Dental science vocabularies
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
mixed dentition
the stage at which a child has both primary and permanent teeth
eruption
teeth break through the gums and are visible
exfoliation
to shed, how the deciduous teeth are lost
resorption
a natural process, which the roots of the primary teeth “dissolve away”
succedaneous
the permanent teeth which come afyer or follow; to succeed
enamel
hardest tissue of the body, covers the dentin layer, 95-98% inorganic matter
dentin
located underneath the enamel and cementum, surrounds the pulp caivty, makes up the bulk of the tooth, 70% inorganic matter
dentino-enamel junction (DEJ)
the point where the dentin and enamel join
cementum
covers the root of the tooth, CEJ, hard tissue most similar to bone, 50% organic matter
pulp
living soft connective tissue made up of blood vessels and nerves, fills the pulp chambers and canals
pulp cavity
area in the middle of the tooth that contains the pulp; consists of pulp canals, pulp horn, and pulp chamber
clinical crown
portion of the tooth above the gingiva
clinical root
portion of the tooth below the gingiva
anatomic crown
portion of the tooth covered in enamel
anatomic root
portion of the tooth covered in cementum
apex of the tooth
the very end of the root, comes to a point
apical foramen
opening in the end of the root
periodontium
structures that surround, support, and are attached to the teeth: gingiva, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, cementum
gingiva
the gum tissue, covers the alveolar bone and surrounds the neck of the tooth
gingival sulcus
the open space between the free gingiva and the tooth
free gingival groove
separates the free gingiva from the attached gingiva
junctional epithelium (JE or epithelial attachment)
site where the gingiva attaches to the tooth
alveolar process (bone)
the bony area which surrounds and supports the teeth
alveolus
the bony socket that holds the teeth together, if a tooth is extracted this is the hole that’s left
periodontal ligament
fibrous attachment of the tooth to the bone embedded into the cementum
morphology
the science of form and structure of the human teeth
cingulum
a bulge or prominence of enamel, located on cervical third of anterior teeth only on the lingual surface
mamelon
rounded or conical prominence on incisal surface of incisor teeth only (3 in number)
fossa
depression either rounded or angular of varying size on occlusal surface and lingual surface of anterior teeth
cusp
a pronounced elevation terminating in a conical or rounded surface found on the occlusal surface
cusp of carabelli
fifth non-functional cusp, maxillary first molar only located on lingual surface
lobe
a developmental segment of the tooth, they fuse to form a groove
developmental groove
formed by the union of two lobes usually on the occlusal surface but may extend over
supplemental groove
indistinct linear depression on occlusal surface as a wrinkled appearance
pit
deep indentation when two fissures cross either on lingual or occlusal surface
marginal ridge
elevated crest of enamel forms the mesial and distal margins
furcation
the area between the roots of the multi-rooted tooth
incisors
cingulum, mamelons present on newly erupted teeth, incisal edge
cuspids/canines
longest and most stable teeth in the mouth, one root, canine eminence
bicuspids/premolars
two or more cusps, maxillary first premolar are two rooted and maxillary second-mandibular first-mandibular second is one rooted
molars
largest and strongest teeth in the mouth, three to five cusps, two to three rooted
third molars
lots of variation; short fused roots
linea alba
white line of tissue where teeth bite together (occlude)
frenum
a narrow band of tissue that connects two structures
eruption process
the process through which the forming tooth comes into and tries to maintain occlusion
attrition
the wearing away of the incisal or occlusal surfaces
edentulous
begins when all teeth are lost or nonexistent
occlusion
the relationship between the upper and lower teeth when they meet in normal contact
alignment
arranged in a row
horizontal alignment
the tongue, lip, and cheek muscles balance each other out and alignment of the teeth reaches a state of equilibrium
vertical alignment
teeth are not naturally set in the bone straight up and down
centric occlusion
refers to the position of the teeth; the buccal cusps of the mandibular premolars and molars rest in the deepest part of the occlusal surface of the maxillary premolars and molars
overjet
the horizontal overlap of the anterior teeth
overbite
the vertical overlap of the anterior teeth
openbite
when the jaws close together and the posterior teeth touch and the anterior teeth do not touch; cause by thumb sucking and tongue thrusting
anterior crossbite
maxillary incisors are positioned lingually to mandibular incisors
posterior crossbite
maxillary posterior teeth are positioned lingually to the mandibular posterior teeth
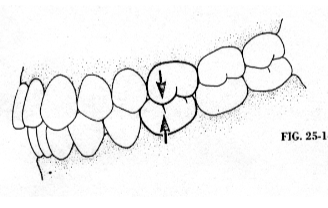
Class I
neutrocclusion; the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary 1st molar is directly in line with the buccal groove of the mandibular 1st molar
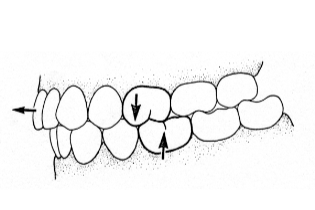
Class II
distocclusion; the maxillary 1st molar is even with or anterior to the mandibular first molar
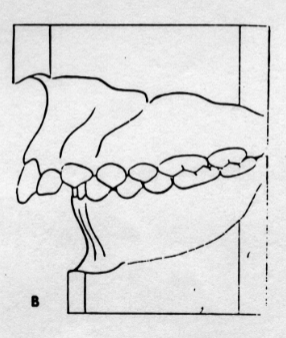
Class II, Division I
the permanent first molars are in class II and the permanent maxillary incisors are normal (slightly protruded)
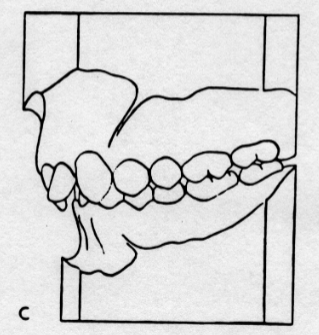
Class II, Division II
the permanent first molars are in class II and the permanent maxillary central incisors are located lingual to the maxillary lateral incisors
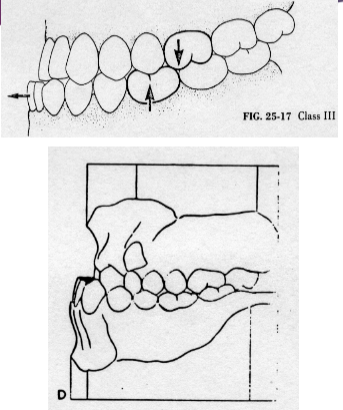
Class III
mesiocclusion, the buccal groove of the mandibular 1st molar is more anterior to the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar