Biology(everything)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Last updated 2:25 PM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Active Transport
Type of transport that requires energy and move against the concentration gradient
2
New cards
Concentration Gradient
when the concentration of particles is higher in one area than another. Cell membrane is inside of it.
3
New cards
Passive Transport
A type of transport that requires no energy. Move along the concentration gradient
4
New cards
Hypertonic
to little
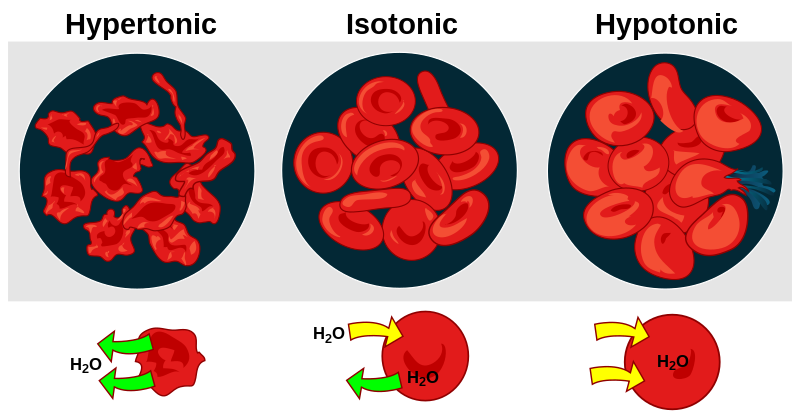
5
New cards
Hypotonic
too much
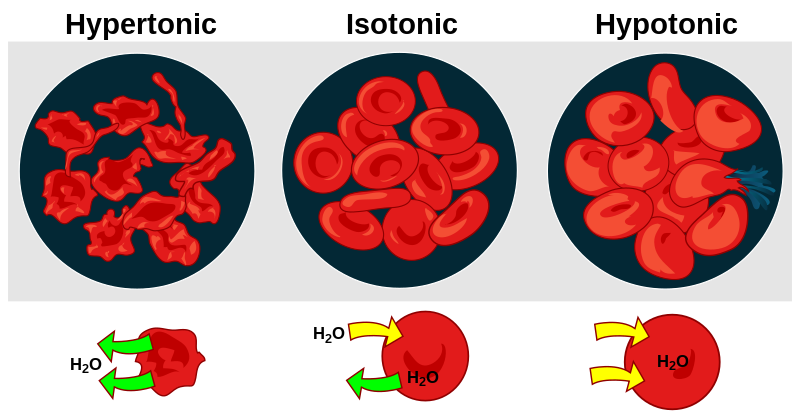
6
New cards
Isotonic
perfect amount
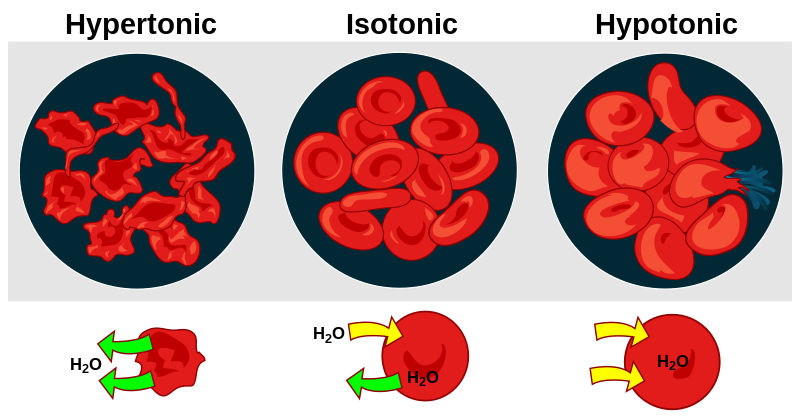
7
New cards
Qualifiers of life
made of cells, response to the environment, reproduction, adaptation, growth and development, homeostasis, energy processing, and evolution.
8
New cards
Molecules
two or more atoms
9
New cards
Atoms
smallest, have nucleus
10
New cards
Organisms
organ systems working together
11
New cards
Organs
Tissue working together
12
New cards
Tissue
formed cells
13
New cards
Cells
basic unit of life
14
New cards
Taxonomic Ranks
Domain,Kingdom,Phylum,Class,Order,Family,Genus,Species
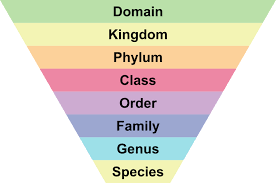
15
New cards
Prokaryotic
having cells that lack membrane-bound nuclei(They don't have a nucleus)(Pro=no)
16
New cards
Eukaryotic
having cells with membrane-bound nuclei(they have a nucleus)(Eu=do)
17
New cards
Heterotrophic
can't make their food themselves
18
New cards
Autotrophic
can make their food themselves
19
New cards
motile
moves
20
New cards
non-motile
doesn't move
21
New cards
sessile
non-motile
22
New cards
Types of Kingdoms
Archaea, Bacteria, Protist, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
23
New cards
Archaea
unicellular prokaryotic organisms that can be heterotrophic or autotrophic and reproduce asexually. Have no cell walls
24
New cards
Bacteria
unicellular,prokaryotic organisms that are motile,heterotrophic or autotrophic, and have cell walls. Reproduce asexually through cell division
25
New cards
Protist
mostly Eukaryotic,heterotrophic or autotrophic organisms that primarily reproduce asexually. Sometimes have cell walls, Unicellular,has organelles.(like a junk drawer)
26
New cards
Fungi
eukaryotic,heterotrophic,single celled or multicellular organisms. Most are sessile and can reproduce asexually,has cell walls.
