spinal cord and spinal nerves
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
what does this describe:
extends inferiorly from brains medulla through verterbral canal
four parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral
ends at L1 vvertebrae with conus medullaris
spinal nerve roots extend inferiorly = cauda equina
2 widened regions with greater number of neurons
spinal cord
cervical enlargement
neurons innervating upper limbs
lumbar enlargment
neurons innervating lower limbs
sensory input from body to brain
afferent conduction
motor commands from brain to body
efferent conduction
neural integration
minimal: most thinking, porcessing and deciosion making occurs at level of the brain
reflexes
responses that do not involve the brain
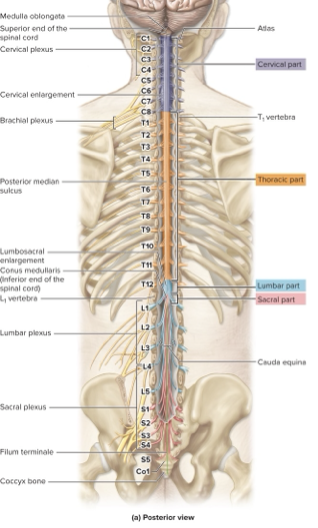
goes cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
know cauda equina and conus medullaris
be able to label
nerve
cablelike bundle of axons
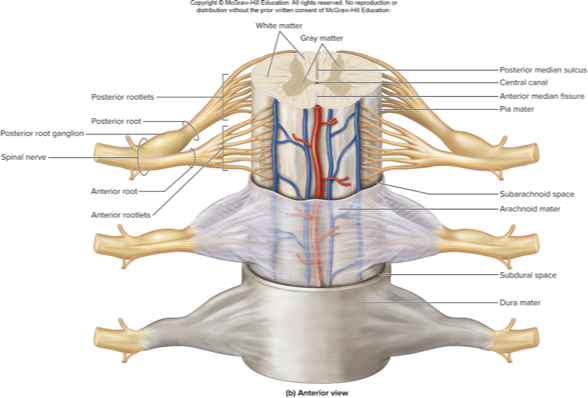
what are the 3 kinds of connective tissue wrappings around nerves and what are they like:
epineurium (around nerve)
perineurium (around fascicle)
endoneurium (around axon)
what does this describe:
rootlets merge to form roots
posterior root contains sensory neurons
posterior root ganglion contains cell bodies of these neurons
each spinal nerve forms where the roots join
sensory and motor neurons in each spinal nerve so they are classified as mixed nerves
spinal nerve gross anatomy
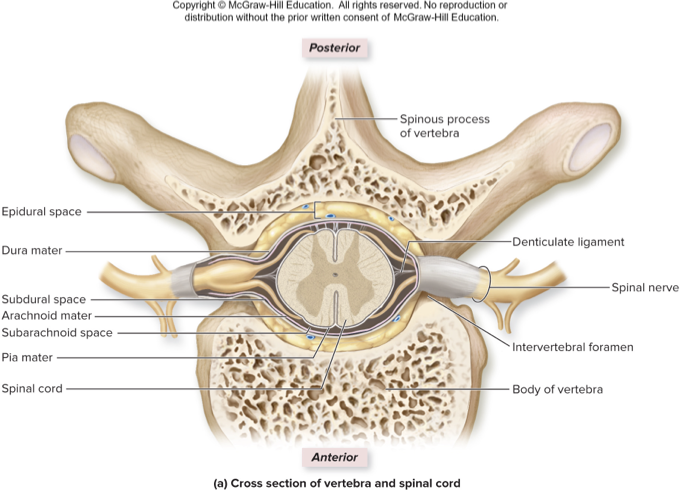
what things are the spinal cord protected by
bone, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid
____ houses the spinal cord
cord passes through the vertebral canal
each spinal nerve exits through an intervertebral foramen
vertebral column
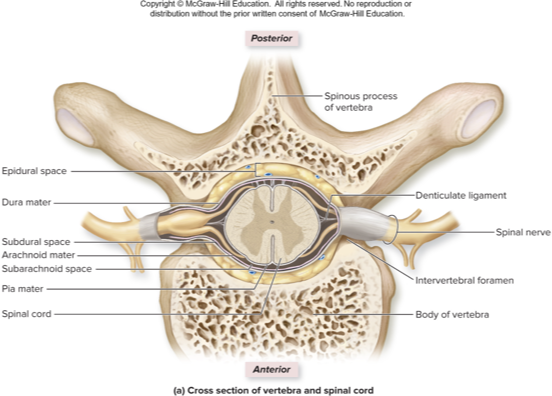
what spinal cord meninge does this describe:
delicate layer adhering to spinal cord
made of elastic and collagen fibers
denticulate ligaments: lateral extensions of pia; help suspend spinal cord
filum terminale: pia anchoring inferior end of spinal cord to coccyx
pia mater
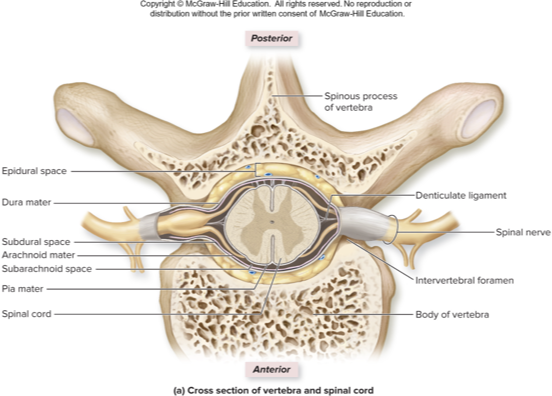
what spinal cord meninge does this describe:
web-like ayer, external to pia
arachnoid trabeculae: fibrous extensions of the membrane
subarachnoid space: area deep to arachnoid through which CSF flows
arachnoid mater
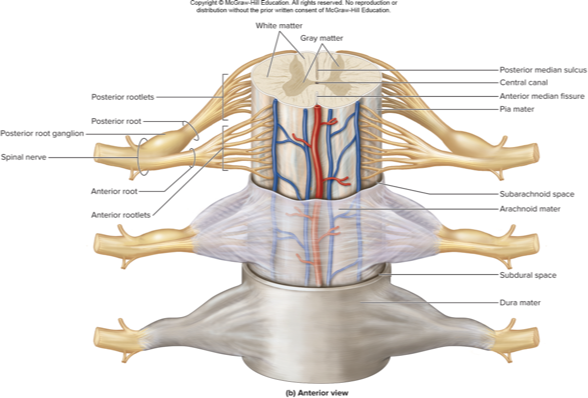
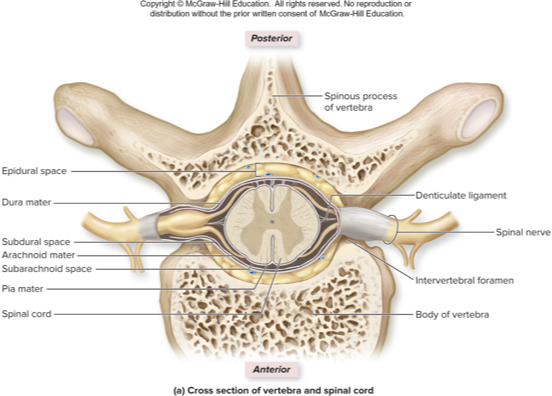
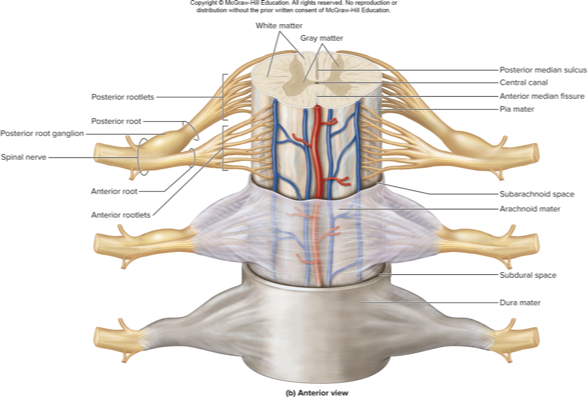
what spinal cord meninge does this describe:
tough, outmost layer
one layer of dense irregular connective tissue that stabilizes spinal cord
subdural space: is between dura and arachnoid
