OCEANS AND ATMOSPHERES TEST #3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
4 major rock types in a typical transgression sequence?
Limestone, Shale, sandstone, and coal
Describe the depositional environments for each rock type?
Coal - wetlands
sandstone - beaches
Shale - shallow marine
Limestone - deep water
Sketch a transgression sequence?
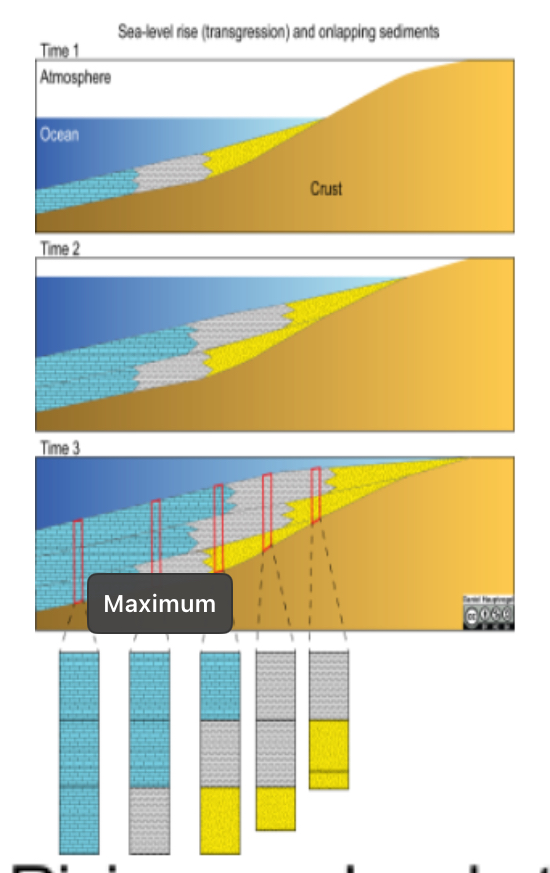
Name two reasonable causes of a transgression sequence?
Rising sea levels - melting glaciers
Thermal expansion
What was initially used as the basis to divide geologic time into periods?
Study of rock layers
What marked the boundary between rock layers?
Oldest at bottom, youngest at top, and also fossils
How did continental crust form?
Volcanic activity at subduction zones where oceanic plates slides beneath another plate.
When in geologic time did life first appear?
Archean - 3.5 BY
What is the earliest fossil evidence for life?
Stromatolites
What is unconformity?
The geological break in the rock record, representing a period of missing rock layers due to erosion or a pause in sedimentation
When did free oxygen first become a significant component of the atmosphere?
2.4 to 2.2 BY
What fossil evidence documents the rise of oxygen in the atmosphere and describe the process in which it is formed?
Banded Iron Formations are formed through Fe dissolved in the ocean reacted its O2 which then form worldwide iron oxide deposits
What sedimentary rock evidence shows the rise of oxygen in the atmosphere and describe the process at which it formed?
Red beds come from sedimentary rocks like sandstone through a process that groundwater alters iron bearing minerals in the sediment after it has been buried.
What is the importance of ozone in the atmosphere?
Creates opportunity for land-dwelling biota by screening UVA, UVB, and UVC wavelengths.
Describe the two ideas of why the dinosaurs went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous?
Catastrophic impact by a 10 km comet or meteorite and a volcanic eruption
are the two competing ideas of extinction of dinosaurs mutually exclusive?
No many believe that it was an effect of both things happening together.
Describe how the pole-equator-pole temperature gradient was different between the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras?
Much shallower in the Mesozoic. In the Mesozoic era the difference between tropical and polar temperatures was significantly less than today with warm conditions in high latitudes. The Cenozoic is more like how it is today with a much steeper gradient.
Compare polar temperatures between these two Eras and give a hypothesis about the cause if this difference in temperature?
Polar temperatures were significantly warmer in the Mesozoic than the Cenozoic. Higher CO2 in the Mesozoic Era, which eventually warmed the polar temperature.
The Anthropocene is an interesting concept; when do you think people “significantly” impacted the environment and by what means?
Industrial Revolution where burning fossil fuels changed the balance of the carbon cycle.
How would you define “significantly”?
