Mitosis- study Guide 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Last updated 4:50 PM on 6/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
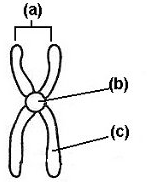
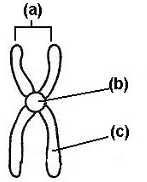
structure b is the
centromere
2
New cards
based on the image, which specific phase is this cell in
prophase
3
New cards
stem cells are
undifferentiated cells that can divide and specialize to form any type of cell
4
New cards
which of the following shows the correct sequence of the cell cycle
G1, S, G2, mitosis, cytokinesis
5
New cards
which type of fibers extend from centrioles in a star-like burst and anchor the spindle apparatus to the cell membrane
aster fibers
6
New cards
in a human cell, how many sister chromatids are present during metaphase
92
7
New cards
what is the number of replicated chromosomes that would be found in a human somatic cell at metaphase
46
8
New cards
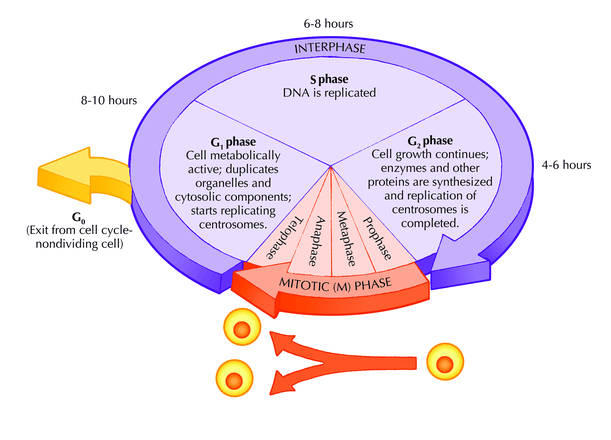
this picture shows which process
cell cycle
9
New cards
chromatin is formed from.. (2)
DNA wrapped around histone proteins, folded nucleosomes
10
New cards
Which of the following must be true about a cell before it enters mitosis (4)
have enough nutrients, be large enough to divide, proteins and organelles required,correctly copied DNA
11
New cards
the longest phase of the cell cycle is
interphase
12
New cards
uncontrollable growth and division of mutated or abnormal cells is known as
cancer
13
New cards
in which stage of the cell cycle is the cell making final preparations for cell division
G2
14
New cards
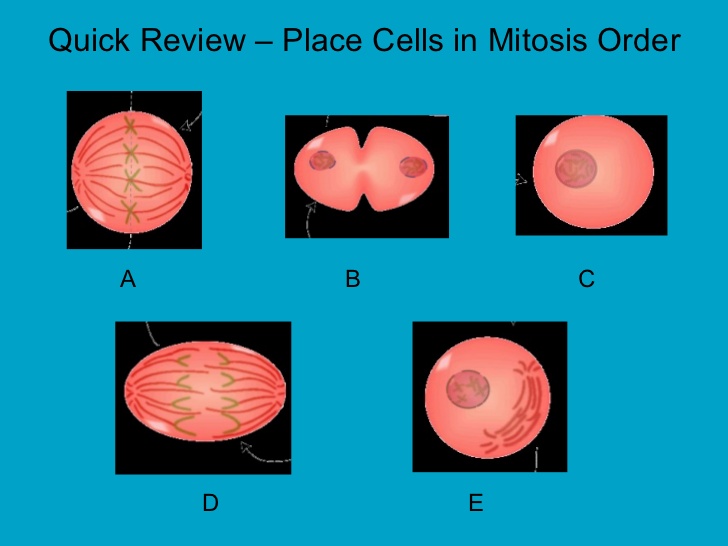
place these cells in order of mitosis
C, E, A, D, B
15
New cards
in the G1 sage of the cell cycle, the cell (3)
grows, carries on normal activities (protein synthesis), makes more organelles
16
New cards
another name for a sex cell is a
gamete
17
New cards
during which checkpoint does the cell check to make sure the chromosomes are properly aligned at the equator of the cell
spindle checkpoint
18
New cards
any substance that is known to increase the risk of developing cancer is called a
carciongen
19
New cards
what is differentiation
a process by which a cell becomes specialized
20
New cards
a benign tumor differs from a malignant tumor in that a benign tumor..
