Amino Acids and Protein Structure (Biochemistry)
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts from amino acids, protein structure, globular/fibrous proteins, enzymes, kinetics, regulation, and disease from the Biochemistry lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins; 20 standard amino acids encoded by DNA (abundant and functionally diverse)
Standard (common) amino acids
The 20 amino acids commonly found in mammalian proteins, encoded by DNA. (common or standard A.As)
Amino group
The -NH2 group attached to the α-carbon of an amino acid; participates in peptide bond formation.
Carboxyl group
The -COOH group attached to the α-carbon; forms peptide bond with the next amino acid.
α-carbon
The central carbon of an amino acid bearing the amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and the side chain (R).
Side chain (R group)
The variable group that determines an amino acid’s unique properties.
Proline
Amino acid with a secondary amino group that forms a rigid ring; disrupts α-helices and helps form extended fibrous collagen formation. (only secondary amino group most are primary)
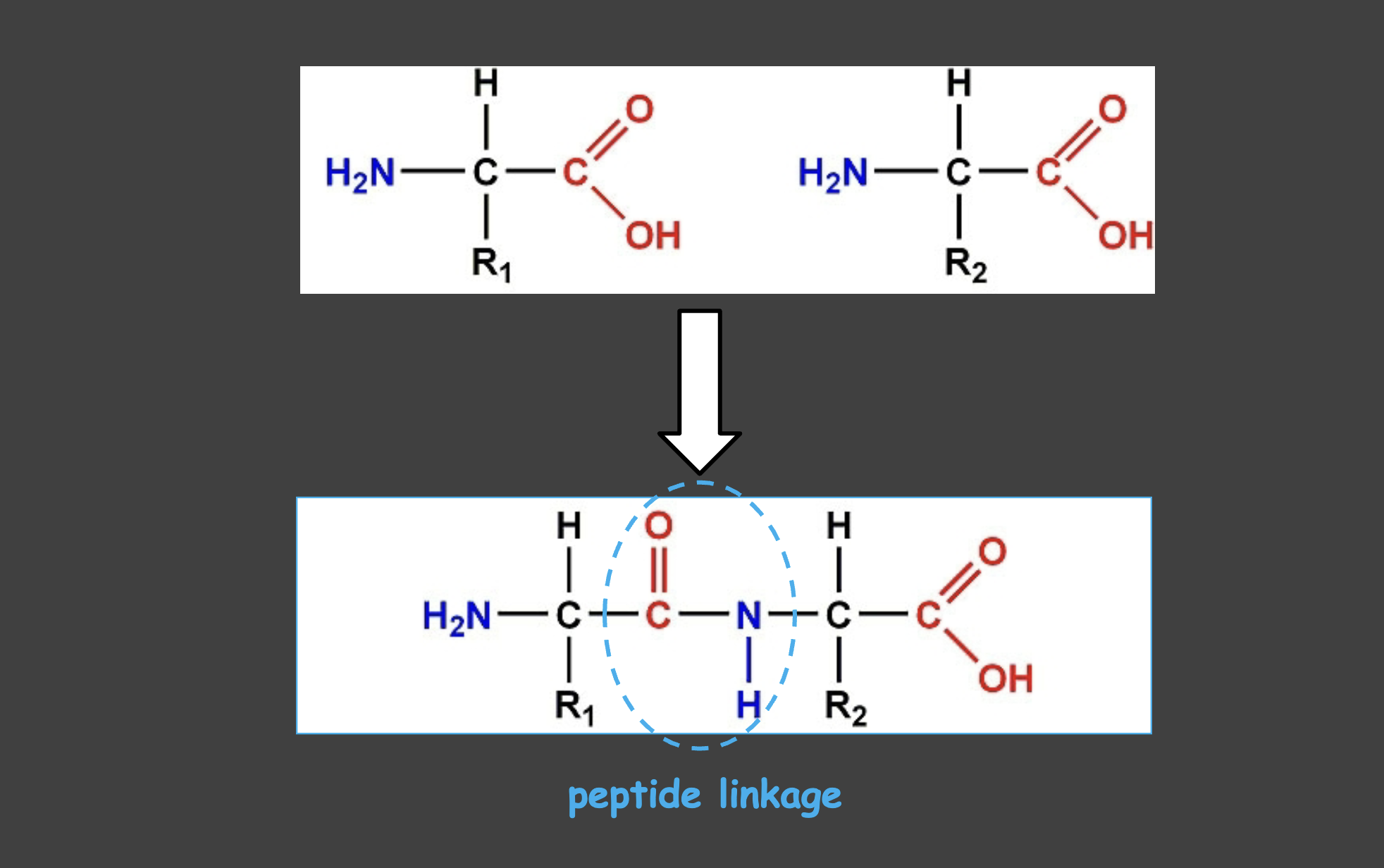
Peptide Linkages
How different amino acids are linked together
Structure of Amino Acid at physiologic ph
Carboxyl (-COO) is deprotonated occurs at 2 PH and amino group (nh3+) occurs at 9 Ph
Amphoteric property
At physiological pH, amino acids can act as both acids and bases.
