Task A. Human Factors
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Hypoxia
A state of oxygen deficiency in the body.
Hypoxic Hypoxia
A result of insufficient oxygen available to the lungs
lack of oxygen absorbed by the body due to atmospheric conditions
Its the most common form of hypoxia
What causes hypoxic hypoxia?
Pilots: The reduction in partial pressure of oxygen at high altitude
blocked airway or drowning
Hypemic Hypoxia
When the blood is not able to carry a sufficient amount of oxygen to the body's cells
What causes hypemic hypoxia?
Blood Loss
Blood diseases
anemia
deformed blood cells
Hemoglobin is unable to bind oxygen molecules
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Smoking
Stagnant Hypoxia
Oxygen deficiency in the body due to poor circulation of blood
What causes Stagnant hypoxia?
Occurs from excessive G's, Cold Temps, or Shock
Histotoxic Hypoxia
The inability of the cells to effectively use oxygen
“Histo” - refers to tissues or cells
“Toxic” - means poison
What causes histotoxic hypoxia?
Drugs
Alcohol
Narcotics
Poisons
What are some symptoms of hypoxia?
Cyanosis
(Blue fingernails and lips)
Feeling of euphoria
Tingling in extremities
Lightheaded / Dizziness
Headache
Confusion
Drowsiness
What are some treatments you can do to combat hypoxia?
Descend to lower altitude
To increase amount of O2 available
Use Supplemental oxygen
What is Useful Consciousness?
Max time to make and carry out rational decisions without supplemental oxygen
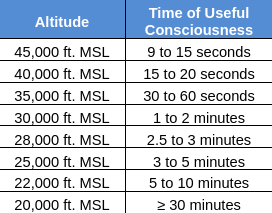
Define Hyperventilation
A breathing rate and depth increase which causes a deficiency of CO2 in the body
What causes Hyperventilation?
Stress
Panic
Anxiety
Hypoxia
What are some symptoms of Hyperventilation?
Feeling of Suffocation
Tingling in extremities
Visual Impairment
Lightheaded or dizzy sensation
Hot and cold sensations
Muscle spasms
Unconsciousness
Rapid heart rate & breathing
Treatments for hyperventilation?
Manually slow and control your breathing back to normal
Talking out loud
Breathing into a paper bag
If unsure, treat for hypoxia (the more dangerous situation)
What are Middle Ear Problems/
Difference in the pressure of the outside air the body and inside the middle ear/nasal sinuses
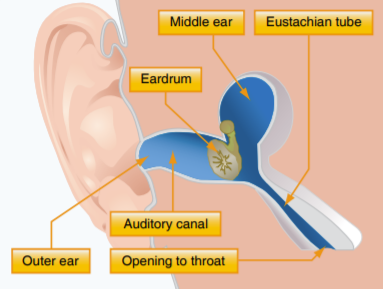
What causes the massive differences in pressure with Middle Ear Problems?
After being at higher altitudes for longer periods of time, when you begin to descend the Eustachian Tubes can close due to the increase in pressure
Excessive pressure for long enough time can result in pain &/or ruptured ear drums
What are some symptoms of middle ear problems?
Severe pain in the ear
Reduce hearing sensitivity
What are some treatments to help middle ear problems?
Yawning
Swallowing
Chewing gum
Valsalva maneuver
How would a sinus problem affect us as pilots?
Usually, our sinus pressure equalizes with pressure at altitude
To much congestion can prevent the pressure from equaling out
What are some symptoms from sinus problems?
Severe Sinus pain
Upper tooth pain
Bloody mucus
What are some treatments to help sinus problems?
Slow descent rates
DO NOT FLY with sinus problems
What is Spatial Disorientation?
Lack of orientation with regard to the:
Position
Attitude
Movement
of the airplane in space
What are the different orientation systems are body uses?
Visual
The eye, by far the largest source of information
Somatosensory
Nerves that sense position based on gravity, feeling, and sound
Vestibular System
Motion sensing system in inner ears
Reports head position, orientation, movement
How does spatial disorientation happen?
A disagreement between 1 or more of the bodies orientation systems
How to counter the sensations from Spatial Disorientation?
Recognize the problem
Disregard the false sensations
Rely on the flight instruments
What is motion sickness?
When your brain gets conflicting info with the body between what it sees and what it feels
What are some symptoms of motion sickness?
General discomfort
Nausea
Dizziness
Paleness
Sweating
Vomiting
What are some steps to help treat motion sickness?
Getting fresh air
Open outside air vents
Loosen clothing
Focus on Non-moving objects outside the airplane
Avoid unnecessary head movements
Fly smooth, straight and level
Land as soon as able
What is Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning?
A tasteless, colorless, and odorless gas that decreases the bloods ability to carry oxygen
Caused by damaged/ leaking exhaust system
How does Carbon Monoxide Poisoning effect the body?
