SOMS1913 WK 2 - Lower respiratory system
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Function of C-shaped hyaline cartilage in the trachea
Ensures airways remain patent (open) while allowing the oesophagus to expand anteriorly into the trachea during swallowing.
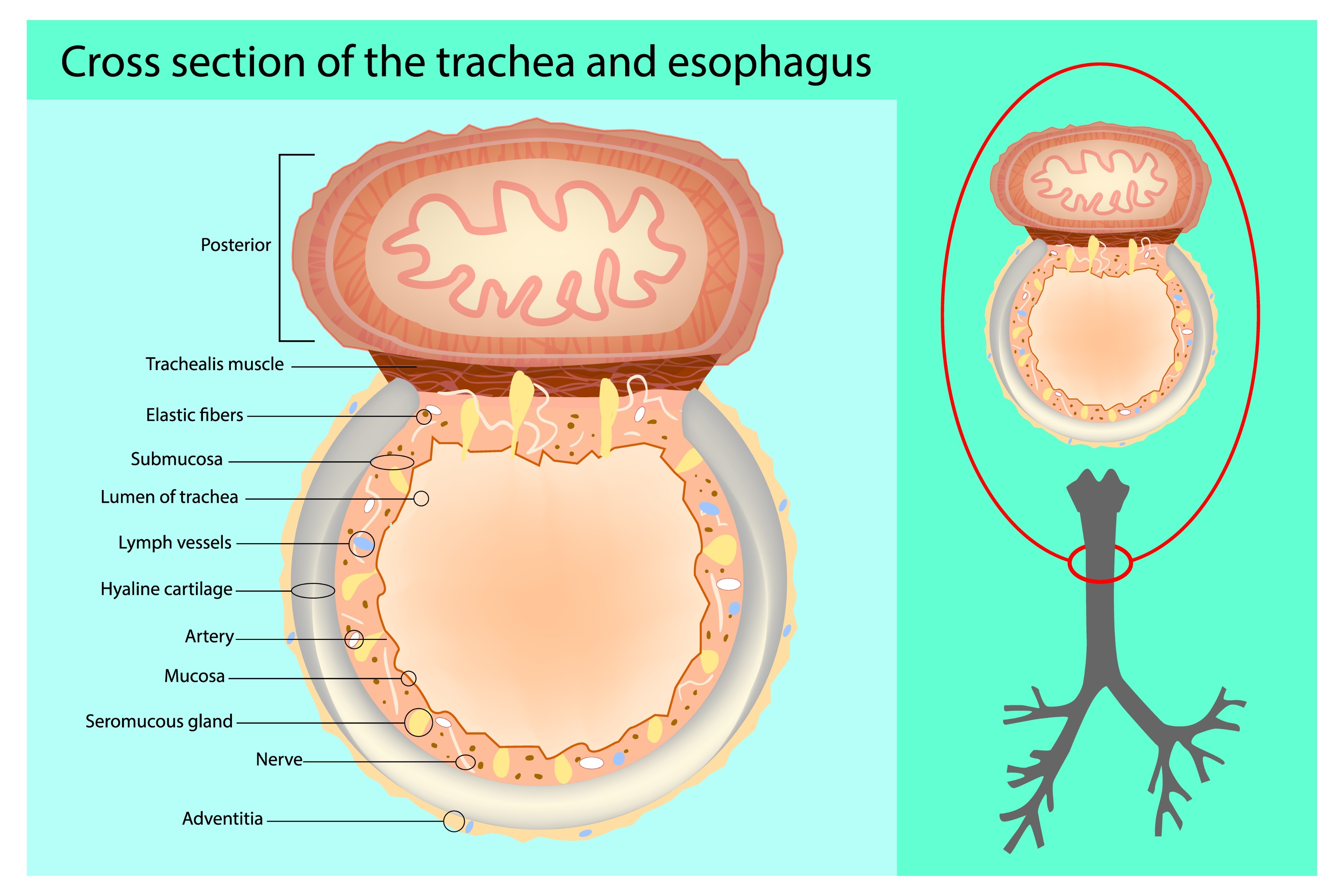
Histological layers of the trachea (internal to external)
Mucosa (Respiratory Epithelium)
Submucosa (contains tracheal glands)
Cartilage layer
Adventitia
Respiratory Epithelium type
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (containing goblet cells).
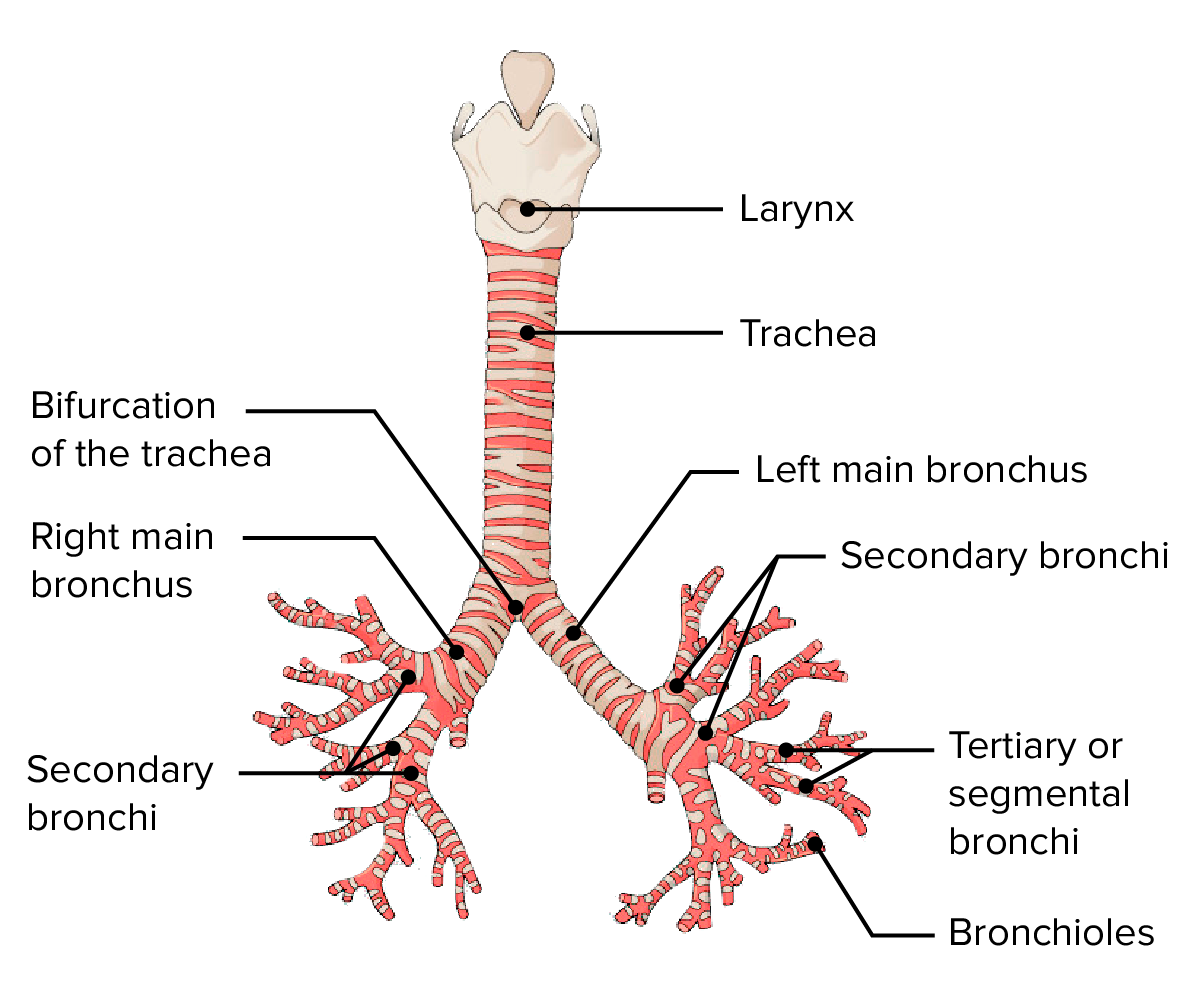
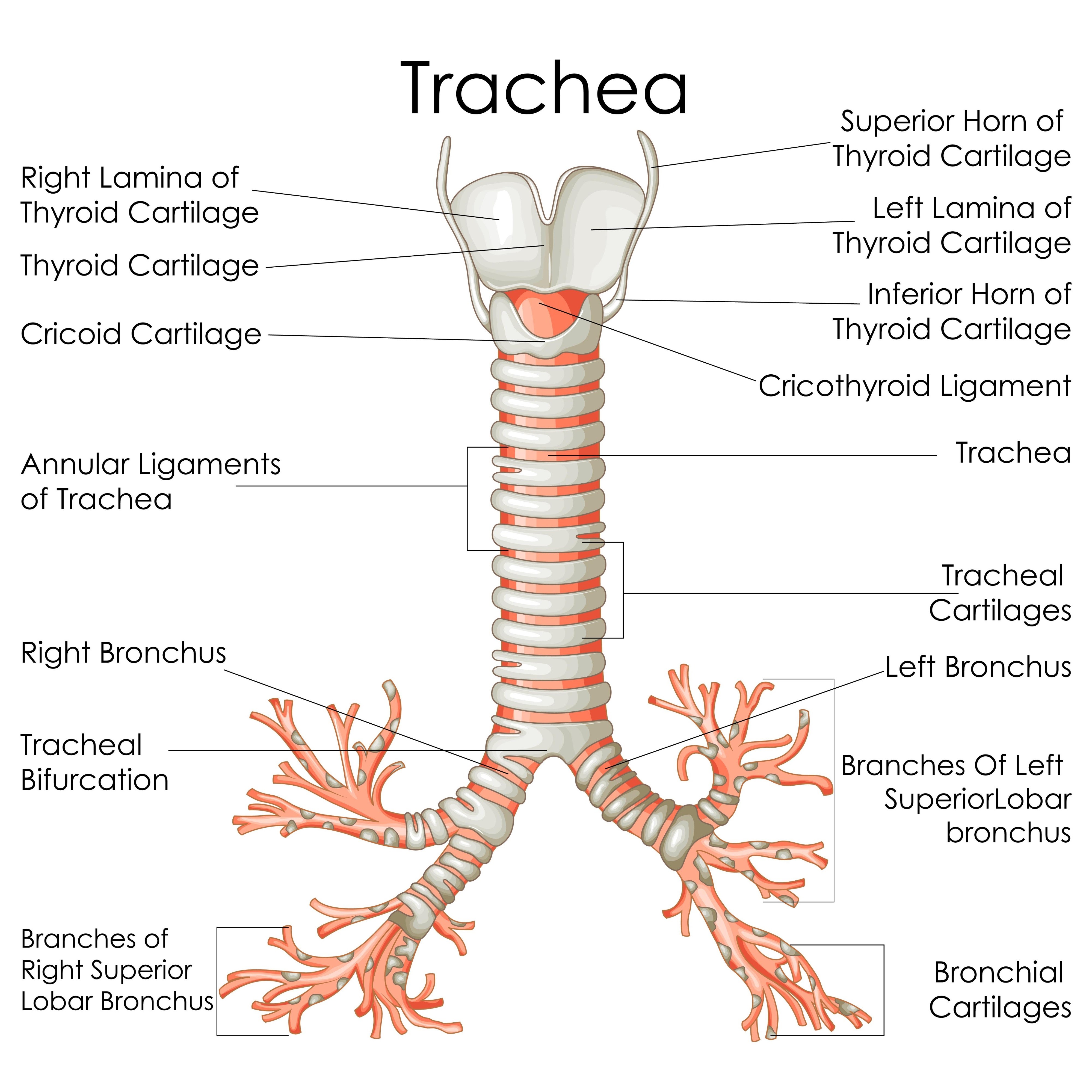
Structural differences: Right vs. Left Main Bronchus
The Right main bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the Left.
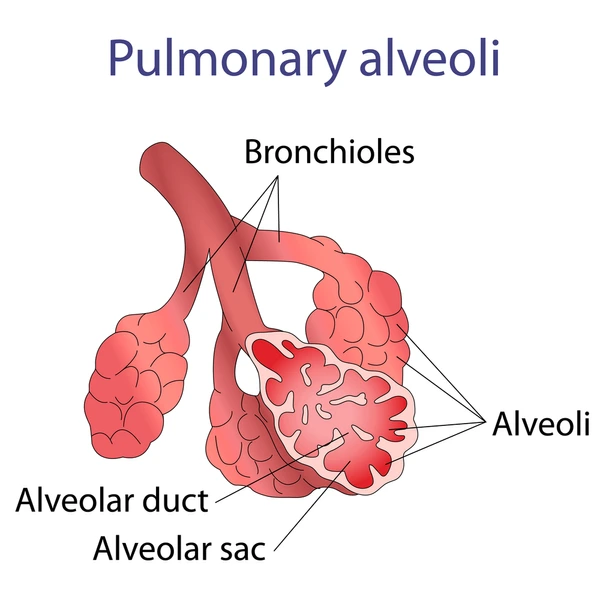
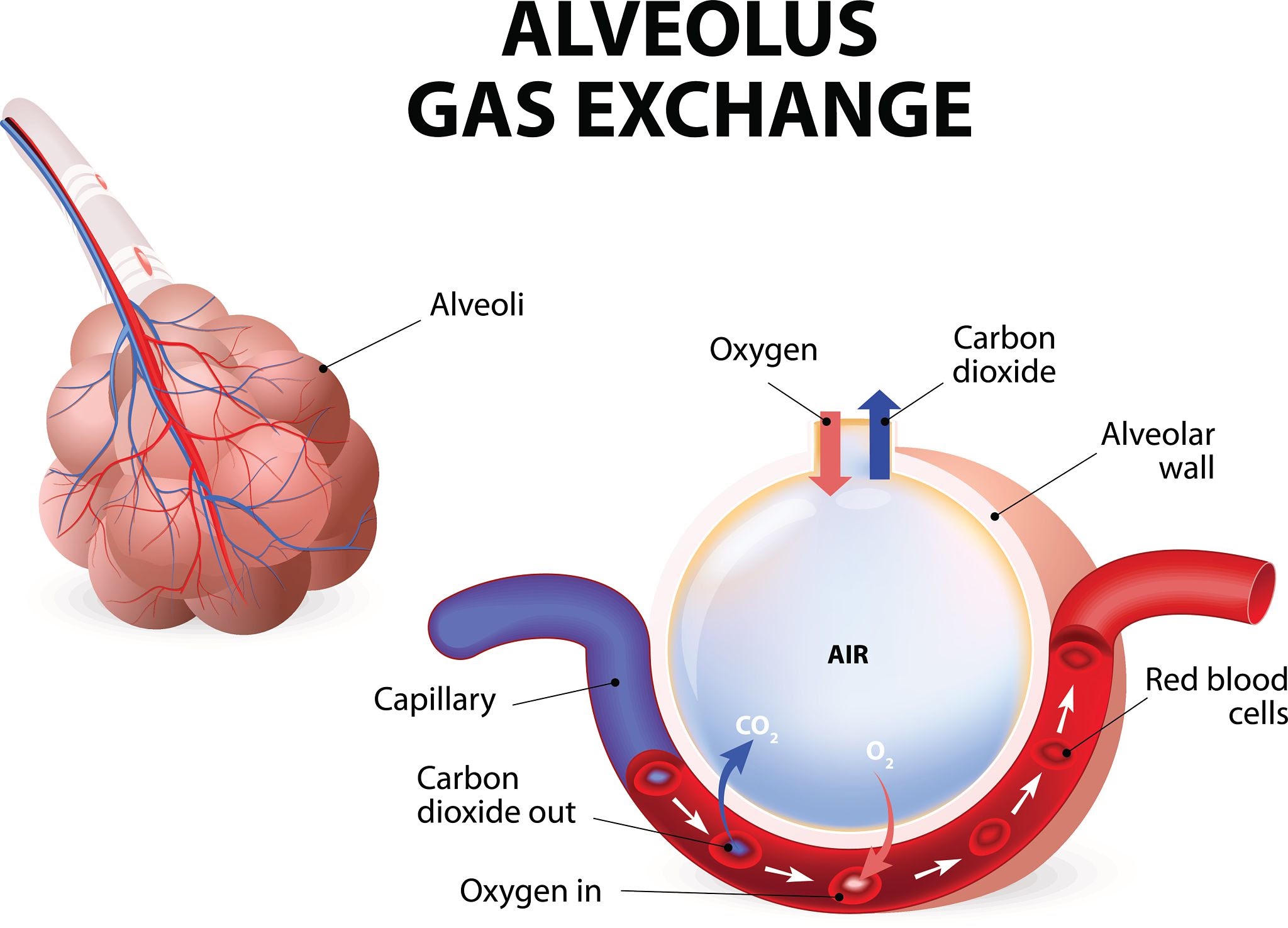
Components of the Respiratory Zone
Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli
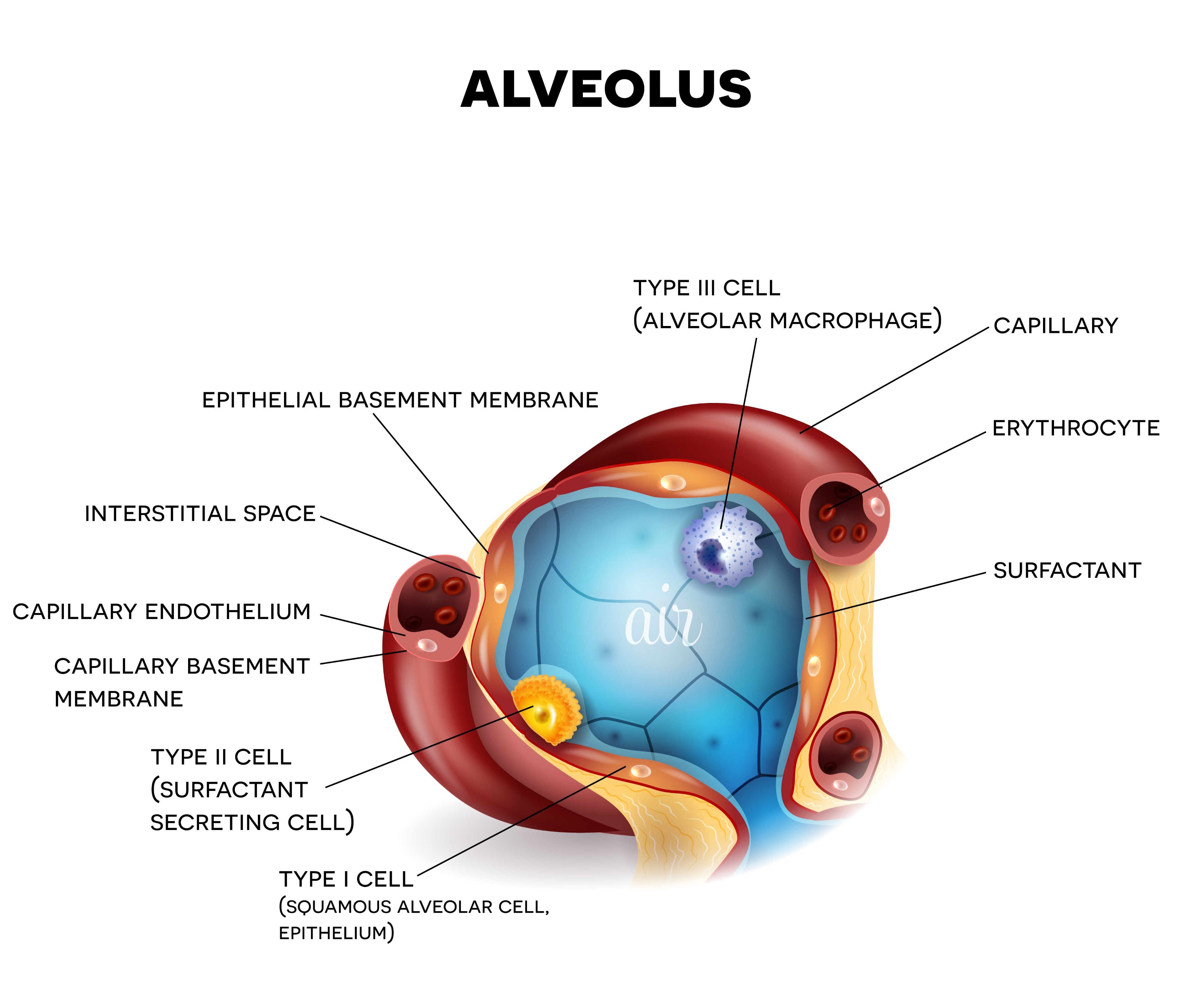
Type II Pneumocyte function
Cuboidal cells that secrete surfactant to reduce surface tension in the alveoli
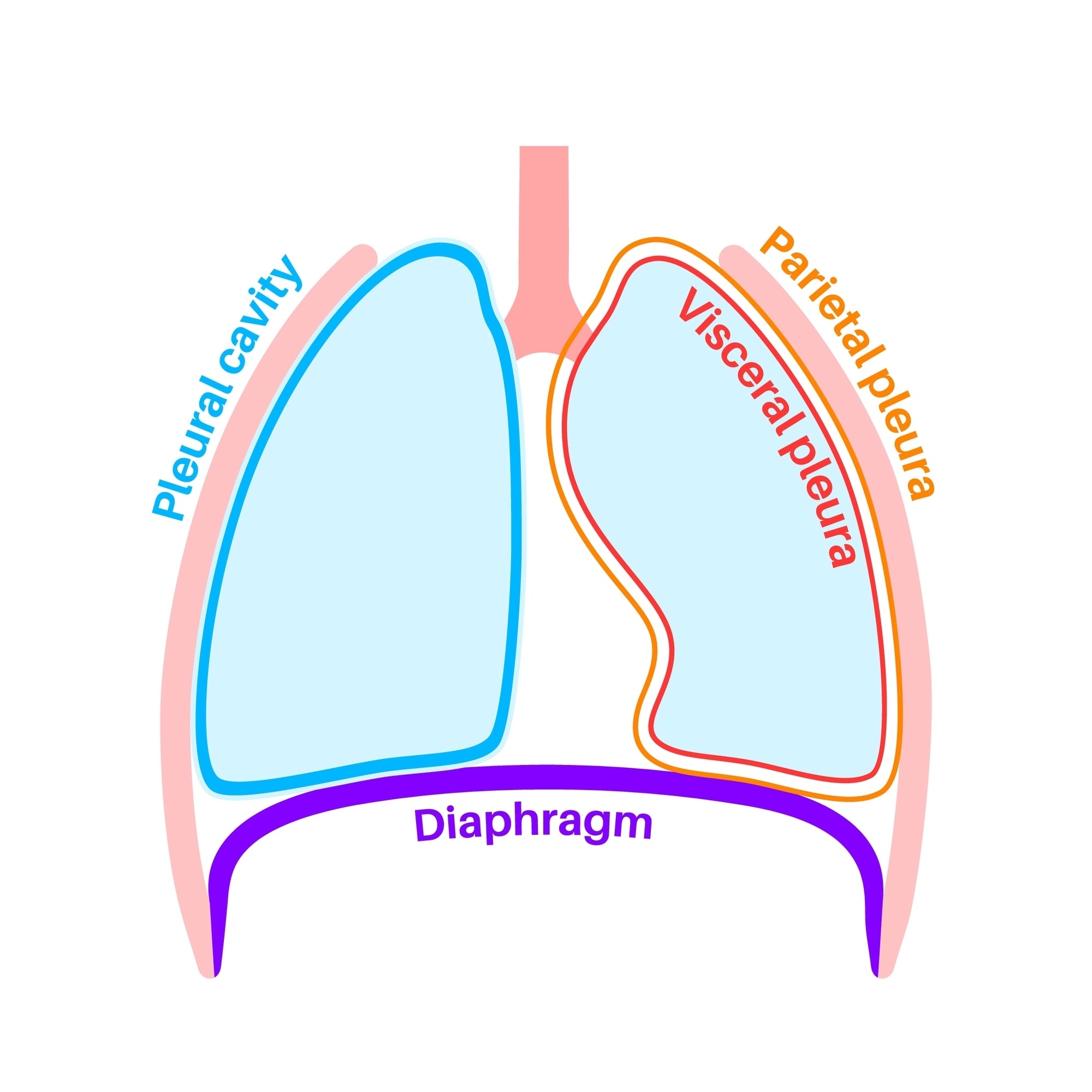
Layers of the Pleura
Parietal pleura (lines thoracic wall) and Visceral