Financial Accounting A
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What is corporate finance?
The processes and practices of communicating a company’s financial and no
What is regulatory framework?
A collective system of rules/regulations and mechanisms that governs the principles and practices of corporate reporting.
Why is there a need for regulation?
Limited liability of shareholders and companies
Separation of management and ownership, especially for large/listed companies
Historical market failures
Other reasons: Comparability,credibility,discipline
What are the 3 main sources of regulation in the UK/
Financial reporting standards
Company law
Stock exchange rules (listed companies only)
Explain what the financial reporting standards are?
Listed companies- must prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRSs in full
Non-listed companies- Choose either full IFRSs or UK based accounting standards
Micro entities- A simplified accounting standard
What are the companies acts requirements?
All companies in the UK are required to comply with companies acts 2006
What are the exchange listing requirements?
Companies that are listed on the stock exchange must comply with additional reporting requirements of the financial conduct authority.
What do the three sources of regulation amount to?
GAAP
What is GAAP?
Generally accepted accounting practices
a complete set of regulations which apply within a certain jurisdiction
What is non-financial reporting?
It is demanded an additional disclosure regarding an entity’s performance in Environment,Social and governance matters
What is the definition for sustainability?
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
What are the two aspects of sustainability?
Dependencies
Impact
What is concerned with dependencies?
Depending on various factors
Resource availability
consumer expectations
climate risks
reputation risks
worker health
health and safety
What is corporate governance?
A set of rules, practices and processes used to direct and control an organisation
What do different GAAPs lead to?
Different financial results
How do we overcome the problem of different GAAPs?
Accounting ‘convergence’- same accounting standard for every country in the world.
What must professional accountants comply with?
The code of ethics of their professional accountancy bodies.
What are the five fundamental principles of the IESBA code of ethics?
Confidentiality
Objectivity
Professional behaviour
Integrity
Professional competence and due care
What are the following attributes a useful financial statement should possess?
Relevance
Faithful Representation
Comparability
Verifiability
Timely
Understandability
What is the objective of IAS1?
Prescribes the basis for presentation of general purpose financial statements, to ensure comparability both with the entity’s financial statements of previous periods and with the financial statements of other entities.
What is the objective of general purpose financial statements? (GPFS)
To provide information about the financial position,performance and cash flows of an entity that is useful to a wide range of users in making economic decisions.
What is IAS1?
A standard issued by the IASB that sets out the overall requirements for preparing and presenting financial statements.
What are the general features of IAS1?
Fair presentation
Going concern and accrual basis
Materiality and aggregation
Offsetting
Frequency of reporting
Comparative information
Consistency of presentation
Definition for going concern
Assumes the entity will continue operating unless stated otherwise
Definition for materiality
Only include information that would influence users decisions
What are the components of financial statements?
Statement of financial position
Statement of profit or loss + statement of other comprehensive income OR statement of comprehensive income
Statement of changes in equity
Statement of cash flows
Notes to the accounts
Comparative information for the preceding period
Should financial statements be prepared on the going concern basis?
YES, unless the entity intends to cease trading oH
How are material items presented in the financial statements?
Separately
What is the general rule with offsetting?
Assets and liabilities, and income and expenses, may not be offset unless required or permitted by an IFRS.
Under the frequency of reporting how often should financial statements be presented?
At least annually.
Can you group non material items together?
Yes, they must be of the same nature
What are current assets?
expected to be realised, sold or consumed in the entity’s normal operating cycle
held primarily for the purpose of trading
expected to be realised within 12 months after the reporting period
What are current liabilities?
Expected to be settled within the entity’s normal operating cycle
held for purpose of trading
due to be settled within 12 months after the reporting period
What is the operating cycle?
The time between the acquisition of assets for processing and their realisation in cash or cash equivalents.
What does the statement of comprehensive income include?