Hemoglobin in your blood is used to transport oxygen to other parts
CO is able to bond with the hemoglobin 200 to 300 time easier than oxygen can
It prevents the hemoglobin from transporting oxygen (hypemic hypoxia)
What are some symptoms of CO poisoning?
Hypemic hypoxia
Headache
Blurred vision
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Loss of muscle power
Chest pain
Confusion
What are some ways to detect CO poisoning?
CO Detectors
Watching for symptoms
Strong odor of exhaust gas
What to do if we detect CO in the cockpit?
Turn off cabin heater
Open all air vents
Use supplemental oxygen
Descent to lower altitude
Land ASAP
2 different categories of stress & fatigue?
Acute
short term
Chronic
long term
Define Fatigue
State of feeling tired, weary, or sleepy that results from
Prolonged mental or physical work
Extended periods of anxiety
Exposure to harsh environments
Loss of sleep.
Define acute fatigue
It is the occurrence from doing everyday life
It can degrade us throughout the day
A proper diet & enough rest helps to recover
Define chronic fatigue
Fatigue over a long period of time – usually has psychological roots or underlying disease
Caused by high-stress levels over larger periods of time
seek treatment/ help with very prolonged rest to help treat
Define Stress
The body’s response to physical and psychological demands placed upon it
Define acute stress
Short term stress
Things that activate our fight or flight
On-going acute stress can develop into chronic stress
Define chronic stress
Stress that exceeds the ability to cope
Caused by constant streams of demands, risks, pressures, & threats that go on for long periods of time
DO NOT FLY
Define Dehydration
Critical loss of water from the body
What are some things that help lead to dehydration?
Hot flight decks / flight lines
Windy days
Humidity
Diuretic drinks
coffee, tea, alcohol, soda
What are some symptoms of dehydration?
Fatigue
inability to concentrate
headaches
cramps
tingling
sleepiness
dizziness
flush face
What are some effects of poor nutrition?
Low energy &/or low blood sugar
Hunger pains
breakdown in good habit patterns
Short attention span
Insufficient vitamin A can impair night vision
Define Hypothermia
The body losing heat faster than it can produce it
Normal: 98.6o F/37o C
Hypothermia: < 95o F/35o C
How to prevent Hypothermia?
COLD
Cover
Overexertion
Layers
Dry
Vestibular Illusions Acronym
ICEFLAGS
Inversion Illusion
Reason - An abrupt change from climb to straight-and-level flight
Illusion - The feeling of tumbling backwards
Result - Disoriented pilot pushes aircraft into a nose low attitude
Coriolis Illusion
Reason - A sudden head movement during a turn that disrupts the normal motion sensing
Illusion - A sensation of spinning or turning around a different axis than intended
Result - A disoriented pilot may incorrectly adjust the aircraft’s attitude to counteract the imagined motion
Elevator illusion
Reason - Abrupt upward or downward acceleration
Usually due to an updraft or downdraft
Illusion - Upward & downward acceleration creates the illusion of being in a climb or descent
Result - Disoriented pilot will push the aircraft into a nose low or nose high attitude
False Horizon
Reason - Sloping cloud formations, an obscured horizon, a dark scene spread with ground lights and stars, and certain geometric patterns of ground light
Illusions - Not being aligned correctly with the horizon
Result - Disoriented pilot puts aircraft into dangerous attitude
Leans illusion
Reason - Abrupt correction of a banked attitude of a turn entered too slowly to stimulate the motion sensing system in the inner ear
Illusion - Banking in the opposite direction
Result - Disoriented pilot rolls back into original dangerous attitude (the turn), thinking (feeling) the airplane is straight and level.
