Science Exam Semester 2 - year 9
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
7 types of electromagnetic waves
Radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultra violet
X-rays
gamma rays
Wave Length and frequency of radio waves
Longest wavelengths and low frequency
Microwaves wave length and frequency
long wavelengths and low frequency
The Wavelength and frequency of infrared
Longish wavelength but not that long and frequency is low but not that low(average)
The wavelength of visible light and frequency
Wavelength is average and frequency is average or medium
The wavelength of the ultra violet and frequency
Wavelength getting smaller and frequency getting more often
Wavelength and frequency of X-rays
Wavelength small and frequency often
Wavelength and frequency of gamma rays
Wavelength very small and frequency very often
What is the speed of light?
The speed of light is a constant speed that does not change at all
What is the law of refelction?
Convex mirrors have the mirror on the outside of the curve
concave mirrors have the mirror on the inside of the curve
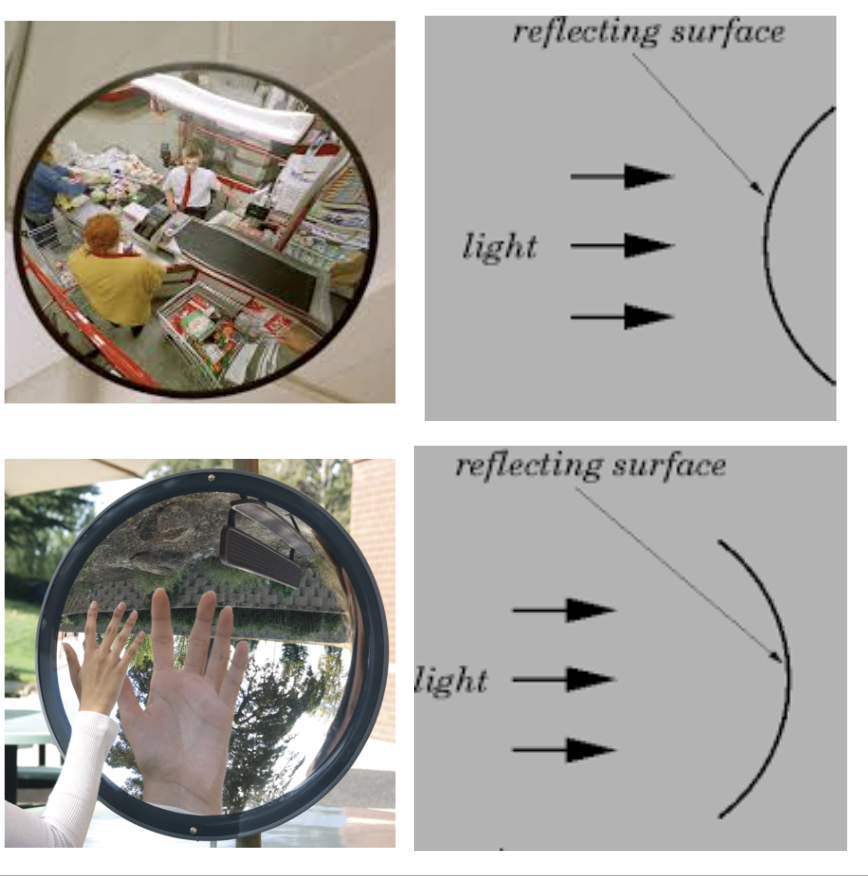

Examples of regular reflection
water surface, plane mirror
Examples of irregular reflection
rough wall, bumpy surface
Order of colours in the visible spectrum
ROYGBIV
What is lateral inversion
the horizontal reversal of an image in a plane mirror, where the left side of the object appears as the right side of the image
How does reflection of light determine the colour of an object?
An object's color is determined by which wavelengths of light it reflects, while it absorbs others
Virtual image
an image between the lense and the focal point will be upright and enlarged. when light doesnt cross-convex mirror, convex lense
Real image
An image formed where light rays converge (join or cross over)
inverted image
an image that appears upside down in comparison to the object
Upright image
An image that appears in the same vertical plane as the object
Concave mirrors common examples
telescopes, makeup mirrors, microscopes
convex mirror common examples
rear view mirrors on cars, road safety mirrors
What is the rule of refraction
When light enters a more dense medium at an angle it is bent towards the normal (because the light slows down).
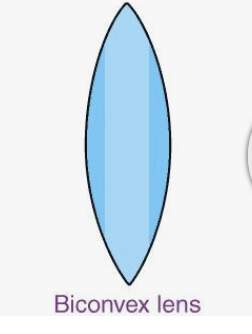
What is a biconvex lens?
a type of lens with two outward-curving convex surfaces that is thicker in the center than at the edges (oval/diamond look)
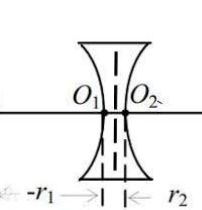
biconcave lens?
