Starred Slides- clinical science exam 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
MHC I
cytotoxic T cells (CD8+)
MHC II
T helper cells (CD4+)
B cells
recognize free floating antigen
T cells
require antigen presentation
CD4: Helper T cells
Help B cells augment production of antibodies• Activate macrophages• Help CD8's to proliferate• Help NK cells to kill infected cells• Neutrophil recruitment
CD8: Cytotoxic T cells
induce apoptosis
What is the ratio of CD4 & CD8 cells?
2:1, shift indicates autoimmune or inflammation
CD25: T regulatory cells
Prevent inappropriate response to "self" (inhibit immune response)• Generate inhibitory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β)
What factors effect the immune system?
Nutrition/malnutrition, trauma, burns, medications, stress 7 implanted prostheses
Epitope
antigen site that binds with T cell receptor
Adaptive immunity
acquired immunity, specificity & memory
HIV pathogenesis
leads to destruction of CD4+ cells. Then the virus re-enters bloodstream & infects remaining lymphocytes. Progressive loss of immune function leads to AIDS
Symptoms of advanced HIV disease
neurological symptoms, dermatologic conditions, and side effects from medication
What is myalgic encephalomyelitis?
Also known as chronic fatigue syndrome. Unexplained fatigue > 6 months. Nociplastic pain