does not metasize
21
New cards
when is DNA replicated in the cell cycle
s phase
22
New cards
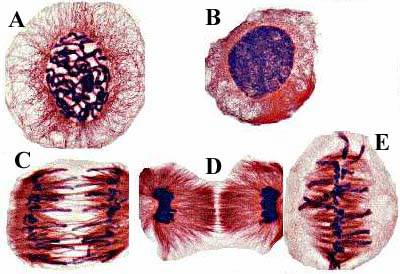
what phase is represented by letter A
prophase
23
New cards
fruit fly body cells have 8 chromosomes. After mitosis, you would expect a resulting fruit fly daughter to have..
8 chromosomes
24
New cards
when an animal cell goes through cytokinesis, ____
the contractile ring pinches off the 2 cells
25
New cards
which of the following is not a part of interphase
mitosis, cytokinesis
26
New cards
neuron cells, like the one pictured, rarely go through cell division. Therefore, we consider them to be in the ____ phase
G0
27
New cards
which of the following relate to G0, (3)
The cell can repair DNA damage, non-proliferative cells stay here, cell can avoid apoptosis
28
New cards
how many daughter cells are created through mitosis
2 genetically identical somatic cells
29
New cards
_____ is a critical point where stop and go signals can regulate the cycle
checkpoint
30
New cards