Zwitterion
Amino acids at physiological pH that carry both positive and negative charges but are overall electrically neutral.
Classes of amino acids
Four categories based on side-chain properties: nonpolar, uncharged polar, acidic, and basic.
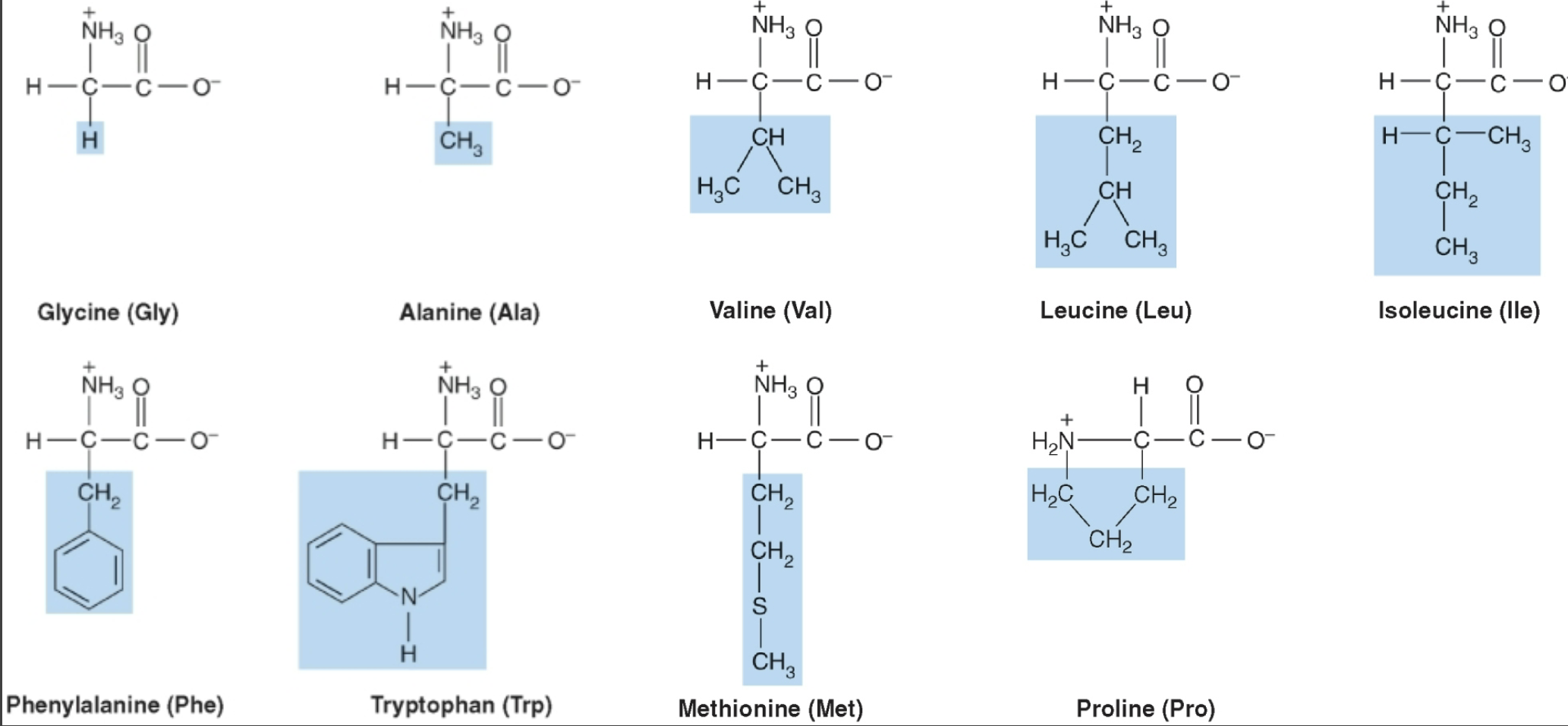
Nonpolar amino acids
Amino acids with hydrophobic/ side chains and has lipid like properties; tend to be in protein interiors (aqueous solution)or membranes (hydrophobic environment)
Biochemistry of Sickle Cell Anemia
In RBCs from substitution of glutamate to Valine at the 6th position of the 2nd beta subunit of hemoglobin A
Subunit of Hemoglobin
4 subunits 2 Alpha and 2 Beta