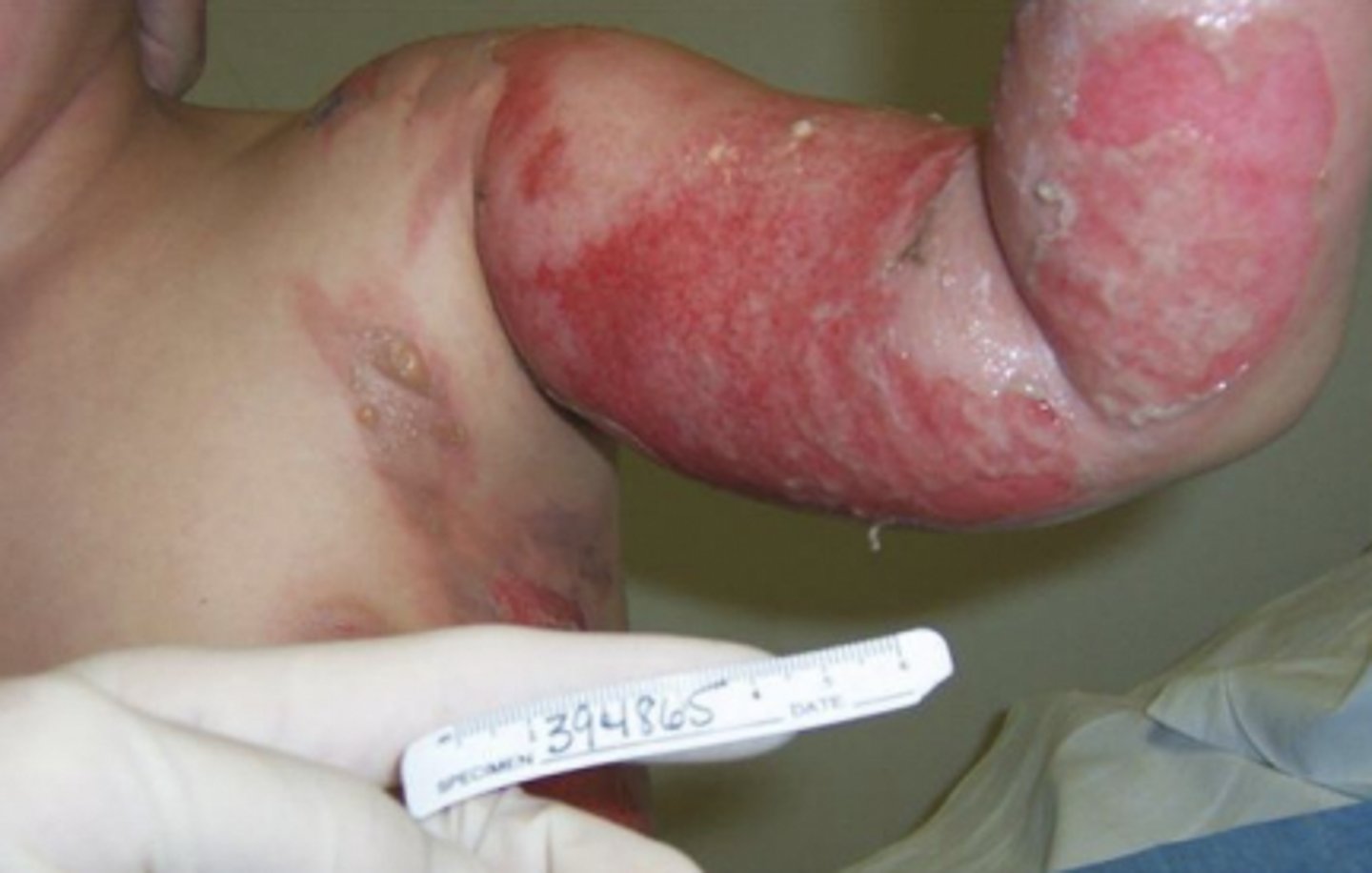
Lipodystrophic syndrome (LDS)
picture of arm (wife beater lol)

Pathogenesis of CFS
complex interaction among multiple systems. CNS, immune & hormonal regulation
Clinical manifestation of ME/CFS
overwhelming fatigue exacerbated by activity (post-exertional malaise)
What is fibromyalgia?
chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain
What is fibromyalgia characterized with?
Allodynia & hyperalgesia
Pathogenesis of FM
Top down: brain function
- sleep or memory problems
Bottom up: identifiable nociceptive or neuropathic pain
Pathogen
Any microorganism with the capacity to cause a disease
- commonly mutate
Signs & symptoms of infectious disease
Varied depending on etiologic agent & systems impacted
Systemic symptoms: fever, chills, malaise
Older adults: confusion, memory impairment & down concentration
Initial: confusion, hypotension, and tachypnea (rapid breathing)
What is the substance that causes a fever?
Pyrogen
Immunosenescence
- Reduced function of immune cells
- Reactivation of dormant infections
- Difficulty responding to new pathogens
What are microorganisms present in tissue?
Colonization
Outcomes of Infection
1. Contaminate body & be destroyed
2. Subclinical infection: no apparent symptoms