epidural space: is between dura and vertebra; houses adipose, areolar connective tissue, blood vessels
dura mater
lumbar puncture
procedure for obtaining CSF for medical diagnosis
needle passes through skin, back muscles, ligamentum flavum, epidural space, dura mater, arachnoid mater into subarachnoid space
adult spinal cord ends at L1; puncture below;
grey matter
made of neuron’s cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons; also glial cells
masses of grey. matter project from center of spinal cord
posterior horns
house axons of sensory neurons and cell bodies of interneurons
anterior horns
house cell bodies of somatic motor neurons
lateral horns
house cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons; only in T1-L2
gray commissure
horizontal band of grey matter surrounding central canal
contains unmyelinated axons connecting left and right gray matter
nuclei
groups of cell bodies
somatic sensory nuclei
receive signals from skin, muscle, joints
visceral sensory nuclei
receive signals from bloods vessels, viscera
somatic motor nuclei
anterior horns
innervate skeletal muscle
autonomic motor nuclei
lateral horns
innervate smooth muscle, heart, glands
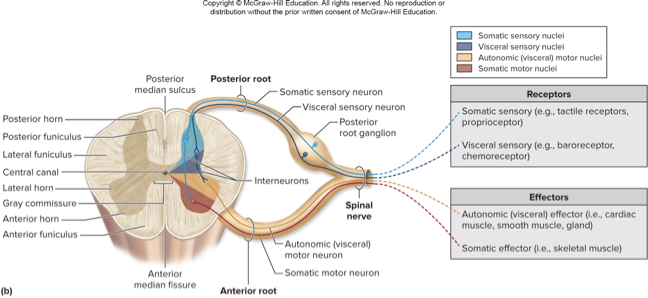
know this pic
white matter
myelinated axons to and from the brain
posterior funiculus
contains sensory tracts
axon bundles called fasciculi
signals about proprioception, touch, pressure, and vibration with a 3 neuron chain
lateral funiculus
contains sensory (ascending) and. motor (descending) tracts
anterior funiculus
contain sensory (ascending) and motor (descending) tracts
axons are in ______ _____ tracts
cell bodies and in _______, _________, and ___________
spinal cord
ganglia, spinal cord gray horns, and brain gray matter
sensory input transmitted through spinal cord originates from general sense receptors
primary (1st order) neuron: has peripheral ending, cell pody. in posteiror root ganglion, and axon leading to secondary neruon
secondary (2nd order) neuron: is an interneuron, receives primary input and extends to tertiary neuron or to cerebellum
tertiary (3rd order): is an interneuron, receives secondary neuron input and extends to somatosensory cortex of parietal lobe or cerebrum
sensory pathways
somatic sensory (somatosensory) receptors
tactile: detect characteristics of an object
proprioceptors: detect stretch in joints, muscles, tendons
carry signals from skin, muscles, and joints
visceral sensory receptors
detect changes like stretch in an organ
carry signals from viscera
what does this describe:
signals about proprioception, touch, and vibration with a 3-neuron chain