Sickle Cell Anemia
in low O2 conditions, valine causes aggregation of hemogolobin leading to a ickled shaped with decreased elasticity. Sickled cells are less efficient at traveling through capillaries leading to vessel occlusion and ischemia
Hemoylsis
The breakdown of RBC occurs much sooner in sickled cells (10-20) rather than 90-120 days in normal RBC. Results in Hemolytic Anemia, too because the destruction rate is faster than the renewal rate in the bone marrow
Uncharged polar amino acids
Amino acids with polar but uncharged side chains (hydropillic and can partake in H-Bonding) (e.g., Ser, Thr, Asn, Gln, Tyr, Cys). Q- Glutamine (2 amine) T-Theronine (Ch3-OH) S-serine (OH-H) C-Cystsine (Sh) N- Aspargine (NH2) Y- Tyrosine (oh-phenyl)
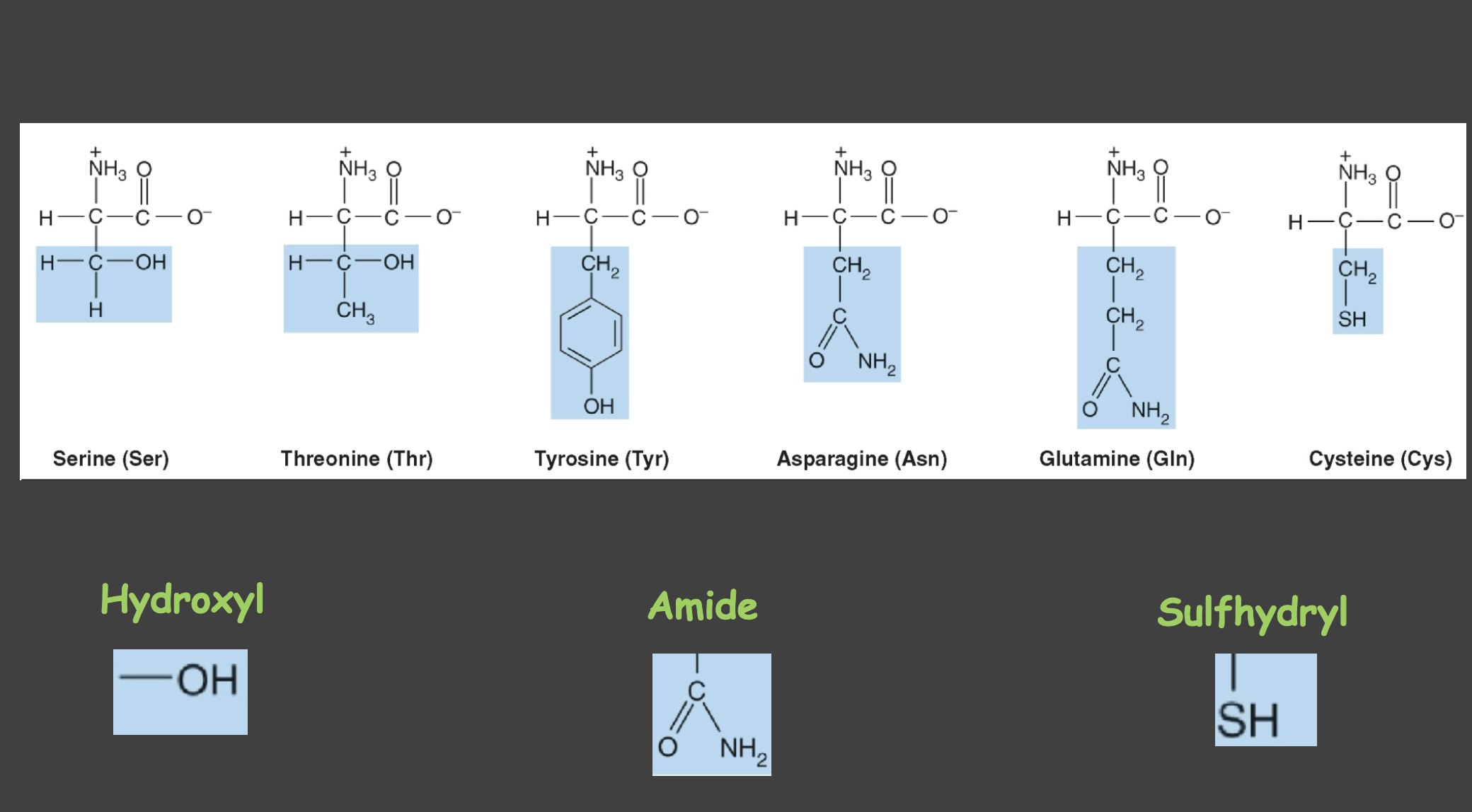
hydroxyl group
serves as attachment site for phosphate group
amide
attachment for oligosaccharcide chains in glycoproteins
sulfhydryl
active sites of enzymes
Acidic amino acids
Aspartate (Asp) and Glutamate (Glu); (proton donors) side chains carry a negative charge at physiological pH. O=C-o- groups
Basic amino acids
Lysine (Lys), Arginine (Arg), Histidine (His); (proton Acceptors) side chains are positively charged at physiological pH (Histidine is partially ionized).
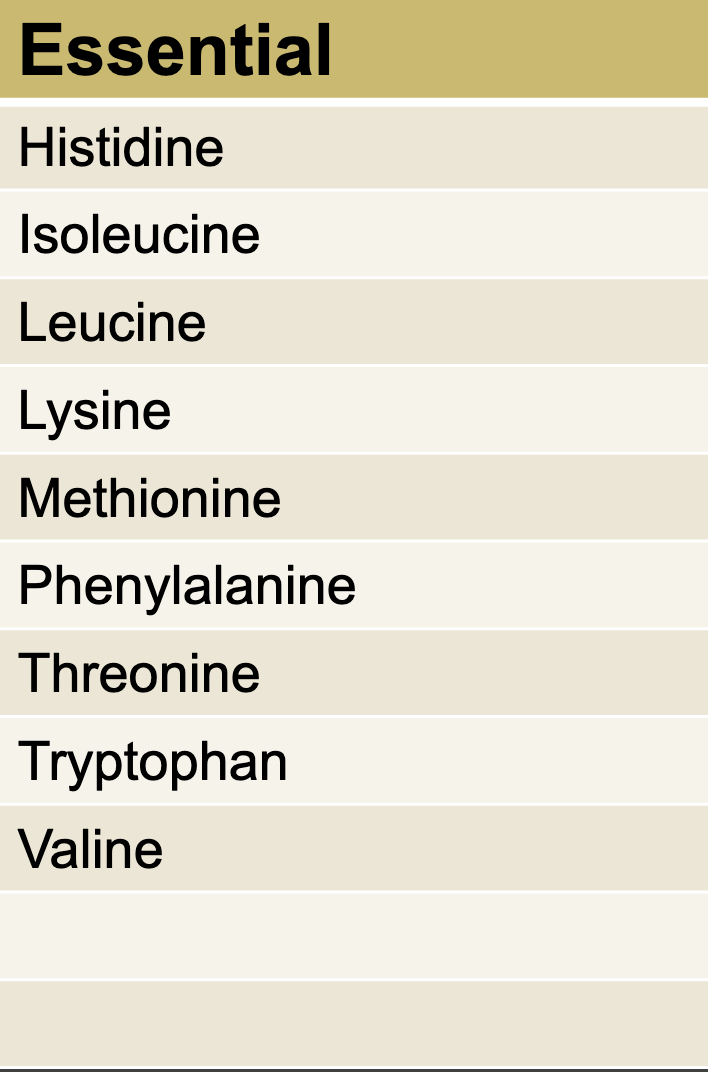
Essential AA
NOT produced by the body No ACG.