3. Infectious disease: development of clinically apparent infection
What is bacteria?
single-celled organisms with well-defined cell walls
- Can grow independently on artificial media
- Bacteria shape; cocci, bacilli, and spirilla
Infection sources, Healthcare Associated Infections
- 1/31 for hospitalization
- Hand washing
- Iatrogenic vectors, catheters, needles, and implants
Clostridium difficile
- Most common of health care associated GI symptoms
- About 50% of cases are acquired in community
- Over age of 65
Manifestation of C diff
diarrhea & fever
C diff facts
Anaerobic: Hand sanitizer ineffective
Incidence: Increase incidence & morbidity
Transmission mode: fecal oral
Staph: methicillin & vancomycin resistant
- One of most common agents on skin
- Leading cause is hospital acquired infections
Risk factors of Staph
insulin dependent, immunosuppression, burns, prosthetics
Pathogenesis of Staph
Inoculation: virulent pathogen, local effect which can lead to travel in bloodstream (sepsis & fever)
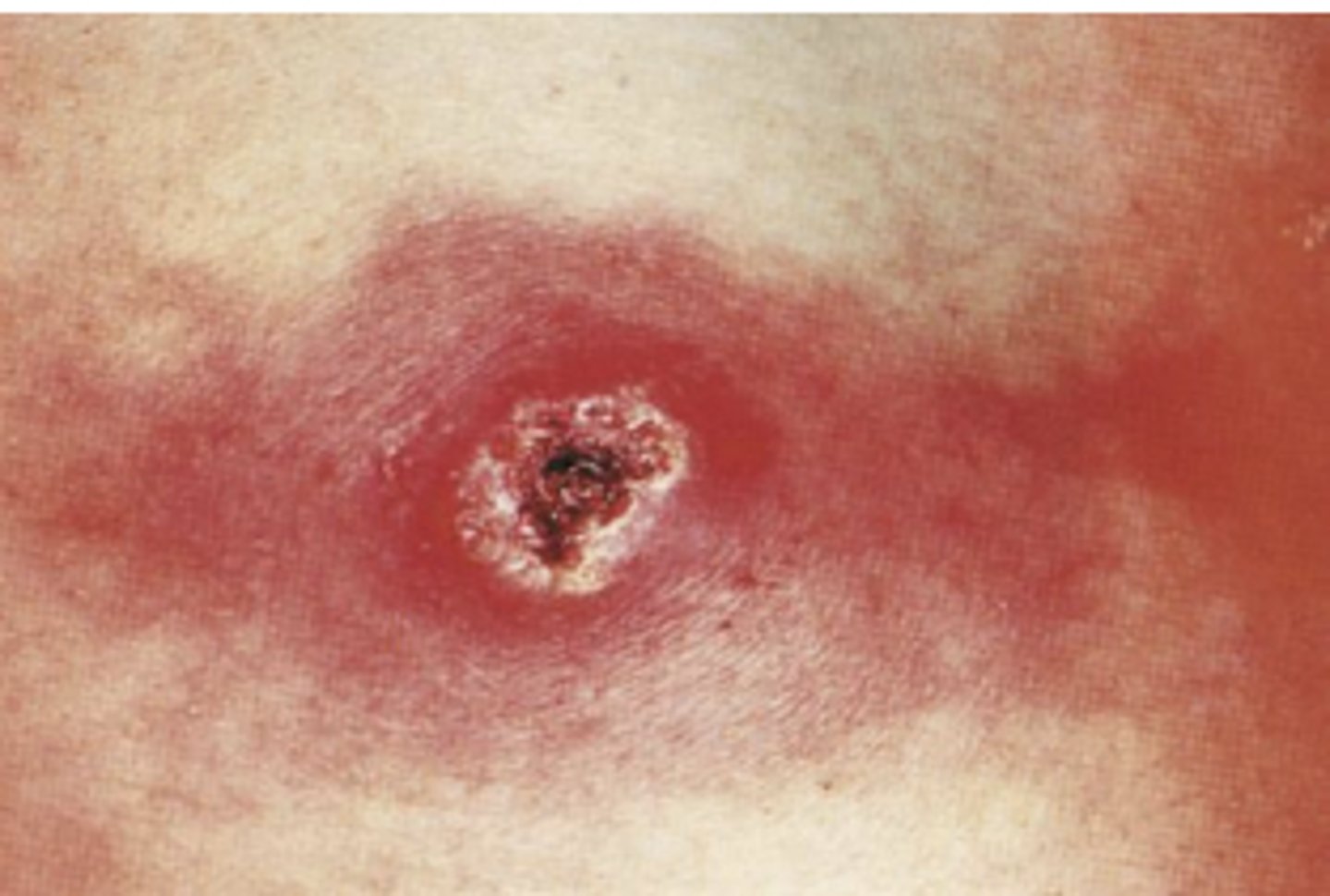
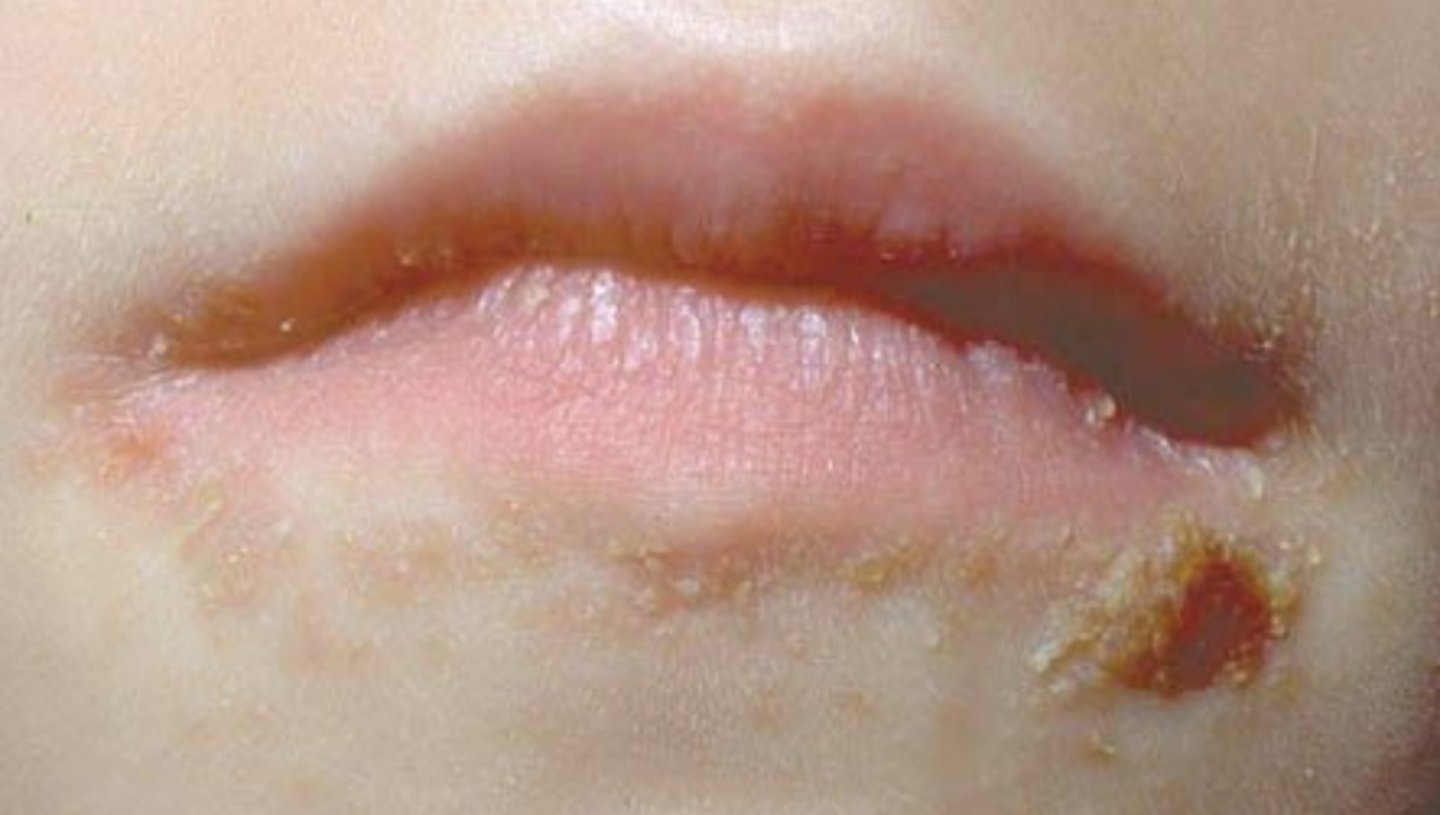
Streptococcal Pharyngitis- Strep throat
- Fever, absence of cough, tonsillar exudates
- Impetigo
Impetigo
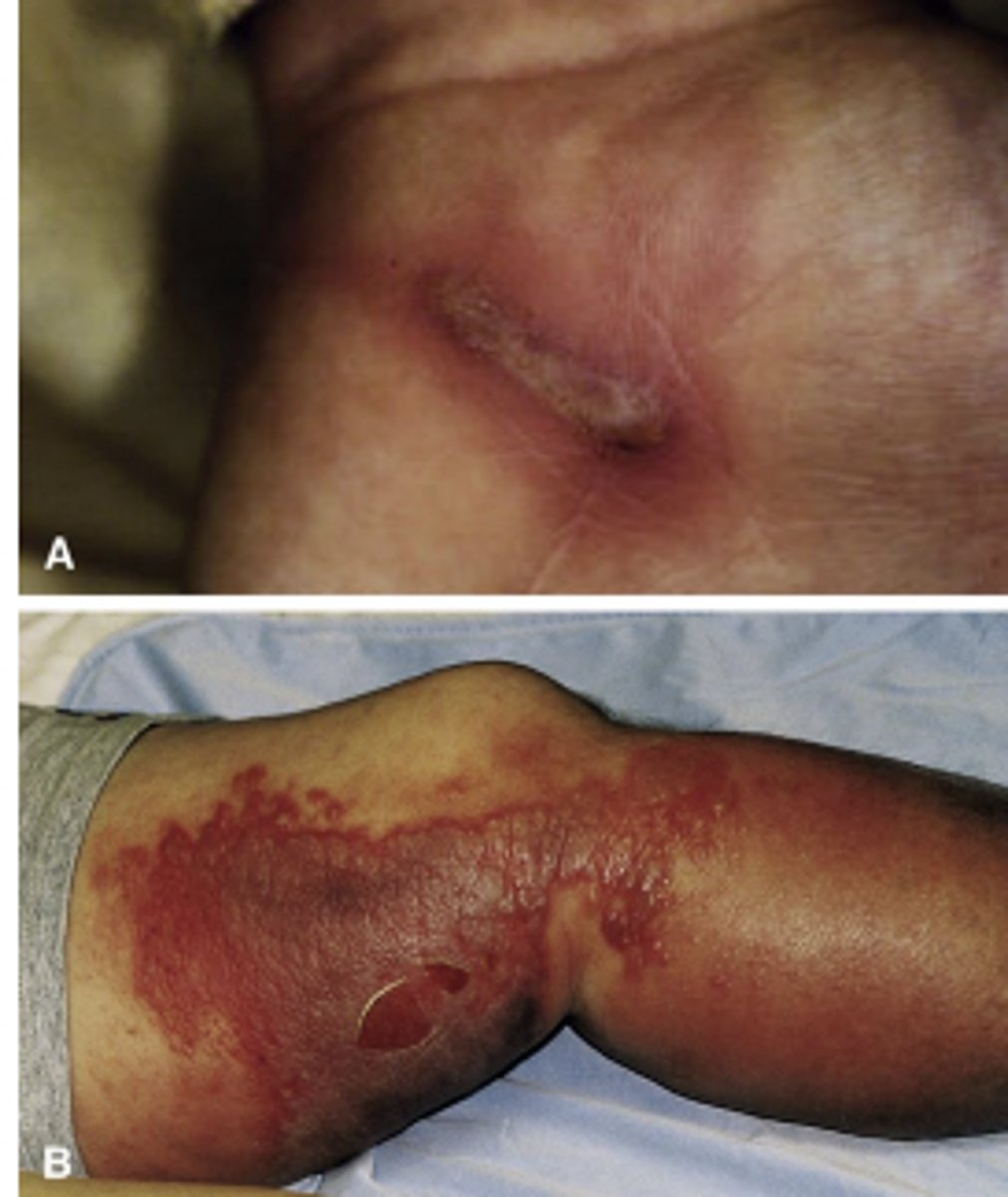
GAS- streptococcal cellulitis
Strep B