a lens with two inward-curving (concave) surfaces that is thinnest at the center and thickest at the edges
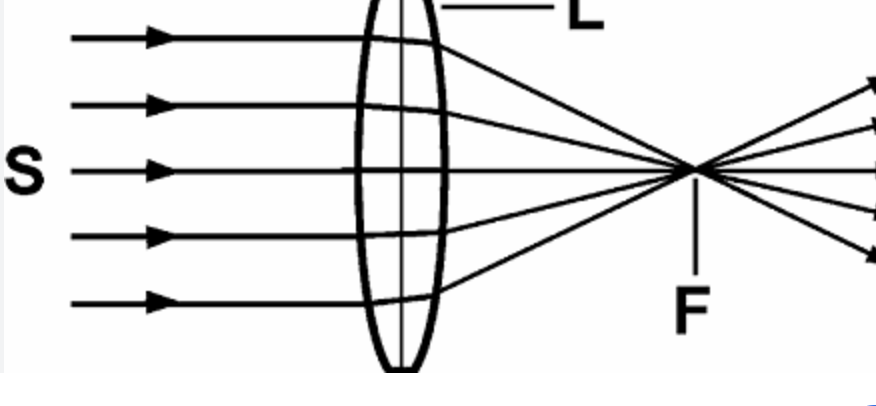
converging lens
a convex lens that is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, designed to bend parallel light rays inward to meet at a focal point
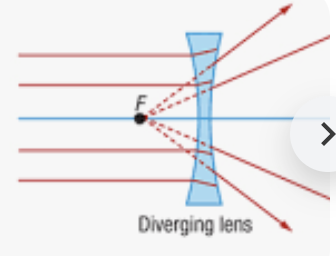
diverging lens
is also known as a concave lens, is an optical lens that causes parallel rays of light to spread out (diverge) as they pass through it
What happens with refraction in a pool of water?
Its causes objects underwater to appear closer or slightly bent because the light bends as it travels
Dispersion of white light
white light seperates into colours (ROYGBIV)
How do we see things?
through a process involving light reflecting off objects and entering our eyes, where the image is processed by the brain to create a visual perception
Why do we see colour/brightness
because light enters our eyes and is detected by photoreceptor cells in the retina, called rods and cones
How does they eye work?
convert light into electrical signals that are interpreted by the brain as images
cornea
Clear window, refracts light, helps to focus the light
pupil
Hole in the iris, which allows light to enter the eye
iris
Coloured, changes size to control the amount of light entering the eye
lens
Refracts light to focus image on the retina. Focal length adjusted by ciliary muscles
retina
light sensitive cells (rods & cones) which change light energy to nerve impulses.
optical nerve
Takes messages from the retina to the brain
sclera
The white, tough outer layer that protects the eye.
liquid humour
Watery at the front, jelly at the back, helps to keep eye’s shape and provide medium for light to travel through.
what role does the eye play in sight
The eye functions as an optical system, first capturing light with the cornea, then controlling the amount of light that enters with the pupil and iris
What parts of the eye will light pass through tostrike the retina?
cornea,pupil,iris
2 vision defects
blurred vision
lazy eye
Describe an ecosystem
a community of living organisms (biotic factors) interacting with each other and their non-living environment (abiotic factors) like water, soil, and weather
Abiotic
non-living parts of the enviroment
Biotic
living organisms
Autotrophs
creates its own food
heterotrophs
feeds off other organisms
xylem
transports water from the roots to the leaves
phloem
transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant
stoma
allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to be released from the leaf
Guard cells
open and close the stomata
Palisade Mesophyll
contain a large amount of chloroplasts Spongy Mesophyll:
Spongy Mesophyll
gaseous exchange
How is water, nutrients, and sugar transported in plants?
The xylem moves it all up to the leaves and the Sugar (glucose) and amino acids are transported to where they are needed, both up and down the plant, through the phloem
Where does photosynthesis occur
chloroplasts
What is required for photosynthesis to occur
sunlight
Where does cellular respiration occur?
begins in the cytoplasm with glycolysis, then moves to the mitochondria
What is required for cellular respiration to occur?
glucose &/ or oxygen
what is areobic respiration?
the process by which cells break down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce a large amount of usable energy in the form of ATP
Areobic respiration worded equation?
Glucose + oxygen ➔ carbon dioxide + water + energy (ATP)
what is anaerobic respiration?
process that generates energy (ATP) in the absence of oxygen
what is the worded equation for anaerobic respiration?
Glucose ➔ lactic acid + energy (ATP)
What is a food chain?
sequence that shows how energy is transferred when one organism eats another
What is a food web?
Its a diagram that shows the sequence that shows how energy is transferred when one organism eats another
How is energy lost and transferd as it moves through trophic levels?
Energy is lost as heat during cellular respiration is also lost
Producers
Producers make there own food
consumers
Eat other organisms to gain energy
dependant variable
The variable that is being measured
independant variable
Thing that is being changed in the experiment
controlled varibables
Things that stay the same in the experiment
Mistakes
personal error
systematic errors
errors the cause the results to be different by the same amount each time
Random errors
Errors that result in completely different results every time
what is chlorophyll
Its a green pigment in the cell
veins
transports nutrients around the plants
cuticle
prevents water loss
whats the geocentric model of the universe?
an ancient astronomical theory that places a stationary Earth at the center of the universe, with the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars revolving around it
Whats the heliocentric model of the universe?
a model of the solar system where the sun is at the center and the Earth and other planets orbit it
how is redshift used to explain the expanding of the universe?
Doppler Effect: When an object moves away from an observer, the light waves it emits are stretched out, increasing their wavelength.
What is a light year?
a unit of astronomical distance, not time, representing the distance light travels in one Earth year
Hubbles evidence of the big bang
Almost all galaxies in the universe are moving away from the Milky Way galaxy
The further away a galaxy is, the more its light is red-shifted, hence the more distant galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way faster (1929)
When did the big bang start?
13.8 billion years ago
What was the universe like before the big bang
mostly hydrogen and helium gas