primary neuron relays signal from skin to brainstem
secondary neuron relays signal from medulla to thalamus
tertiary neuron relays signal to primary somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus)
posterior funiculus - medial lemniscal pathway
what does this describe:
signals related to crude tough, pressure, pain and temperature with a 3 neuron chain
primary neuron relays signal from skin to spinal cord
secondary neuron relays signal from spinal cord to thalamus
tertiary neuron relays signal from thalamus to cerebral cortex
anterolateral pathway
what does this describe:
signals about proprioception with a 2-neuron chain
primary neuron relays signal from skin to spinal cord
secondary neuron relays signal from spinal cord to cerebellum
spinocerebellar pathway
what does this describe:
control effectors such as skeletal muscles
start in brain and include at least 2 neurons
motor pathways
in motor cortex, cerebral nucleus, or brainstem nucleus; contacts lower motor neuron
upper motor neuron
in cranial nerve nucleus or spinal cord anterior horn; excites muscle
lower motor neuron
pathway between brain and skeletal muscles
direct (pyramidal) pathway
what does this describe:
upper motor neurons originate in brainstem nuclei and take complicated route to spinal cord
indirect pathway
what kind of indirect motor pathway does this describe:
regulates precise movement and tone in flexor limb muscles
consists of rubrocpinal tracts originating in midbrain
lateral pathway
what kind of indirect motor pathway does this describe:
regulates muscle tone and movements of head, neck, proximal limb, trunk
medial pathway
what does this describe:
from reticular formation
help control reflexes related to posture and balance
reticulospinal tracts
what does this describe:
from superior and inferior colliculi
regulate reflexive orienting responses to visual and auditory stimuli
tectospinal tracts
what does this describe:
from vestibular nuclei of brainstem
help maintain balance during sitting, standing, walking
vestibulospinal tracts
how can you treat spinal cord injuries
prompt use of steroid after injury may preserve muscle function
early antibiotics have reduced number of deaths due to pulmonary and urinary infections
neural stem cells may be used in the future to regenerate CNS axons
dermatomes
segment of skin supplied by single spinal nerve
some overlap in innervated regions
can help localize damage to one or more spinal nerves
involved in referred visceral pain
shingles
reactivation of chickenpox infection
virus remaining latent in posterior root ganglia