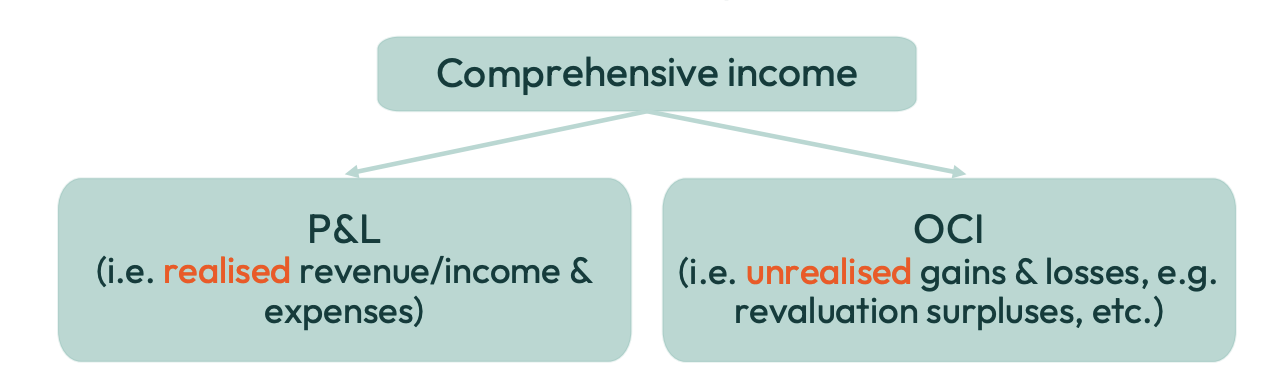
What is the statement of changes in equity?
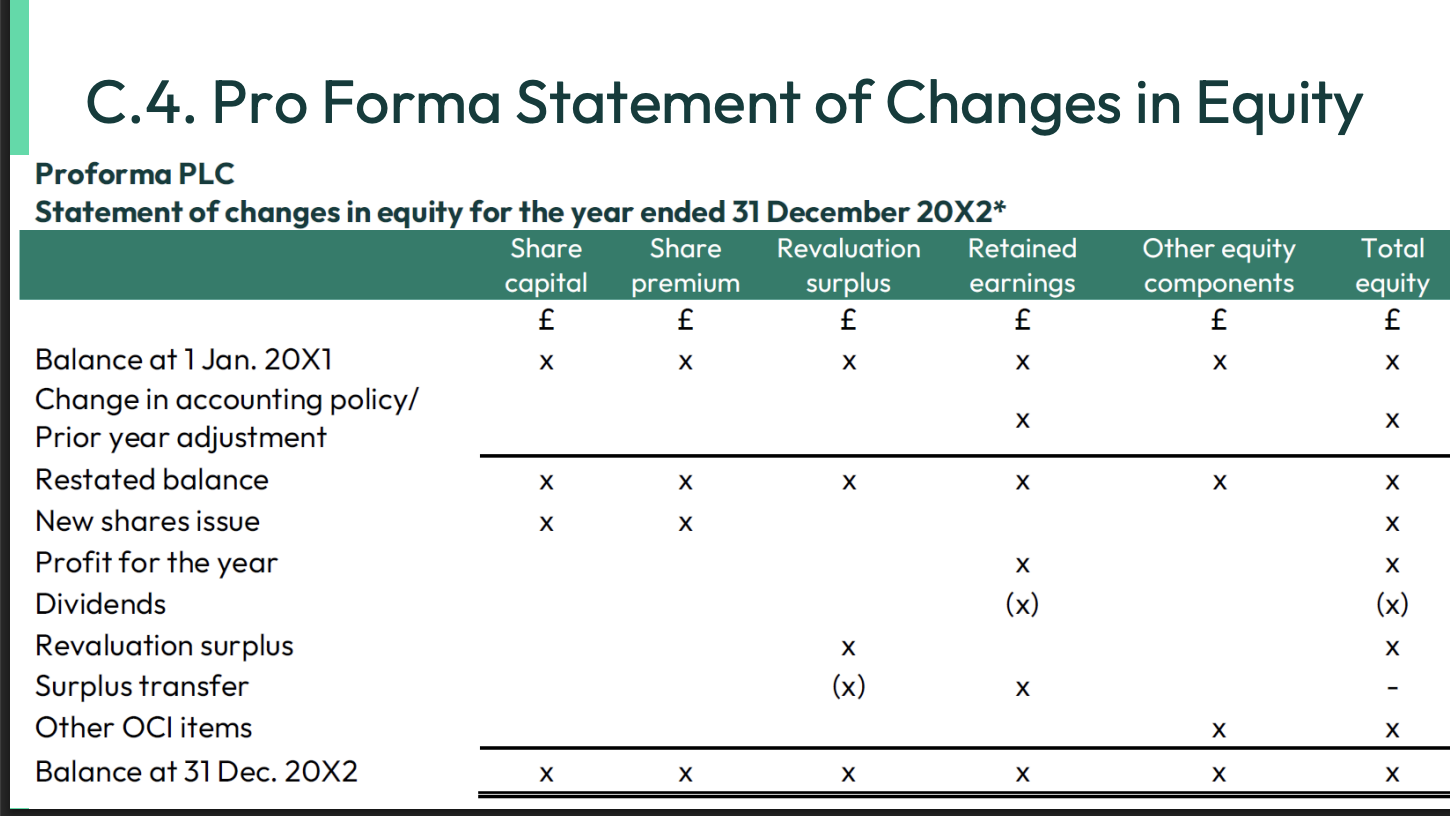
What is the only other comprehensive income I need to know for this module?
