Chordates
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
How many extant vertebrate species? extinct?
70000
>100x extinct
Two major groups of vertebrates? describe each
non amniotes (mostly aquatic)
embryo protected by membranes
amniotes (mostly trestrial)
additional 3 membranes, one being amnion
Animals in each group?
non amniotes:
Jawless fishes (“Agnathans”)
Cartilaginous fishes (Chondrichthyes)
Bony fishes (“Osteichthyes”)
Amphibians (salamanders, frogs, caecilians)
amniotes:
“Reptiles"
Turtles (Testudines)
Lepidosauria (lizards, snakes, tuatara)
Crocodilia
Birds (Aves) (technically reptiles due to close ancestry to crocodilia)
Mammals
Systematics (examples)
= evolutionary classification
reflects evolutionary relationships and for organization
Chinese algae eater > fish
Aracari > bird
Central stoneroller > fish
Taxon
Named taxonomic unit at any level (plural=taxa)
Binomial nomenclature
scientific naming of species, standardized by Linnaeus (1700s) (genus, species) (unique for all)
Homo sapiens (Humans)
Felis concolor (cougar)
Hierarchy of classification (name all, which italicized? what should they reflect?)
Higher levels more inclusive
lower less
Kingdom (e.g., Animalia)
Phylum (e.g., Chordata)
Class (e.g., Mammalia)
Order (e.g., Carnivora)
Family (e.g., Felidae)
Genus (e.g., Felis)
Species (e.g., concolor)
reflect a degree of relatedness, shared ancestry, not how similar
Phylogenetic systematics (what is it, what are ancestors, can they change or are they set in stone?)
hierarchy based on ancestry
ancestor is nodes
can change as hypotheses and evolutionary relationships change
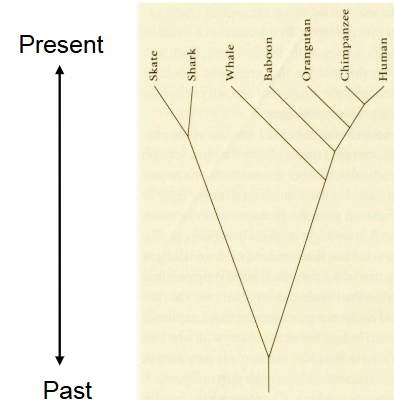
Monophyletic taxa
group, share a common ancestor, includes all descendants
One line in, no line out
natural groupings
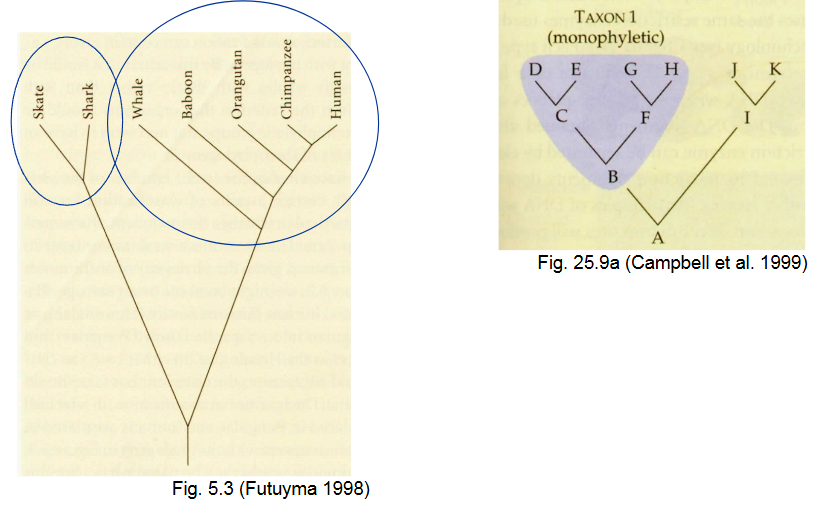
How do we identify monophyletic groups? (Apomorphy, Plesiomorphy, synapomorphy, symplesiomorphy)
derived/apomorphic characters
Apomorphy= character different from ancestral (novel/derived trait) (the guy that got it first)
feather in birds
hair in mammals
jaws in vertebrates
Plesiomorphy= ancestral character (og trait)
synapomorphy (shared derived) helps find common ancestry. feathers in all birds, meaning common ancestor.
Notochord in chordates, common ancestor
symplesiomorphy doesnt indicate recent.
