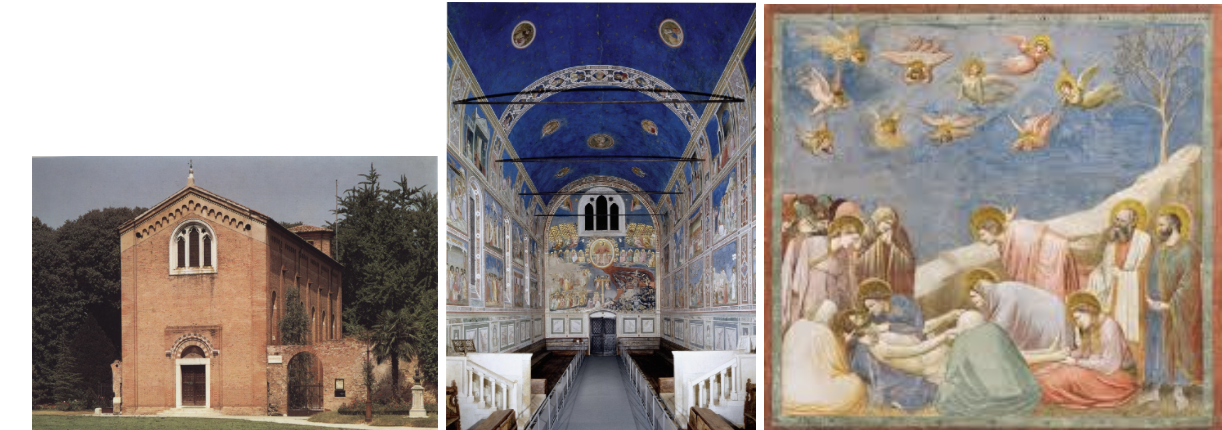

Arena (Scrovegni) Chapel and Lamentation: (Late Gothic/Early Renaissance
Patron: Scrovegni, Banker
Family made a fortune through loaning money for interest, which is the sin of usury
To atone for the sins, Enrico built the chapel which contains many images, some of which are related to usury or stealing, and his guilt as a banker that charged interest on loans
Giotto’s Lamentation:
Fresco
Artist: Giotto di Bondone (artist that moves us out of the medieval and into the renaissance)
Moves away from flat, frontal, and floating
Debate: is it Medieval, or is it Renaissance? (transitional piece)
Jesus has just been brought down off the cross, now Mary is holding him
She has one leg down and one leg up (very realistic and Renaissance)
Numerous displays of emotions
Lament: to have deep sorrow
All halos are gold, as all people are saints
Giotto painted the interior, numerous scenes from the Bible.
Mary and Jesus are not in the middle of the painting, the diagonal mountain leads the eyes down to them
Jesus’ followers mourning his death
Emotion, St. John’s head and hands show emotion
Mary Magdalene weeps while cradling Jesus’ feet
Painting to the left was Jonah being swallowed by the whale. Parallel explored in early Christian art
Early use of perspective and multiple positions
Indication of light and the way it falls seems natural, shadowing
Sadness conveyed through mourning angels and barren tree
Figures shown from the back, not flat, frontal, and floating like in Byzantine art