Revaluation Surplus
What is the updated formula for SOCIE?
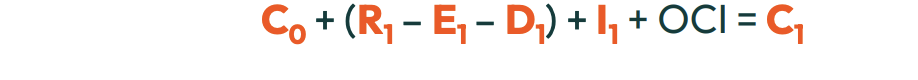
What should notes to the accounts include?
A statement of compliance with IFRS
Information about the basis of preparation of FS and the specific accounting policies used
What is conceptual framework?
A system of interrelated concepts that underpins the preparation and presentation of financial statement.
Is conceptual framework mandatory?
NO, it is not a mandatory pronouncement that reporting entities must comply with.
What are the 3 groups of people that the conceptual framework helps?
Standards setter- they develop accounting standards
Preparers- develop consistent accounting policies
All parties- understand and interpret accounting standards
What are the 7 components of conceptual framework?
Objectives of financial reporting
Qualitative characteristics of useful financial information
Financial statements and the reporting entity
The elements of financial statements
Recognition and derecognition
Measurement
Presentation and disclosure
Explain the first component of conceptual framework: Objectives of financial reporting
The purpose is to provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to existing and potential investors, lenders and other creditors in making decisions about providing resources to the entity.
Useful information helps primary users to assess what?
Decision usefulness- The prospects for future net cash inflows to an entity
Stewardship- How efficiently and effectively the entity’s management and governing board have discharged their responsibilities to use the entity’s resources.
What are the two types of qualitative characteristics?
Fundamental - relevance and faithful representation
Enhancing- Comparability, Verifiability, Timeliness and understandability
What are the enhancing qualitative characteristics?

Are both fundamental qualitative characteristics essential to financial information being useful?
Yes, both relevance and faithful representation are needed.
When it comes to financial statements and the reporting entity what should financial information consist of?
Statement of financial position- showing recognised assets, liabilities and equity
Statement of profit or loss- showing the entity’s income and expenses
Other statements/notes
What are financial statements prepared on the assumption of?
That the reporting entity is a ‘going concern’ and will continue in the foreseeable future.
What is a reporting entity?
An entity that chooses, or is required to, prepare financial statements.
Not necessarily a legal entity
What is the definition for an asset?
A present economic resource (a right that has the potential to produce economic benefits)
Controlled by the entity
As a result of past events
Explain how rent prepayment is an example of an asset?
Right= to receive future accomodation service
Controlled= tenancy agreement confers legal rights
Past event= Payment of cash to the landlord in advance
What is the definition for a liability?
A present obligation
To transfer an economic resource
as a result of past events
Explain how a loan is a liability?
Present obligation= legal duty (to pay the lender) that the entity has no practical ability to avoid
Transfer of economic resources= cash payments to the lender
Past event= the act of borrowing
Definition for equity?
The residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities
Definition for income
Increases in assets, or decreases in liabilities
that result in increases in equity
other than those relating to contributions from holders of equity claims
Definition for expenses
Decreases in assets, or increases in liabilities
that result in decreases in equity
other than those relating to distributions to holders of equity claims
What is recognition?
Including an item that meets the definition of one of the financial statement elements in P&L or SFP.
Should an item be recognised in the financial statement?
An item is recognised only if it provides information that is useful to users
Info must be relevant to user needs
Info must offer a faithful representation
When might we NOT recognise an item?
There is uncertainty as to whether the asset or liability exists
The probability of an inflow, or outflow of economic benefits is low
There is a very high level of ‘measurement uncertainty’ regarding the item
What is derecognition?
The removal of all (or part) of a recognised asset or liability
Asset: Normally when an entity loses control of that asset (e.g. disposal)
Liability: When the entity no longer has a present obligation for that liability (full repayment of debt)
What is component six in conceptual framework?
Measurement- assigning monetary amounts at which the elements of the financial statements are to be recognised and reported.
What are the different types of measurement?