pleura (covers lung surface), separated by the pleural cavity
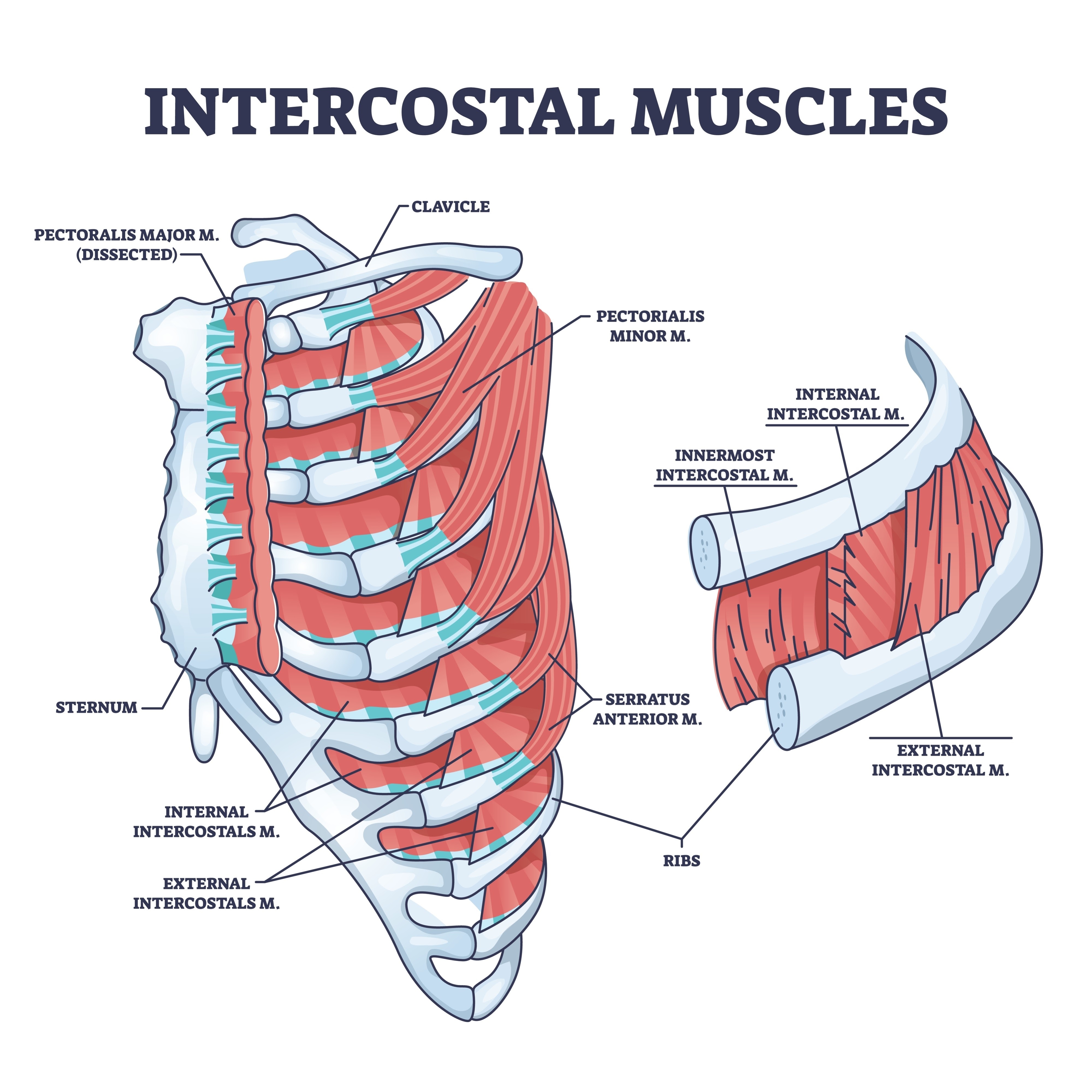
Primary muscles of quiet inhalation
The Diaphragm (main muscle) and the External Intercostal muscles
Pump-handle mechanism
Movement of ribs 2–6 that increases the anterior-posterior dimension of the thoracic cavity
Bucket-handle mechanism
Movement of ribs 7–10 that increases the transverse (lateral) dimension of the thoracic cavity.
Definition of Dalton's Law
In a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures exerted by each gas if it were present alone
Formula for Henry's Law
Cx = Sol * Px (Concentration depends on solubility and partial pressure)
External vs. Internal Respiration
External: Exchange between alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. Internal: Exchange between systemic capillaries and tissues.
Cooperative Binding of Hemoglobin
When one O2 binds, Hb changes shape (Tense to Relaxed), making it easier for more O2 to bind.