cytokinesis divides the,
cytoplasm
31
New cards
structure C is pointing to ONE __ ___
sister chromatid
32
New cards
True or false: cancer cells do not pass cell cycle chekpoints, ans so they undergo apoptosis and die
false
33
New cards
when a plant cell goes through cell division _____
cell plate develops, seperates the two nuclei
34
New cards
when in the cell cycle do chromosomes condense and appear
prophase
35
New cards
when might apoptosis be initiated
when DNA damage cannot be repaired
36
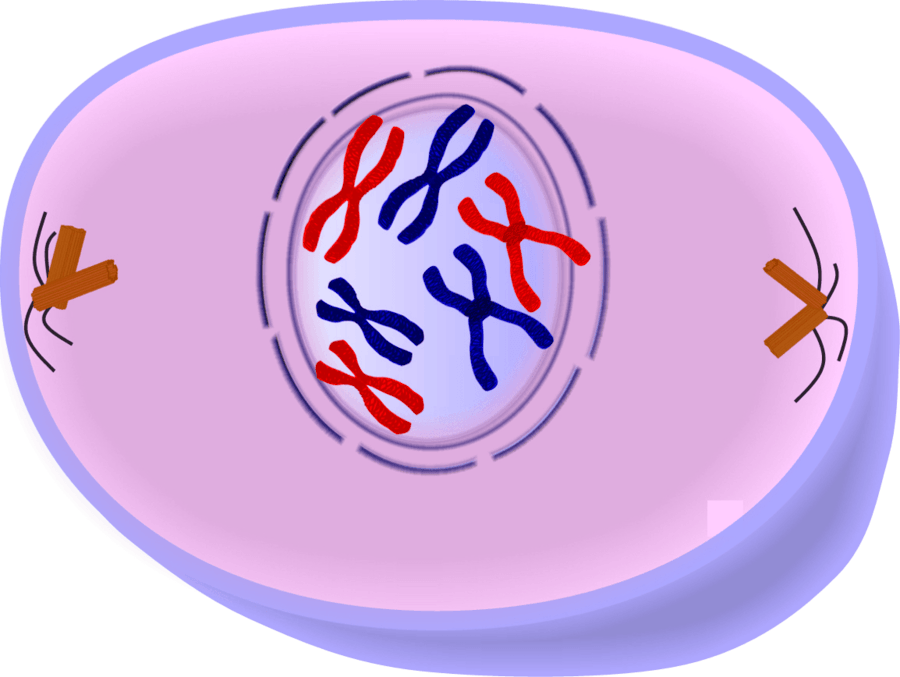
New cards
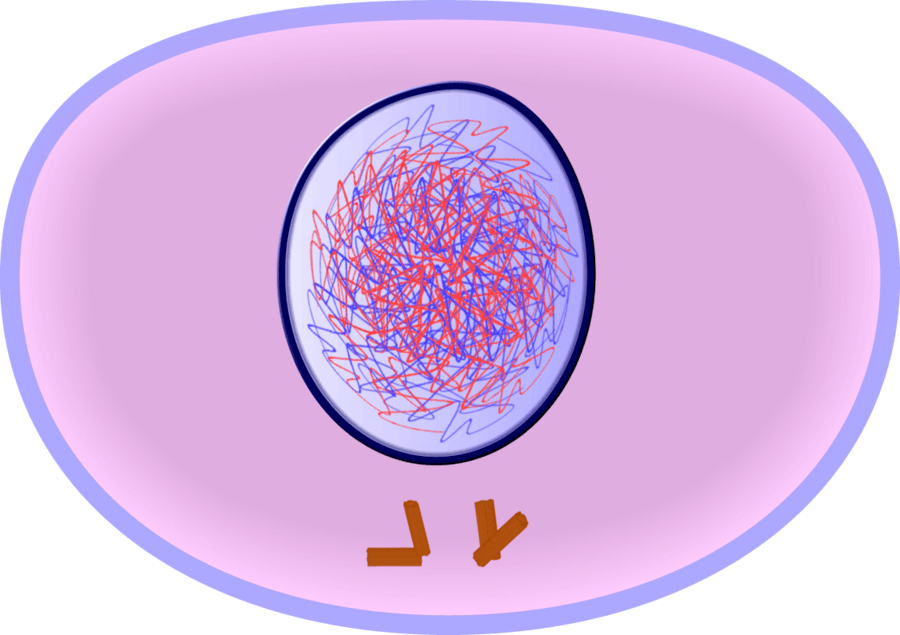
based on the image, which phase of the cell cycle is this cell in
interphase
37
New cards
the individual halves of replicated chromosomes are called ______
sister chromatids
38
New cards
the stages of mitosis in order
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
39
New cards
When cancer spreads to other tissues of the body, it is called
Metasis
40
New cards
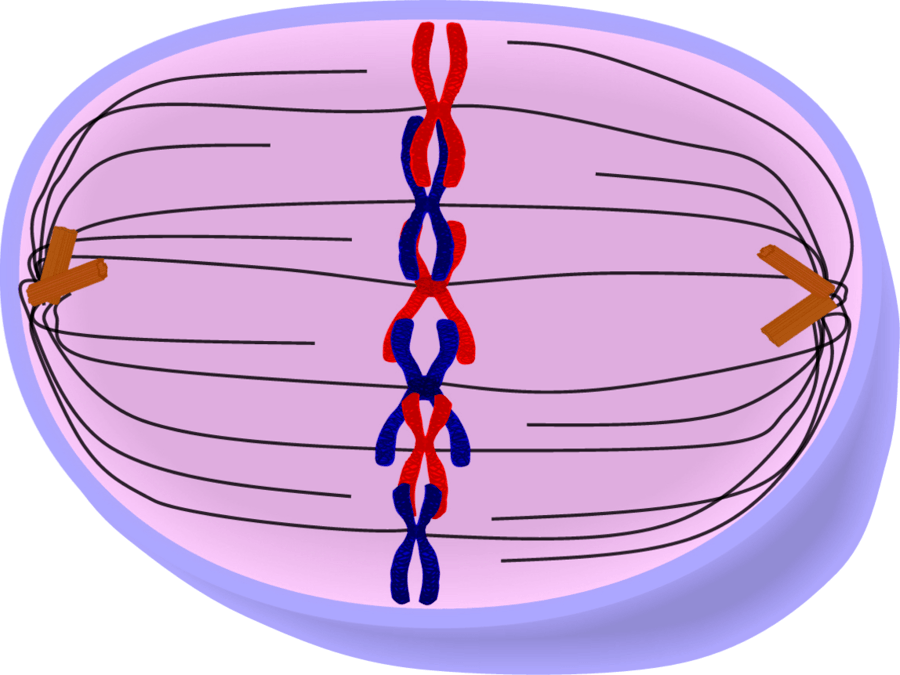
What phase is this cell in?