Pregnant women and neonate infections (GI & vaginal tracts)
- Transmission through labor
- Decreased over last decade
Common cause of community acquired phenomena
- Transmission is inhalation of droplets
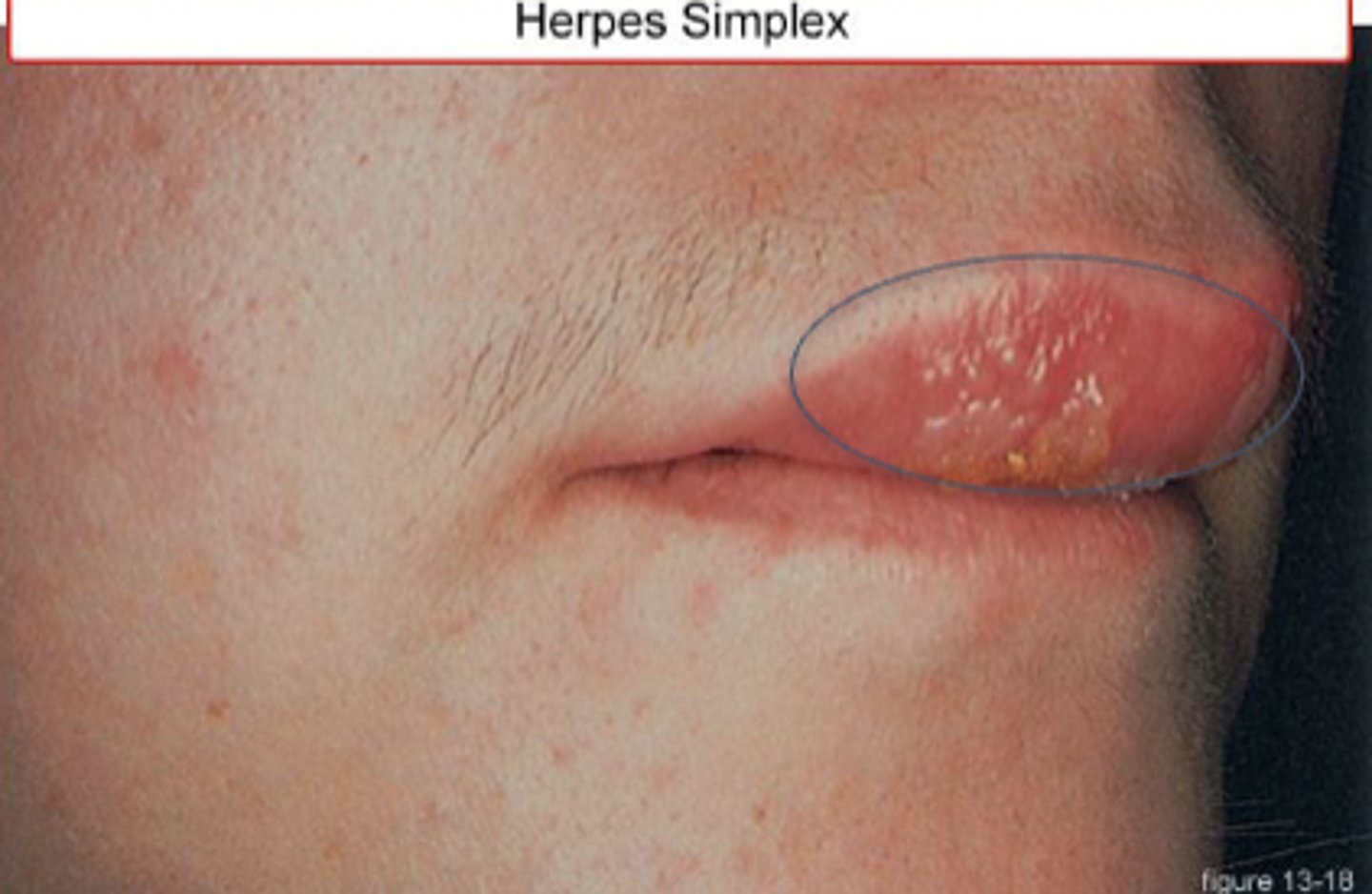
HSV
HSV-1 Cold Sores, 70% Americans over 14
HSV-2 Genital Herpes, 11.9% Americans
Transmission of HSV-1 and HSV-2
Shedding, direct skin to skin
VZV (varicella zoster virus)
chicken pox and shingles
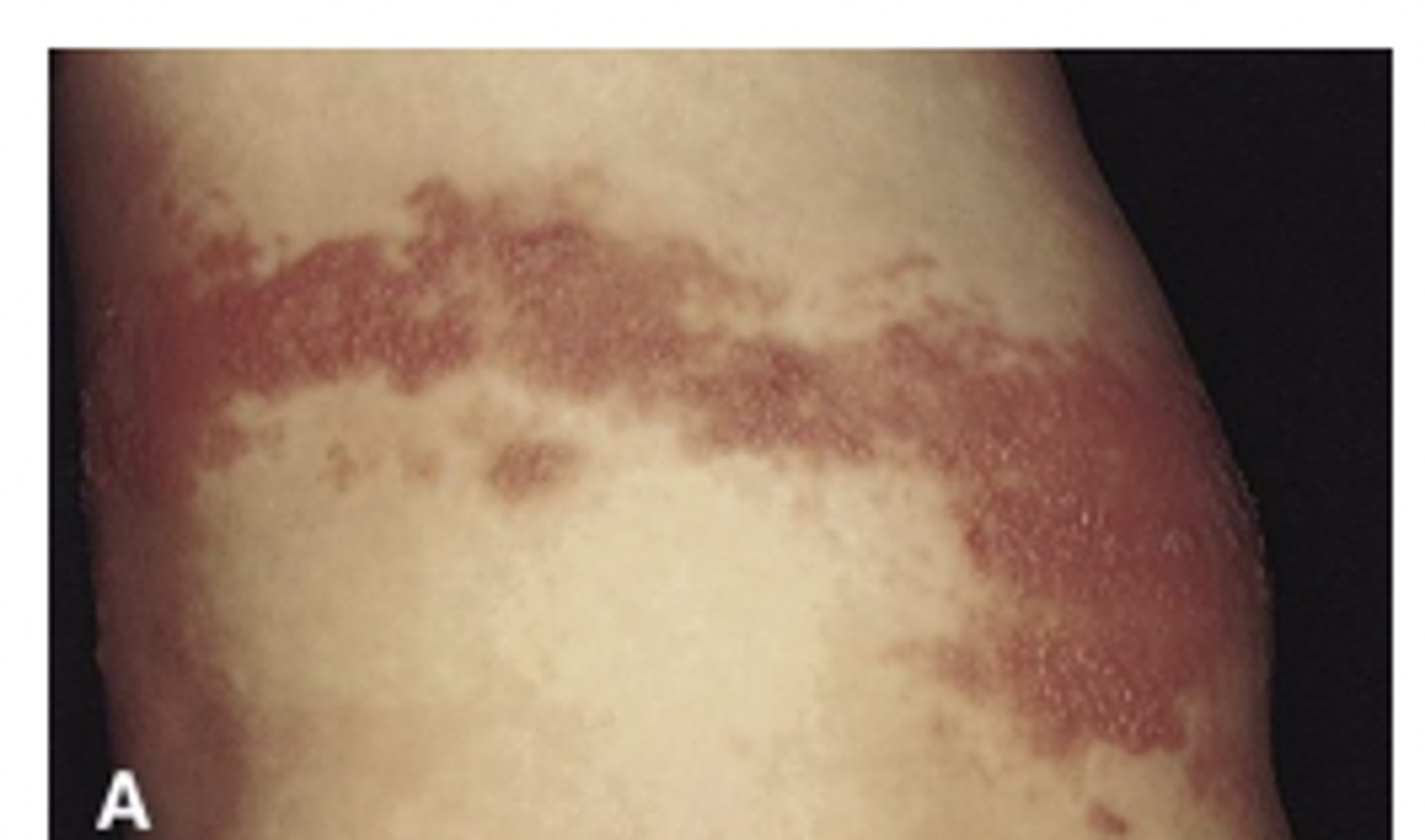
Transmission of VZV
highly contagious & airborne
Symptoms of VZV
pain/tingling, fever, chills, malaise 1-3 days prior to eruption of red papules
MONO manifestations
Swollen lymph nodes, fever, sore throat, headache, abdominal pain, and malaise
Influenza
sub-divided by surface protein
Transmission: inhaled aerosolized virus or direct contact with large droplets
Manifestation of influenza
abrupt onset, high fever, chills, malaise, myalgia, headache and non-productive cough
Lyme disease
infectious multi-systemic disorder
- Hallmark bullseye rash
Manifestations: flu-like onset
Unilateral poly-arthritis of large joints
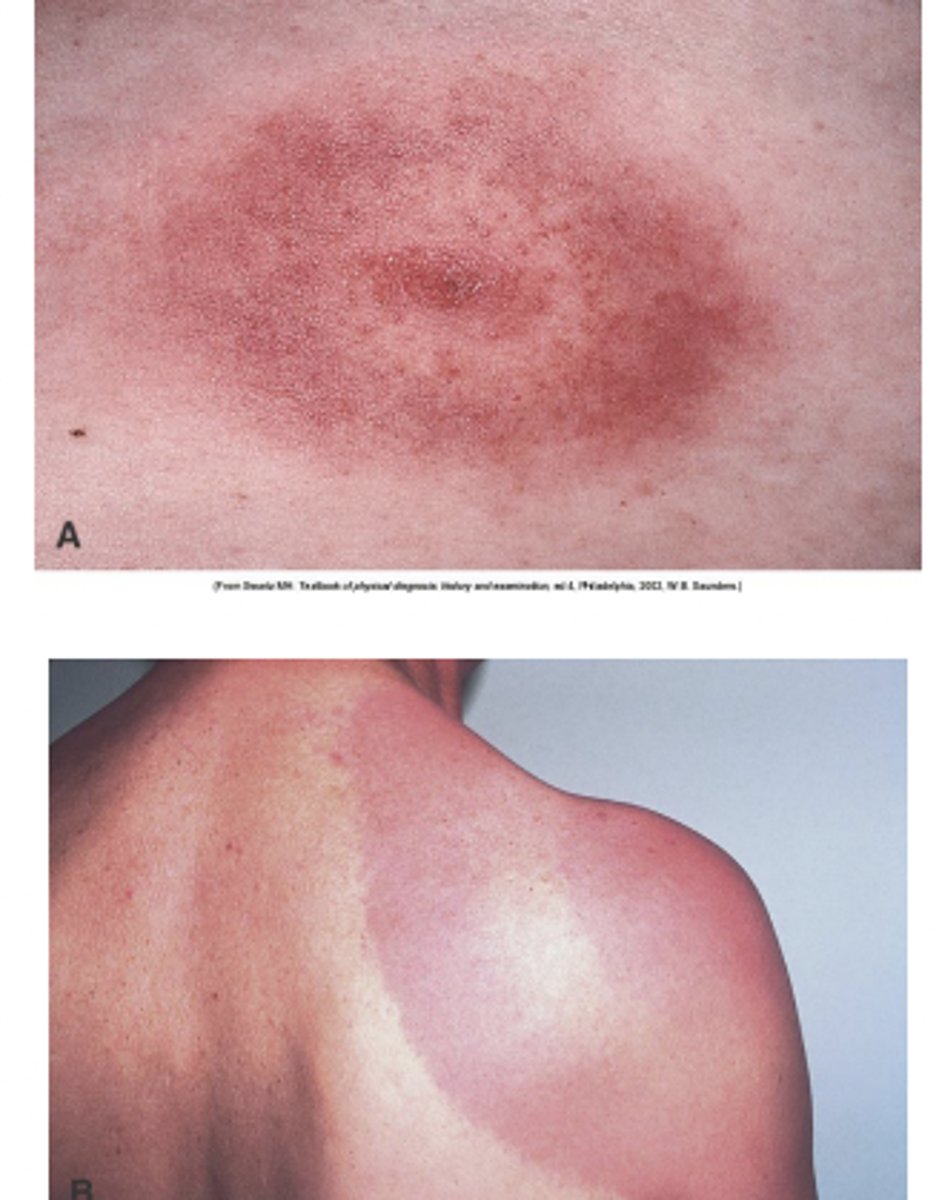
Stage 1 of Lyme Disease
5-14 days post tick bite
- Red, slowly expanding bullseye
- Flu like symptoms
Stage 2 of Lyme disease
weeks to months
- Skin, nervus system, heart, joints