reactivated, travels through sensory axons to dermatome
rash and blisters along the dermatome
burning and tingling pain
antiviral medication to reduce sensitivity
vaccine to prevent or reduce disease sensitivity
what does this describe:
network of interweaving anterior rami of spinal nerves
four main plexuses occur bilaterally: cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral
individual rami branch repeatedly (damage to one nerve or spinal segment does not deprive a muscle or skin region of all innervation)
nerve plexuses
what does this describe:
anterior rami of C1-C4
branches innervate: anterior neck muscles, skin of neck, portions of head and shoulders
from rami of C3-C5 it gives rise to phrenic nerve
cervical plexuses
what does this describe:
from anterior rami of C5-T1
trunks divide into anterior and posterior divisions
axons innervate anterior and posterior parts of upper limbs
brachial plexuses
brachial plexus injuries
minor injuries treated with rest
severe injuries may require nerve grafts or transfers
axillary; compressed axilla or damaged, difficulty abducting arm
radial: humeral shaft fractures or injuries to elbow, paralysis of extensor muscles in forearm, numbness along posterior arm
posterior cord:may be injured by improper use of crutches
what does this describe:
anterior rami of L4-S4
sciatic nerve: largest and longest nerve in the body, formed from portions of anterior and posterior sacral plexus, composed of tibial division and common fibular division
sacral plexuses
tibial nerve in sacral plexus
from anterior division of sciatic
innervates hamstrings and hamstring part of adductor magnus muscle
splits into lateral and medial parts
receives sensory signals from skin on sole of foot
common fibular nerve
from posterior division of sciatic
innervates short head of biceps femoris muscle
splits into deep fibular nerve and superficial fibular nerve
sacral plexus injuries
superior or inferior gluteal nerves
can be injured by poorly placed gluteal injection
sciatica: injury to sciatic nerve; extreme pain down posterior thigh and leg, may be caused by herniated intervertebral disc
what does this describe:
rapid, preprogrammed, involuntary responses of muscles or glands to a stimulus
a stimulus is required to initiate
response is rapid: involves chain of few neurons
response is preprogrammed: always the same
the response is involuntary: no intent or awareness of the reflex before it happens
survival mechanism
reflexes
reflex arc
neural pathway responsible for generating the response
what is the pathway of reflex arc
somatic receptors: in skin, muscles or tendons
