CPR Basic Life Support
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
causes of cardio pulmonary arrest
-anaesthetic complications
-severe trauma
-severe electrolyte disturbances
-hypovolaemia
-vagal stim
-cardiac arrhythmias
-cardioresp disorders
-debilitating or end stage disease
-myocardial hypoxia
-drugs and toxins
-pH abnormalities
-electrolyte disturbances
-temp problems
what can cause acute failure of cardio resp systems
-lack of oxygen to tissues
-unconsciousness and systemic cellular death
-cerebral hypoxia (brain death within 4-6 mins)→ Tells you how long you have to get o2 to brain and get supply back to the brain
signs of cardiopulmonary arrest
Loss of consciousness
Apnoea or agonal gasping
No corneal reflex or palpebral reflex
No heart sounds
No palpable pulse
Central eye position
Pupils fixed and dilated
Bleeding stops at surgical site
Mucous membrane grey/blue/white
CRT altered (can be normal!)
Dry cornea
General muscle flaccidity
ECG arrhythmias (VF, VT, Asystole, PEA/EMD)
can you rely on apnoea to know if CPA
takes a long time so cannot rely on this, must see sooner
CPR initial assessment
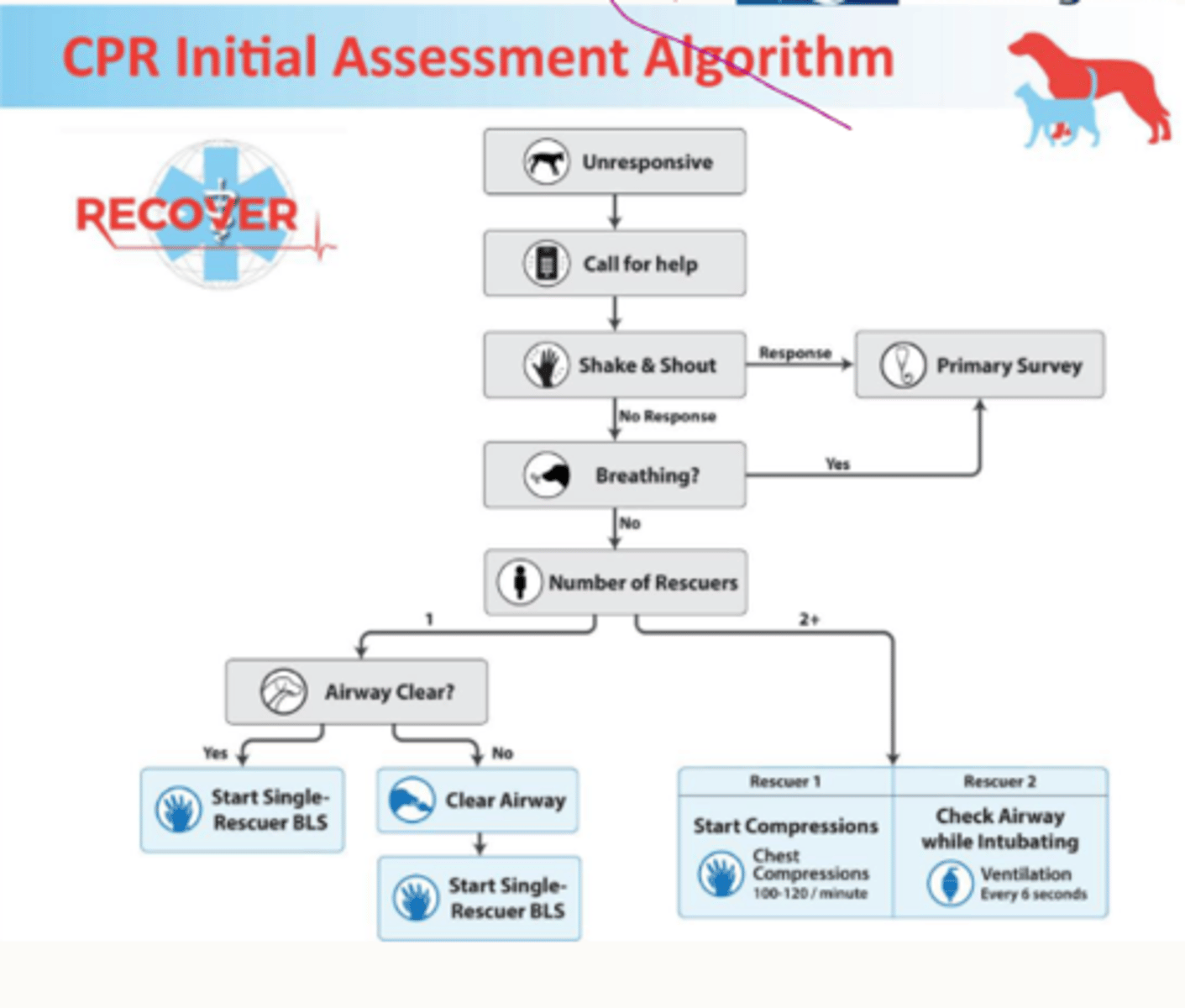
what 2 components make up basic life support
1. chest compressions
2. ventilation
how quick should you want to make a decision if dead or not
15s
how basic life support should run
2 full minutes with no pauses
-chest compressions 100-120/min
-ventilation every 6 secs
CPR algorithm
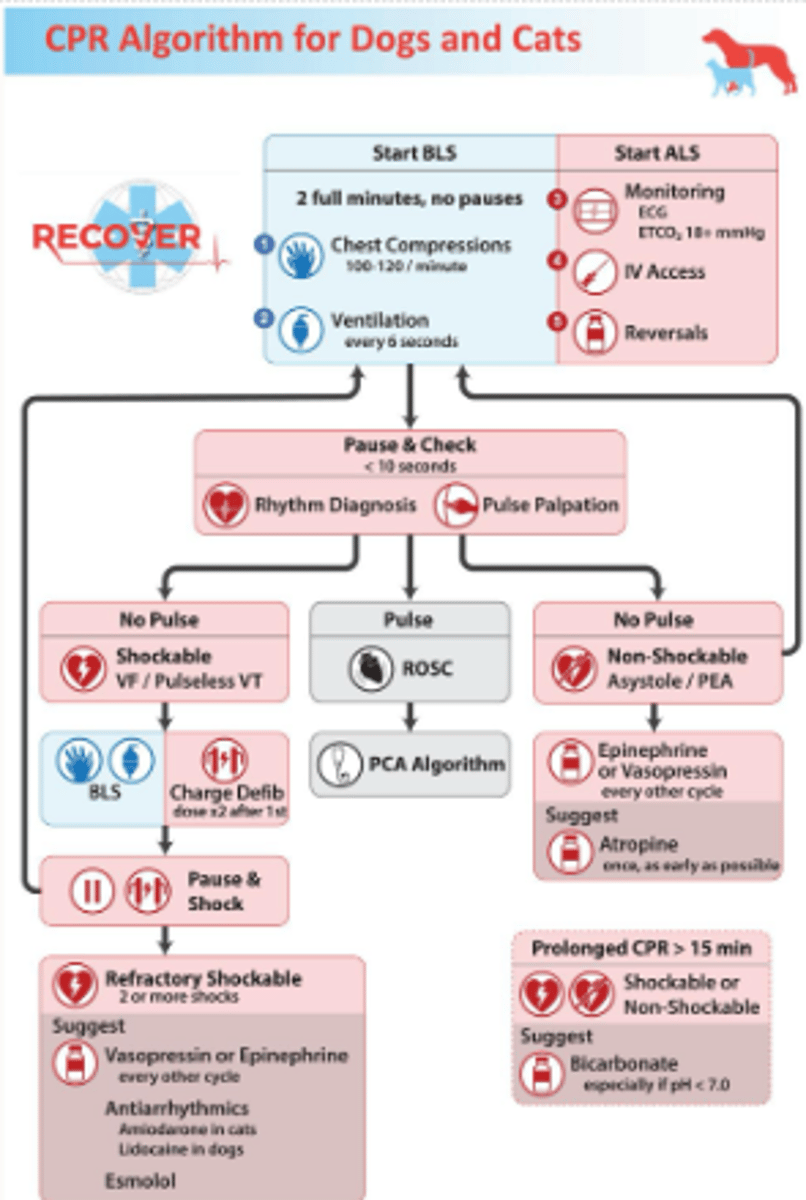