Mammals with hair are close to eachother but animals without hair arent inheritaely close due to that absence
homologous
there is a chance that traits evolved independently in different lineages. Birds and mammals being warm blooded for example. To know if from same ancestor, they have to be homologous, where likeness is due to shared ancestry.
Analogous
resemblance between species, but different branches
similar roles but independent
also called homoplasy (plas = form)
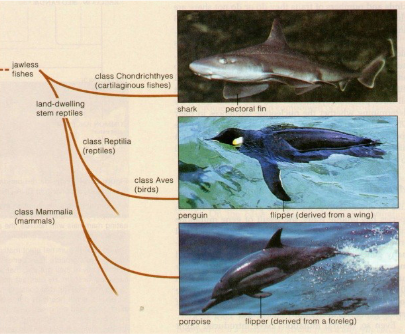
Causes of Homoplasy/Analogous
Convergent evolution: evolve independently in animals that have diverged for a long time (bats and birds, wings)
Parallel evolution: evolved independently but diverged recently (elongate hind legs in jerboa (africa) and kangaroo rat (NA)
Evolutionary reversal: re-evolution (streamlined body and fins of aquated whales and dolphins, whereas sharks retained there still)
All of these independent evolution, not inherited
polyphyletic taxa
artificial grouping, two more distant lineages
ex. “aquatic vertebrates”
more than one line going in, none going out
paraphyletic taxa
dont include all species derived from common ancestor
cant be selective about which to choose and which to not choose
Pongidae, Hominidae
One in, one out
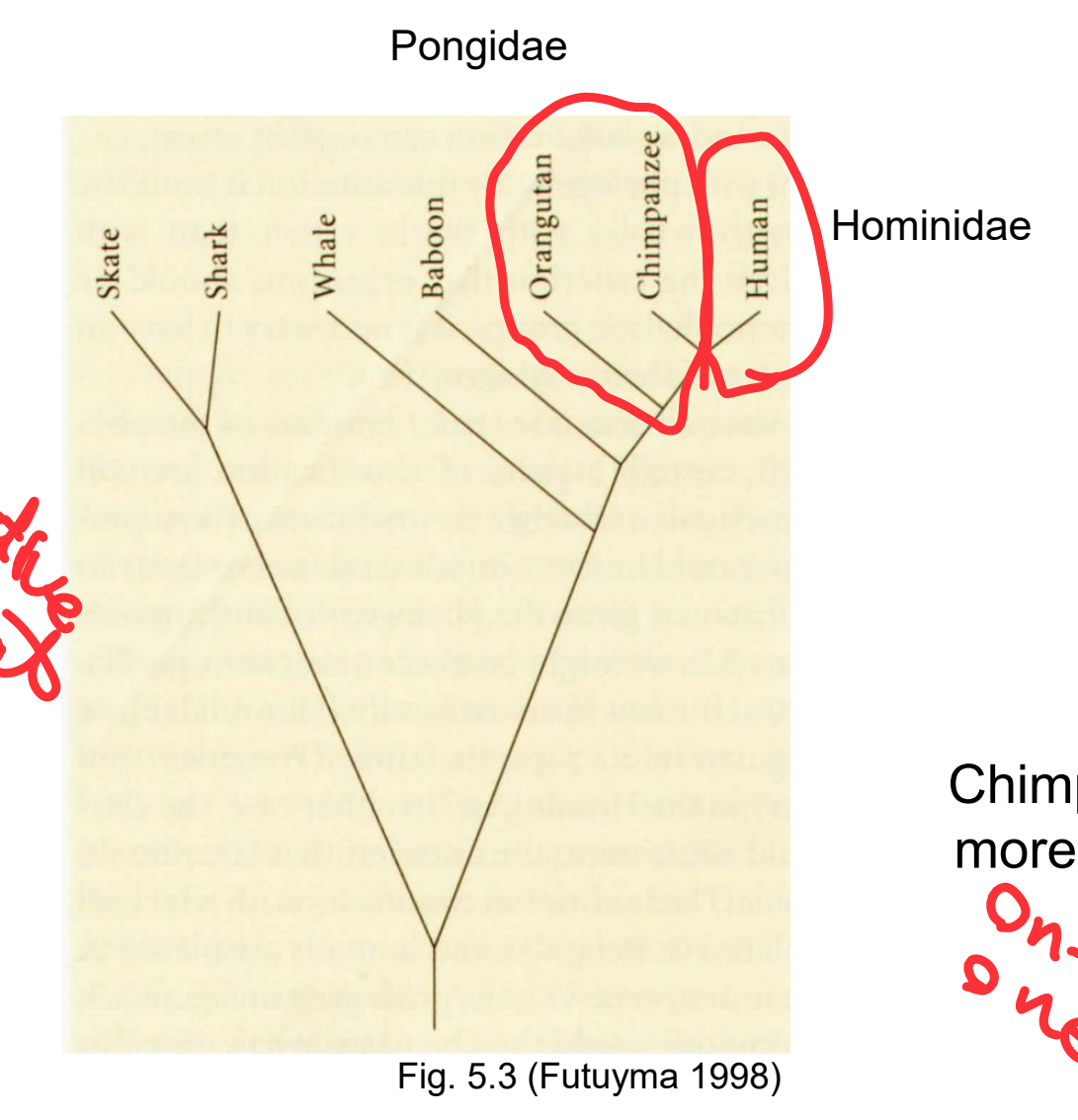
Traditonal Groups
traditional groups are paraphyletic mostly
some polyphyletic
Paraphyletic:
Dinosaurs if birds excluded
“reptiles” and “fishes”
Polyphyletic:
warm blooded (birds and mammals)
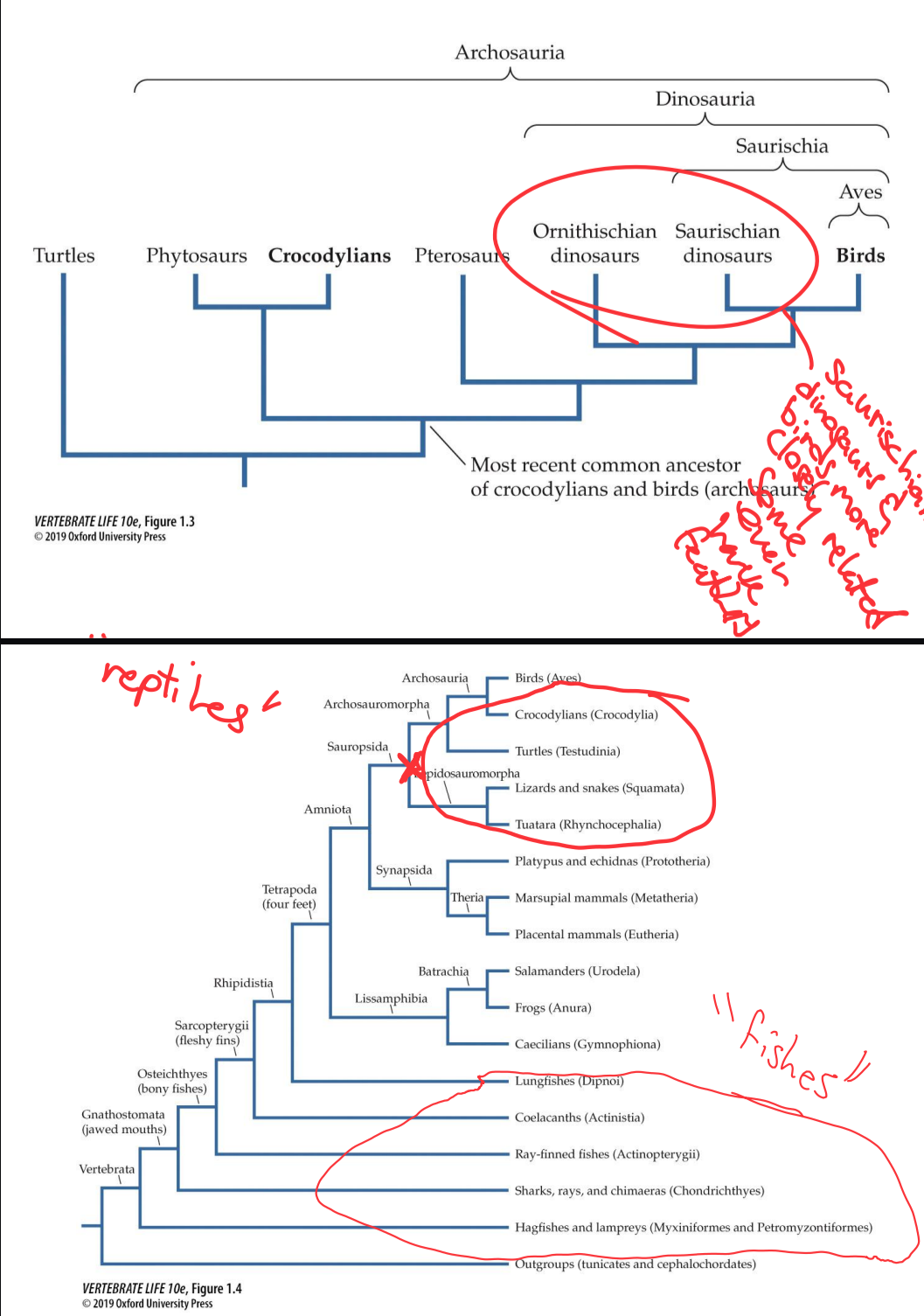
Sister groups
two closest lineages (birds and saurischian dino)
Crown groups
extant species, ends of branches
Stem groups
extinct groups, stems of branches
Three subphyla of Chordata
Vertebrata
plus non vertebrates:
cephalochordata (lancelets)
Urochordata (tunicates, sea squirts)
Who are chordates closely related to? why?