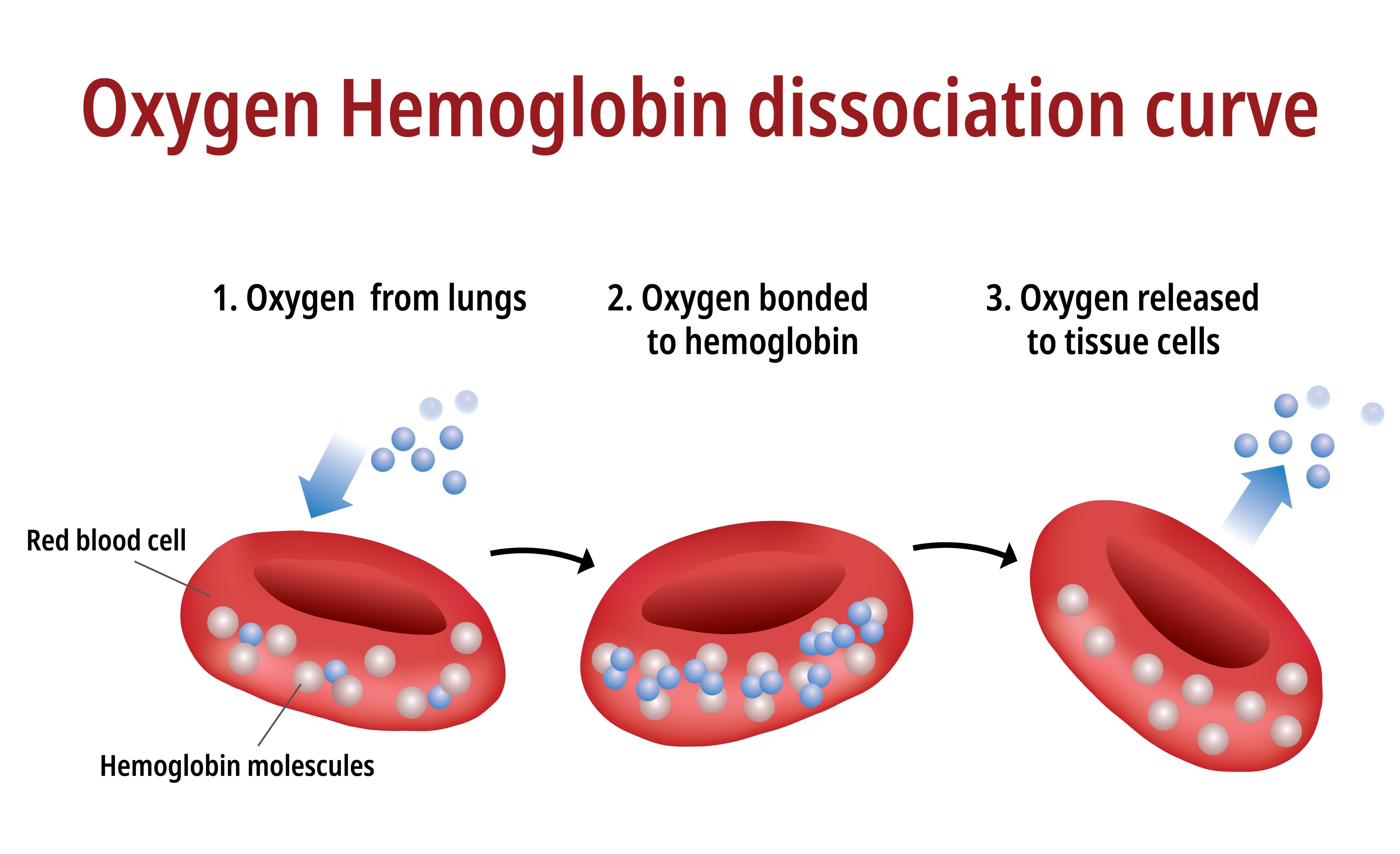
Factors shifting Oxygen-Hemoglobin Curve to the RIGHT
Increased Temp, Increased PCO2, Increased H+ (lower pH), Increased 2,3-DPG.
The Bohr Effect
Decrease in Hb affinity for O2 due to high CO2 or low pH (helps unload O2 at tissues).
The Haldane Effect
Deoxygenated blood has a higher affinity for CO2.
The Chloride Shift
Exchange where HCO3- diffuses OUT of RBCs and Cl- diffuses IN to maintain electrical balance.
