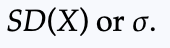MATH 1160 Week 5 - Ch 13.1-13.3 - Conditional Probability part 2 & Random Variables
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Random variable
A random variable assumes any of several different values as a result of some random event.
Discrete random variable
A random variable that can take one of a finite (or countably infinite) number* of distinct outcomes.
Discrete random variable
A random variable that can take one of a finite (or countable infinite) number of distinct outcomes
Continuous random variable
A random variable that can take on any of an uncountably infinite number of outcomes, typically, an interval (bounded or infinite) of values
Probability model or probability distribution
A function that associates a probability P with each value of a discrete random variable X, denoted
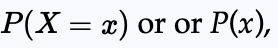
Expected value
The expected value of a random variable is its theoretical long-run average value, the mean of its probability distribution model. It is denoted u or E(X), and is found using:
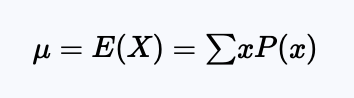
Variance
The variance of a random variable is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean. For discrete random variables, it can be calculated as:

Standard deviation
he standard deviation of a random variable describes the spread in the model and is the square root of the variance, denoted: