Stats Year 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Hypothesis testing
The use of statistical techniques to test a particular claim (the hypothesis). A sample from the population is used to see if the result from the sample is consistent with the claim.
Process of a hypothesis test - Set up/ state the hypotheses
the null hypothesis (H0) - where p takes a particular value/ the value you would expect
alternative hypothesis (H1) - the probability you’re testing (one-tailed or two-tailed?)
Process of a hypothesis test - Setting the significance level
This is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis if in fact it is true
Process of a hypothesis test - Carrying out the test (P-values)
Use a sample to obtain a test statistic (the value of X in X ∼ B(n,p))
probability of obtaining a value at least as extreme as the test statistic, if the null hypothesis is true
For X has a value, use X ∼ B(n,p) to calculate…
P(X > x) if H1: p > x
P(X < x) if H1: p < x
2 x P(X > x) if H1: p ≠ x
Whether the value of X given is in the critical region will determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Process of a hypothesis test - Carrying out the test (Critical regions)
Use a sample to obtain a test statistic (the value of X in X ∼ B(n,p))
set of values for the test statistic X for which you would reject the null hypothesis. The critical value is the value for X for which you change from not rejecting the null hypothesis to rejecting it.
For H1: p > x, use X ∼ B(n,p) to find the lowest value for r for which P(X > r) is less than the significance level.
For H1: p < x, use X ∼ B(n,p) to find the highest value for r for which P(X < r) is less than the significance level.
For H1: p ≠ x, the critical region has 2 parts to it, Split the significance level into 2, one for the lower tail and one for the upper tail. Then use X ∼ B(n,p) to find the lowest value for r for which P(X > r) is less than half the significance level and to find the highest value for r for which P(X < r) is less than half the significance level.
Whether the value of X given is in the critical region will determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Process of a hypothesis test - The conclusion
Reject H0 - if p-value is less than sig level/ test statistic lies in critical region → there is sufficient evidence to suggest that H1 is true
Not reject H0 - if p-value is more than sig level/ test statistic doesn’t lie in critical region → there is not sufficient evidence to suggest that H1 is true
Process of a hypothesis test order - 1
Set up/ state the hypotheses
Process of a hypothesis test order - 2
Setting the significance level
Process of a hypothesis test order - 3
Carrying out the test
Process of a hypothesis test order - 4
The conclusion
One-tailed test
When you think a result is more likely H1: p > x
When you think a result is less likely H1: p < x
Two-tailed test
When you think there’s a bias in general H1: p ≠ x
Uses of binomial distribution
to model situations in which: you are carrying out trials on random samples of size n; there are 2 possible outcomes, success (where probability p is fixed) and failure; trails are independent of each other
Binomial distribution notation
X ~ B(n,p) where X is the number of successes, n is number of trials, p is probability
P(X = r) = nCr pr (1-p)n-r
Cumulative binomial probability
the probability of a range of results, written as P(X < 5)
Mean or expectation of a binomial distribution calculation
np
Experiment/ trial
Any situation involving uncertrainty
Outcome
the result of a trial or experiment
Sample space
The set of all possible outcomes of a trial or experiment
event
can be used to describe one or more possible outcomes from a trial or experiment
Mutually exclusive events
2 events that can never occur together. This means P(A U B) P(A) + P(B)
Independents events
When the occurrences of on of 2 events has no effect on the other occurring. This means P(A U B) P(A) x P(B)
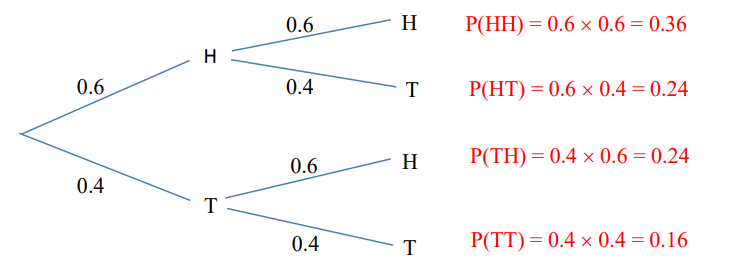
Tree diagram
Shows the outcomes of events and the probability of the outcome happening. Useful when dealing with events that have just 2 or 3 possible outcomes.
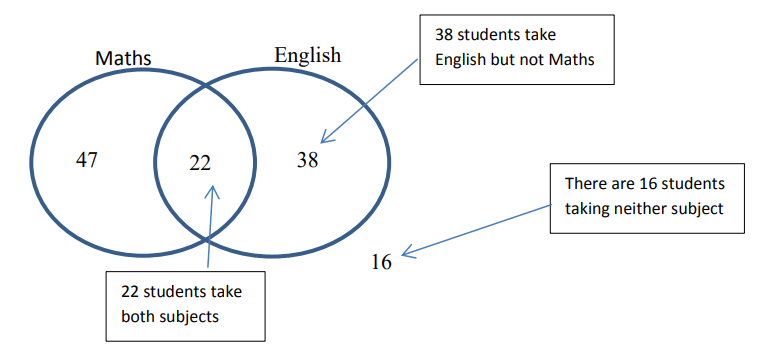
Venn diagram
Shows the outcomes of events and the probability of the outcome happening in combination with other events. Useful when dealing with events that are not mutually exclusive.
Simple random sampling
The items in the sample are chosen by a random process such as drawing from a box. Every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
Opportunity sampling
Choosing individuals for a sample as opportunity arises, such as interviewing passers-by
Systematic sampling
Involves selecting individuals from a population by a systematic method, such as selecting every 10th individual on a list of the population
Stratified sampling
Used when the population can be divided into subgroups (strata) using criteria such as age or gender, and ensures that all strata are represented in the sample. Sometimes there is a requirement that the numbers sampled from each stratum is proportional to the sizes of the strata (this is called proportional stratified sampling). Otherwise, weighting is used
Quota sampling
Used when the population can be divided into strata. A certain number of items from each stratum are required
Cluster sampling
Used when the population consists of subgroups which are each reasonably representative of the population (e.g. year 6 classes in several schools). A sample is taken from just a few of these subgroups
Self-selected sampling
Used when individuals choose to be part of a sample, e.g. a survey posted on the internet
Mean x̄
A measure of central tendency found by adding up the data items and dividing by the number of data items
Median
A measure of central tendency that is the midpoint of the data when they are placed in numerical order
Mode
A measure of central tendency that is the most frequently occurring data value
Range
A measure of variation that is the difference between the highest and lowest values from the data
Interquartile range
A measure of variation that is the difference between the upper quartile (3/4 of data) and lower quartile (1/4 of data).
Variance
A measure of variation which is the measure of the spread of the sample
Variance equation
= (Σxi2 - nx̄2) / (n-1)
Standard deviation
A measure of variation is the square root of the variance
Bivariate data
Data which involves 2 variable e.g. height and weight
Positive correlation
Positive gradient of the line best of fit of bivariate data
Negative correlation
Negative gradient of the line best of fit of bivariate data
Outliers
An unusually high or low value in a data set. They are either any data value which is more than 2 standard deviations away from the mean or any data value which is more 1.5 times the interquartile range above the upper quartile or below the lower quartile.
Cleaning data
dealing with missing data, errors and outliers. How you deal with these issues depends on the situation and what you are using the data for