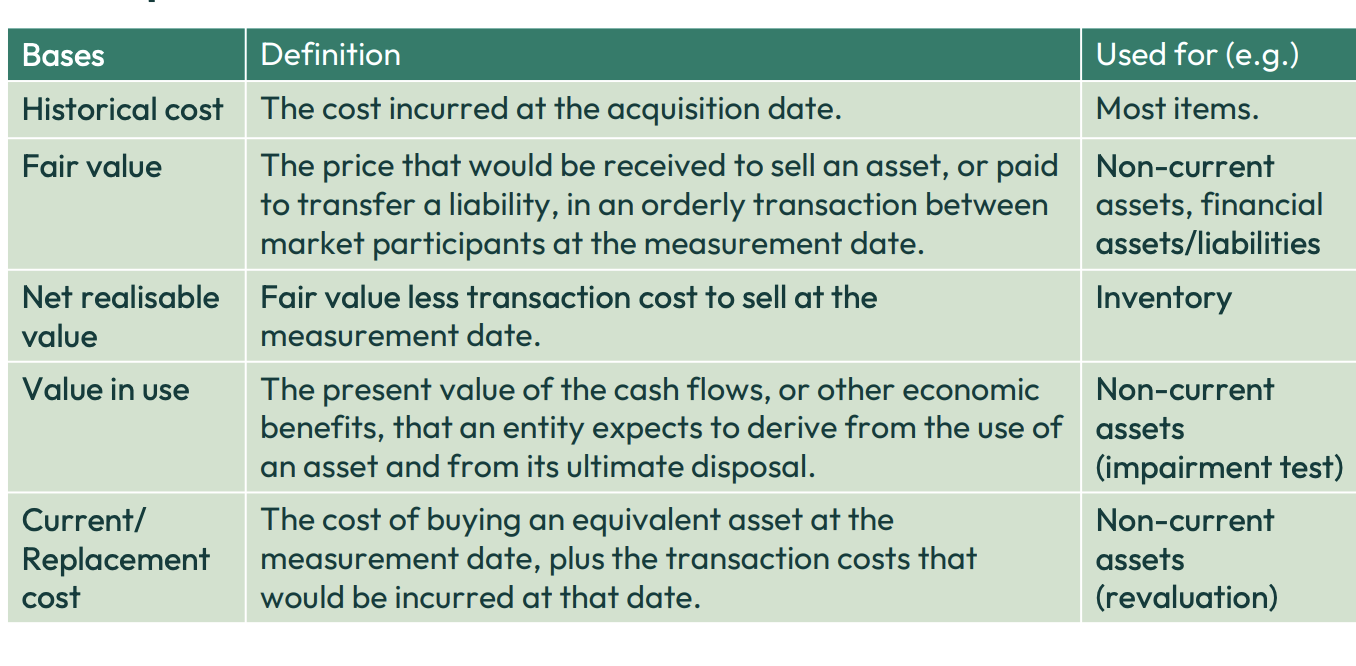
What does the conceptual framework recommend when considering which measurement basis to use?
Relevance
Faithful representation
Measurement consistency
What is component 7 of the conceptual framework?
Presentation and Disclosure
What is included in Presentation and disclosure?
Effective communication of financial information enhances relevance and faithful represenation
Effective communication requires that: Information is classified in such a way that similar items are grouped together, and dissimilar items are separated.
Information is aggregated in such a way that both unnecessary detail and excessive aggregation are avoided.
Definition for relevance?
Information must be capable of influencing decisions (including materiality)
Definition for faithful representation?
Information must be complete, neutral, and free from error
What is PPE defined as?
Tangible items held
for use in the production or supply of goods or services
for rental to others
for administrative purposes
expected to be used during more than one period
What are some examples of PPE?
Land and buildings
Plant and machinery
Office equipment, motor vehicles, fixtures and fittings
When would the cost of an item of property,plant and equipment be recognised as an asset?
If it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the entity
the cost of the item can be measured reliably
Is revenue expenditure e.g. routine servicing, repair and maintenance,small spare parts part of PPE?
No but they are expensed through P&L
What happens to the signifcant components of PPEs?
Major parts of a PPE should be identified (and depreciated separately)
Replacement of major parts should be treated as additions to PPE
What happens to the costs of major inspections on PPE?
Some PPEs will require major inspections in order to be operated continually If the recognition criteria are met, the cost of major inspections is to be treated as an addition to that PPE
What is measurement in relation to PPE?
An item of PPE that qualifies for recognition as an asset shall be measured at its cost
What are the elements of cost?
Purchase price
Costs directly attributable to bring asset to location and condition for it to be capable of operating in the manner intended by management
Estimates of costs of dismantling/removing item and restoring the site, obligation for which arises when the item is acquired or used
What are costs excluded from PPE?