what are the 2 types of chest compressions
cardiac pump
thoracic pump
cardiac pump done in
-cats
-small dogs
-keel chested dogs (e.g. greyhound)
-rabbits
thin or compliable chest
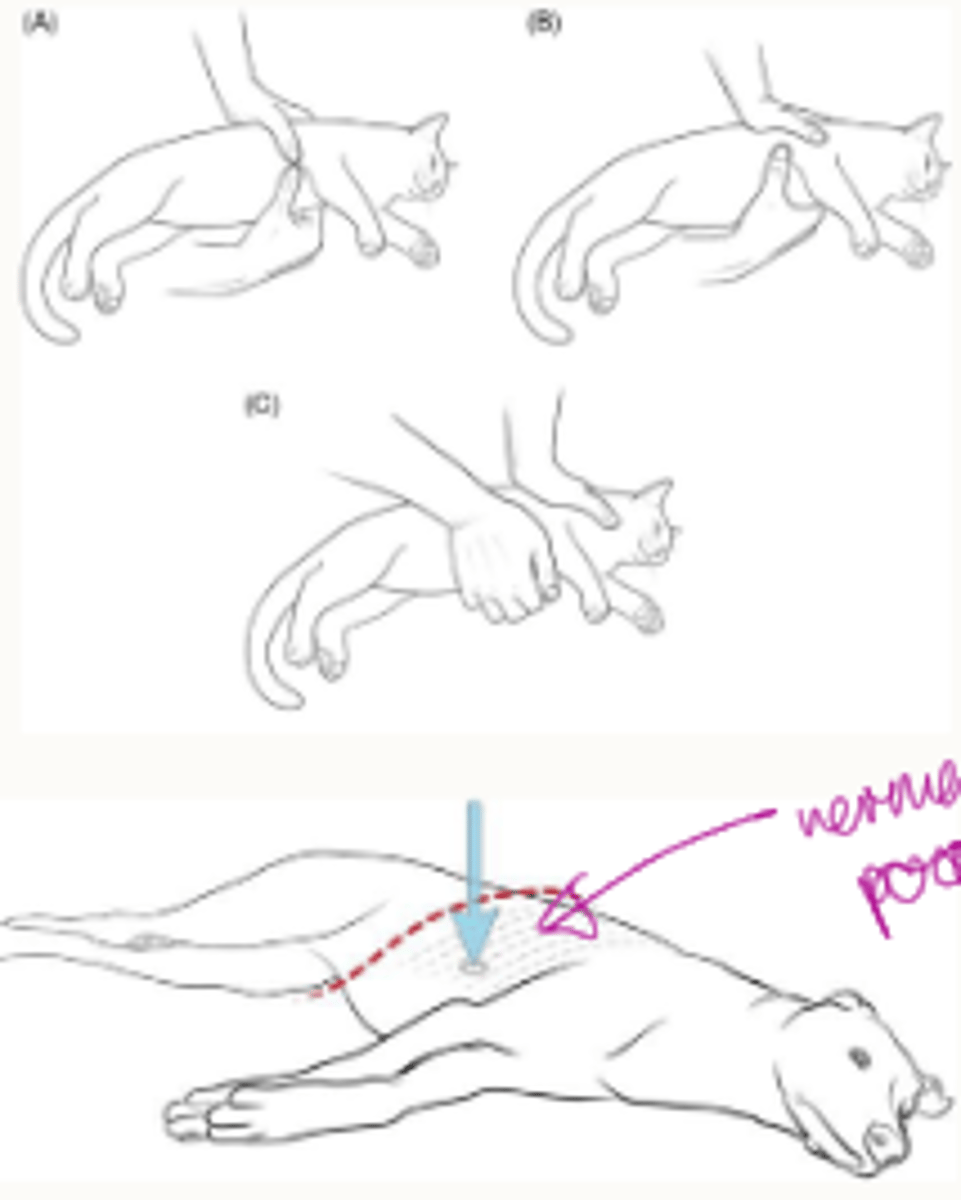
how is cardiac pump carried out
-compress ventricles
-in smaller patients: wrapping the hand around the chest
-in a larger, narrow chested breed: is the normal hand position in terms of you're holding your hands over each other and then you're compressing
down onto the chest, but you're aiming to compress over where the heart directly is
thoracic pump used in
-medium to large dogs
-foals
-calves
-sheep
how is thoracic pump carried out
-don't have the ability to compress directly over the heart because they've got a wider chest.