- Meningitis, facial nerve palsy
Stage 3 of Lyme Disease
months to years
- Joint symptoms, polyneuropathy, cognitive impairment
pruritus
itching
urticaria
hives; an eruption of wheals on the skin accompanied by itching
Rash
eruption on skin
Xeroderma
excessive dryness of skin
Vesicles
< 5mm (blister)
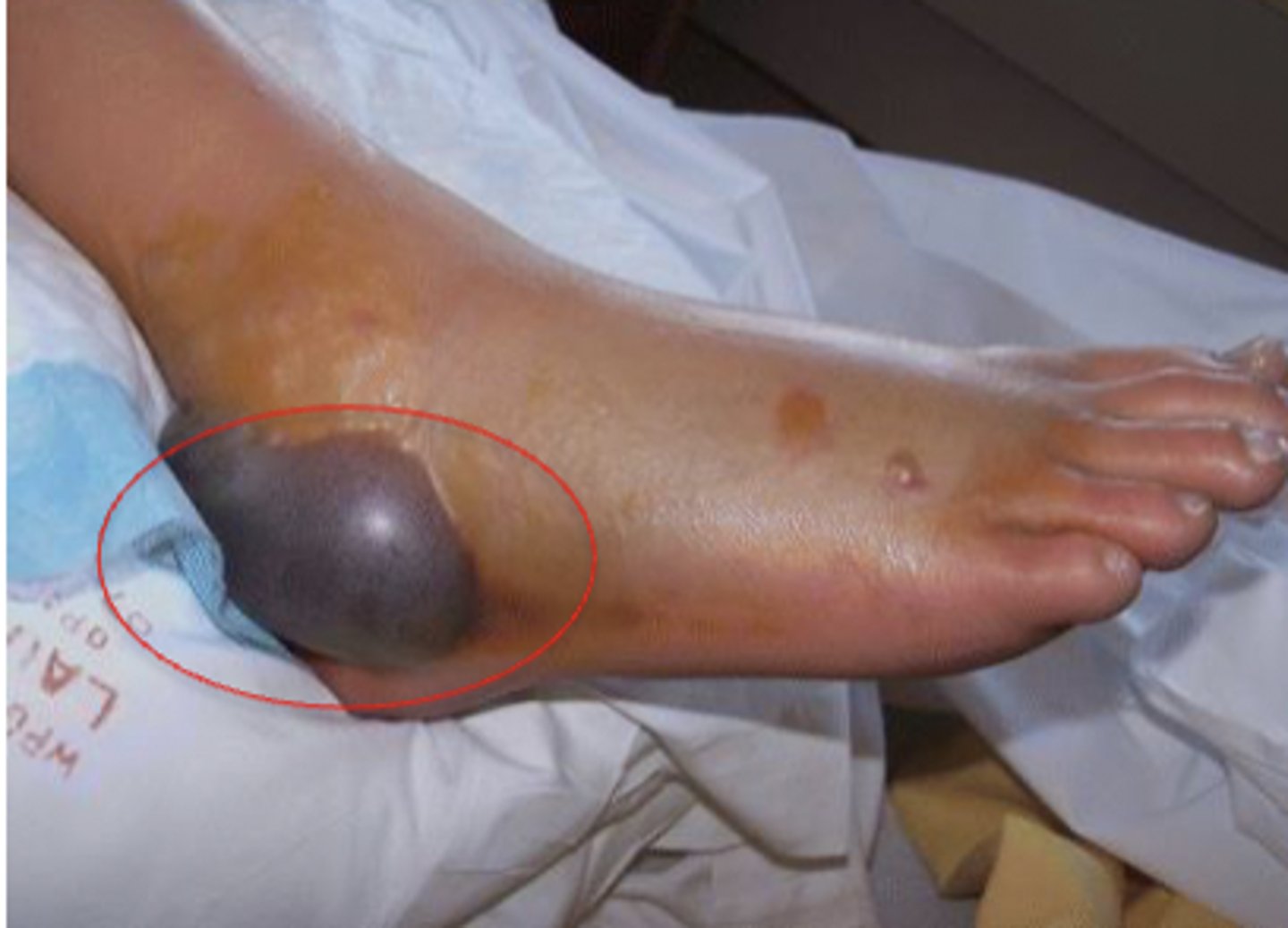
Bulla
> 5mm (blister)
Macule
lesion measuring less than 2 cm in diameters. Not raised nor depressed
Papules
slightly elevated induration of skin, <1 cm
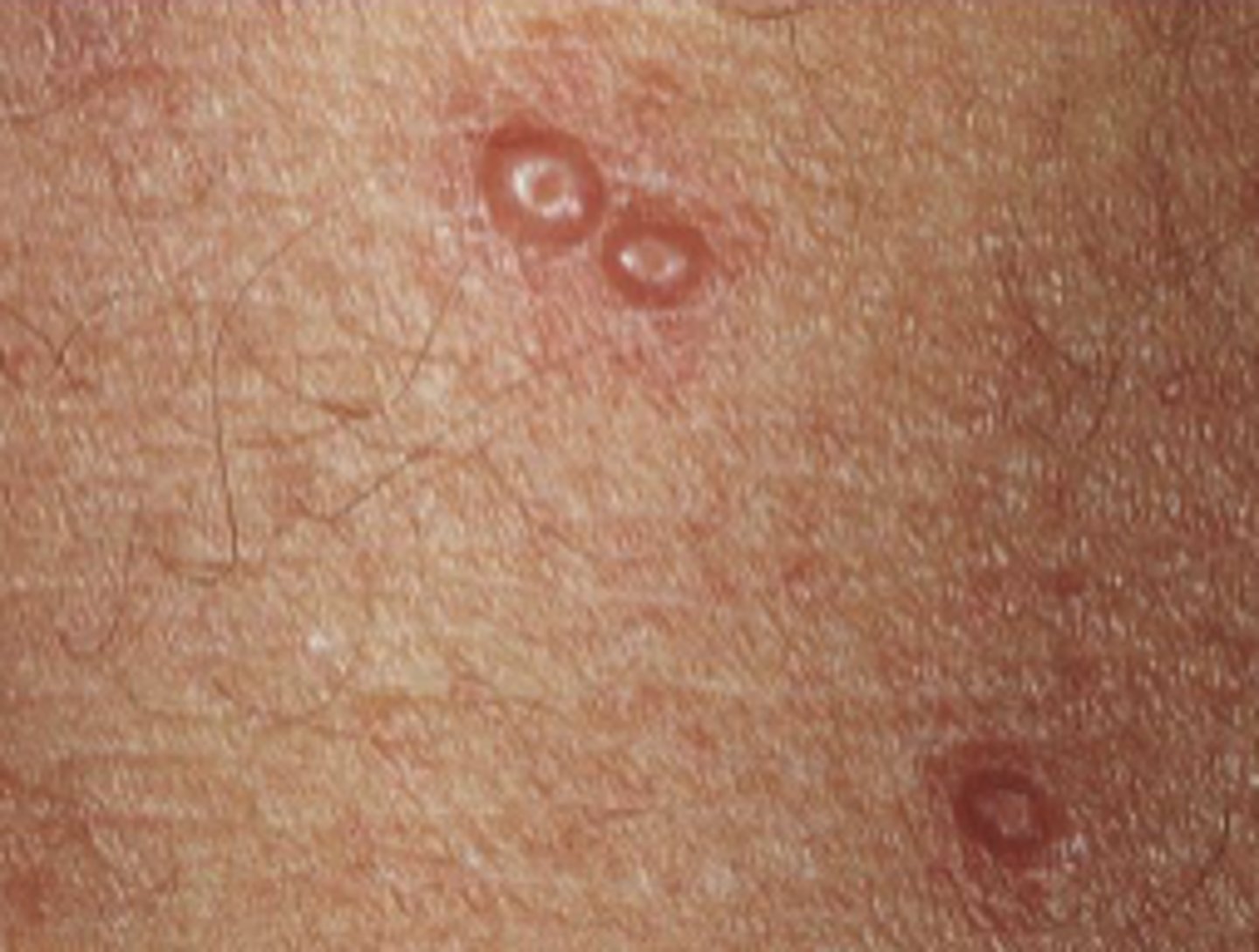
plaque
elevated flat-topped area, > 5 mm across
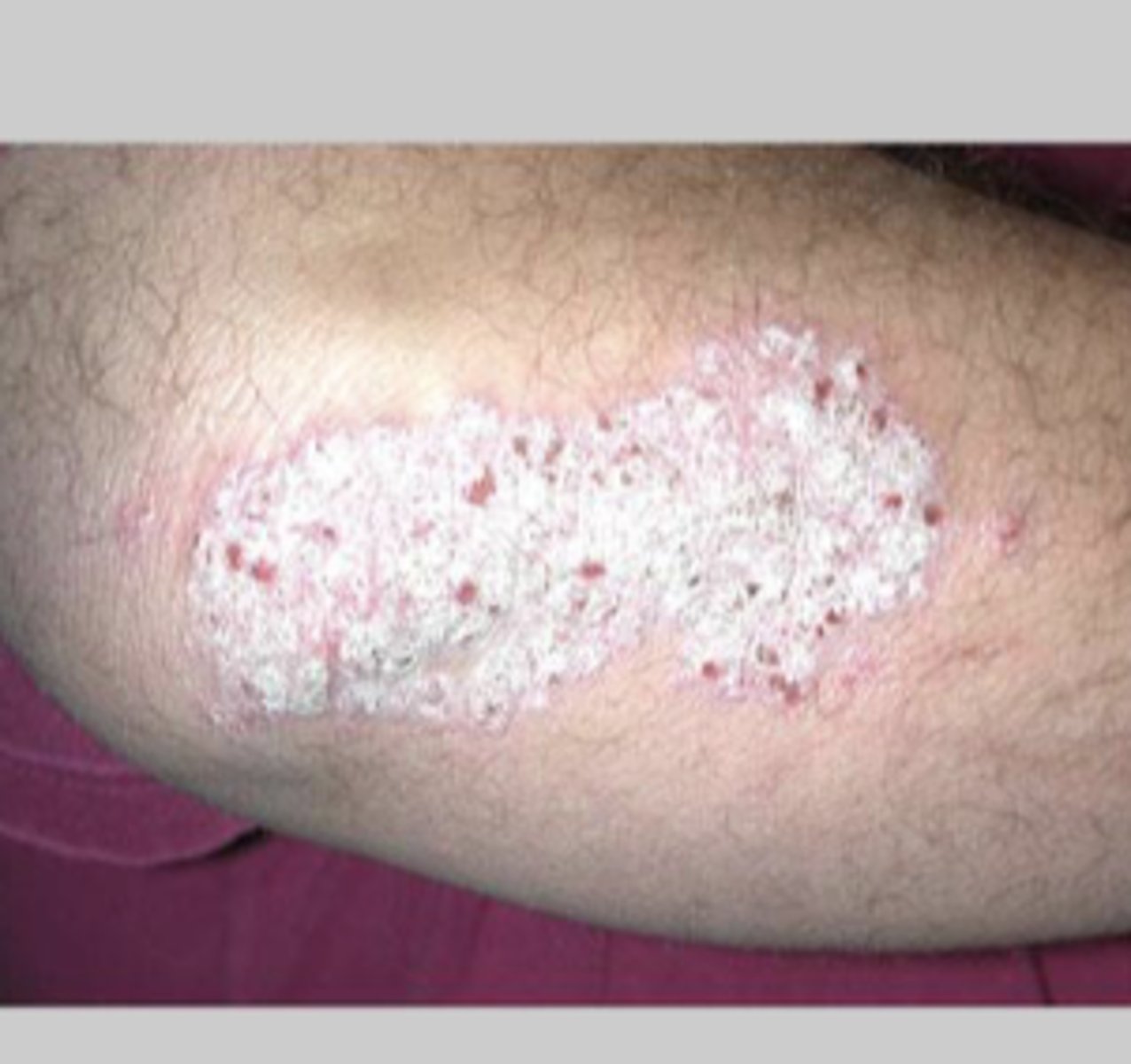
Scale
dry, platelike sheet of keratin
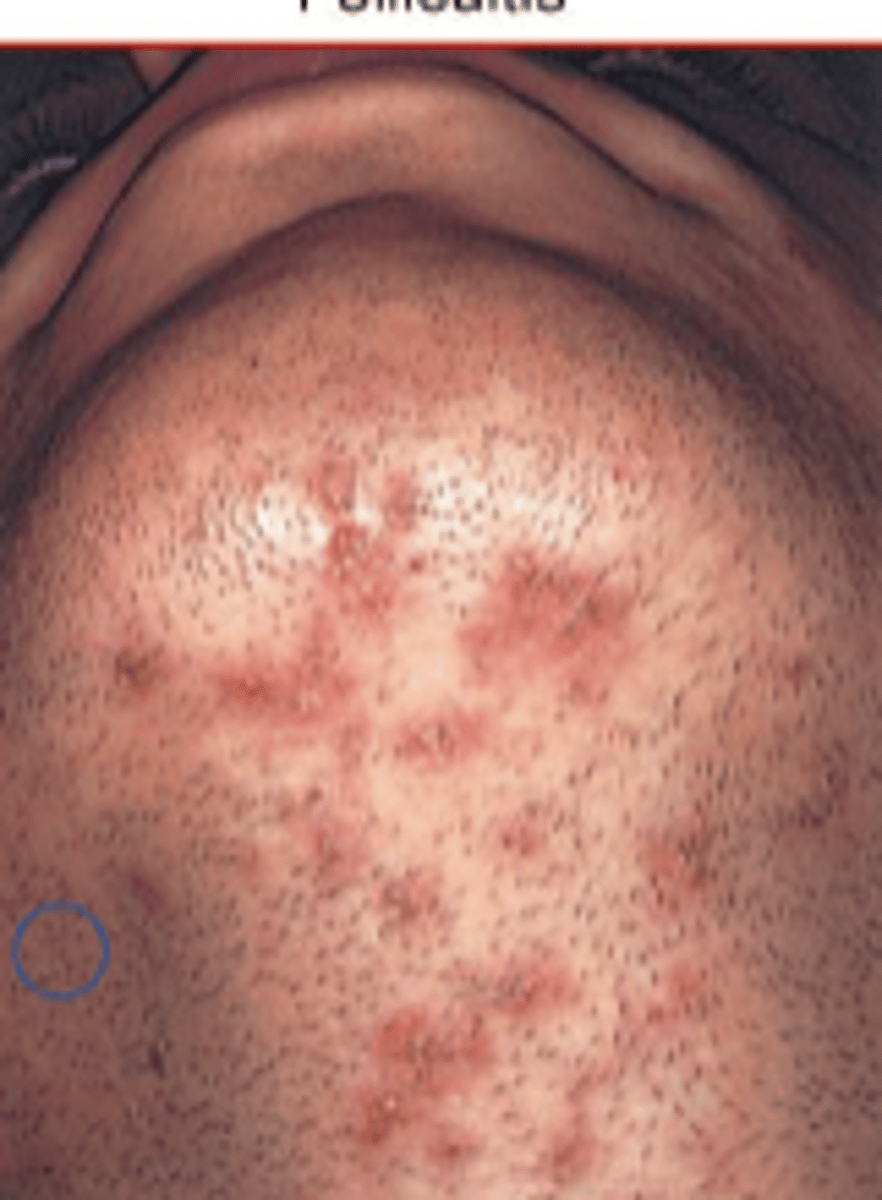
Folliculitis
papule formed around single central hair follicle
furnucle
focal suppurative infection of central hair shaft and surrounding subcutaneous tissue
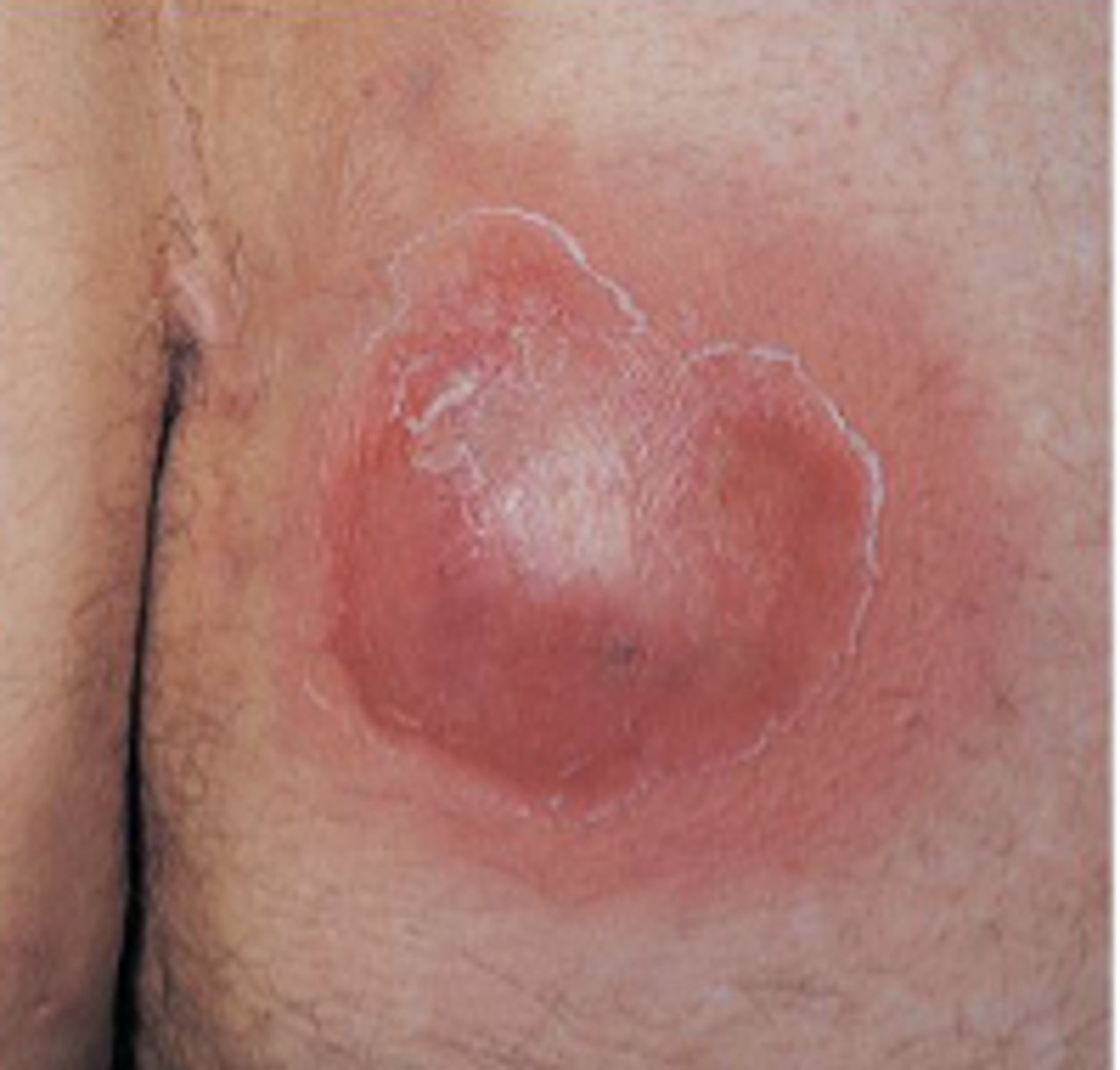
Carbuncle
cluster of furuncles with connection through sinuses
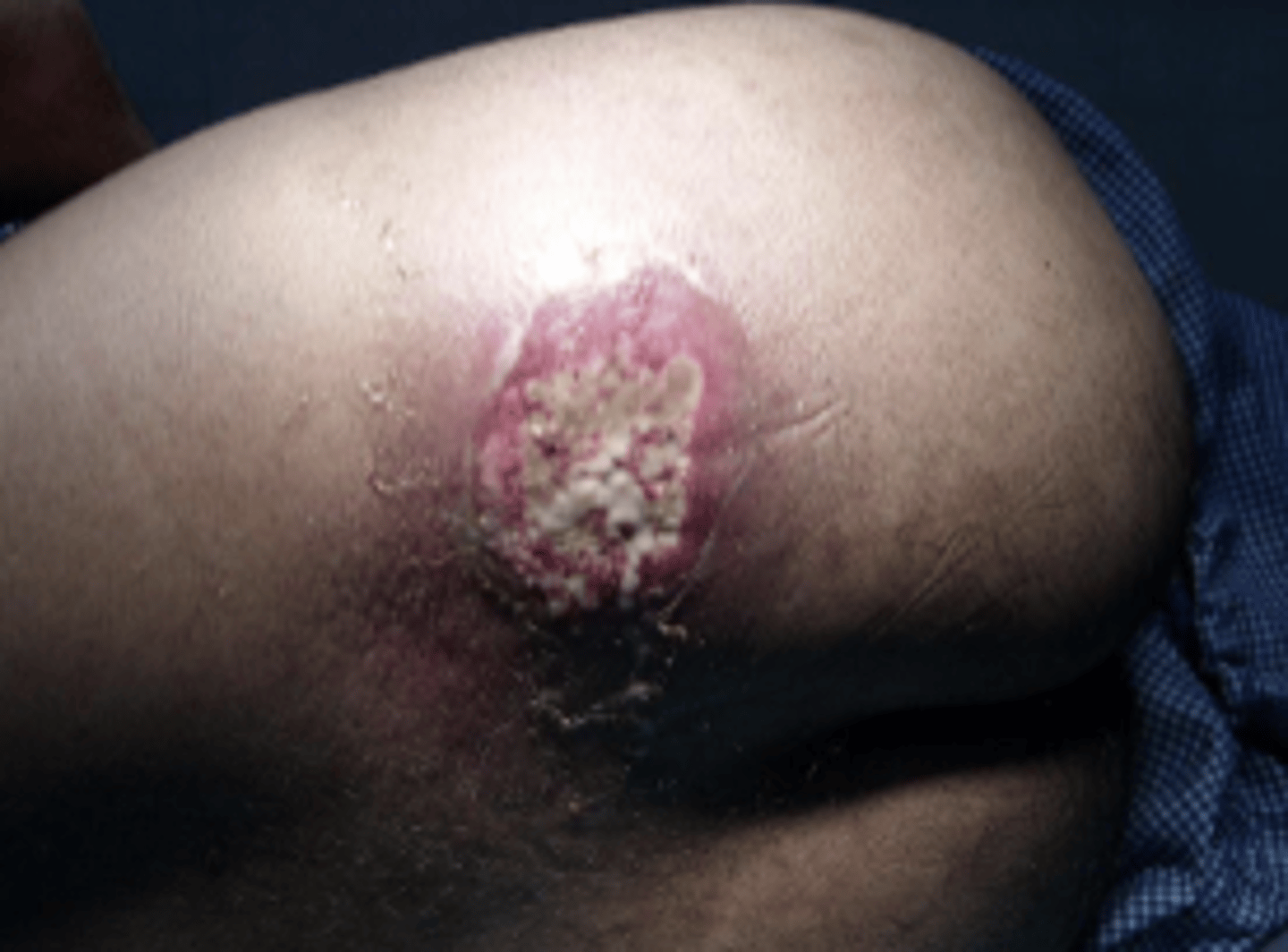
Atopic Dermatitis
genetic predisposition
- Early: red, ozzing, crusting rash
- Later: dry, thickened, brownish gray color
- Xerosis and pruitis
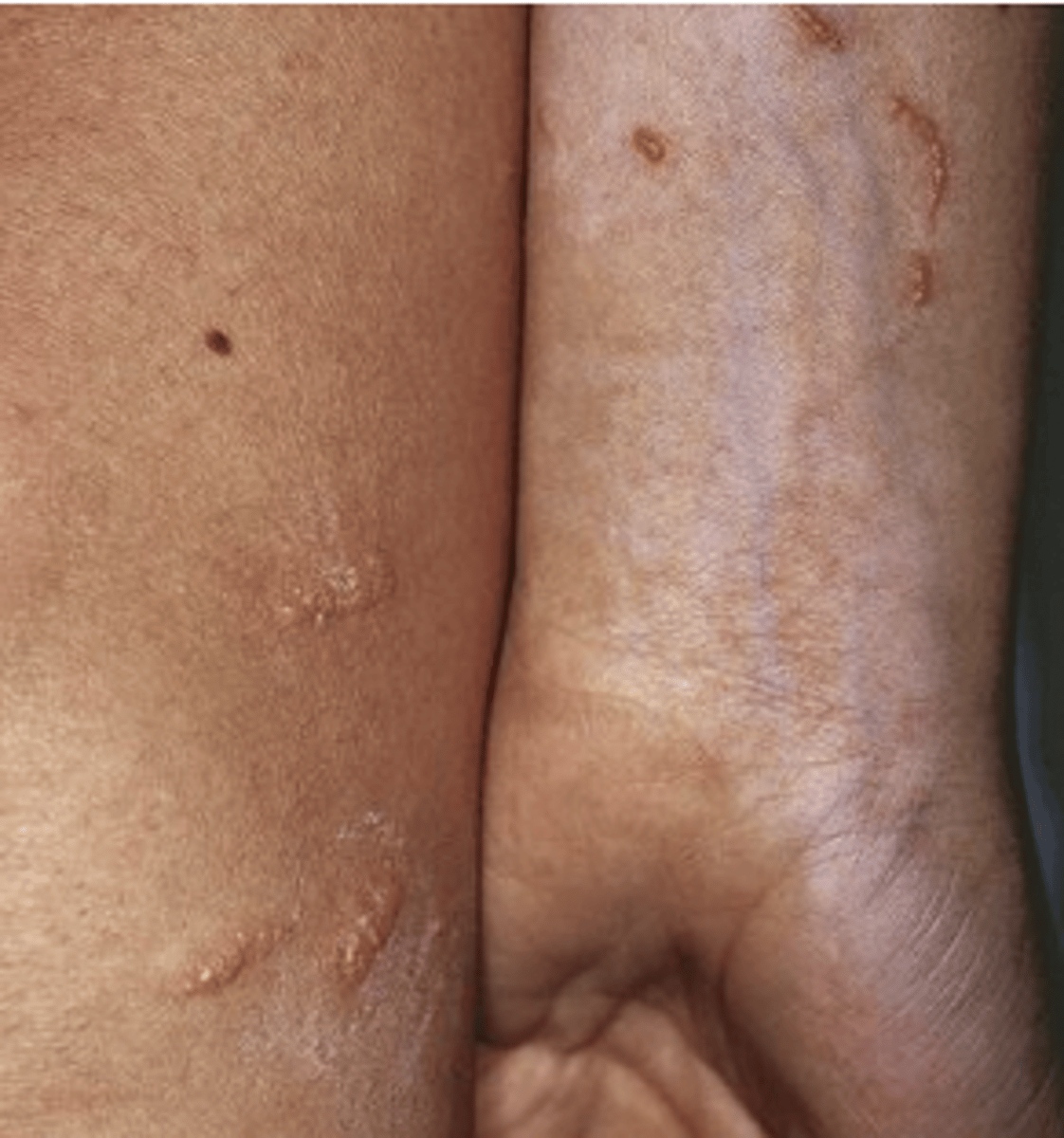
What is contact dermatitis?
Acute or chronic skin inflammation caused by exposure to an external agent