Costs of introducing a new product or service
Costs of conducting business in a new location or with a new class of customer
Administration and other general OVERHEAD costs
Costs incurred AFTER the PPE can operate in the manner intended
What are the 2 ways of measuring PPE by subsequent measurement?
Cost Model
Revaluation Model
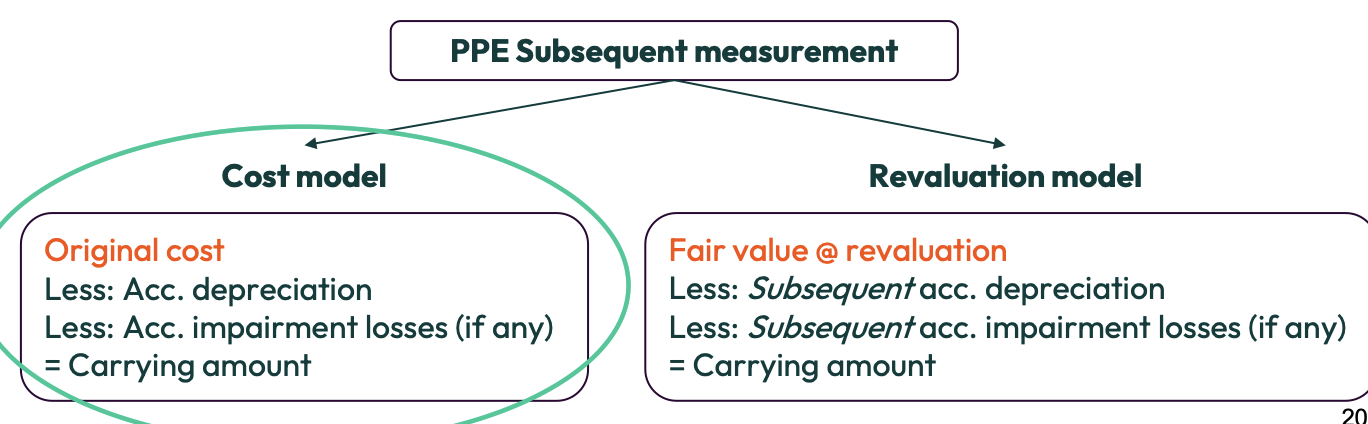
What is the cost model? (formula)
Original cost - acc depreciation - acc impairment losses = carrying amount
What is the cost model? (definition)
Assets are recorded at what they cost less depreciation and impairment
When using the cost model to measure PPE must it be applied across an entire class of PPE?
Yes
What does it mean, a class of PPE?
