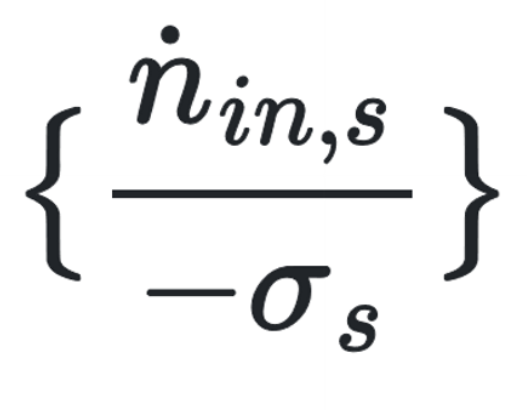Conservation of Mass (Ref Page)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How is amount of material expressed?
mass or moles
Mass (m)
a quantity of matter that has weight in a gravitational field
Mole (n)
an amount of any substance containing Avogadro’s number of molecules of that substance
1 mole = 6.02e23 atoms
Molecular Weight (M)
related to mass and number of moles; common units of g/mol or lbm/lbm-mol
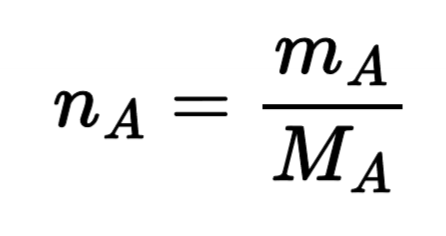
Mass Flow Rate
describes the transport of material over a period of time
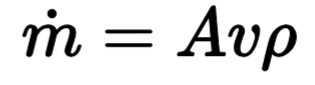
Cross sectional area of a cylindrical tube
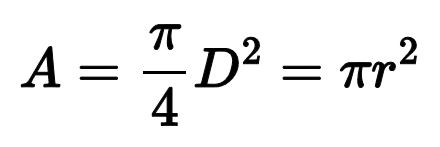
Algebraic Mass Equation
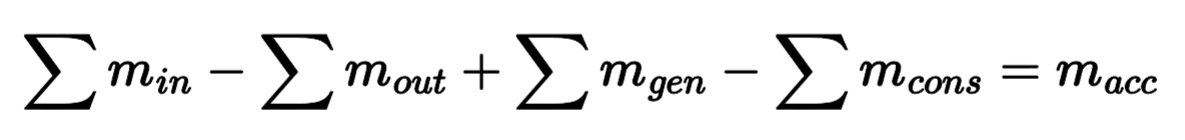
Differential Mass Equation
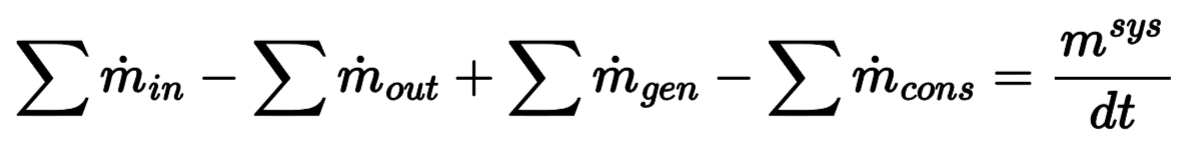
Integral Mass Equation
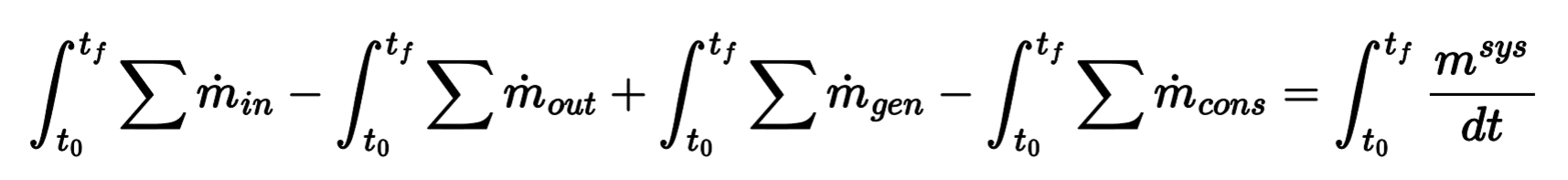
What can the mass accounting equations be used for?