- Priutitis, erythema, edema
- Removal of offending agent for management
What is eczema?
superficial itch inflammation of skin
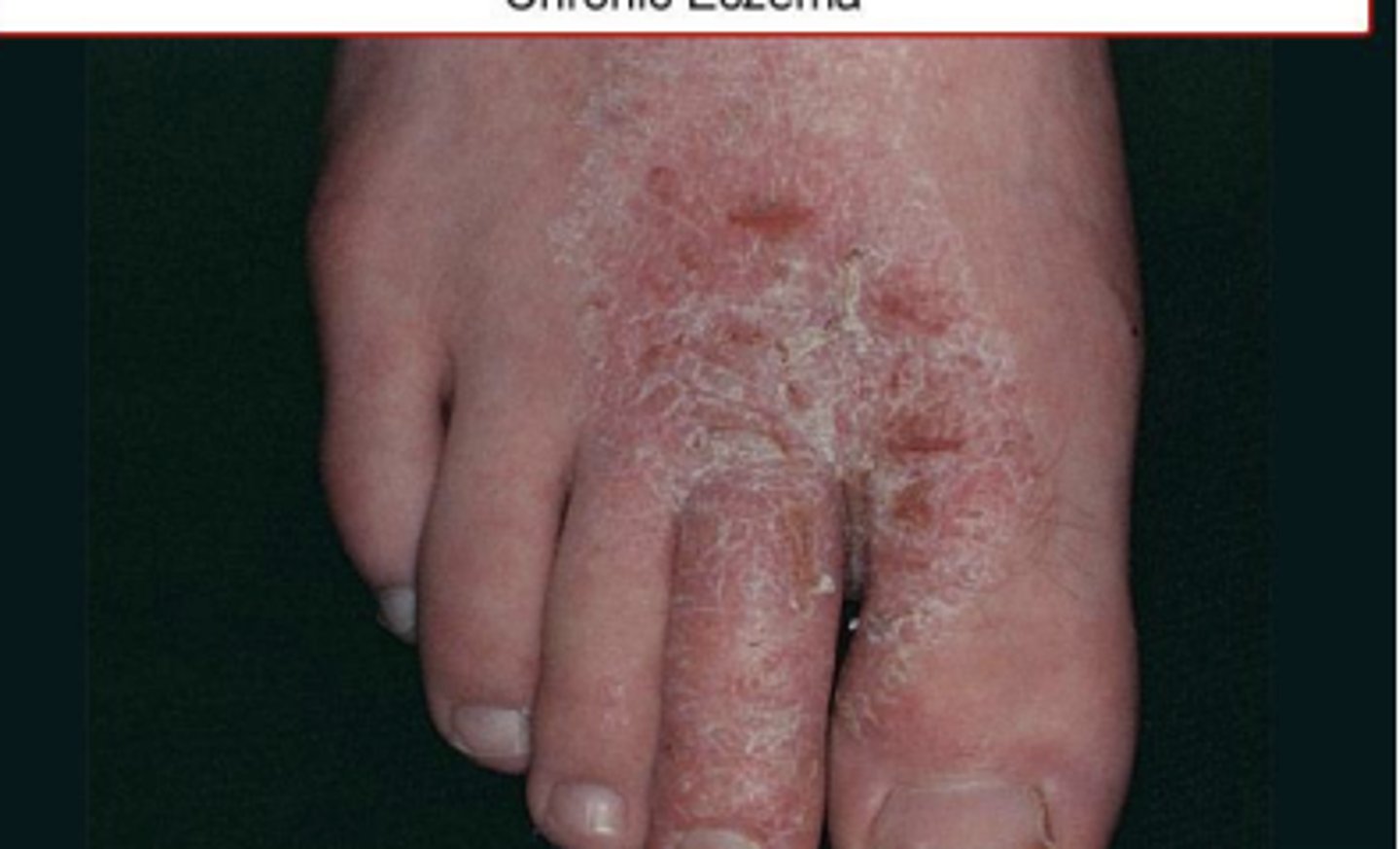
Stages of eczema
- Acute: extensive erosions with serous exudate or erythema
- Subacute: erythematous, excoriated scaling plaques
- Chronic: brownish- grey color & thickened skin
ABCDE of mole
A- asymmetry
B- border
C- color
D- diameter
E- elevation

Verrucae
benign viral infections of skin caused by HPV
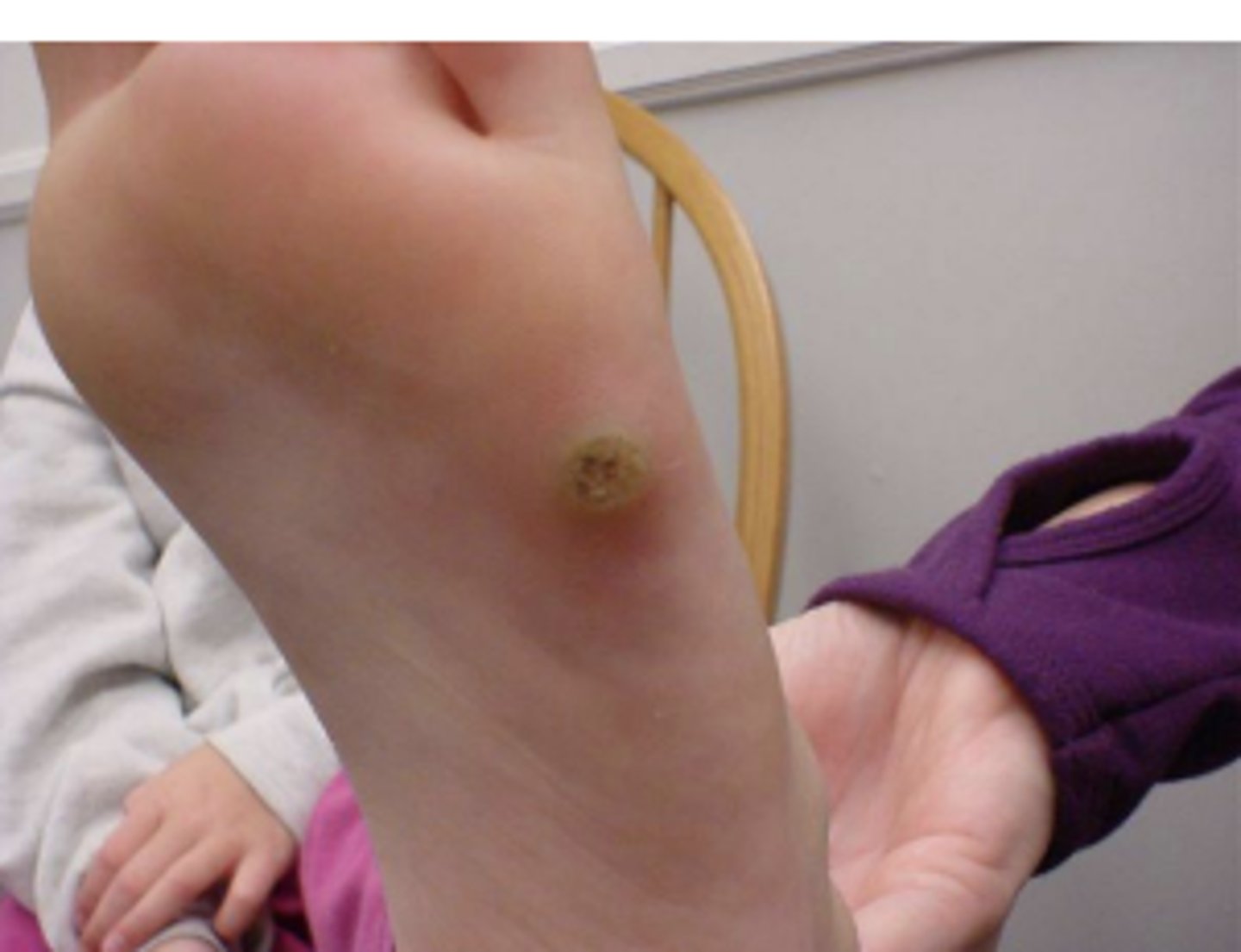
Tinea corporis (ringworm)
Red lesions in a circular pattern blanched in the center caused by fungus, NOT a worm
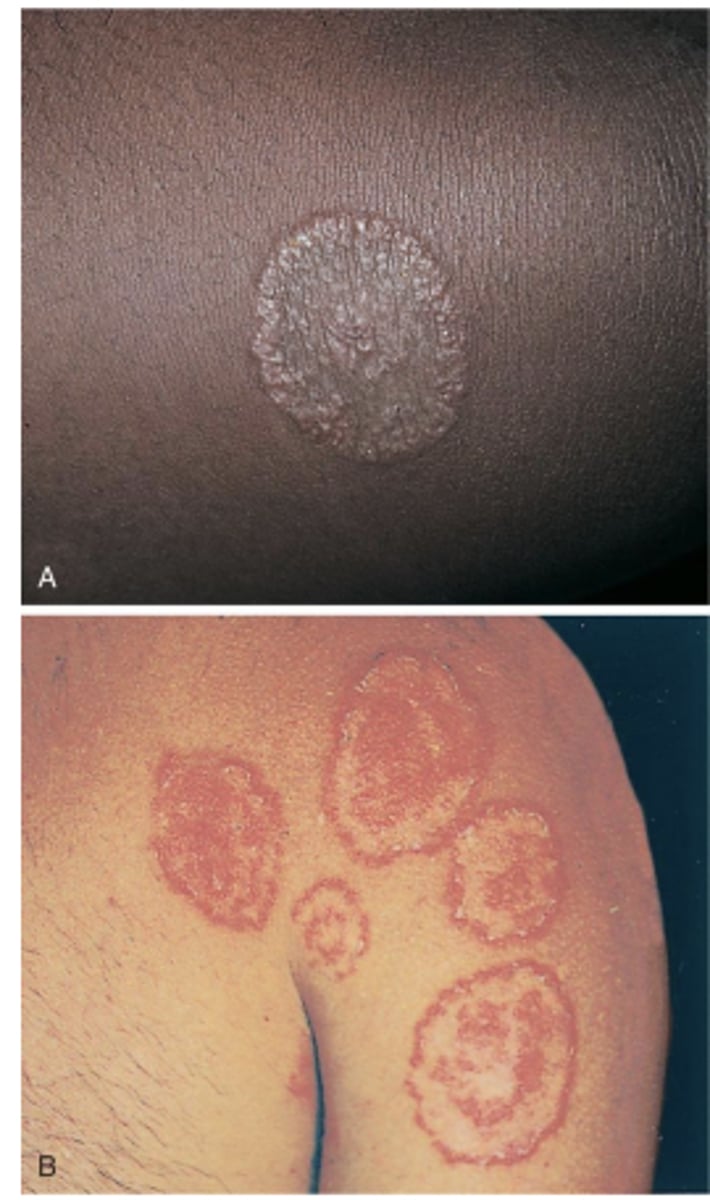
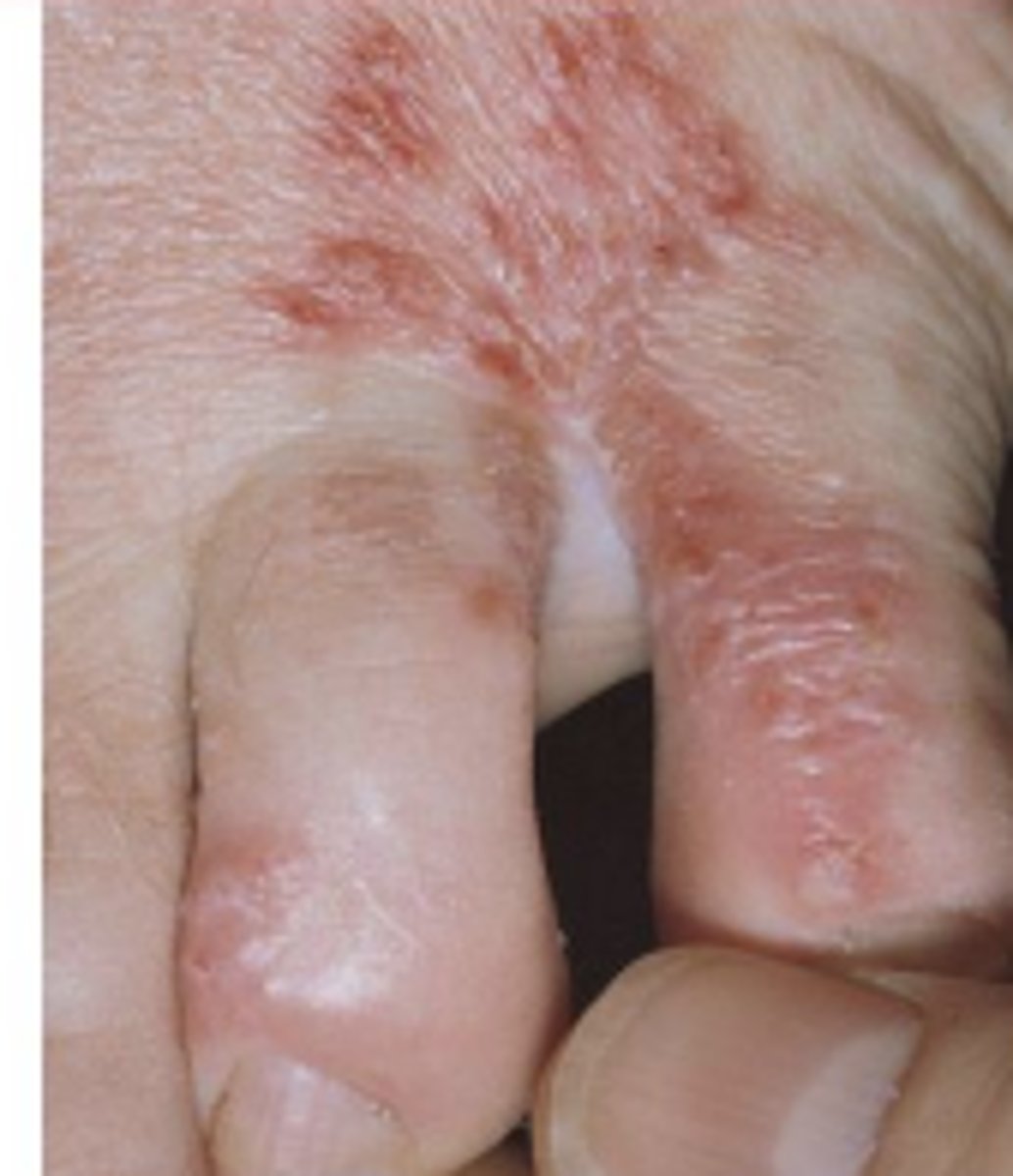
Tinea pedis
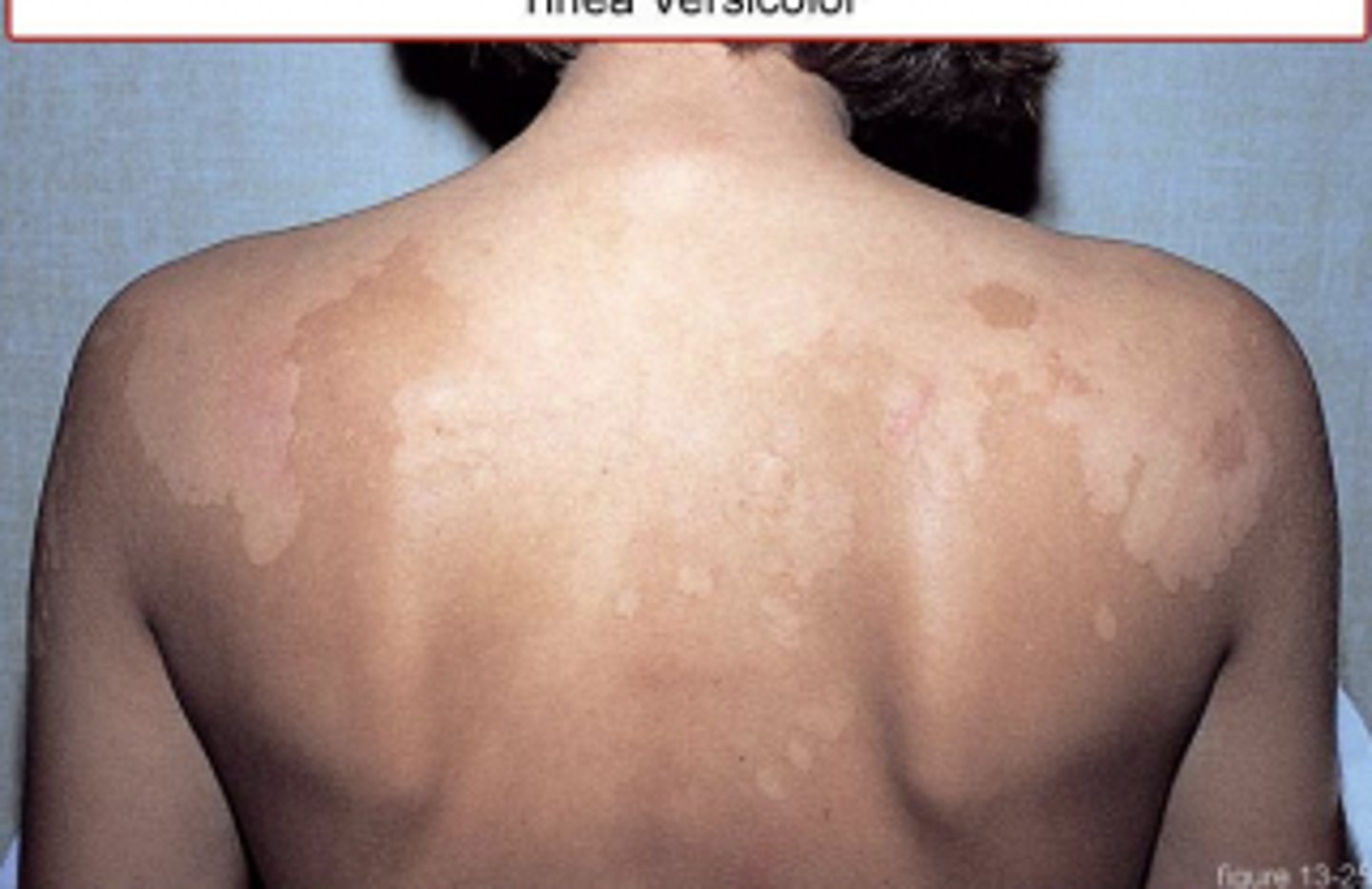
Tinea versicolor
Skin cancer
most prevalent form of CA, affects nearly all Caucasian people over 65 years old
- Most rapidly increasing forms of cancer
- Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun
Basal Cell carcinoma
slow growing skin tumor from undifferentiated epidermis basal cells
- Can cause local destruction
- Slightly elevated, pearly or ivory color, rolled edges, visible blood vessels
- "Sore that will not heal"
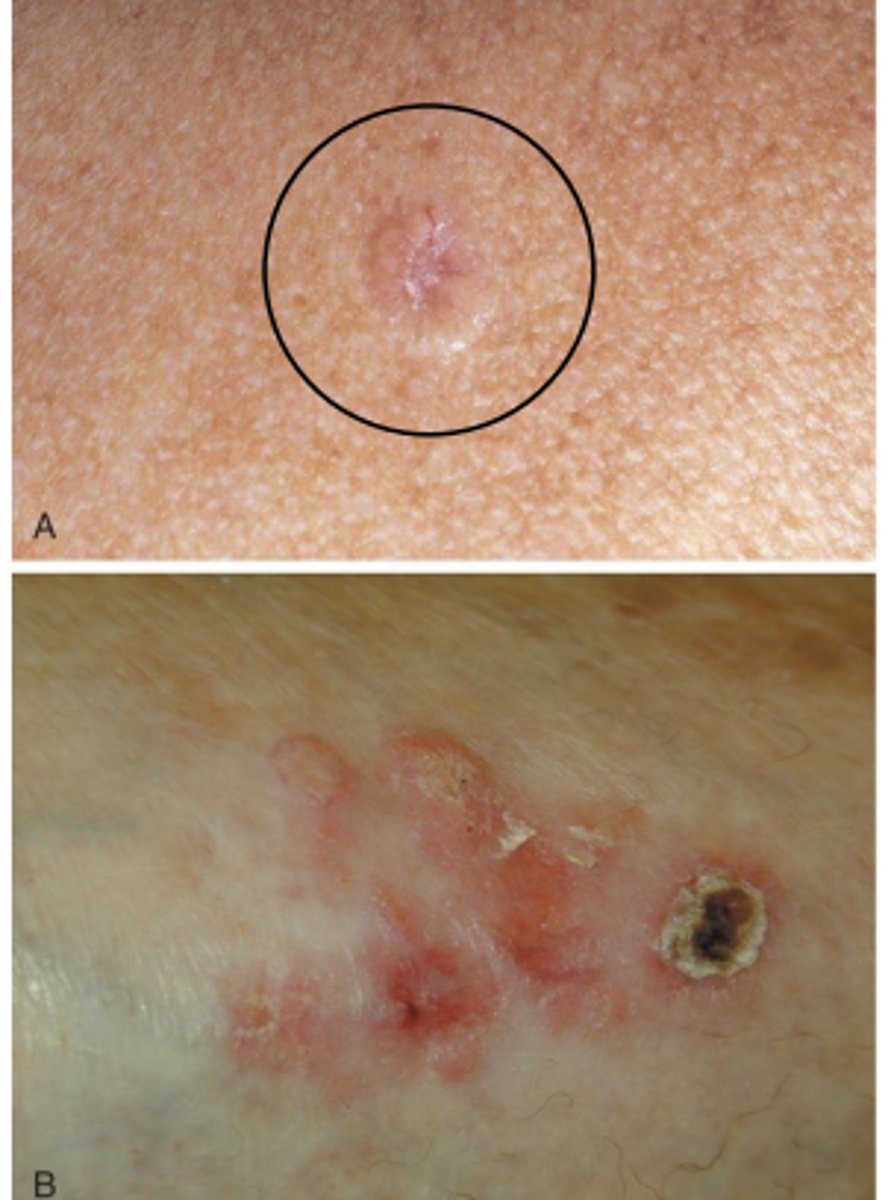
Malignant Melanoma
neoplasm of the skin originating from melanocytes