-place hand over widest part of chest
-or on their back if v wide chest
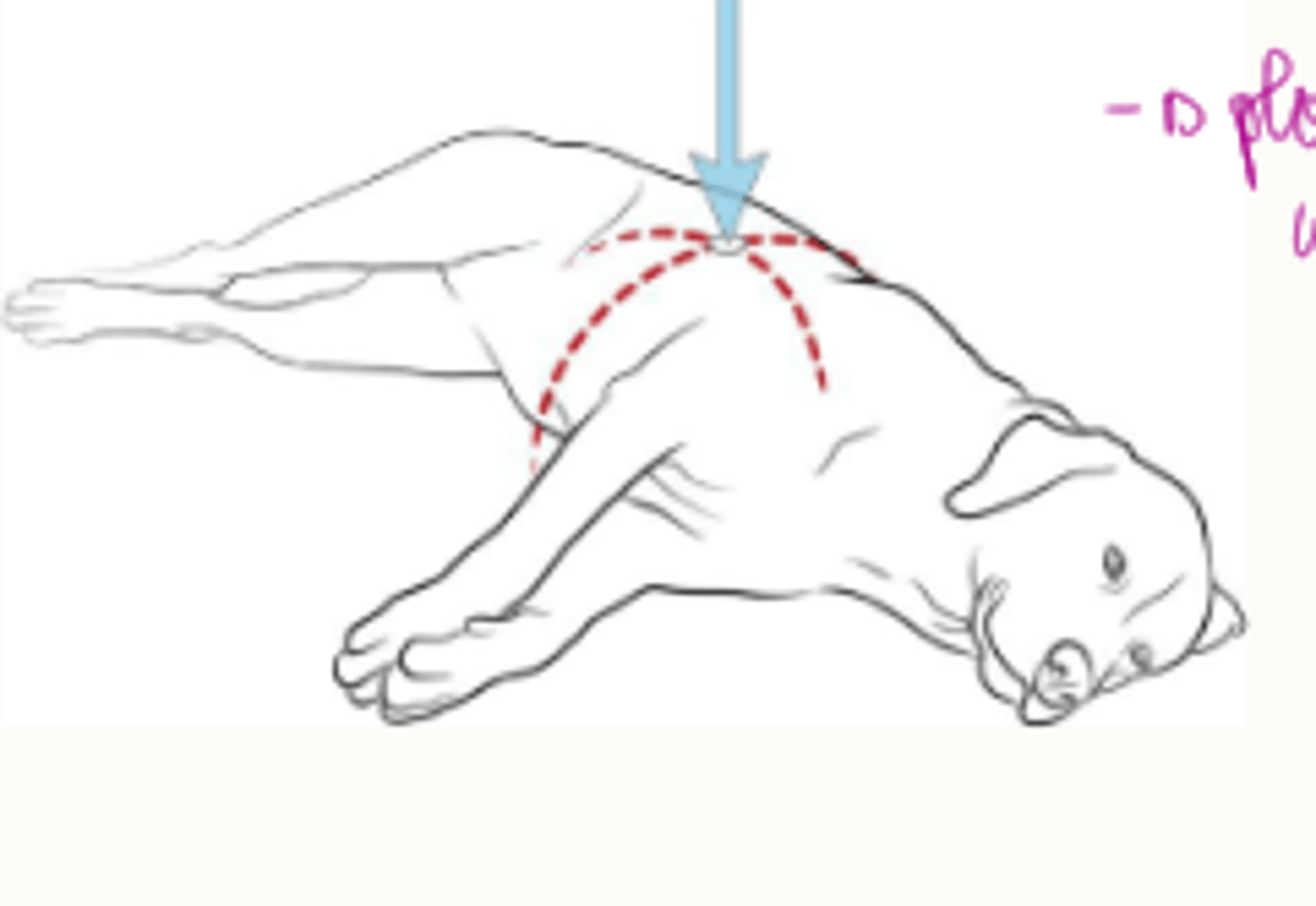
CPR in bull dogs
on back
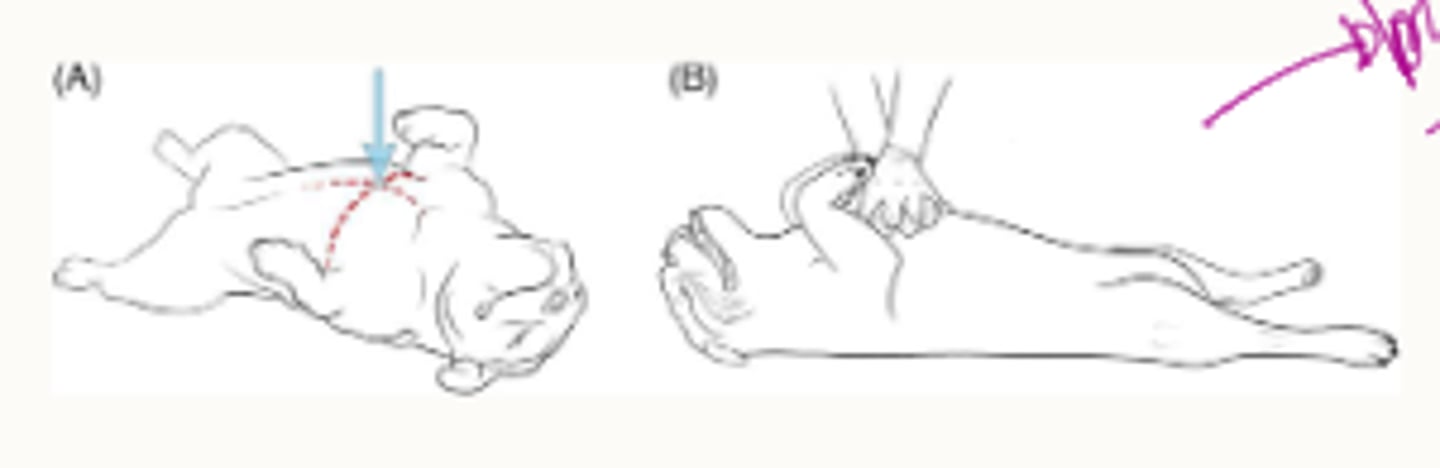
cardiac pump focus
-pumping ventricles of heart
-ventral 1/3 thorax, ribs 3-6
how many pumps per mins in cardiac pump
100-120 per 2 mins
when is the cardiac pump less effective
-obesity
-pericardial effusion
-pneumothorax
thoracic pump focus
-thorax, not heart
-works through changes intrathoracic pressures
positioning of thoracic pump
-lateral recumbency
-widest part of chest
-compress to 1/3-1/2 width
-in dorsal recumbancy 1/4 width
what is a danger with the positioning of the thoracic pump
Sternum directly over heart, sternum can damage heart
beats per mins thoracic pump
100-120 per 2 mins
what is the internal cardiac compressions
-trans diaphragmatic or lateral thorax approach
-in surgery already
-better than external compressions
-hand is acc on the heart
drawbacks of internal cardiac compressions
-takes time
-training required
-post arrest care more complex and intensive → bc have open chest
large animal cpr
-need lots of people
-tiring
-aim for highest compression rate can
potential options for large animals