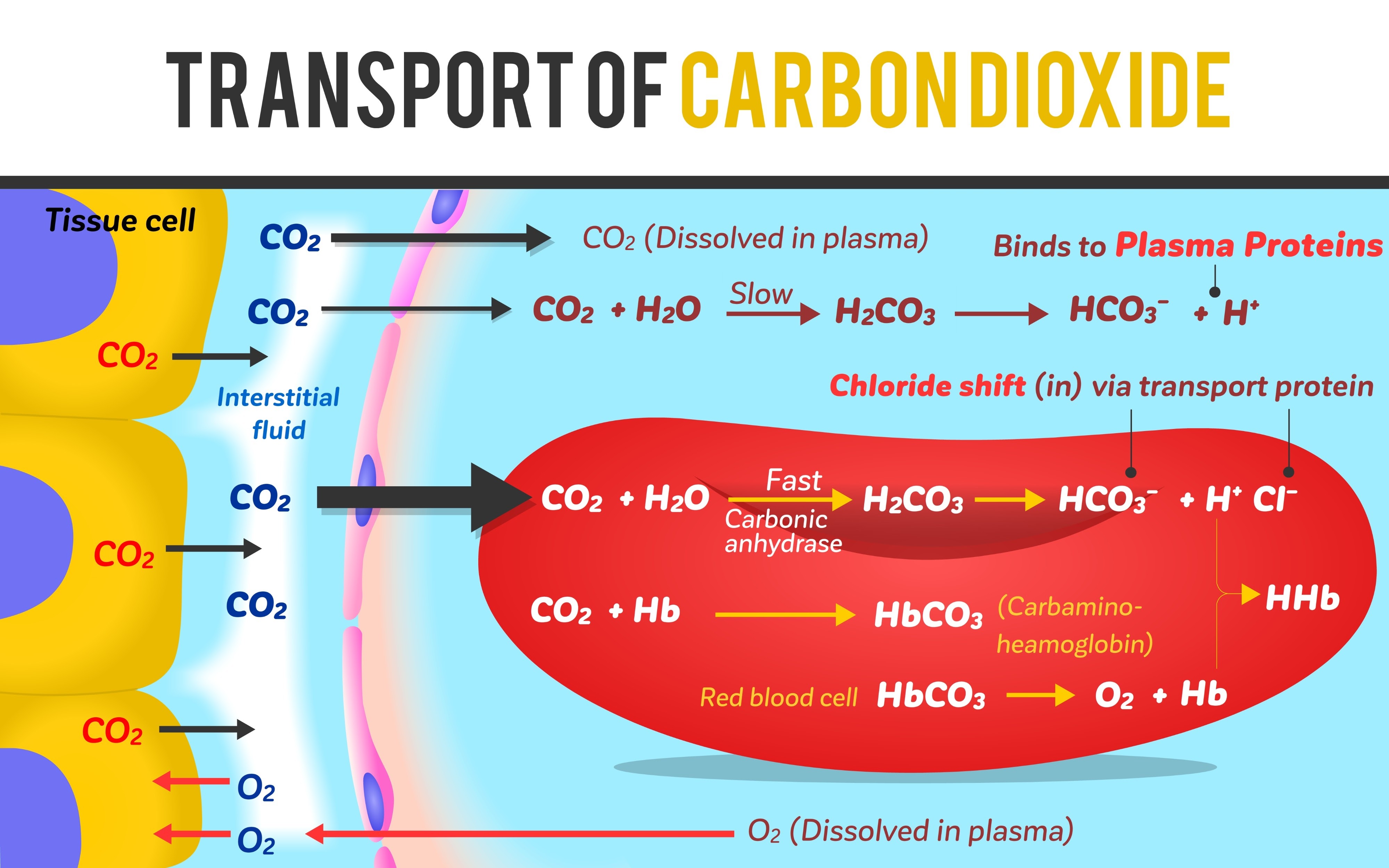
Carbonic Anhydrase function
Enzyme in RBCs that catalyzes: CO2 + H2O <-> H2CO3.
Primary method of CO2 transport
As Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) (approx 70%).
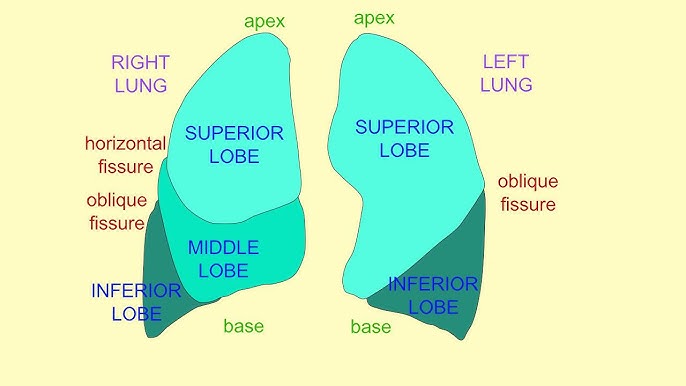
Lobes of the Lungs
Right: 3 lobes (Upper, Middle, Lower). Left: 2 lobes (Upper, Lower).
The Carina
Internal ridge where trachea bifurcates (T4/T5); highly sensitive cough reflex site.
Nerve supply to the Diaphragm
Phrenic nerve (C3, C4, C5).
P50 Value
Partial pressure where Hb is 50% saturated. Higher P50 = Lower affinity.
Bronchopulmonary Segments
Functionally independent units (10 per lung) each supplied by its own bronchus and artery.
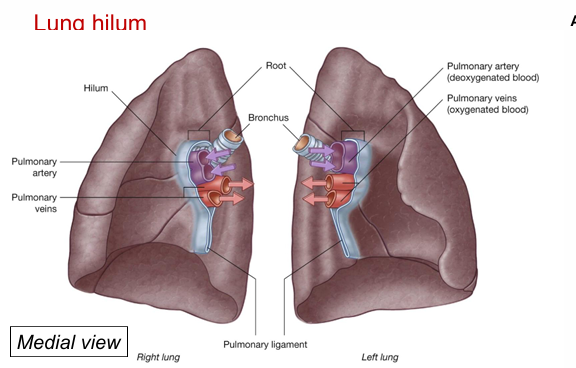
Hilum of the lung
Roots where vessels leave the lung.
Bronchi are posterior
Pulmonary arteries are superior to the pulmonary veins
Pulmonary veins are most inferior.