Metaphase
41
New cards
This is the phase in mitosis in which sister chromatids (now daughter chromosomes) move away and are pulled apart by spindle fibers to opposite sides of the cell
Anaphase
42
New cards
What is the difference between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells
Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into more cell types than adult stem cells
43
New cards
which type of fibers attach to the centromere region of the chromsomes
Kinetochore microtubles
44
New cards
the organelle that helps in cell division and produces spindle fibers
Centrosomes
45
New cards
the organelle that helps in cell division and produces spindle fibers
centrosome
46
New cards
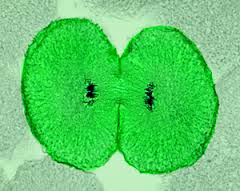
name the phase
telophase
47
New cards
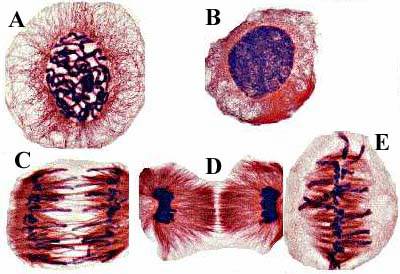
what phase is represented by letter C
Anaphase
48
New cards
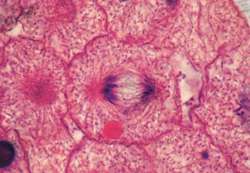
name the phase
Anaphase
49
New cards
in a human cell, how many daughter chromosomes are present during prophase
0
50
New cards
which stage of the cell cycle does the cell grow to mature size
G1
51
New cards
which type of fibers do not connect to a chromosome
Free microtubles
52
New cards
in a human cell, how many replicated chromosomes are present by the end of telophase
92
53
New cards
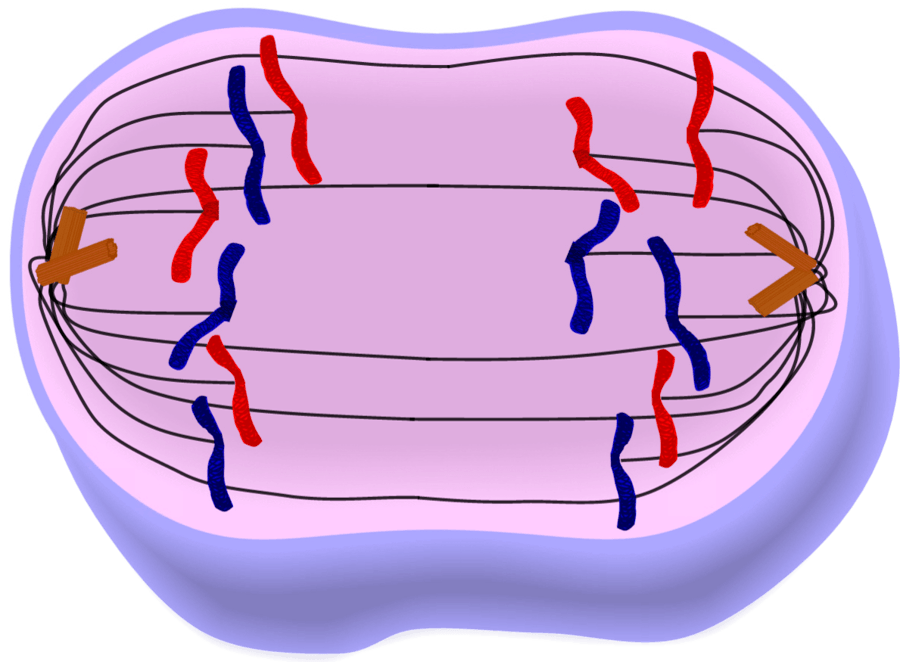
based on this image, which specific phase is this cell in?