27
New cards
Plantae
autotrophic,eukaryotic,multicellular organisms. Are sessile and can reproduce asexually or sexually. Have cell walls
28
New cards
Animalia
eukaryotic,heterotrophic,multicellular organisms. Are motile and most commonly reproduce sexually. No cell wall.
29
New cards
Archaea Bacteria
Domain is Archaea,prokaryotic,no organelles, unicellular,both heterotrophic and autotrophic,has cell wall
30
New cards
Amoeba
single celled,animal like,no cell wall(Protist)
31
New cards
Giant Kelp
plant like,single celled,have to touch each other to survive(Protist)
32
New cards
Types of Domains
Eukarya, Archaea,Bacteria
33
New cards
Protons
number of _______ determine type of "element"
34
New cards
monomers
smallest functioning unit
35
New cards
polymers
largest complex structure(made of of multiple monomers)
36
New cards
Biomolecules
made up of monomers
37
New cards
Carbohydrates
monomers are monosaccharides and disaccharides, gives immediate energy(Ex. sugars,fibers,starches), polymer is cellulose.
38
New cards
Lipids
hydrophobic,insulation,polymer is diglycerides,triglycerides,store energy, monomer is Glycerol and fatty acids(Ex.oil,butter,animal fat,avocado,nuts)
39
New cards
Enzymes
is a protein,monomer is amino acid, many polymer types. speed things up
40
New cards
Excretory system
Kidneys, Bladder
41
New cards
Kidneys
filters out waste
42
New cards
Bladder
creates urine
43
New cards
Circulatory system
heart,veins
44
New cards
Heart
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs and pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
45
New cards
Pulmonary Artery
pumps blood to the lungs
46
New cards
Pulmonary Vein
Brings blood back to the heart from the lungs
47
New cards
Endocrine System
Thyroid, Pancreas, Pituitary Gland, Hypothalamus, Pineal Gland, Adrenals, Gonads
48
New cards
Pancreas
breaks down food, and creates enzymes
49
New cards
Thyroid
releases hormones that control metabolism, growth, weight
50
New cards
Hypothalamus
very important, and helps stress, control center homeostasis
51
New cards
Gonads
testicles, and ovaries
52
New cards
Pineal Gland
controls blood sugar
53
New cards
Adrenals
produces adrenaline
54
New cards
Pituitary Gland
controls growth
55
New cards
Nervous System
brain, nerves, spine
56
New cards
Brain
controls everything
57
New cards
microorganism
small living thing(bacteria, protist, fungi) critical to survival
58
New cards
Body lines of defense
skin,secretions of mucus, tears, sweat,saliva, and white blood cells(wbc)
59
New cards
Immune system
recognizes, attacks and destroys the invaders. Maintains homeostasis, fights antigens, we can't survive without it.
60
New cards
Innate Immunity
protects you against all antigens; involves barriers that keep harmful materials from entering your body. These barriers form the first line of defense in the immune response.
61
New cards
Skin
1st line of defense, most important barrier against disease. Protects through sweat, oil from glands, and barrier. Nonspecific
62
New cards
Tears and Saliva
contain enzyme-lysozyme. breaks down cell wall of some bacteria.
63
New cards
Secrete Mucus
traps bacteria and other invaders, nonspecific, apart of the first line of defense.
64
New cards
cilla
small hairs that trap particles and pathogens from entering the body. located in the ear and nose. A part of the first line of defense
65
New cards
Inflammatory Response
Second line of defense, caused by white blood cells moving to the infected tissue. White cells release chemical signals that trigger the immune system to make more white blood cells. Some wbc destroy pathogens by engulfing the invader(endocytosis)
66
New cards
histamine
chemical that causes capillary vessels to dilate (swell/become larger). Dilation makes it easier for white blood cells to pass through. Dilation causes swelling, redness pain and sometimes fever.
67
New cards
Fever
increased body temp; uncomfortable environment for pathogens to survive. Type of wbc that triggers the Hypothalamus in the brain to elevate the body temp. Wbc develops,m./ at a faster rate as temp increases. Part of the second line of defense. Nonspecific
68
New cards
Specific Immunity
Immune system is able to recognize cells as healthy or unhealthy; is able to distinguish between cells of "self" or " non self" recognition based off on protein markers found on cell membrane.
69
New cards
Antigens
Protein markers on the surface of cells;bacteria, viruses, or other foreign cells, trigger an immune response. Type of response depends on the type of it
70
New cards
Acquired Immunity
another word for Specific Immunity; Natural immunity is acquired from exposure to the disease organism through infection with the actual disease.
