Atomic structure and radioactivity
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are the basic features of a atoms structure?
The atom size is 1×10-10cm
The nucleus is less than 1/10000 of the radius of the atom
The nuclues contains protons (positive) and neutrons (neutral) meaning the nuclues has a positive charge
Surrounded by electrons (negative) in energy levels
Atoms have a overall negative charge
What are happens to the energy levels further from the nucleus?
They have higher energy then shells closer to the nuclues
How do electrons change energy levels if they lose or gain energy?
If the atom absorbs electromagnetic radiation an electron can move from a lower energy level to a higher energy level
The atom can now emit electromagnetic radation and the electron returns back to the lower energy level
The electromagnetic radation by transfering energy to the or taking it back
What does the atomic number show?
The number of protons and electrons
What does the mass number show?
Protons and neutrons
How do we find the number of neutrons?
Subtract the atomic number and mass number
What are isotopes?
Isotopes of atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
What are ions?
Atoms can lose electrons from their outer shells which are shown with postive or negative ions
Loose electron = +1 charge
Gain electron = -1 charge
What did ancient greeks belive atoms where?
Tiny spheres which cannot be divided that make up everything
What was discovered in 1897 by scientist?
Atoms contain tiny negative particles called electrons
This showed atoms must have an enternal structure
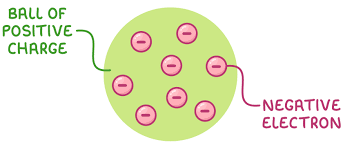
What did the plum pudding model suggest?
An atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it
Describe the alpha-scattering experiment
Take a piece of gold foil
Then fire tiny alpha particles (positive charge) at the gold foil
Why is gold foil used in the alpha-scattering experiment?
Gold can be hammered thin
What happened in the alpha-scattering model? What does the mean?
Some particles passed straight through
Told us atoms are mainly empty space
Some particles changed direction as they passed through the foil
The centre of an atom must have a positive charge meaning they must have reflected (both are postitive)
Some particles bounced off the foil
The mass of the atom must be concentrated in the centre which is now called the nucleus
Describe the nuclear model before Niel Bohr
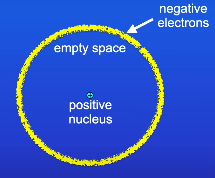
What did Niels Bohr suggest?
Electrons orbit around the nucleus at specific distances
These orbits are now called energy levels/shells
Describe the updated nuclear model after Neils Bohrs discovery
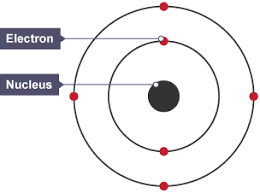
What did James chadwick discover?
Neutrons
What do some isotopes have?
A unstable nucleus
What is ionising power?
When radiation collides with atoms, that can cause atoms to lose electrons and form ions
What is radioactive decay?
When the unstable nucleus in a isotope gives out radiation to become stable
Radioactive decay is a totally random process and is unpredictable
What is the activity? What is this measured in?
The rate at which the nucleus decays
This is measured in Becquerel (Bq)
1 Bq = 1 decay per second
What can we use to measure the rate of decay? What is the count rate?
Geiger-muller tube
The count rate is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector
What is the difference between count rate and activity?
Activity is the rate at which unstable nuclei decay, whereas count rate is the rate at which radioactive emissions are detected
What are the four types of radation given out while the nucleus decays?
A alpha particle
Beta particles
Gamma rays
A neutron
Describe alpha particles
Consist of two protons and neutrons
This means a alpha particle is the same as a helium nucleus
What are the properties of alpha particles?
Large and can travel around 5cm in air before they collide with other air particles and stop
Alpha particles can be stopped with a sing sheet of paper and are easy to stop → penetrating power
Very strongly ionising
Describe beta particles
An electron which is ejected from the nucleus at very high speed
A beta particle is formed inside the nucleus when a neutron changes into a proton and an electron
What are the properties of beta particles?
Beta particles can reach around 15cm in the air before stopping
Beta particles can be stopped by a few millimetres of aluminium → penetrating power
Quite strongly ionising
Describe gamma rays
Not particles
A type of electromagnetic radiation
What are the properties of gamma rays?
Gamma radiation can travel several metres in air before stopping
Gamma rays can be stopped by several centimetres of lead → penetrating power
Weakly ionisng
Describe a neutron
Neutral charge
What does a nuclear equation show us?
Shows us whats produced when radioactive nucleus decay
What is the rule of alpha decay?
During alpha decay, the atomic number decreases by 2
During alpha decay, the atomic number decreases by 4
Example of alpha decay
Has two protons and neutrons which is the same as a helium atom
Alpha decay is represent by the helium symbol 42He
22688Ra → Rn + 42He
(radium) (radon) (alpha)
Atomic number = 88 -2 = 86
Mass number = 226 - 4 = 222
What is the rule of beta decay?
The atomic number increases by 1 but the mass number does not change
Example of beta decay
In beta decay, a neutron changes to a proton and an electron
The electron is ejected from the nucleus and becomes a beta particle (0-1e)
2913Al → ?Si + 0-1e
Atomic number = 13 + 1 = 14
Mass number = stays the same (29)
What is the rule of gamma decay?
Both the atomic number and the mass number are not changed at all
What are the two definitions of half-life?
The half-life of a radioactive isotop is the time it takes for the number of nuclei of the isotope in a sample of halve
Half-life is also the time it takes for the count rate (or activity) from a sample containing the isotope to fall to half its inital level
What is a long and short half-life?
A long half-life means it takes a while for the nuclues to decay in half whilst a short long-life means it occurs quickly
How can we work out the half-life from a graph?
Half the number of undecayed nuclei and find the point of the graph where this number lines up with the time and find that number
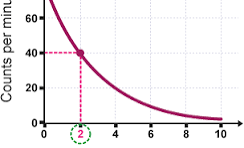
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of 15 days and an initial count rate of 200 counts per second. Determine the count rate after 45 days
15 goes into 45 3 times
So half 200 3 times
200 counts
100 counts
50 counts
What is the risk of ionising radation?
Can lead to a risk of cancer
What is irradiation?
Exposing an object to nuclear radation eg sterelisation
How are objects sterilised?
The object to be sterilised is wrapped in plastic to stop bacteria from entering
Place the object under a radioactive isotope in a lead shield to protect workers
The gamma radation irradiates the object
This kills any bacteria present
What is the key fact about irradation?
Doesnt become radioactive as the objecy only comes in contact with the radation and not the actual isotope
How can precautions be taken to avoid the affects of ionising radiation?
Shielding eg lead apron to stop beta and gamma radiation or lead walls and glass
Monitoring
What is radioactive contamination?
When unwanted radioactive isotopes end up on other materials
Why is contamination hazardous?
The radioactive atoms decay and emit ionising radiation
How dangerous is it to be contaminated by alpha radiation?
Strongly ionising but easily stopped by dead cells on the skin surface
Can be dangerous if swallowed or inhaled
How dangerous is it to be contaminated by beta radiation?
Quite ionising and can penetrate skin into the body
How dangerous is it to be contaminated by gamma radiation?
Weakly ionising and can penetrate the body but likely to pass straight through
What is peer view?
Findings scientist have made checked by other scientist