- Surgical excision
- 100% curable if detected early
Manifestations of Polymyositis & Dermatomyositis
General- fatigue, malaise, weight loss
UE- trouble lifting overhead
LE- squatting, walking & standing from chair
Heliotrope rash
Purple rash over the upper eyelids, often seen in dermatomyositis
Gottron's papules (dermatomyositis)
Lacy, pink, raised areas typically found over IP joints
Diagnosis of Polymyositis & Dermatomyositis
progressive symmetric weakness, elevated CPK & EMG will be abnormal
Systemic effects of burns
Integumentary, CV changes, Renal/GI changes, Pulmonary artery hypertension & immune system suppression
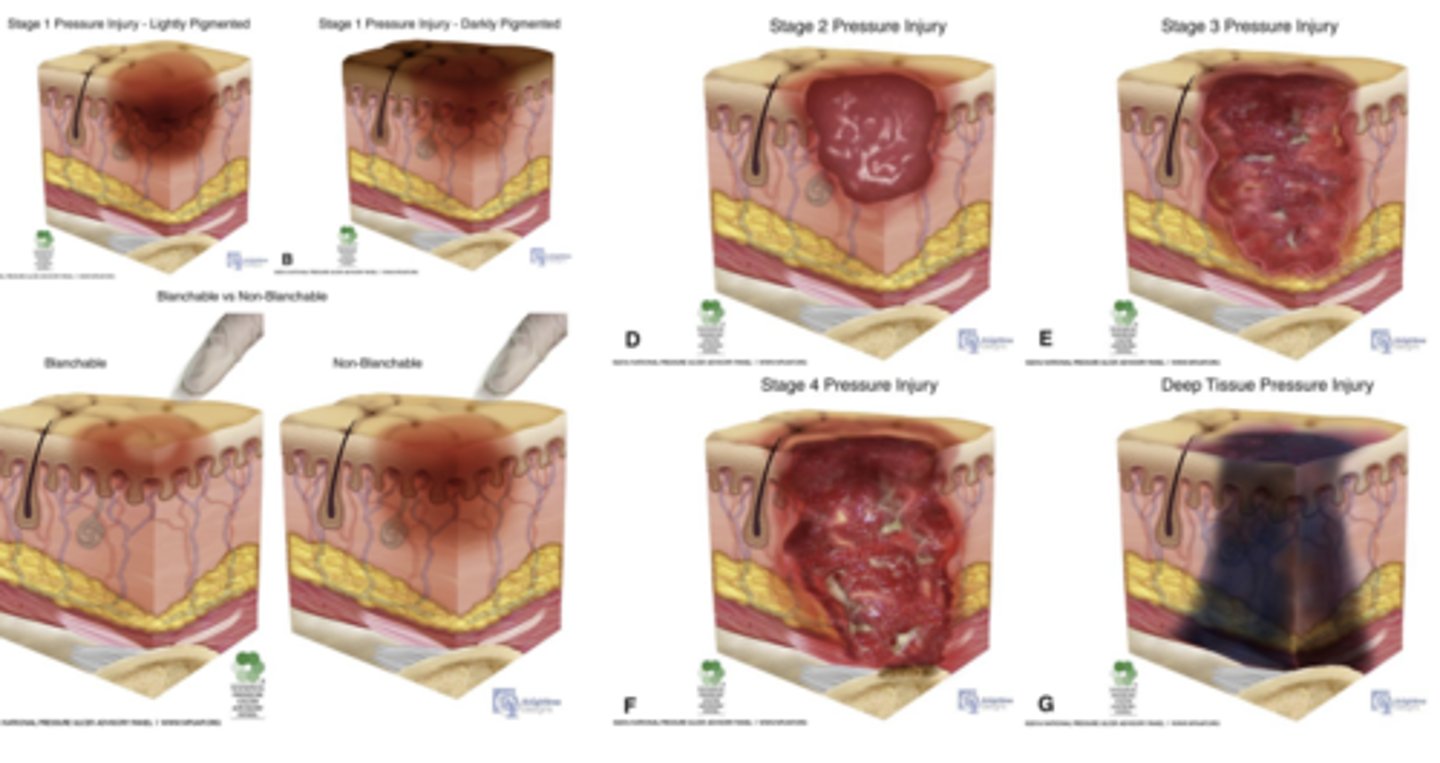
Pressure Injury Stages
TNM staging system

Tumor: refers to size of primary tumor
Tx- cannot be assessed
T0- no evidence of primary tumor
Tis- carcinoma in situ
T1-4 - progressive increase in tumor size & involvement
Nodes: regional lymph nodes involved
Nx- nodes cannot be assessed
N0- no metastasis to regional lymph nodes
N1,2,3- increasing degree of involvement of regional lymph nodes
Metastases (0-1)
Mx- presence of stant metastases not assessed
M0- no metastases
M1- distant metastases
Most prevalent cancer in the world?
Lung cancer
What % of people diagnoses with cancer will be cured or survive 5+ years after treatment?
60%, 3/5
What % of people will be diagnosed with a form of invasive cancer in lifetime?
33.3%, 1/3
endogenous cancer risk factors
Genetics, hormones, immunodeficiency & age
Exogenous cancer risk factors
Lifestyle, viral exposure, chemicals & radiation exposure
Modifiable risk factors of cancer
Lifestyle behaviors, pollution, household fuels, contaminated injections, obesity, sexual behavior & sexual activity
Non-modifiable risk factors of cancer
Age, exposure to viruses, exposure to hormones, sex, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, heredity & stress
General manifestations of cancer
initially asymptomatic, thickening or lump, sore that does not heal & pain
Systemic signs of cancer
unexplained weight loss, change in bowel habits, nagging cough, fatigue, malaise, weakness, and fever
Lung cancer manifestation
Persistent dry, non producing cough
Exertional dyspnea
Colon cancer manifestation
Change in bowel function
Color- blood in stool
Shape- ribbons
Type I Hypersensitivity
Local- urticaria, erythema, priuritis, rhinitis
Type II hypersensitivity
Body's own tissue is recognized as "non-self"
Type III Hypersensitivity
Excessive circulation of antigen-antibody complexes. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Type IV Hypersensitivity
cell mediated (no antibodies)