71
New cards
lymphocytes
white blood cells; two types, provides immunity against antigens
72
New cards
B lymphocytes
one type of wbc; provides immunity against antigens within plasma and other body fluids
73
New cards
T lymphocytes
one type of wbc ; provides immunity against antigens within cells
74
New cards
Cellular Immunity
Wbc in 2nd line of defense ingest infected cells, enzymes inside wbc remove protein markers and display them on their cell membrane surface. T-cells bind to these wbc and activate development of more T-cells. T-cells differentiate into either killer or helper T-cells.
75
New cards
Killer T-cells
travel to infected site, attaches to infected cell and releases enzymes that destroy it. Produces memory cells
76
New cards
Helper T-cell
stimulate killer T-cells
77
New cards
Memory cells
remember past invaders and destroy them when they come back
78
New cards
Antibody Immunity
when antigen makes it past 1st and 2nd line of defense, helper T-cells trigger wbc called B lymphocytes to activate and develop
79
New cards
B lymphocytes
type of wbc; differentiate into memory and antibody producing cells
80
New cards
Antibody
protein carried in the blood stream that binds to an antigen; Y-shaped and fits into an antigen like lock and key. Specific to each invader. Making new ones takes about 7 days
81
New cards
Lysogenic Cycle
a cycle of viral infection, replication, and cell destruction.
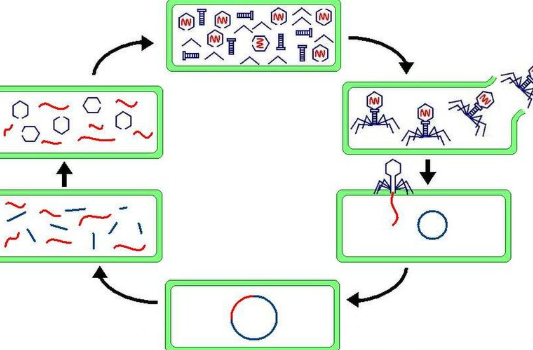
82
New cards
Chemotrophs
make their own food by obtaining their energy from inorganic molecules
83
New cards
Decomposers
Prokaryotes that break down dead organisms and wastes
84
New cards
Lytic Cycle
a cycle where a virus can replicate its DNA using a host cell.
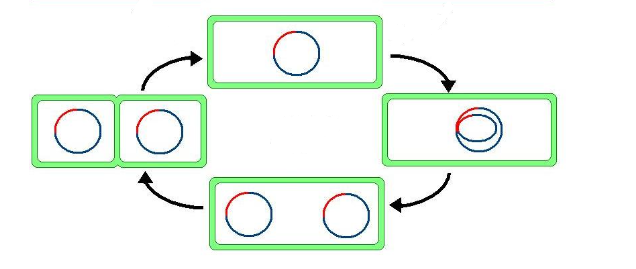
85
New cards
viruses are surrounded by a protective protein coating; they don't have cell walls that can be attacked by antibiotics like bacteria does. Antibiotics Alter the Metabolic State of Bacteria, which Contributes to the Resulting Death or Stasis.
Why antibiotics affect bacteria but not viruses?
86
New cards
Capsid
The protective outer coat of a virus
87
New cards
Pili
short, thin, hair-like projections inside E Coli. These can help it stick to other cells or transfer genetic material.
88
New cards
Conjugation
the process through which bacterial cells transfer pieces of genetic material using pili.
89
New cards
No, they are completely dependent on their cellular hosts for energy production and protein synthesis. They replicate only within cells of the host that they infect.
Do viruses have organelles?
90
New cards
Vaccine
a weakened form of a pathogen that is put into someone to help them build immunity to that certain pathogen.
91
New cards
Bacteriophage
viruses that infect and replicate only in bacterial cells.
92
New cards
Retrovirus
any of a group of RNA viruses which insert a DNA copy of their genome into the host cell in order to replicate. (Ex. HIV.)
93
New cards
The lock and key model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate are equal shaped. It supposes that the substrate fits perfectly into the active site of the enzyme.
What does a lock and key infection mean?
94
New cards
Some protists are harmful, as they cause severe diseases like Malaria, Sleeping sickness, Amoebic Dysentery. But many protists are beneficial, as they are the foundation for food chains, produce the oxygen we breathe, and play an important role in nutrient recycling.
What are the benefits and harms of protists?
95
New cards
are used in the production of enzymes, organic acids, vitamins, and antibiotics; can also destroy crops, cause diseases in humans (Ex. candidiasis and ringworm), and ruin clothing and food with mildew and rot.
What are the benefits and harms of fungi?
96
New cards
Antibiotics
medicines that fight bacterial infections in people and animals.
97
New cards
Obligate Aerobes
an organism that requires oxygen to grow
98
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
organisms that can grow and survive only in the absence of oxygen.
99
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
bacteria that can grow in both the presence or absence of oxygen.
100
New cards
Carl Linnaeus
developed taxonomy