Autokinesis Illusion
Reason - Darkness
Illusion - When stared at for a period of time, a static light will appear as it is moving
Result - Disoriented pilot may attempt to align aircraft with the light and lose control
Graveyard Spiral illusion
Reason - Loss of altitude during a turn that has stopped stimulating the motion sensing system
Illusion - A seemingly Wings level descent
Result - Disoriented pilot pulls back on the controls, tightening the spiral and increasing the loss of altitude
Graveyard Spin
Reason - Recovery from a spin that has ceased stimulating the motion sensing system
Illusion - Being in a spin in the opposite direction
Result - Disoriented pilot returns the aircraft to its original spin
Somatogravic illusion
Reason - A rapid acceleration, often during takeoff
Illusion - Rapid acceleration can create the illusion of being in a nose up attitude & rapid deceleration can create the illusion of being in a nose down attitude
Result - Disoriented pilot puts the aircraft in a nose low (dive attitude) or in a nose up (stall attitude)
Optical Illusions Acrynom
G-FRRAP
Ground Lighting Illusions
Reason: Lights along a straight path, such as a road, and even lights on moving trains
Illusions: Can create the illusion of runway and approach lights
Result: The pilot may attempt to land on a path, road, or train
Featureless Terrain Illusion
Reason: An absence of ground features, as when landing over water, or darkened areas
Illusion: Can create the illusion that the aircraft is at a higher altitude than it is
Result: The pilot who doesn’t recognize this will fly a lower approach
Runway Width Illusion
Reason: A narrower or wider than usual runway
Illusion:
Narrow – Appear to be at a higher altitude than you are
Wider — Appear to be at a lower altitude than you are
Result:
Narrow – A lower than normal approach
Wider – A higher than normal approach
Runway and Terrain Slope Illusion
Reason: Sloping runway, terrain, or both
Illusion:
Upslope – Appear to be higher than you are
Downslope — Appear to be lower than you are
Result:
Upslope – A lower than normal approach
Downslope – A higher than normal approach
Atmospheric Illusions
Reason: Rain on the windscreen, Atmospheric Haze, Penetration of fog
Illusion: Rain - Illusion of greater height; Haze –Greater distance; Fog – Pitching up
Result: Rain & Haze - A lower than normal approach; Fog – steepens the approach, often abruptly
Preventing landing Illusions
Anticipate them during approaches; Use glide slope or VASI/PAPI systems whenever possible
Reason: Bright runway and approach lighting systems
Illusion: Can create the illusion of less distance to the runway
Result: The pilot who does not recognize this illusion will fly a higher approach
How Nitrogen & Scuba diving effects you when flying
Scuba diving results in a significant increase in the amount of nitrogen dissolved in the body
@ sea lvl, nitrogen is = outside and inside the body
w/ reduced atmospheric pressure, trapped nitrogen can get released
If it gets released to quickly bubbles can form in
Bloodstream
Spinal Cord
Brain
Leading to very severe pain or even death
How long should you wait after scuba diving to fly?
12 hours after a dive not requiring controlled ascent & below 8,000' MSL (+24Hours if above 8,000' MSL)
24 hours after a dive requiring controlled ascent & below 8,000' MSL
What rule do we follow with alcohol and aviation?
14 CFR part 91.17
"8 hours bottle to throttle"
8 hrs. & not feeling the alcohols effects is safest
Histotoxic hypoxia
Altitude multiplies the effects of alcohol on the body
What rules do we follow with drugs/ medication in aviation?
Unless FAA Approved, DO NOT FLY while taking Meds
14 CFR part 61.53
Prohibits flying if taking certain medication would prevent obtaining a medical certificate
14 CFR part 91.17
Prohibits drug use that affect you in any ways contrary to safety
Look on FAA website for approved OTC drugs
what are ADM, CRM, & SRM?
Aeronautical decision making
Crew Resource Management
Single-pilot resource management
What are some Human Factors that could lead to:
Loss of Situational Awareness?
Disorientation?
Task Prioritization Distractions?
Affected Performance?
IMSAFE
Illness
Medication
Stress
Alcohol
Fatigue
Emotion / Eating
What are the hazardous attitudes?
Macho
Anti-authority
Impulsivity
Resignation
Invulnerability
Macho antidote
Taking chances is foolish
Anti-authority antidote
Follow the rules. They are usually right.
Impulsively antidote
Not so fast, think first
Resignation antidote
I'm not helpless. I can make a difference.
Invulnerability antidote
I'm not special, It CAN happen to me
Good workload management practices?
Thinking ahead of the aircraft
Do what you can ahead of time to make situations easier to deal with
Get ATIS
Preset next needed Frequency
Run Checklists
Prepare for & recognize ahead of time any high stress/ workload situations
How to combat expectation bias?
Your experiences & expectations can influence behavior
Individuals are vulnerable to thinking they See &/or Hear what they are expecting to See &/or Hear
What are the 3 Stresses that affect performance?
Physical
Physiological
Psychological
What is Physical Stress?
Associated with the environment
Temp
Unfamiliar noises &/or vibrations
Lack of oxygen
What is Physiological Stress?
Physical conditions such as
Fatigue
Lack of physical fitness
Missed meals
Poor Sleep
Illness
What is Psychological Stress?
Social or emotional factors
Relationship Problems
Death in the family
Sick child
Money Problems
Whats the recommended altitudes for supplemental oxygen use?
10,000' day
5,000' night
Eyes require more oxygen at night
Oxygen Requirements for unpressurized cabins
12,500ft MSL to 14,000ft MSL
The minimum crew must have oxygen for flights over 30 minutes @ these altitudes
Above 14,000ft MSL
The minimum crew must have oxygen provided for the whole flight above this altitude
15,000ft MSL & Above
Passengers must be at least offered Supplemental oxygen the whole time above these altitudes
Oxygen Requirements for pressurized cabins
Above FL250
Additional 10 min of o2 is available per occupant in the event of depressurization
Above FL350
One pilot must wear o2 mask unless both pilots are at controls with quick donning masks and flight is below FL410.
If one pilot leaves controls above FL350
Other pilot must wear o2 mask regardless regardless of mask type.