Defined by the scale, magnitude, and permanence of human-induced changes to the Earths system that will have an impact on the rock layers.
Do you agree with using spikes in cesium-137, as an indicatorr of nuclear weapons testing, to define the boundary into the Anthropocene and explai
I agree with using it because it provides a clear global marker of nuclear testing but humans significant impact on earth occured earlier.
What it the accepted cause of the Eocene thermal maximum?
The massive and rapid release of large amounts of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere and oceans.
What are the three variations in the earths orbit, interchangeably referred to as orbital or Milankovitch forcing, impact climate over the ice age timescales?
Eccentricity, Obliquity, and Orbital Precession
Which if any of these impacts the total amount of radiation reaching the earth and why?
Eccentricity because it changes the distance the earth is from the sun.
Which of these impacts polar climate the most and why?
Obliquity because the change in axial tilt directly affect the seasons in the high latitudes.
Which affects seasonality the most and why?
Precession because it causes the seasons to shift over a long period of time altering the length and intensity of the seasons.
How does the precession orbital cycle impact monsoon systems in Africa?
The stronger heating of the land compared to the ocean creates a low-pressure system that draws in moist air from the Atlantic, driving the Summer monsoon.
How does the periodicity ice ages change of the last two million years?
41,000 cycle to a 100,000 year cycle
What are the major factors driving changes in glacial periods?
Milankovitch cycles
What are their periodicities?
Eccentric - 100,000 years
Axial Tilt - 41,000 years
Precession - 21,000 years
Little ice age
1429-1820, caused by low solar activity and high volcanic activity
Increased explosive volcanic effects
Short term cooling from sulfur dioxide in stratosphere reflecing sunlight, long term warming from the release of co2
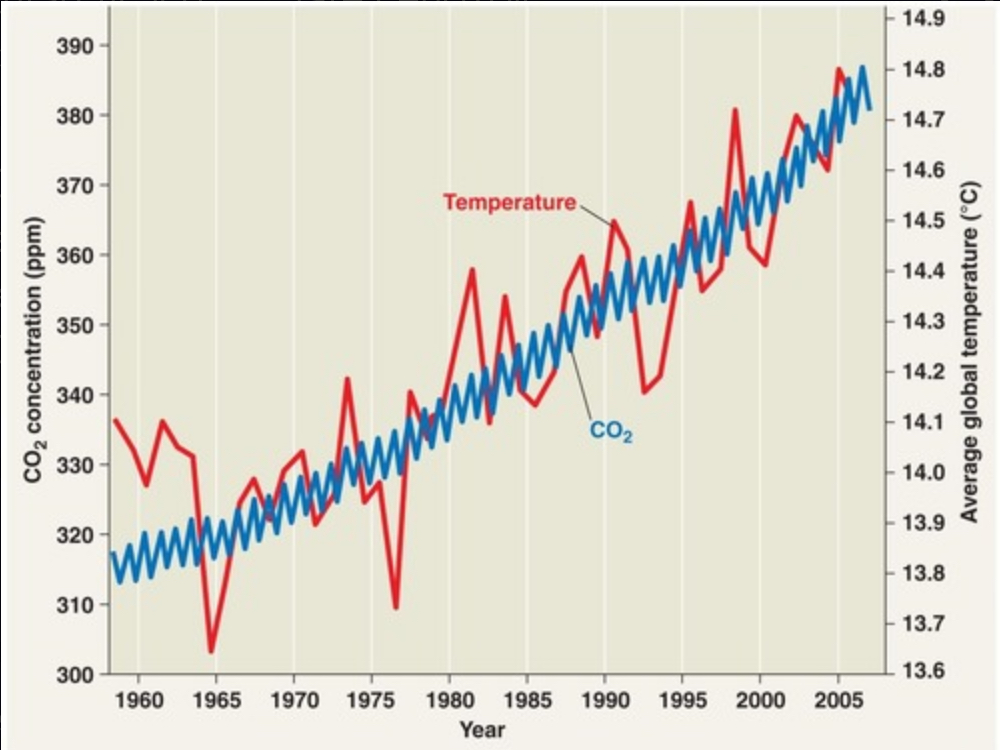
CO2, sea level, surface temp Cenozoic eon