pline up and throw body onto caudo-dorsal lung field (conga line)
OR
-one person at a time for two mins jumping up and down in horse chest
horse positioned for cpr
lateral recumbency on solid surface
ventilation steps
-assess airways (clear it manually or with suction)
-secure control (ET tube or tracheostomy
how can you assess the airways
•May need to clear this manually e.g a tennis ball
•Or with suction e.g. blood or vomit
how can you get secure control of the airways
•Orotracheal intubation with ET tube.
•Or
•Emergency Tracheostomy
emergency tracheostomy
-3-5mm incision and blunt disection
-trachea entered 2-4 cm caudal to larynx, ET tube between rings
-large gauge needle with syringe and ET for instany access
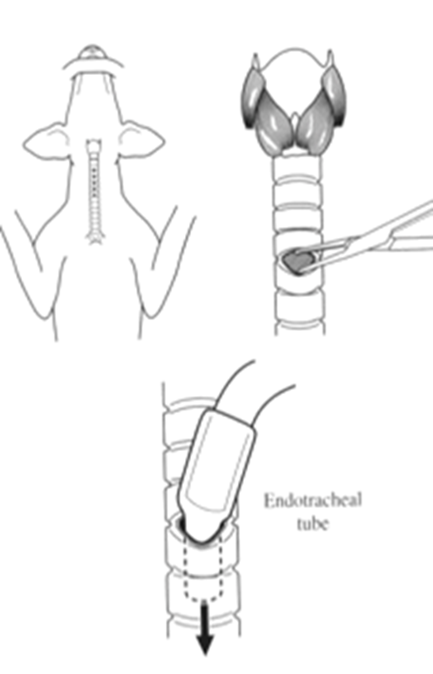
once an airway is established what is required
positive pressure ventilation (PPV)
how do you do positive pressure ventilation
-ET tube connected to MABU bag, anaesthetic machine or demand valve
-mouth to snout/nose/mask vent
what risks of mouth to snout are there
zoonotic
what is the max inspiratory pressure
40cmH2O
what is the tidal volume max
10ml/kg
too high tidal volume can cause
iatrogenic barotrauma, pulmonary haemorrhage, pneumothorax
what is the ventilation rate
10 breaths per min