anaphase
54
New cards
in a human cell, how many replicated chromosomes are present in interphase
92
55
New cards
This is the cell cycle checkpoint that makes sure DNA has been replicated correctly during S phase
G2/M checkpoint
56
New cards
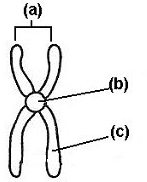
structure A refers to the __ __
Sister chromatin
57
New cards
which phase is a cell in when it is not actively dividing
Interphase
58
New cards
What are the 3 reasons for mitosis
repair damaged tissue, replace dead cells, grow and develop
59
New cards
Difference between somatic cells and gametes
Somatic Is body, gametes are sex cells
60
New cards
What happen during G1
Cell grows and makes more organelles, may go to g0
61
New cards
What happens during S phase
DNA replication occurs
62
New cards
what happens during G2
Produce proteins and any additional organelles for mitosis
63
New cards
In the S phase, DNA is in what form
chromatin
64
New cards
Centrosome ______ in S phase
duplicate
65
New cards
Cell is committed to divide because it cannot _______
un-synthesize DNA
66
New cards
Substances that are classified as carcinogens
smoking, sunlight, processed meats, alcohol
67
New cards
How does cancer have effects like hair loss, nausea, and vomiting
cancer has these side effects because the different types of treatments target rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles and stomach lining cells.
68
New cards
What is the new way to treat cancer
immunotherapy
69
New cards
What are the 3 most common treatments for cancer
chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery
70
New cards
Explain the reason that hereditary factors do not guarantee the development of cancer
the first mutation is inherited and a lady present at birth, but if the mutation spreads, there can be cancer.
71
New cards
The mutations in _____ are not passed on through cancer
Somatic cells
72
New cards
Label a spindle apparatus
label Centrosome, centriole, aster fibers, kinetochore, free spindle fibers, replicated chromosome
73
New cards
What is the role of the spindle apparatus in mitosis
pulls the sister chromatids to each side of the cell to create 2 new cells
74
New cards
The g1/S checkpoint
Check cell size, ATP and resource levels, DNA status
75
New cards
failing the G1/S checkpoint
stop signal, may enter g0
76
New cards
Passing G1/S
Go signal, DNA replication can begin
77
New cards
G2/M checkpoint
checks DNA replication
78
New cards
failing the G2/M checkpoint
DNA is not Ok, finish replication or repair DNA,
79
New cards
Cells can’t repair ____
chromosomes
80
New cards
DNA must be repaired before _____
mitosis
81
New cards
Passing the g2/M checkpoint
DNA is ok, cell is large enough, procedures to mitosis
82
New cards
When does the spindle checkpoint occur
during metaphase
83
New cards
Spindle checkpoint
Checks for proper alignment of chromosomes (metaphase)
84
New cards
Bad spindle checkpoint
mitosis stops until alignment is corrected
85
New cards
good spindle outcome
Proceeds to anaphase
86
New cards
Difference in telophase in plant and animal cells
in telophase, cleavage furrow in animal cells; in plant cells, a cell plate forms
87
New cards
Difference of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells
animal cells have contractile ring, in plant cells; vesicles from the Golgi body accumulate and fuse at the equator, cellulose molecules bond together, cell plate becomes cell wall
88
New cards
A chromosome has _____
one chromatid
89
New cards
What are the two reasons cells divide (3)
Reproduce, grow and develop, to heal
90
New cards
Maintaining the proper __ __requires__ __
SA:V ratio; division
91
New cards
Cells spend _____ of their time in interphase
Roughly 90%
92
New cards
What is the longest phase of interphase
G1
93
New cards
Mitosis is not
cell division
94
New cards
Mitosis is the division of the ____
nucleus
95
New cards
DNA exists as _____ most of the time
Chromatin
96
New cards
3 steps of mitosis, of chromatin condensing into chromosomes
DNA wraps around histones to form nucleosomes, nucleosomes fold and condense to form chromatin, crhomatin condenses= chromosomes
97
New cards
chromosomes only exist during
mitosis
98
New cards
when counting chromosomes, they are counted by the
Centromere
99
New cards
A chromosome has one _______
chromatid
100
New cards
a replicated chromosome has _______ chromatids called sister chromatids