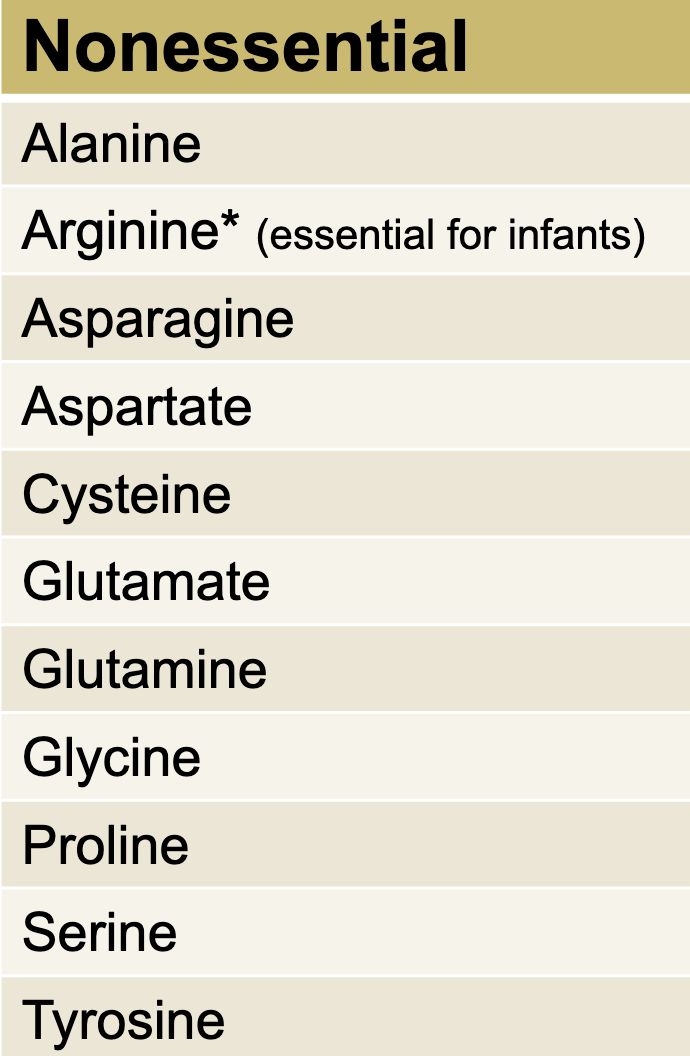
Non-Essential AA
A-C-G
Enantiomers
All AAs in mammailian proteins are of L-configuration
-mirror images
-clockwise - R
-counter clockwise- L
glycine as a special case
Glycine is not chiral because it has two hydrogen atoms on the α-carbon.
pKa
Acid dissociation constant; pKa = -log10(Ka); indicates acid strength (lower pKa = stronger acid).
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log([A−]/[HA]); relates pH to acid/base species in buffers. WHen weak acid is greater than conjugate base pH > pKa
Buffer
A solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists pH change; AA contains weakly acidic a-carboxyl groups and basic a-amino groups
pH buffer should be within ± 1 pH unit of the acids pKa value
Maximal buffering when weak = conjugate base
Max Buffering Capcity
When ph= pKa
Isoelectric point (pI)
pH at which a molecule has no net electric charge; for amino acids with two pKa values, pI lies between them. pKa When Form 1 = 23(the Amino acid is electrically neutral) (form 2 Predominates
Titration of an amino acid
Plot of pH as titrant is added; shows different pKa values and the pI where net charge is zero.
if pH < pKa protonated acid form (HA) predom (COOH or Nh3+)
if pH > pKa depotonated base form (A-) predom (COO- or NH2)
DNA to protein relationship
DNA sequence determines the amino acid sequence of a protein via transcription to RNA and translation.
Primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Peptide bond
Amide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next.
can e hydrozled nonenzymatically by strong acid or base or at high temperature
Peptidases (proteaese)
Enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds;
exopeptidases
cut at the end of ptoteins
aminopeptidases
cuts amino end
carboxypeptidases
cuts carboxyl end
endopeptidases
cleaves within a protein
N-terminus and C-terminus
N-terminus is the amino end of a polypeptide; C-terminus is the carboxyl end.
residue
each component AA
Naming polypeptides
AA have their suffixes changed to -yl with exception of C terminal
N- valine- glycine- leucine: vallyglylyleucine
Trans vs cis peptide bonds
Peptide bonds are generally trans due to steric hindrance in the cis form.
Stop Codons
UAA UGA UAG
Which protein contains a-helices
Keratain (most common protein) (hair nail skin) Myoglobin too
Amino acid enantiomers (D/L)
Optical isomers; most mammalian proteins use L-amino acids; glycine is not chiral.
Secondary structure
Regular sub-structures formed by hydrogen bonding in the polypeptide backbone (α-helix and β-sheet).
α-helix
Right-handed spiral; 3.6 amino acids per turn; side chains extend outward; proline disrupts the helix.
β-sheet
Sheets formed by hydrogen bonding between backbone C=O and N–H of adjacent strands; can be parallel or antiparallel. (side by side)
Tertiary structure
Three-dimensional folding of a single polypeptide; stabilized by hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic effects by side chains which are attracted and repulsed
Chaperones
Proteins that assist in proper protein folding.
Denaturation
Unfolding of a protein’s structure; loss of secondary/tertiary structure without peptide bond cleavage; caused by heat, strong acid and bases, detergents, heavy metals, organic solvents, and mechanical mixing (may or may not be reversible)
What is dental amalgam
mixture of metals including mercury
Quaternary structure
3D structure formed by the assembly of multiple polypeptide chains; subunits may be independent or cooperative. (held together by noncovalent interactions: Hbonds ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions)
Protein Misfolding
caused from trial and error
are tagged and degraded by cell by unqiuloine
can accumalte due to age
Amyloid Disease
accumuation of insoluble, spontanous aggregating misfolder protein called amyloid of Beta- pleated sheets
leads to alzherim and Parkison (affects nervous system)
Prion Diseases
caused by prion protein (prp)
highly resistant to proteolytic degreading
TSE → causative agent that leads to Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease in human, scrapie in sheep and mad cow disease
Infections Prp Sc
noninfection: prpC
Prp Sc includes a 3D confimation change in PrpC that is resistant to degradition
Structure and Function of Myoglobin
Function: Resrvoir for oxygen and carrier that increases rate of transport of O2 within the muscle cell
Structure Consists of a single polypetide chain with a heme group
Structure and function of Hemoglobin
Found in RBC
Function: transport O2 from lungs to capillaries of tissues and also tranport H+ and Co2 from tissues to the lungs
Structure: Transport 4 molecules of O2 on its 4 heme group
Hemoglobin A (HB A )
consists of 4 polypeptide chains - 2a and 2B by non covlanet
each subunit has stretches of a-helical and heme binding pocket
Forms of HBa
Oxgeated form = R relaxed state
Deoxygenated form T Taut State
O2 dissociation curve
Hemo :Sigmodial shape
myogolbin : hyperbolic shape
Cooperative binding
as O2 binds the binding of O2 is enhanced
Location of O2 and its affinity for O2
Lungs: hemo quickly saturauted
Tissues: gives up about half O2
myoglobin has a greater for O2 especially when O2 is very low in muscle cells(strenous activity)
bohr effect
The effect a change in O2 binding affinity of Hb due to the binding of other ligands to Hb
ligands include:
(H+ pH) increase in Ph leads to shift right -→ decreasing O2 affinity
2,3 Biphosphoglveryate Increased leads to decreaed binding for affinity O2 (shift right)
Co2 Increased leads to decreased affinity = shift right
These ligands stablilze the T state deoxygented form of O2
Carbon Monoxide
CO binding to 4 heme sites leads to increased affinity of O2 binding it tightly and it cant release leading to no celluar respiration
Hemoglobinopathies
genetric disorders of hemoglobin due to structural abnoramilies, insufficent quaitines of normal Hb or both
Ex.