A grouping of assets of a similar nature.
e.g. land,buildings,machinery, motor vehicles
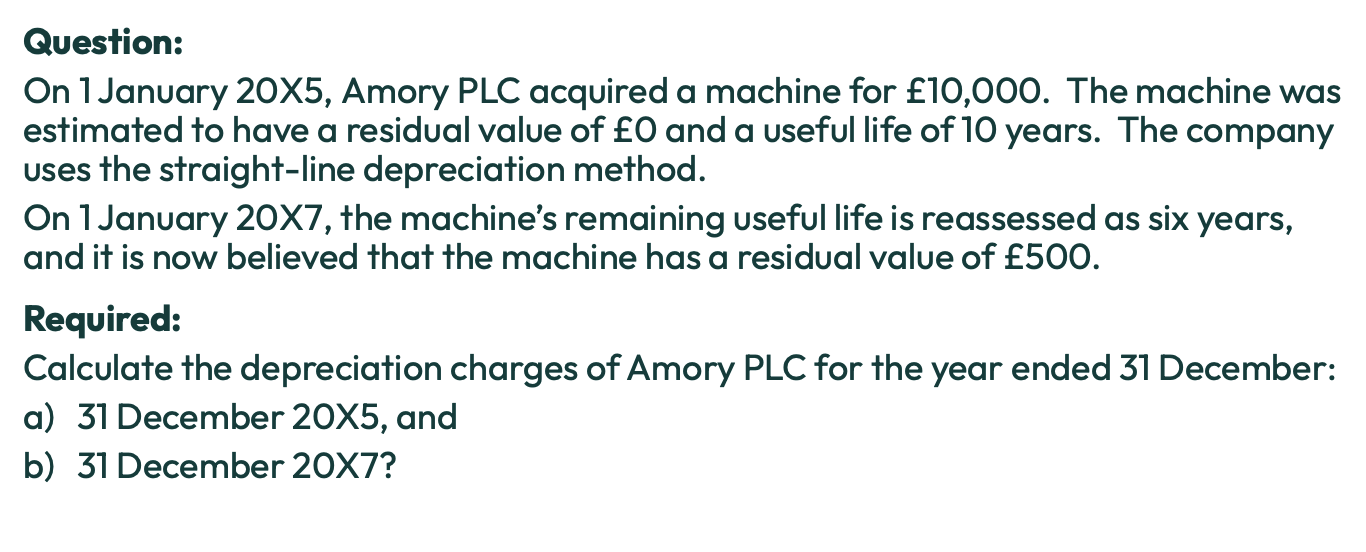
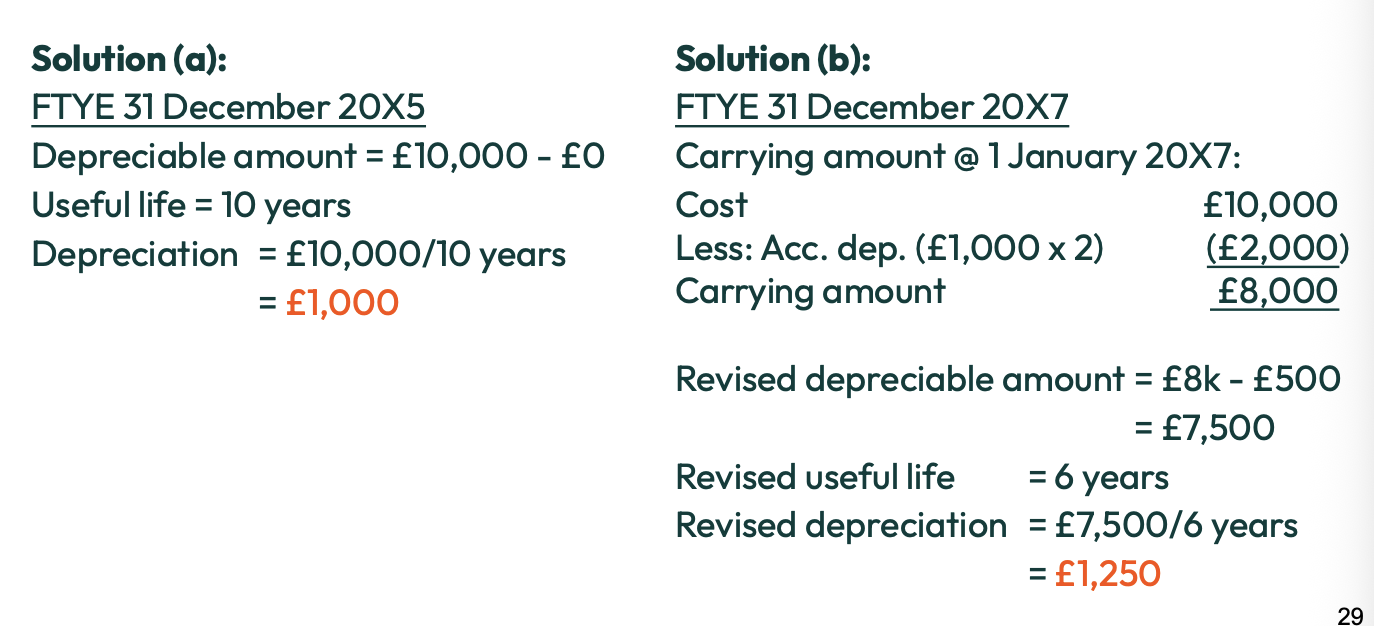
Depreciation definition?
The systematic allocation of the depreciable amount of an asset over its useful life
What is depreciable amount?
The original cost - residual value
When do we charge depreciation?
When the asset is capable of operating in the manner intended by management
When would depreciation cease?
If the PPE is derecognised or classified as held for sale
Depreciaition doesn’t cease when the PPE has become idle
Definition for accumulated depreciation?
Total amount of depreciation that has been charge on an asset since the date it was acquired
Formula for carrying amount?