afferent nerve fibers: carry information from receptors to posterior horn of spinal cord or the brainstem
integrating center: a point of synaptic contact between neurons in gray matter; determines whether efferent neurons issue signal to muscles
efferent nerve fibers: carry motor impulses to skeletal muscle
effectors: the somatic effectors carry out the response
what are ways reflexes can be classified
spinal or cranial
somatic or visceral: is it skeletal muscle or cardiac, smooth, gland
monosynaptic or polysynaptic: direct or interneurons
ipsilateral or contralateral
innate or acquired
4 common spinal reflexes
stretch, golgi tendon, withdrawal, crossed-extensor
stretch and golgi tendon reflexes rely or ______
proprioceptors
a _____ is a proprioceptor that detects stretch in a muscle
muscle spindle
fibers not within spindle are _________ innervated by large alpha motor neurons
extrafusal muscle fibers
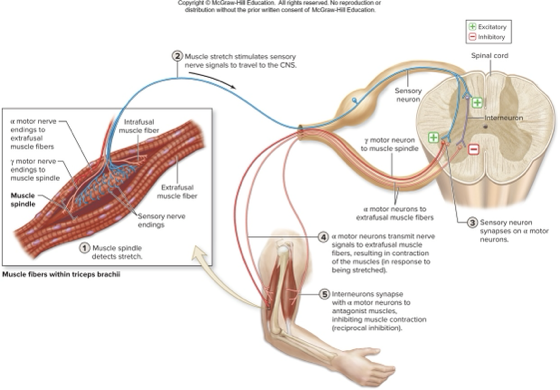
what does this describe:
reflexive contraction of a muscle after it is stretched
stretch is detected by muscle spindle proprioceptor
can be spinal, somatic, monosynaptic, ipsilateral, innate
when stretched, spindles sensory axon fires impulses to spinal cord, sensory axon excites alpha motor neurons causing contraction, sensory axon excites interneurons of antagonist muscle
stretch reflex
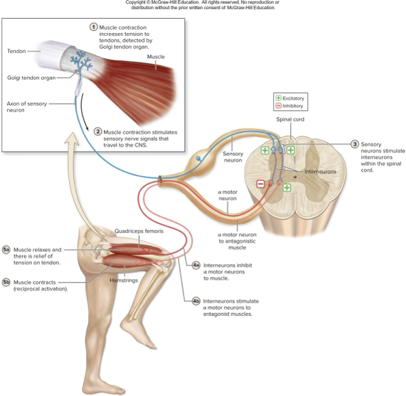
what does this describe:
prevents muscle from contracting excessively
golgi tendon organs detect excessive tension
some excited interneurons inhibit motor neurons of same muscle
some excited interneurons excite motor neurons of antagonist muscle (reciprocal activation)
golgi tendon reflex
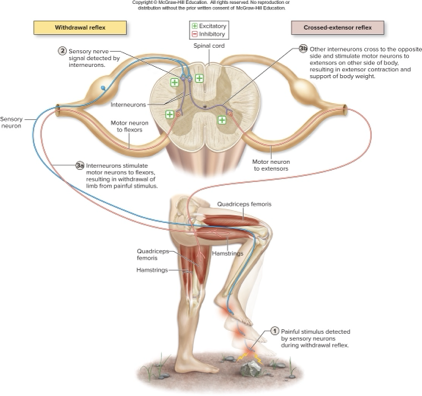
what does this describe:
pulls body part away from painful stimulus
stimulus excites nociceptor sensory neuron that transmits signal to spinal cord and excites interneurons
interneurons excite motor neurons of flexors so flexor muscles contract and limb is withdrawn
withdrawal reflex
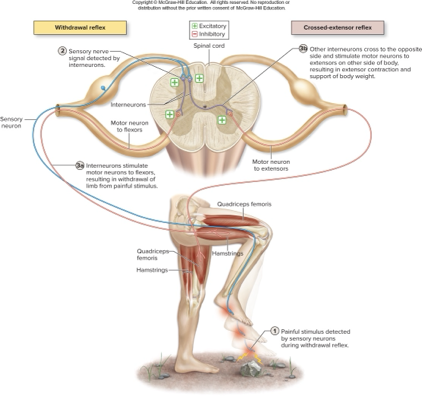
what does this describe:
occurs in conjunction iwth withdrawal reflex
some interneurons excited by nociceptor senesory neuron cross midline and excite extensor motor neurons on other side
allows opposite side limb to support body weight while hurt limb withdrawls
reflexes in clinical setting
useful for diagnoses
can test function of specific muscles
hypoactive reflex: diminished or absent; damage to spinal cord or muscle disease or damage to nueromuscular junction
hyperactive reflex: abnormally strong repsonse; may indicate damage to brain or spinal cord
clonus: rhythmic oscillating movements with reflex testing