sickle cell anemia (Hb S)- glutatmete is substitued with valine
Hemoglobin C (HB C) glutatmte is sub with lysine
H SC (HB S+C)
Thallaseeia syndrome: decreased proection of normal HBC
Globular vs Fibrous Proteins
Globular are funcational Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
Fibrourous are structure (collagen elastic and a-keratin)
Collagen
Most abduant in human Body, 3 polypeptide helices
Type 1 is found in teeth, bone, skins, and tendons
AA comp of collage is distinctive
1. glycine- approx 1/3 of AA residue
2. Proline and 4-hydroyproline 30%
Hydroxproline and hydroxylysine are NOT PRESENT IN MOST OTHER PROTEINS
Hydroxyproline
Post-translationally modified proline; important for collagen stability.
Elastin
Elastin gives connective tissue its rubber-like properties; stretches and recoils; found in lungs and arterial walls and alastic ligaments
Keratin
Fibrous protein in hair, nails, and skin; α-helical coiled-coil structure; forms protofilaments and filaments.
Heme
Iron-containing prosthetic group in hemoglobin and myoglobin that binds oxygen.
Myoglobin
Globular hemeprotein in muscle; stores and transports O2; single polypeptide; high O2 affinity.
Hemoglobin
Tetrameric globular protein in red blood cells; transports O2 (and CO2/H+); exhibits cooperative binding.
Globular vs fibrous proteins (recap)
Globular: soluble, functional proteins (e.g., enzymes, Hb, Mb). Fibrous: structural proteins (e.g., collagen, elastin, keratin).
Biosysthesis Of Collagen
#3 selected proline and lysine residues hydroxylated (vitamin C importeter here)
#4 Triple helix is formed and procollagen is produced
#8 N and C are cleaved by procollage peptidaes producing tropocollage
Defects of Collagen Sysnthesis
Ehlers Dalos sydrome= fragile stretchy skin and loosejoints
Osteogensis imperfect = bones that bend and fracture easily
Glycoproteins and glycosylation
Proteins with attached oligosaccharides; N-linked (Asn) and O-linked (Ser/Thr) glycosylation affecting function.
Enzymes
Protein catalysts that increase reaction rates and are not consumed in the reaction.
Cofactors and coenzymes
Nonprotein components required for enzyme activity; cofactors can be inorganic/organic; coenzymes are organic (often vitamin derivatives).
Oxidoreductase
changes OH to a O=
Transferase
transfer functional groups between substrates
hydrolase
catalyzes the hydrolysis of chemical bonds, breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones by adding water.
lyase
catalyze the breaking of bonds by means of a reverse reaction of hydration. breaking off a bond
isomerase
catalyzes the conversion of a molecule from one isomer to another, altering its structure without adding or removing atoms.
ligase
catalyzes the joining of two molecules by forming a new bond, typically accompanied by the consumption of ATP.
translocase
moves molecules across or within membrane
Synthase
catalzyes a synthesis process
synthetase
catalyzes a sysnthesis process and requires ATP or another nucleotirde triphosphate
Phosphatase
removes phosphate group
Phosporylase
breaks bond by adding inogrnic group
Kinase
transfer a phosphate group from a hige energy molecucle such as ATP
Oxidase
an enzyme that catalyzes oxidation reduction rxn using O2 as E acceptor (removing e-)
Oxygenase
oxidize a subsrate by trasnferring oxygen atoms to it (adding e-)
Properties of Enzymes
Active Site: contains AA side chain that does substrate binding and cataylsis
effcient: faster than uncatalzyed reaction
specific: interactis with one or few substrate
regulated: can be regulated Increased/decreased so rate of product formation responds to cellular needs
location: in specific organelles within the cell
Holoenzyme vs apoenzyme
Holoenzyme is an enzyme with its prosthetic group/cofactor; apoenzyme is the protein part without the nonprotein component.
Cofactor vs Coenyzme
Cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is required for the biological activity of a protein, while coenzyme is a specific type of cofactor, often an organic molecule, that assists enzyme function.