Cost - acc depreciation
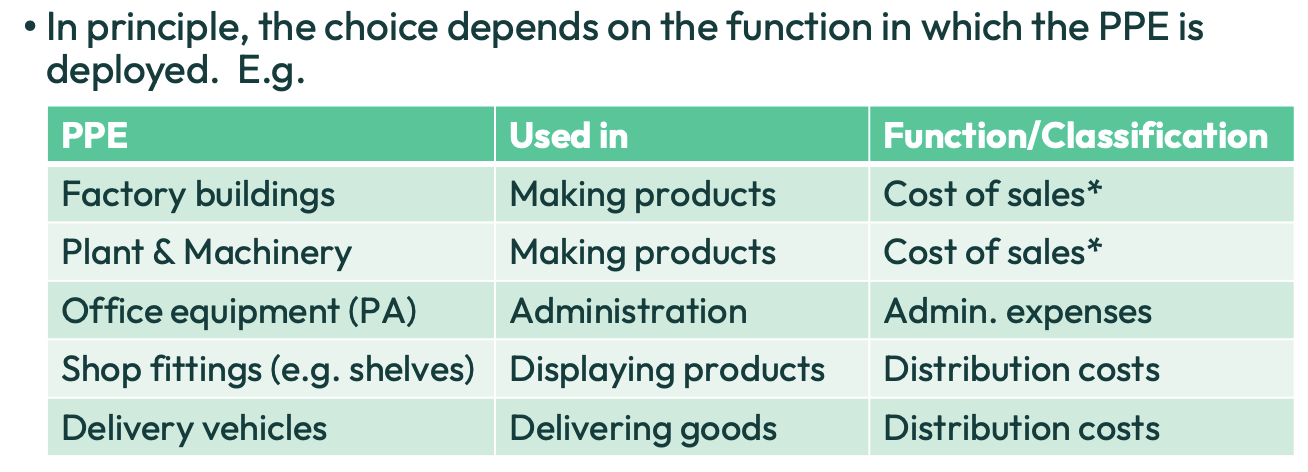
Where do we present depreciation in the P&L statement?
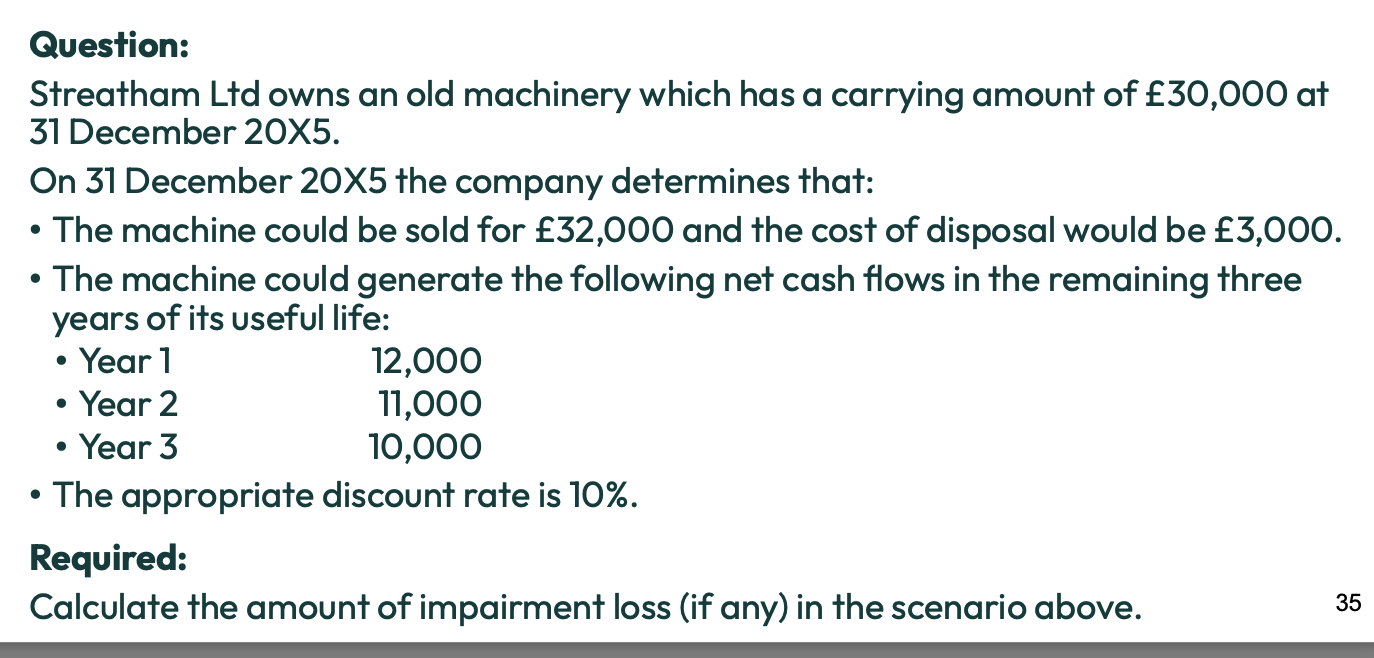
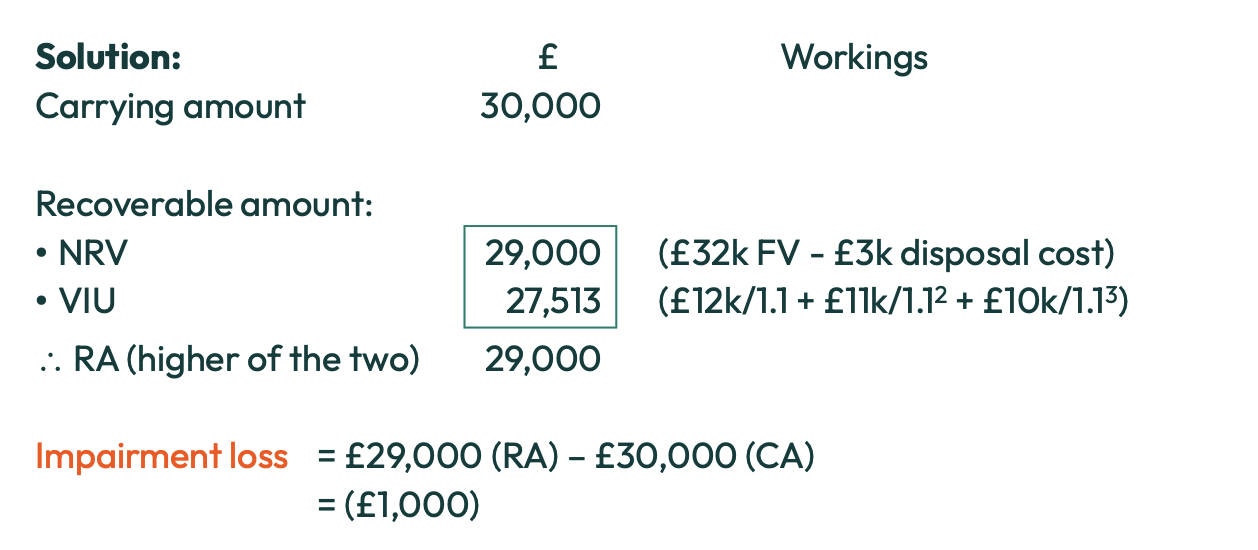
What is recoverable amount?
Amount that could be recovered through the use or sale of the asset
What is impairment?
An asset’s carrying amount is greater than its recoverable amount
The asset’s value must be reduced on the SFP
impairment loss is record in SPL
What is the recoverable amount of an asset the higher of?
Fair value - costs of disposal (NRV)
Value in use
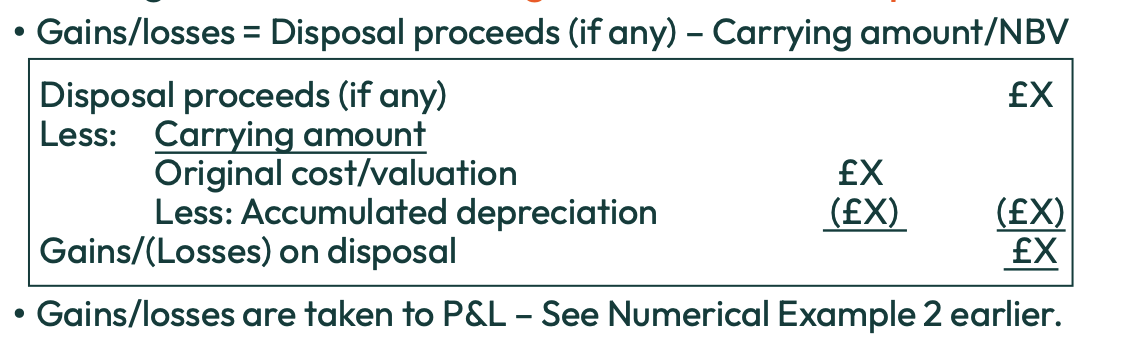
When should a PPE be derecognised?
It is disposed of
No further economic benefits are expected from its use or disposal
Does Derecognition lead to gains or losses on disposal?
Yes
What is the convention of consistency?
An entity should use the same accounting policies from one accounting period to the next unless a justified change is required
What does IAS 16 say about the property in PPE?
it is acquired for use in an entity’s operation and is generally used up over the period of its useful life.
What does IAS 40 define investment property as?
Land or buildings ( or both, or part of a building) held to earn
rentals or capital appreciation or both
rather than for use in the production or supply of goods and services or for administrative purposes or sale in the ordinary course of business