close: Echinodermata (sea stars) and phylum Hemichordata
They are the only deuterostomes (synamorphy)
Deuterostomes vs protostomes
Blastopore=
Deu: second mouth, first came the anus
Pro: first mouth, first came mouth
Five synapomorphies of chordates
Notochord (rod for support and muscle, replaced by vertebrae in most)
Dorsal Hollow nerve chord (forms spinal chord, induced by notochord, not just nerve chord has to be dorsal hollow)
Postanal tail (segmented muscular tail, all chordates during embryonic)
Pharyngeal (gill) slits (pair openings anterior pharynx, first as feeding, respiration in fish)
Endostyle/Thyroid gland (endostyle in adult non vert, and larval lampreys, secretes mucus, ciliated glandular tissue on pharynx floor)
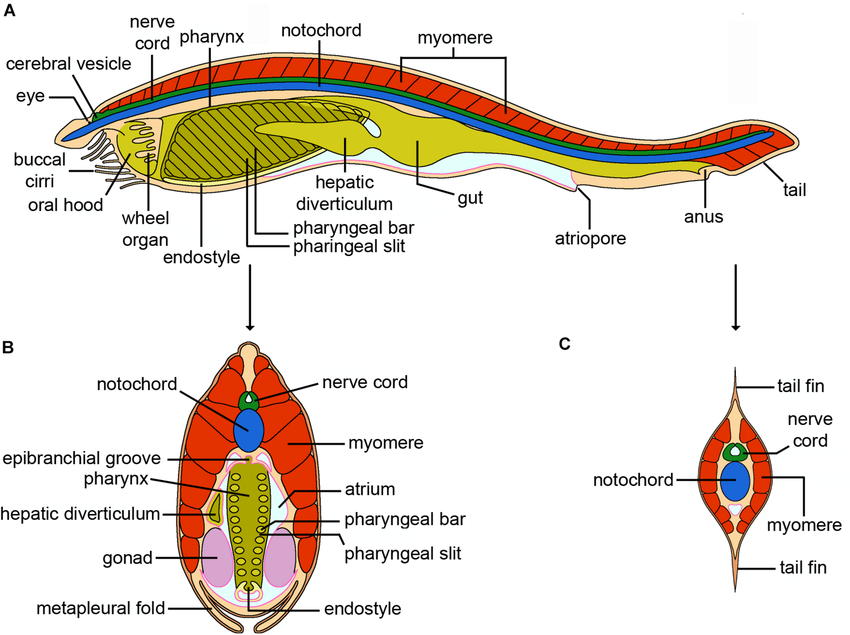
Cephalochordata (what, lifestyle, myomeres)
25 fishlike species (lancelet or amphioxus)
burrowing, sedentary
elongation notochord aids in burrowing, past the head.
pharyngeal slits for feeding, not gas exchange
Myomeres = blocks of striated muscle (like salmon)
contraction of myomeres bends the body
Cephalo= head
Urochordate
Tunicates, sea squirts
Uro=tail
2000 marine species
sedentary adult but free swimming larvae, large ciliated pharynx for filtering
encased in fibrous “tunic”
Free