total mass
species & element mass
total moles
element & species moles
Total flow rate of stream
sum of molar flow rates - mole of s / time
sum of mass flow rates - mass of s / time
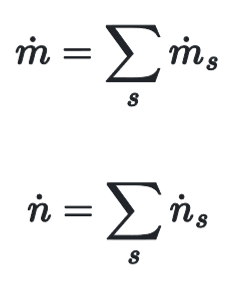
Weight & Mole Fraction Sums
All weight & mole fractions in a stream sum to 1
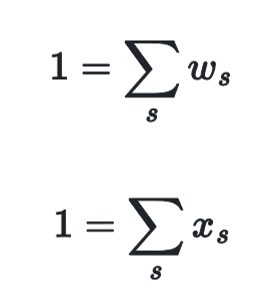
Weight & Mole Fraction Relation to Molar Flow Rates
the weight fraction equals the species mass flow rate divided by the stream’s mass flow rate
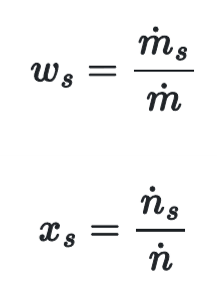
Relating molecular weight to flow rates
The molecular weight equals the mass flow rate divided by the molar flow rate (makes sense b/c still ends up being mass over moles since time unit cancels)
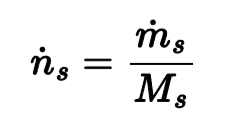
Differential equations for open, nonreacting, steady-state systems
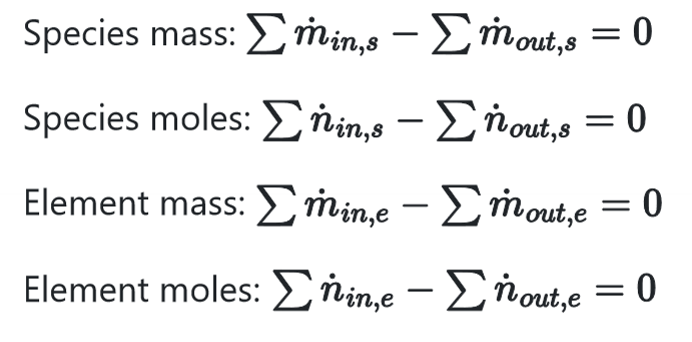
What does it mean if we define a system as open?
The is an in and out term in accounting equation
What does it mean if we define a system and nonreacting?
there is no generation or consumption terms in the accounting equation
What does it mean if we define a system as steady-stade?
there is no accumulation term in the accounting equation
Reaction Rate (R)
the extent to which a reaction proceeds, represented in moles or mol/time
Characteristics of reaction rate
constant
no tied to a specific species/compound
How to find R
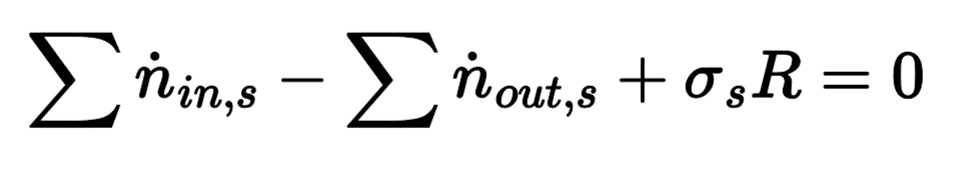
Fractional conversation (f) of a reactant
how much of the reactant reacts in the system relative to how much is introduced
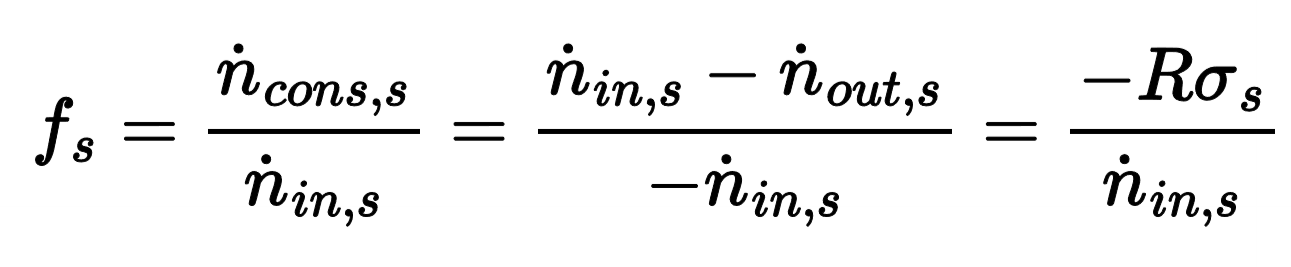
Limiting Reactant
the reactant consumed first; defined by minimum equation value